Deck 9: A Two-Period Model: The Consumption–Savings Decision and Credit Markets
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: A Two-Period Model: The Consumption–Savings Decision and Credit Markets
1
The endowment point is the consumption bundle in which
A) first-period consumption is equal to zero.
B) second-period consumption is equal to zero.
C) the consumer finds the most utility.
D) consumption is equal to disposable income in each period.
E) consumption is equal to savings in each period.
A) first-period consumption is equal to zero.
B) second-period consumption is equal to zero.
C) the consumer finds the most utility.
D) consumption is equal to disposable income in each period.
E) consumption is equal to savings in each period.
consumption is equal to disposable income in each period.
2
The simplest device to analyze dynamic decisions is a
A) one-period model.
B) two-period model.
C) model that includes only the number of years of a typical consumer's lifetime.
D) continuous time model.
E) dynamic time model.
A) one-period model.
B) two-period model.
C) model that includes only the number of years of a typical consumer's lifetime.
D) continuous time model.
E) dynamic time model.
two-period model.
3
If the consumer is a lender then
A)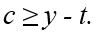
B)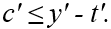
C)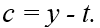
D)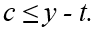
E)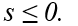
A)
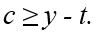
B)
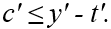
C)
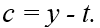
D)
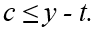
E)
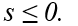
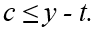
4
To ensure a well-defined solution to the consumers' intertemporal choice problems,we must assume that consumers' preferences exhibit the properties that
A) they are all identical and that more is always preferred to less.
B) more is preferred to less and that the consumer prefers diversity.
C) the consumer likes diversity and that more is sometimes preferred to less.
D) more is sometimes preferred to less and that first-period consumption and second-period consumption are both normal goods.
E) more is sometimes preferred to less and that first-period consumption and second-period consumption are both inferior goods.
A) they are all identical and that more is always preferred to less.
B) more is preferred to less and that the consumer prefers diversity.
C) the consumer likes diversity and that more is sometimes preferred to less.
D) more is sometimes preferred to less and that first-period consumption and second-period consumption are both normal goods.
E) more is sometimes preferred to less and that first-period consumption and second-period consumption are both inferior goods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
We assume that the representative consumer's preferences exhibit the properties that
A) they are convex and that more is always preferred to less.
B) more is always preferred to less and that each consumer has one strictly favorite period of time for consumption.
C) each consumer has one strictly favorite period of time for consumption and that current and future consumption are both normal goods.
D) current and future consumption are both normal goods and that the consumer likes diversity in his or her consumption bundle.
E) current and future consumption are both normal goods and that more is always preferred to less.
A) they are convex and that more is always preferred to less.
B) more is always preferred to less and that each consumer has one strictly favorite period of time for consumption.
C) each consumer has one strictly favorite period of time for consumption and that current and future consumption are both normal goods.
D) current and future consumption are both normal goods and that the consumer likes diversity in his or her consumption bundle.
E) current and future consumption are both normal goods and that more is always preferred to less.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Consumption smoothing refers to
A) the tendency of all consumers to choose the same amount of current consumption.
B) the tendency of consumers to seek a consumption path over time that is smoother than income.
C) the tendency of consumers to seek an income path over time that is smoother than consumption.
D) consumer's concerns about going heavily into debt.
E) balance savings with consumption over time.
A) the tendency of all consumers to choose the same amount of current consumption.
B) the tendency of consumers to seek a consumption path over time that is smoother than income.
C) the tendency of consumers to seek an income path over time that is smoother than consumption.
D) consumer's concerns about going heavily into debt.
E) balance savings with consumption over time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If we represents a two-period consumer's lifetime wealth and r denotes the real rate of interest,the horizontal (current consumption)intercept of the consumer's budget line is equal to
A)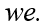
B)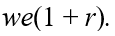
C)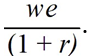
D)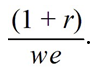
E)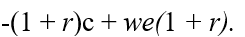
A)
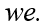
B)
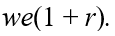
C)
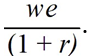
D)
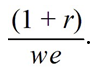
E)
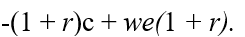

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A consumer's budget constraint in the future period is
A) c' = y'- t' + (1 + r)s.
