Deck 15: Public Goods, Externalities, and Government Behavior
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/197
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 15: Public Goods, Externalities, and Government Behavior
1
Goods that exhibit nonrivalry in consumption and nonexcludability create a(n)
A)private good problem.
B)adverse selection problem.
C)asymmetric information problem.
D)free-rider problem.
E)principal agent problem.
A)private good problem.
B)adverse selection problem.
C)asymmetric information problem.
D)free-rider problem.
E)principal agent problem.
D
2
A free-rider problem occurs when the consumption of a good is excludable.
False
3
A lighthouse has the feature of rivalry.
False
4
National defense is a good example of a free-rider problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
An example of a public good is
A)education.
B)cable TV.
C)milk.
D)national defense.
E)bottled water.
A)education.
B)cable TV.
C)milk.
D)national defense.
E)bottled water.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
An example of a good for which there is rivalry in consumption is
A)national defense.
B)clean air.
C)grapes.
D)education.
E)a radio signal transmitted through the air.
A)national defense.
B)clean air.
C)grapes.
D)education.
E)a radio signal transmitted through the air.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A public good is any good produced by the government.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The biggest government-produced item that serves the economy as a whole is
A)the postal service.
B)police protection.
C)national defense.
D)education.
E)highways.
A)the postal service.
B)police protection.
C)national defense.
D)education.
E)highways.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The free-rider nature of a good prevents the private market from supplying the good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A public good exhibits nonrivalry in consumption and is nonexcludable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Information has the features of a(n)
A)exclusive good.
B)public good.
C)private property right.
D)private good.
E)rivalrous and excludable good.
A)exclusive good.
B)public good.
C)private property right.
D)private good.
E)rivalrous and excludable good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Consumption of a public good has the characteristics of rivalry and excludability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A private firm would have difficulty producing and selling
A)grapes.
B)cars.
C)hamburgers.
D)national defense.
E)lumber.
A)grapes.
B)cars.
C)hamburgers.
D)national defense.
E)lumber.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A good or service that is characterized by nonrivalry in consumption and nonexcludability is called a(n)
A)free good.
B)economic good.
C)public good.
D)private good.
E)noneconomic good.
A)free good.
B)economic good.
C)public good.
D)private good.
E)noneconomic good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A producer cannot at low cost exclude people from the benefits of
A)computers.
B)grapes.
C)national defense.
D)lumber.
E)cars.
A)computers.
B)grapes.
C)national defense.
D)lumber.
E)cars.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Private markets do not provide national defense because it is impossible to exclude any single individual from receiving the benefit of national defense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The aspect of a good in which one person's increased consumption of it does not decrease the amount available for consumption by others is called
A)exclusiveness.
B)nonexcludability.
C)rivalry.
D)nonrivalry.
E)excludability.
A)exclusiveness.
B)nonexcludability.
C)rivalry.
D)nonrivalry.
E)excludability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Federal, state, and local governments would be least likely to produce
A)computers.
B)highways.
C)national defense.
D)police protection.
E)the postal service.
A)computers.
B)highways.
C)national defense.
D)police protection.
E)the postal service.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A free-rider problem occurs when
A)people who pay for a good do not benefit from the good.
B)people who do not pay for a good benefit from the good.
C)no one benefits from the good.
D)no firm produces the good.
E)the good does not exist.
A)people who pay for a good do not benefit from the good.
B)people who do not pay for a good benefit from the good.
C)no one benefits from the good.
D)no firm produces the good.
E)the good does not exist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A lighthouse
A)can project a light that simultaneously benefits many ships that pass.
B)is a service that is always provided by the government.
C)provides the feature of rivalry in the consumption of light.
D)can easily exclude ships from using its light if the ship owners do not pay.
E)can easily charge its users for the services provided.
A)can project a light that simultaneously benefits many ships that pass.
B)is a service that is always provided by the government.
C)provides the feature of rivalry in the consumption of light.
D)can easily exclude ships from using its light if the ship owners do not pay.