B) c' + (1 + r)s = y'- t'.
C) c + s = y - t.
D) c' = y' - t' - (1 + r)s.
E) y' - t' = (1 + r)s.
A) c' = y'- t' + (1 + r)s.
B) c' + (1 + r)s = y'- t'.
C) c + s = y - t.
D) c' = y' - t' - (1 + r)s.
E) y' - t' = (1 + r)s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Bonds are assumed to trade directly
A) through the Bank of Canada.
B) through the federal government.
C) through financial intermediaries.
D) in the credit market.
E) in the stock market.
A) through the Bank of Canada.
B) through the federal government.
C) through financial intermediaries.
D) in the credit market.
E) in the stock market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
In the two-period model of the economy,
A) borrowing rates of interest are greater than lending rates of interest.
B) borrowing rates of interest are less than lending rates of interest.
C) there e s only one real interest rate.
D) borrowing rates of interest are equal to lending rates of interest.
E) there is only one nominal interest rate.
A) borrowing rates of interest are greater than lending rates of interest.
B) borrowing rates of interest are less than lending rates of interest.
C) there e s only one real interest rate.
D) borrowing rates of interest are equal to lending rates of interest.
E) there is only one nominal interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The consumer's lifetime budget constraint states that
A) the present value of lifetime consumption must be equal to the present value of lifetime gross income.
B) the present value of lifetime consumption must be equal to the present value of lifetime disposable income.
C) the present value of lifetime consumption plus the present value of lifetime taxes to be paid must be equal to the present value of lifetime income.
D) the present value of lifetime taxes to be paid by the consumer must be equal to the present value of government spending.
E) he present value of lifetime consumption must be equal to the present value of savings.
A) the present value of lifetime consumption must be equal to the present value of lifetime gross income.
B) the present value of lifetime consumption must be equal to the present value of lifetime disposable income.
C) the present value of lifetime consumption plus the present value of lifetime taxes to be paid must be equal to the present value of lifetime income.
D) the present value of lifetime taxes to be paid by the consumer must be equal to the present value of government spending.
E) he present value of lifetime consumption must be equal to the present value of savings.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
For all bonds to be indistinguishable,
A) all consumers must never be expected to default on their debts.
B) the government must guarantee all bonds.
C) all consumers must be identical.
D) they must be traded through financial intermediaries.
E) only government can issue bonds.
A) all consumers must never be expected to default on their debts.
B) the government must guarantee all bonds.
C) all consumers must be identical.
D) they must be traded through financial intermediaries.
E) only government can issue bonds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A consumer's budget constraint in the current period is
A) c = y - t.
B) y = c + i + g.
C) y = c - s.
D) c + s = y + t.
E) c + s = y - t.
A) c = y - t.
B) y = c + i + g.
C) y = c - s.
D) c + s = y + t.
E) c + s = y - t.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
If we represents a two-period consumer's lifetime wealth and r denotes the real rate of interest,the vertical (future consumption)intercept of the consumer's budget line is equal to
A)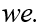
B)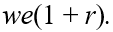
C)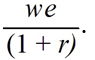
D)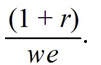
E)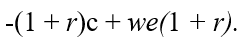
A)
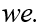
B)
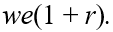
C)
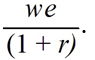
D)
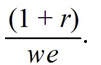
E)
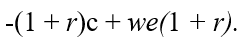

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The endowment point is the consumption bundle in which
A) savings are zero.
B) households maximize utility.
C) permanent income is maximized.
D) households are indifferent to interest rate changes.
E) current consumption is equal to future consumption.
A) savings are zero.
B) households maximize utility.
C) permanent income is maximized.
D) households are indifferent to interest rate changes.
E) current consumption is equal to future consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Consumption-savings decisions involve intertemporal choice as this is a decision involving a tradeoff between
A) consumption and investment.
B) consumption and saving.
C) current and future investment.
D) current and future consumption.
E) consumption per worker and income per worker.
A) consumption and investment.
B) consumption and saving.
C) current and future investment.
D) current and future consumption.