E)can easily charge its users for the services provided.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Because of the free-rider problem associated with postal services, the government provides postal delivery.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
How is technology changing the public good features of television broadcasting?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The costs of government services
A)include the dollar costs and any deadweight losses from the increased taxes needed to finance the services.
B)include the dollar costs but do not include any deadweight losses from the increased taxes needed to finance the services.
C)include neither the dollar costs nor any deadweight losses from the increased taxes needed to finance the services.
D)do not include the dollar costs but do include any deadweight losses from the increased taxes needed to finance the services.
E)are always considered to be zero.
A)include the dollar costs and any deadweight losses from the increased taxes needed to finance the services.
B)include the dollar costs but do not include any deadweight losses from the increased taxes needed to finance the services.
C)include neither the dollar costs nor any deadweight losses from the increased taxes needed to finance the services.
D)do not include the dollar costs but do include any deadweight losses from the increased taxes needed to finance the services.
E)are always considered to be zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
What is a free-rider problem and how does the government deal with this type of problem?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Once a station broadcasts an unscrambled radio program over the airwaves,
A)everyone is willing to pay a market price for it.
B)only one listener can tune in at a time.
C)the station can collect revenues easily from listeners.
D)anyone can tune in to it.
E)the program becomes a private good.
A)everyone is willing to pay a market price for it.
B)only one listener can tune in at a time.
C)the station can collect revenues easily from listeners.
D)anyone can tune in to it.
E)the program becomes a private good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Modern technology is constantly changing the degree to which particular goods exhibit nonrivalry and nonexcludability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A user fee can be used to solve the free-rider problem if the good is totally nonexcludable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A direct survey regarding the willingness of consumers to pay for a project that may benefit them is called a
A)tax credit.
B)tax.
C)contingent valuation.
D)marginal benefit.
E)user fee.
A)tax credit.
B)tax.
C)contingent valuation.
D)marginal benefit.
E)user fee.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A government will increase the supply of a public good as long as the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost of supplying the good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Government production of a good makes it a public good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The government provides all public goods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Postal delivery is a service that has
A)rivalry in consumption and excludability.
B)none of these.
C)nonrivalry in consumption and excludability.
D)rivalry in consumption and nonexcludability.
E)nonrivalry in consumption and nonexcludability.
A)rivalry in consumption and excludability.
B)none of these.
C)nonrivalry in consumption and excludability.
D)rivalry in consumption and nonexcludability.
E)nonrivalry in consumption and nonexcludability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The government provides national defense because free riders make it difficult for private markets to supply the socially desirable amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
An example of a good produced by the government that does not have the features of a public good is
A)the judicial and legal system.
B)postal delivery.
C)police protection.
D)national defense.
E)highways.
A)the judicial and legal system.
B)postal delivery.
C)police protection.
D)national defense.
E)highways.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Balancing the costs and benefits of a good or service is called
A)cost minimization.
B)cost-benefit analysis.
C)marginal revenue analysis.
D)profit maximization.
E)average benefit analysis.
A)cost minimization.
B)cost-benefit analysis.
C)marginal revenue analysis.
D)profit maximization.
E)average benefit analysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A fee charged for the use of a good normally provided by the government is called a
A)private remedy.
B)user fee.
C)tax.
D)sales tax.
E)revenue enhancer.
A)private remedy.
B)user fee.
C)tax.
D)sales tax.
E)revenue enhancer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
It is easy to measure the benefits of government-provided services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Radio and television broadcasting services in the United States partially avoid a free-rider problem by
A)using advertising to pay for the services.
B)converting the services from excludable to nonexcludable goods.
C)converting the services from private to public goods.
D)broadcasting unscrambled programs over the airwaves.
E)charging the government for their services.
A)using advertising to pay for the services.
B)converting the services from excludable to nonexcludable goods.
C)converting the services from private to public goods.
D)broadcasting unscrambled programs over the airwaves.
E)charging the government for their services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
In order to determine the quantity of a government-provided service that should be produced, one should consider the
A)price minus the average cost of the service.
B)marginal cost and benefit of the service.
C)total cost and benefit of the service.
D)average cost and benefit of the service.
E)marginal benefit and average cost of the service.
A)price minus the average cost of the service.