E) consumption per worker and income per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
If we represents a two-period consumer's lifetime wealth and r denotes the real rate of interest,the slope of the consumer's budget line is equal to
A)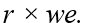
B)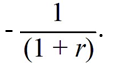
C)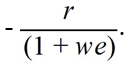
D)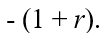
E)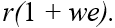
A)
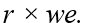
B)
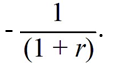
C)
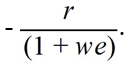
D)
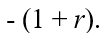
E)
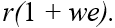

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Intertemporal decisions involve economic decisions
A) made within a given period of time.
B) made in between two periods of time.
C) involving tradeoffs across periods of time.
D) that ignore concerns about the future.
E) that are made only once.
A) made within a given period of time.
B) made in between two periods of time.
C) involving tradeoffs across periods of time.
D) that ignore concerns about the future.
E) that are made only once.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A one-period bond is a promise to repay
A)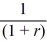 units of goods in the second period.
units of goods in the second period.
B) r units of goods in the second period.
C) (1 + r) units of goods in the second period.
D) the original amount lent.
E) the real interest rate.
A)
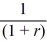 units of goods in the second period.
units of goods in the second period.B) r units of goods in the second period.
C) (1 + r) units of goods in the second period.
D) the original amount lent.
E) the real interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A key variable in intertemporal choice is
A) consumption.
B) investment.
C) output per worker.
D) real interest rate.
E) total factor productivity.
A) consumption.
B) investment.
C) output per worker.
D) real interest rate.
E) total factor productivity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
An increase in second-period income results in
A) an increase in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
B) an increase in first-period consumption, a decrease in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
C) a decrease in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
D) an increase in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and a decrease in saving.
E) a decrease in first-period consumption, a decrease in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
A) an increase in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
B) an increase in first-period consumption, a decrease in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
C) a decrease in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
D) an increase in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and a decrease in saving.
E) a decrease in first-period consumption, a decrease in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In the data,which of the following is most volatile?
A) real GDP
B) consumption of durables
C) consumption of nondurables
D) consumption of services
E) aggregate income
A) real GDP
B) consumption of durables
C) consumption of nondurables
D) consumption of services
E) aggregate income

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A permanent increase in income leades to
A) a large increase in current consumption.
B) a small increase in current consumption.
C) a small decrease in future consumption.
D) a small increase in future consumption.
E) a large decrease in future consumption.
A) a large increase in current consumption.
B) a small increase in current consumption.
C) a small decrease in future consumption.
D) a small increase in future consumption.
E) a large decrease in future consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The property of diminishing marginal rate of substitution follows from the property that the indifference curves are
A) downward sloping.
B) upward sloping.
C) bowed in toward the origin.
D) bowed out from the origin.
E) negatively sloped.
A) downward sloping.
B) upward sloping.
C) bowed in toward the origin.
D) bowed out from the origin.
E) negatively sloped.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A consumer is a lender if
A) optimum current consumption is less than current disposable income.
B) optimum current consumption is greater than current disposable income.
C) current disposable income is greater than future disposable income.
D) the consumer's indifference curves are relatively flat.
E) the consumer's indifference curves are negatively sloped.
A) optimum current consumption is less than current disposable income.
B) optimum current consumption is greater than current disposable income.
C) current disposable income is greater than future disposable income.
D) the consumer's indifference curves are relatively flat.
E) the consumer's indifference curves are negatively sloped.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
If consumers expect a tax cut to be temporary,
A) consumption remains unchanged.
B) the increase in consumption will be much larger than for a permanent tax cut.
C) the decrease in consumption will be much smaller than for a permanent tax cut.
D) the overall effects are much larger than for a permanent tax cut.
E) the increase in consumption will be much smaller than for a permanent tax cut.
A) consumption remains unchanged.
B) the increase in consumption will be much larger than for a permanent tax cut.
C) the decrease in consumption will be much smaller than for a permanent tax cut.
D) the overall effects are much larger than for a permanent tax cut.
E) the increase in consumption will be much smaller than for a permanent tax cut.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A change in the stock market is a good indicator of a change in
A) current income.
B) future income.
C) wealth.
D) the future growth rate of real GDP.
E) current consumption.
A) current income.
B) future income.
C) wealth.
D) the future growth rate of real GDP.
E) current consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The two primary explanations for the excess volatility of consumption are
A) consumers' limited life spans and credit market imperfections.
B) credit market imperfections and changes in market prices.
C) changes in market prices and distorting taxes.
D) distorting taxes and consumers' limited life spans.
E) changes in market prices and consumer's limited life spans.
A) consumers' limited life spans and credit market imperfections.
B) credit market imperfections and changes in market prices.
C) changes in market prices and distorting taxes.
D) distorting taxes and consumers' limited life spans.
E) changes in market prices and consumer's limited life spans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A permanent decrease in taxes leads to
A) a large increase in current consumption.
B) a small increase in current consumption.
C) a small decrease in current consumption.
D) a large decrease in future consumption.
E) no changes to consumption.
A) a large increase in current consumption.
B) a small increase in current consumption.
C) a small decrease in current consumption.
D) a large decrease in future consumption.
E) no changes to consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A good proxy for the flow of consumption services would be
A) aggregate consumption.
B) consumption of services and consumption of durables.
C) consumption of durables and consumption of nondurables.
D) consumption of nondurables and consumption of services.
E) consumption of durables and services.
A) aggregate consumption.
B) consumption of services and consumption of durables.
C) consumption of durables and consumption of nondurables.
D) consumption of nondurables and consumption of services.
E) consumption of durables and services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
According to Friedman,a primary determinant of a consumer's current consumption is
A) current employment.
B) current levels of GDP.
C) rate of expected savings in the second period.
D) permanent income.
E) temporary income.
A) current employment.
B) current levels of GDP.
C) rate of expected savings in the second period.
D) permanent income.
E) temporary income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Aggregate consumption is
A) positively related to savings.
B) negatively related to real GDP.
C) more volatile than aggregate income.
D) less variable than aggregate income.
E) more variable than savings.
A) positively related to savings.
B) negatively related to real GDP.
C) more volatile than aggregate income.
D) less variable than aggregate income.
E) more variable than savings.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
An increase in first-period income results in
A) an increase in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
B) an increase in first-period consumption, a decrease in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
C) a decrease in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
D) an increase in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and a decrease in saving.
E) a decrease in first-period consumption, a decrease in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
A) an increase in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
B) an increase in first-period consumption, a decrease in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
C) a decrease in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.
D) an increase in first-period consumption, an increase in second-period consumption, and a decrease in saving.
E) a decrease in first-period consumption, a decrease in second-period consumption, and an increase in saving.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A martingale has the property that
A) it is inherently unpredictable.
B) the best prediction of its value tomorrow is its value today.
C) the best prediction of its future growth rate is its current growth rate.
D) the best prediction of its value tomorrow can be computed by looking at its past behavior.
E) the best prediction of its value tomorrow can be computed by looking at the past two periods.
A) it is inherently unpredictable.
B) the best prediction of its value tomorrow is its value today.
C) the best prediction of its future growth rate is its current growth rate.
D) the best prediction of its value tomorrow can be computed by looking at its past behavior.
E) the best prediction of its value tomorrow can be computed by looking at the past two periods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
For the consumer to be at an optimum,it must be the case that
A)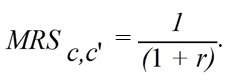
B)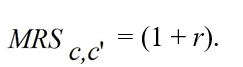
C)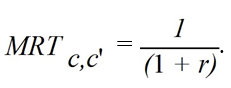
D)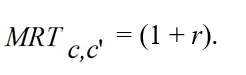
E)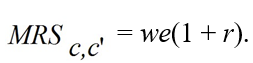
A)
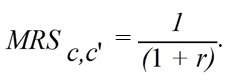
B)
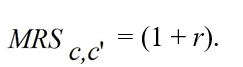
C)
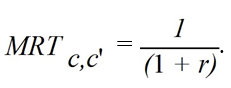
D)
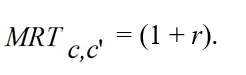
E)
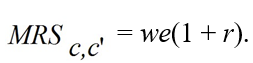

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The marginal rate of substitution of current consumption for future consumption is
A) the slope of the indifference curve.
B) minus the slope of the difference curve.
C) the downward slope of the budget constraint.
D) the endowment point.