B)marginal cost and benefit of the service.
C)total cost and benefit of the service.
D)average cost and benefit of the service.
E)marginal benefit and average cost of the service.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Contingent valuations give the most reliable estimate of the marginal benefits of a public good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The negative effect of cigarette smoking on a smoker is an externality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Exhibit 15-1 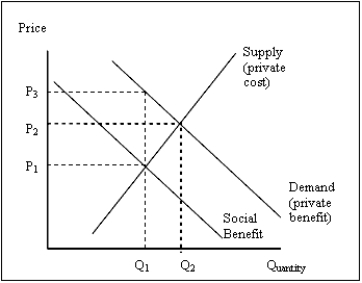
Refer to Exhibit 15-1. The graph illustrates the presence of
A)social efficiency.
B)a positive externality.
C)a negative externality.
D)private market disequilibrium.
E)government intervention.

Refer to Exhibit 15-1. The graph illustrates the presence of
A)social efficiency.
B)a positive externality.
C)a negative externality.
D)private market disequilibrium.
E)government intervention.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
When a good is produced or consumed, the side effects on the people who are not directly involved in the market are called
A)transaction costs.
B)complements.
C)free riders.
D)externalities.
E)public goods.
A)transaction costs.
B)complements.
C)free riders.
D)externalities.
E)public goods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Marginal social cost minus marginal external cost equals
A)average cost.
B)marginal profit.
C)marginal private cost.
D)marginal private benefit.
E)marginal internal cost.
A)average cost.
B)marginal profit.
C)marginal private cost.
D)marginal private benefit.
E)marginal internal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Exhibit 15-1 
Suppose that people value the continued presence of certain species of animals in rural areas, but home-building in those areas reduces the populations of the animals. Home-building creates
A)a positive externality.
B)a negative externality
C)a positive internality.
D)a negative internality.
E)a free-rider problem.

Suppose that people value the continued presence of certain species of animals in rural areas, but home-building in those areas reduces the populations of the animals. Home-building creates
A)a positive externality.
B)a negative externality
C)a positive internality.
D)a negative internality.
E)a free-rider problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A negative externality occurs when the purchase of a product
A)causes the seller of the product to lose profits.
B)increases market competition.
C)causes the government to lose tax revenues.
D)adversely affects the well-being of an individual outside of the market.
E)causes a lower market price.
A)causes the seller of the product to lose profits.
B)increases market competition.
C)causes the government to lose tax revenues.
D)adversely affects the well-being of an individual outside of the market.
E)causes a lower market price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Suppose that the production of a good causes negative externalities. What will happen if the good is produced at the level at which the marginal private cost curve meets the demand curve?
A)The level of output will be socially desirable.
B)The level of output will result in a net social cost.
C)There will be a surplus.
D)The producers will incur losses.
E)There will be no buyer in the market.
A)The level of output will be socially desirable.
B)The level of output will result in a net social cost.
C)There will be a surplus.
D)The producers will incur losses.
E)There will be no buyer in the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In a competitive market with a negative externality, firms produce an
A)amount and quality of output most desired by the market.
B)amount sometimes less and sometimes more than the efficient quantity.
C)efficient amount of output.
D)amount less than the efficient quantity.
E)amount more than the efficient quantity.
A)amount and quality of output most desired by the market.
B)amount sometimes less and sometimes more than the efficient quantity.
C)efficient amount of output.
D)amount less than the efficient quantity.
E)amount more than the efficient quantity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
An example of a positive externality is when
A)an automobile emits a pollutant.
B)your neighbor plants a beautiful garden that visible from your house.
C)a virus spreads throughout a child care center.
D)an electric utility burns coal and emits smoke.
E)any act has a negative effect, or cost, on the well-being of others.
A)an automobile emits a pollutant.
B)your neighbor plants a beautiful garden that visible from your house.
C)a virus spreads throughout a child care center.
D)an electric utility burns coal and emits smoke.
E)any act has a negative effect, or cost, on the well-being of others.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
An externality is the effect that occurs when the production or consumption of a good directly affects a third party.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
An example of a good with a positive externality is
A)acid rain.