E) the slope of the lifetime budget constraint.
A) the slope of the indifference curve.
B) minus the slope of the difference curve.
C) the downward slope of the budget constraint.
D) the endowment point.
E) the slope of the lifetime budget constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The property of diminishing marginal rate of substitution implies that
A) the more current consumption the consumer has, the less future consumption she is willing to give up for one more unit of current consumption.
B) the less current consumption the consumer has, the less future consumption she is willing to give up for one more unit of current consumption.
C) the more current consumption the consumer has, the more future consumption she is willing to give up for one more unit of current consumption.
D) the indifference curves are bowed away from the origin.
E) the indifference curves have a constant slope.
A) the more current consumption the consumer has, the less future consumption she is willing to give up for one more unit of current consumption.
B) the less current consumption the consumer has, the less future consumption she is willing to give up for one more unit of current consumption.
C) the more current consumption the consumer has, the more future consumption she is willing to give up for one more unit of current consumption.
D) the indifference curves are bowed away from the origin.
E) the indifference curves have a constant slope.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The optimal consumption bundle is where
A) c = s.
B) c = y - t - s.
C) the marginal rate of substitution in the current period equals the marginal rate of substitution in the future period.
D) budget constraint.
E) MRS = 1 = r.
A) c = s.
B) c = y - t - s.
C) the marginal rate of substitution in the current period equals the marginal rate of substitution in the future period.
D) budget constraint.
E) MRS = 1 = r.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The idea that a permanent increase in income causes a larger increase in consumption than a temporary change in income is called the
A) Friedman-Lucas theory.
B) permanent income hypothesis.
C) Ricardian equivalence theorem.
D) intertemporal substitution effect.
E) steady state theorem.
A) Friedman-Lucas theory.
B) permanent income hypothesis.
C) Ricardian equivalence theorem.
D) intertemporal substitution effect.
E) steady state theorem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A consumer is a borrower if
A) optimum current consumption is less than current disposable income.
B) optimum current consumption is greater than current disposable income.
C) future disposable income is greater than current disposable income.
D) the consumer's indifference curves are relatively steep.
E) the consumer's indifference curves are positively sloped.
A) optimum current consumption is less than current disposable income.
B) optimum current consumption is greater than current disposable income.
C) future disposable income is greater than current disposable income.
D) the consumer's indifference curves are relatively steep.
E) the consumer's indifference curves are positively sloped.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
In a two-period model,government spending is financed through
A) taxes and transfer payments.
B) taxes and issuing debt.
C) taxes and redeeming debt.
D) taxes only.
E) issuing bonds.
A) taxes and transfer payments.
B) taxes and issuing debt.
C) taxes and redeeming debt.
D) taxes only.
E) issuing bonds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The government's future period budget constraint is:
A) G' + (1+r)B = T'
B) G' + T' = (1 + r)B
C) G + G' = T - T'
D) B = G - T
E) G' = T' + (1 + r)B
A) G' + (1+r)B = T'
B) G' + T' = (1 + r)B
C) G + G' = T - T'
D) B = G - T
E) G' = T' + (1 + r)B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
A key channel for interest rate effects on real activity will be through
A) temporary income.
B) permanent income.
C) aggregate consumption.
D) aggregate investment.
E) consumption and savings.
A) temporary income.
B) permanent income.
C) aggregate consumption.
D) aggregate investment.
E) consumption and savings.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
For a competitive equilibrium in a two-period model,which of the following is true?
A) Y = C + G
B) C = Y + S
C) Y = C - T
D) C = Y + T
E) Y = C + I
A) Y = C + G
B) C = Y + S
C) Y = C - T
D) C = Y + T
E) Y = C + I

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
For a lender,an increase in the real interest rate
A) definitely reduces current consumption and increases future consumption.
B) reduces current consumption and has an uncertain effect on future consumption.
C) has an uncertain effect on current consumption and increases future consumption.
D) has an uncertain effect on both current and future consumption.
E) definitely reduces current consumption and future consumption.
A) definitely reduces current consumption and increases future consumption.
B) reduces current consumption and has an uncertain effect on future consumption.
C) has an uncertain effect on current consumption and increases future consumption.
D) has an uncertain effect on both current and future consumption.
E) definitely reduces current consumption and future consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
For a borrower,an increase in the real interest rate
A) definitely reduces current consumption and increases future consumption.
B) reduces current consumption and has an uncertain effect on future consumption.
C) has an uncertain effect on current consumption and increases future consumption.
D) has an uncertain effect on both current and future consumption.
E) definitely reduces current consumption and future consumption.
A) definitely reduces current consumption and increases future consumption.
B) reduces current consumption and has an uncertain effect on future consumption.
C) has an uncertain effect on current consumption and increases future consumption.
D) has an uncertain effect on both current and future consumption.
E) definitely reduces current consumption and future consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
In the case where current and future consumption are perfect complements,an increase in the real interest rate
A) involves only income effects.
B) has ambiguous effects depending on whether the substitution or income effects dominate.
C) involves only subsitution effects.
D) involves a substitution effect only for lenders.
E) is relevant only for borrowers.
A) involves only income effects.
B) has ambiguous effects depending on whether the substitution or income effects dominate.
C) involves only subsitution effects.
D) involves a substitution effect only for lenders.
E) is relevant only for borrowers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The private supply of credit is an increasing function of the real interest rate if
A) the substitution effects outweighs the income effects when added across all consumers.
B) the income effects outweighs the substitution effects when added across all consumers.
C) the income effect outweighs the substitution effects for borrowers.
D) the substitution and income effects cancel each other.
E) consumers are rational.
A) the substitution effects outweighs the income effects when added across all consumers.
B) the income effects outweighs the substitution effects when added across all consumers.
C) the income effect outweighs the substitution effects for borrowers.
D) the substitution and income effects cancel each other.
E) consumers are rational.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
For a competitive equilibrium in a two-period model,which of the following is true?
A) each consumer picks first- and second-period consumption given the real interest rate
B) there must be an equal number of borrowers and lenders.
C) the present value of government spending must be greater than the present value of taxes.
D) the financial market clears.
E) all deficits are financed by issuing debt.
A) each consumer picks first- and second-period consumption given the real interest rate
B) there must be an equal number of borrowers and lenders.
C) the present value of government spending must be greater than the present value of taxes.
D) the financial market clears.
E) all deficits are financed by issuing debt.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The substitution effect of a change in the real interest rate is an example of
A) a negative substitution effect.
B) a positive substitution effect.
C) an intertemporal substitution effect.
D) a temporary substitution effect.
E) a permanent substitution effect.
A) a negative substitution effect.
B) a positive substitution effect.
C) an intertemporal substitution effect.
D) a temporary substitution effect.
E) a permanent substitution effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If government spending is held constant and Ricardian equivalence holds,
A) an increase in the government budget deficit is always matched by a reduction in private savings.
B) an increase in government savings is always matched by an increase in the government budget deficit.
C) an increase in government savings is always matched by an equal increase in private savings.
D) an increase in government savings is always matched by an equal reduction in private savings.
E) an increase in government savings is always matched by an increase in the real interest rate.
A) an increase in the government budget deficit is always matched by a reduction in private savings.
B) an increase in government savings is always matched by an increase in the government budget deficit.
C) an increase in government savings is always matched by an equal increase in private savings.
D) an increase in government savings is always matched by an equal reduction in private savings.
E) an increase in government savings is always matched by an increase in the real interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The Ricardian equivalence theorem implies that
A) government debt policy must be handled correctly for the economy to prosper.
B) the amounts of government spending are neutral.
C) an increase in government spending has no effect on the economy, as long as there is an equal change in taxes.
D) the timing of taxes collected by the government is neutral.
E) the present value of government spending must be equal to the present value of taxes.
A) government debt policy must be handled correctly for the economy to prosper.
B) the amounts of government spending are neutral.
C) an increase in government spending has no effect on the economy, as long as there is an equal change in taxes.
D) the timing of taxes collected by the government is neutral.
E) the present value of government spending must be equal to the present value of taxes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
An important reason why Ricardian equivalence may fail is if
A) borrowing and lending is done through intermediaries.
B) government debt incurred today may not be paid off until after some current consumers are deceased.
C) state and local governments also engage in debt finance.
D) some consumers are borrowers, while other consumers are lenders.
E) real interest rates start to increase.