B)an oil spill.
C)air pollution.
D)a contagious disease.
E)research.
A)acid rain.
B)an oil spill.
C)air pollution.
D)a contagious disease.
E)research.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Exhibit 15-1 
Refer to Exhibit 15-1. The amount of externality is reflected in the difference between
A)P1 and P2.
B)P1 and P3.
C)P2 and P3.
D)$0 and P1.
E)$0 and P3.

Refer to Exhibit 15-1. The amount of externality is reflected in the difference between
A)P1 and P2.
B)P1 and P3.
C)P2 and P3.
D)$0 and P1.
E)$0 and P3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The marginal cost of production as viewed by society as a whole is called the marginal
A)social cost.
B)internal cost.
C)transactions cost.
D)private cost.
E)external cost.
A)social cost.
B)internal cost.
C)transactions cost.
D)private cost.
E)external cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Exhibit 15-1 
Refer to Exhibit 15-1. The price and quantity combination that represents social efficiency for this market is
A)P1 and Q1.
B)P1 and Q2.
C)P2 and Q1.
D)P2 and Q2.
E)P3 and Q1.

Refer to Exhibit 15-1. The price and quantity combination that represents social efficiency for this market is
A)P1 and Q1.
B)P1 and Q2.
C)P2 and Q1.
D)P2 and Q2.
E)P3 and Q1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Exhibit 15-2 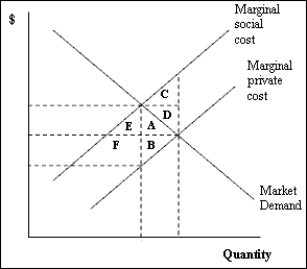
Refer to Exhibit 15-2. The diagram illustrates an example of
A)a free-rider problem.
B)efficiency.
C)a tax.
D)a positive externality.
E)a negative externality.

Refer to Exhibit 15-2. The diagram illustrates an example of
A)a free-rider problem.
B)efficiency.
C)a tax.
D)a positive externality.
E)a negative externality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Exhibit 15-2 
Refer to Exhibit 15-2. The deadweight loss due to externality is represented by the area
A)A + B.
B)C + D.
C)A + B + C + D.
D)E + F.
E)A + B + E + F.

Refer to Exhibit 15-2. The deadweight loss due to externality is represented by the area
A)A + B.
B)C + D.
C)A + B + C + D.
D)E + F.
E)A + B + E + F.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A situation in which the costs of producing or the benefits of consuming a good spill over onto those who are neither producing nor consuming the good is called a(n)
A)transaction cost.
B)property right.
C)free rider.
D)externality.
E)public good.
A)transaction cost.
B)property right.
C)free rider.
D)externality.
E)public good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What is involved in a cost-benefit analysis aimed at determining whether to increase the size of a city police force?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
When a negative externality occurs,
A)social costs are less than private costs.
B)social costs are greater private costs.
C)social costs are equal to private costs.
D)social costs are negative.
E)private costs are negative.
A)social costs are less than private costs.
B)social costs are greater private costs.
C)social costs are equal to private costs.
D)social costs are negative.
E)private costs are negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Costs to society will equal costs to a private firm when
A)the firm misallocates resources in its market.
B)third parties bear some of the costs of producing the firm's product.
C)harmful externalities occur in the firm's market.
D)no externalities occur as the firm produces its product.
E)beneficial externalities occur in the firm's market.
A)the firm misallocates resources in its market.
B)third parties bear some of the costs of producing the firm's product.
C)harmful externalities occur in the firm's market.
D)no externalities occur as the firm produces its product.
E)beneficial externalities occur in the firm's market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Education
A)is a public good.
B)provides a positive externality.
C)causes a free-rider problem.
D)exhibits nonrivalry in consumption.
E)exhibits nonexcludability in consumption.
A)is a public good.
B)provides a positive externality.
C)causes a free-rider problem.
D)exhibits nonrivalry in consumption.
E)exhibits nonexcludability in consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Suppose that the production of a good causes positive externalities. What will happen if the good is produced at the level at which the marginal private benefit curve meets the supply curve?