A) borrowing and lending is done through intermediaries.
B) government debt incurred today may not be paid off until after some current consumers are deceased.
C) state and local governments also engage in debt finance.
D) some consumers are borrowers, while other consumers are lenders.
E) real interest rates start to increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
If the government reduces current taxes,government bonds increase,and according to Ricardian equivalence in the credit market
A) the supply curve of private savings shifts to the left to keep the real interest rate constant.
B) the real interest rate increases.
C) private savings decreases by an amount equal to the increase in government bonds.
D) the supply curve of private savings shifts right to keep the real interest rate constant.
E) the supply curve of private savings shifts to the right and the real interest rate increases.
A) the supply curve of private savings shifts to the left to keep the real interest rate constant.
B) the real interest rate increases.
C) private savings decreases by an amount equal to the increase in government bonds.
D) the supply curve of private savings shifts right to keep the real interest rate constant.
E) the supply curve of private savings shifts to the right and the real interest rate increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
An increase in the real interest
A) increases savings for both borrowers and lenders.
B) increases savings for borrowers, but has an uncertain effect on the savings of lenders.
C) increases savings for lenders, but has an uncertain effect on the savings of borrowers.
D) has an uncertain effect on the savings of both borrowers and lenders.
E) reduces savings for both borrowers and lenders.
A) increases savings for both borrowers and lenders.
B) increases savings for borrowers, but has an uncertain effect on the savings of lenders.
C) increases savings for lenders, but has an uncertain effect on the savings of borrowers.
D) has an uncertain effect on the savings of both borrowers and lenders.
E) reduces savings for both borrowers and lenders.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Ricardian equivalence suggests that the government must pay off its debt by
A) reducing government spending in the future.
B) increasing taxes in the future.
C) transferring surpluses to the debt.
D) reduces private savings in the future.
E) increases the real interest rate.
A) reducing government spending in the future.
B) increasing taxes in the future.
C) transferring surpluses to the debt.
D) reduces private savings in the future.
E) increases the real interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The government's present value budget constraint states that
A) taxes must equal government spending in each period.
B) the present value of government spending must be equal to the present value of consumers' disposable incomes.
C) the present value of government spending must be equal to the present value of taxes.
D) the government may run deficits each and every year, as long as the deficits are sufficiently small.
E) governments can increase spending as long as deficits are financed by issuing debt.
A) taxes must equal government spending in each period.
B) the present value of government spending must be equal to the present value of consumers' disposable incomes.
C) the present value of government spending must be equal to the present value of taxes.
D) the government may run deficits each and every year, as long as the deficits are sufficiently small.
E) governments can increase spending as long as deficits are financed by issuing debt.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The government's current period budget constraint is:
A) G + B = T
B) G' = T' + (1 + r)B
C) G = T + B
D) G + T = B
E) G + S = B
A) G + B = T
B) G' = T' + (1 + r)B
C) G = T + B
D) G + T = B
E) G + S = B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The Ricardian Equivalent Theorem implies that a change in the timing of taxes
A) has a positive effect on both consumption and the real interest rate.
B) has a negative effect on both consumption and the real interest rate.
C) affects consumption negatively and the real interest rate positively.
D) affects consumption positively and the real interest rate negatively.
E) has no effect on consumption or the real interest rate.
A) has a positive effect on both consumption and the real interest rate.
B) has a negative effect on both consumption and the real interest rate.
C) affects consumption negatively and the real interest rate positively.
D) affects consumption positively and the real interest rate negatively.
E) has no effect on consumption or the real interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
An increase in the real interest rate is an example of a
A) pure substitution effect.
B) substitution effect and a positive income effect.
C) substitution effect and a negative income effect.
D) substitution effect and an income effect whose sign depends on whether the consumer is initially a borrower or a lender.
E) positive substitution effect and a negative income effect.
A) pure substitution effect.
B) substitution effect and a positive income effect.
C) substitution effect and a negative income effect.
D) substitution effect and an income effect whose sign depends on whether the consumer is initially a borrower or a lender.
E) positive substitution effect and a negative income effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
In Japan the ratio of government debt to real GDP is 220%,while in Greece it is 143%.Despite this,Greece is viewed as on an unsustainable course,while Japan is not.What could explain this?
A) The political system is more corrupt in Japan.
B) Legislators are more efficient in Japan than in Greece at issuing new debt.
C) The prospects for economic growth in Japan are much better than in Greece.
D) The real interest rate is much higher in Japan than in Greece.
E) Japan's proximity to China.
A) The political system is more corrupt in Japan.
B) Legislators are more efficient in Japan than in Greece at issuing new debt.
C) The prospects for economic growth in Japan are much better than in Greece.
D) The real interest rate is much higher in Japan than in Greece.
E) Japan's proximity to China.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Ricardian equivalence is often attributed to David Ricardo and more attributed to
A) Gerald O'Driscoll.
B) Adam Smith.
C) Milton Friedman.
D) Robert Barro.
E) Robert Lucas.
A) Gerald O'Driscoll.
B) Adam Smith.
C) Milton Friedman.
D) Robert Barro.
E) Robert Lucas.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
In our two-period model,the government must pay off all debt,in reality
A) this is approximately correct.
B) only developing countries can perpetually run deficits.
C) governments take longer than two-periods to pay off debt, but almost always do.
D) only countries in the European Union are unlikely to ever pay off their debt.
E) governments rarely pay off all of their debt.
A) this is approximately correct.
B) only developing countries can perpetually run deficits.
C) governments take longer than two-periods to pay off debt, but almost always do.
D) only countries in the European Union are unlikely to ever pay off their debt.
E) governments rarely pay off all of their debt.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
When there are credit market imperfections,an increase in government debt may be advantageous because it
A) discourages credit-constrained consumers from borrowing too much.
B) increases the welfare of credit-constrained consumers.
C) eliminates the problems that cause credit market imperfections.
D) encourages more private saving.
E) borrow at higher interest rates than consumers.
A) discourages credit-constrained consumers from borrowing too much.
B) increases the welfare of credit-constrained consumers.
C) eliminates the problems that cause credit market imperfections.
D) encourages more private saving.
E) borrow at higher interest rates than consumers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
The phenomenon that some consumers pay a higher interest rate when they borrow than the interest rate they receive when they lend is best described as an example of
A) irrational behavior.
B) a credit market imperfection.
C) a vast banking conspiracy.
D) the burden of public debt.
E) competitive disequilibrium.
A) irrational behavior.
B) a credit market imperfection.
C) a vast banking conspiracy.
D) the burden of public debt.
E) competitive disequilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
In order for the government to sustain a primary deficit forever,
A) real GDP must grow faster than the real interest rate.
B) real GDP must grow slower than the real interest rate.
C) it must borrow from other governments.
D) it must eventually lend to other governments.
E) real GDP must grow at the same rate as the real interest rate.
A) real GDP must grow faster than the real interest rate.
B) real GDP must grow slower than the real interest rate.
C) it must borrow from other governments.
D) it must eventually lend to other governments.
E) real GDP must grow at the same rate as the real interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Distorting taxes can invalidate Ricardian equivalence because
A) they confuse consumers about the need for government to repay its debt.
B) alternative ways of collecting the same tax revenue produce different amounts of lost welfare.
C) they are inferior to lump-sum taxes.
D) they are more popular, politically, than lump-sum taxes.
E) the distortions are only faced by the business sector.
A) they confuse consumers about the need for government to repay its debt.
B) alternative ways of collecting the same tax revenue produce different amounts of lost welfare.
C) they are inferior to lump-sum taxes.
D) they are more popular, politically, than lump-sum taxes.
E) the distortions are only faced by the business sector.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
When different consumers pay different amounts of taxes,Ricardian equivalence may fail because
A) alternative ways of collecting the same tax revenue can have different welfare effects.
B) consumers can become jealous of one another.
C) such differences in taxes create credit market imperfections.
D) higher taxes on more talented people may be politically popular.
E) such differences in taxes create welfare losses to the business community.
A) alternative ways of collecting the same tax revenue can have different welfare effects.
B) consumers can become jealous of one another.
C) such differences in taxes create credit market imperfections.
D) higher taxes on more talented people may be politically popular.
E) such differences in taxes create welfare losses to the business community.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
What is consumption smoothing and how is it affected with an increase in temporary and permanent income?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