A)The level of production will be socially desirable.
B)The level of production will result in a net social cost.
C)The level of production will result in a net social benefit.
D)The producers will incur losses.
E)There will be no buyers in the market.
A)The level of production will be socially desirable.
B)The level of production will result in a net social cost.
C)The level of production will result in a net social benefit.
D)The producers will incur losses.
E)There will be no buyers in the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Which of the following is least likely to involve a positive externality?
A)A can of soda
B)Research
C)A university
D)An interstate highway
E)A hospital
A)A can of soda
B)Research
C)A university
D)An interstate highway
E)A hospital

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The private market is said to underproduce a good that causes a negative externality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Marginal external benefit equals
A)marginal social benefit plus marginal private benefit.
B)marginal social benefit minus marginal private benefit.
C)marginal social benefit times marginal private benefit.
D)total social benefit minus total private benefit.
E)total social benefit plus total private benefit.
A)marginal social benefit plus marginal private benefit.
B)marginal social benefit minus marginal private benefit.
C)marginal social benefit times marginal private benefit.
D)total social benefit minus total private benefit.
E)total social benefit plus total private benefit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
A positive externality occurs when the marginal social benefits are less than the marginal private benefits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
A negative externality occurs when marginal social costs exceed marginal private costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Externalities have become international in recent years, paralleling the growth of international trade and finance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
When a positive externality exists, the equilibrium quantity that emerges from a competitive market is
A)too high.
B)too low.
C)just right.
D)sometimes too high and sometimes too low.
E)zero.
A)too high.
B)too low.
C)just right.
D)sometimes too high and sometimes too low.
E)zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
An example of an international negative externality is when
A)a Mexico City firm dumps hazardous chemicals into a local river.
B)a Midwest utility burns fuel that affects trees in upstate New York.
C)China uses copyright-protected, U.S.-made software.
D)a U.S.firm benefits from a Japanese firm's research.
E)a U.S.firm causes acid rain that falls in Canada.
A)a Mexico City firm dumps hazardous chemicals into a local river.
B)a Midwest utility burns fuel that affects trees in upstate New York.
C)China uses copyright-protected, U.S.-made software.
D)a U.S.firm benefits from a Japanese firm's research.
E)a U.S.firm causes acid rain that falls in Canada.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Marginal private cost refers to the marginal cost of production as viewed by society as a whole.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The marginal benefit from consumption of a good as viewed by a private individual is called marginal
A)internal benefit.
B)external benefit.
C)social benefit.
D)external cost.
E)private benefit.
A)internal benefit.
B)external benefit.
C)social benefit.
D)external cost.
E)private benefit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Exhibit 15-2 
In the case of negative externalities, a competitive market may not generate an efficient amount of production.

In the case of negative externalities, a competitive market may not generate an efficient amount of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
If output is produced at the level at which the marginal social benefit curve and the supply curve intersect, then
A)the level of output is socially desirable.
B)the level of output results in a net social cost.
C)the level of output results in a net social benefit.
D)producers will incur losses.
E)there will be no buyers in the market.
A)the level of output is socially desirable.
B)the level of output results in a net social cost.
C)the level of output results in a net social benefit.
D)producers will incur losses.
E)there will be no buyers in the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
When the external benefits in a market are taken into account, the good's price is higher and the amount bought and sold is greater.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Explain why, in the case of negative externalities, a competitive market produces a greater-than-economically-efficient quantity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
A positive externality raises
A)marginal social benefits above marginal private benefits.
B)marginal benefits above marginal costs.
C)marginal private benefits above marginal social benefits.
D)marginal private costs above marginal social costs.
E)marginal social costs above marginal private costs.
A)marginal social benefits above marginal private benefits.
B)marginal benefits above marginal costs.
C)marginal private benefits above marginal social benefits.
D)marginal private costs above marginal social costs.
E)marginal social costs above marginal private costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
A negative global externality occurs when one country does research and others benefit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
A positive externality occurs when one person's activity makes another person better off.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Marginal social cost equals the sum of marginal costs of producers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 197 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








