Deck 5: A Closed-Economy One-Period Macroeconomic Model
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 5: A Closed-Economy One-Period Macroeconomic Model
1
A closed economy is characterized by
A) the absence of trade with other economies.
B) the absence of use of money for transactions.
C) no growth in population.
D) a Cobb-Douglas production function.
A) the absence of trade with other economies.
B) the absence of use of money for transactions.
C) no growth in population.
D) a Cobb-Douglas production function.
the absence of trade with other economies.
2
In a one-period economic model,the government budget constraint requires that government spending
A) = taxes + transfers.
B) = taxes + borrowing.
C) > 0.
D) = taxes.
A) = taxes + transfers.
B) = taxes + borrowing.
C) > 0.
D) = taxes.
= taxes.
3
Which of the following is not a property of a competitive equilibrium?
A) markets clear.
B) consumers and firms optimize given market prices.
C) the government budget constraint is satisfied.
D) increasing total factor productivity.
A) markets clear.
B) consumers and firms optimize given market prices.
C) the government budget constraint is satisfied.
D) increasing total factor productivity.
increasing total factor productivity.
4
Making use of an economic model is a process of
A) solving hundreds of simultaneous equations.
B) running experiments to determine how changes in the endogenous variables will change the exogenous variables.
C) running experiments to determine how changes in the exogenous variables will change the endogenous variables.
D) resolving inconsistencies in the actions of economic agents.
A) solving hundreds of simultaneous equations.
B) running experiments to determine how changes in the endogenous variables will change the exogenous variables.
C) running experiments to determine how changes in the exogenous variables will change the endogenous variables.
D) resolving inconsistencies in the actions of economic agents.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In a general equilibrium model
A) all markets but one clear.
B) there are no fluctuations.
C) all prices are exogenous.
D) all prices are endogenous.
A) all markets but one clear.
B) there are no fluctuations.
C) all prices are exogenous.
D) all prices are endogenous.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
An economy that has no interaction with the rest of the world is called
A) an isolated economy.
B) a closed economy.
C) a parochial economy.
D) a rogue nation.
A) an isolated economy.
B) a closed economy.
C) a parochial economy.
D) a rogue nation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The production possibilities frontier in the one-period model is a
A) behavioral relationship between consumption and leisure.
B) behavioral relationship between consumption and government spending.
C) technological relationship between consumption and leisure.
D) technological relationship between consumption and government spending.
A) behavioral relationship between consumption and leisure.
B) behavioral relationship between consumption and government spending.
C) technological relationship between consumption and leisure.
D) technological relationship between consumption and government spending.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
For a competitive equilibrium to occur,all of the following has to happen except
A) agents are price takers.
B) the government sets taxes at zero.
C) markets clear.
D) the actions of all agents are consistent.
A) agents are price takers.
B) the government sets taxes at zero.
C) markets clear.
D) the actions of all agents are consistent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In an economic model,an exogenous variable is
A) a stand-in for more complicated variables.
B) determined by the model itself.
C) determined outside the model.
D) a variable that has no effect on the workings of the model.
A) a stand-in for more complicated variables.
B) determined by the model itself.
C) determined outside the model.
D) a variable that has no effect on the workings of the model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
An economy that engages in international trade is called
A) a cooperative economy.
B) a modern economy.
C) an engaged economy.
D) an open economy.
A) a cooperative economy.
B) a modern economy.
C) an engaged economy.
D) an open economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not a reason for solving the model with a PPF?
A) It merges the household and firm problems into one graph.
B) It is simpler to solve the social planner problem.
C) It highlights the fact that the marginal rate of substitution should equal the marginal rate of transformation.
D) It highlights the fact that firms make no profit in equilibrium.
A) It merges the household and firm problems into one graph.
B) It is simpler to solve the social planner problem.
C) It highlights the fact that the marginal rate of substitution should equal the marginal rate of transformation.
D) It highlights the fact that firms make no profit in equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In an economic model,an endogenous variable is
A) a stand-in for more complicated variables.
B) determined by the model itself.
C) determined outside the model.
D) a variable that has no effect on the workings of the model.
A) a stand-in for more complicated variables.
B) determined by the model itself.
C) determined outside the model.
D) a variable that has no effect on the workings of the model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The production possibilities frontier represents
A) all combinations of consumption and leisure for fixed output.
B) all equally affordable combinations of consumption and leisure for a given wage.
C) all technologically feasible combinations of consumption and leisure.
D) all equally liked combinations of consumption and leisure.
A) all combinations of consumption and leisure for fixed output.
B) all equally affordable combinations of consumption and leisure for a given wage.
C) all technologically feasible combinations of consumption and leisure.
D) all equally liked combinations of consumption and leisure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Fiscal policy encompasses all of the following except
A) expenditures by the government.
B) monetary injection by the government.
C) taxation by the government.
D) borrowing by the government.
A) expenditures by the government.
B) monetary injection by the government.
C) taxation by the government.
D) borrowing by the government.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following relationships does not hold in the one-period model?
A) G=T
B) Y=C+G
C) Y=zF(K,N)
D)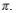 =Y-wN-C
=Y-wN-C
A) G=T
B) Y=C+G
C) Y=zF(K,N)
D)
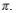 =Y-wN-C
=Y-wN-C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
In a competitive equilibrium all these relationships hold but one. Which one?
A) Nd=Ns
B) Y=G+C
C) G=T
D) w=z
A) Nd=Ns
B) Y=G+C
C) G=T
D) w=z

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Fiscal policy refers to a government's choices over its
A) expenditures, taxes, transfers, and borrowing.
B) expenditures, taxes, issuance of money, and borrowing.
C) expenditures, foreign affairs, issuance of money, and borrowing.
D) issuance of money, taxes, environmental regulations, and foreign affairs.
A) expenditures, taxes, transfers, and borrowing.
B) expenditures, taxes, issuance of money, and borrowing.
C) expenditures, foreign affairs, issuance of money, and borrowing.
D) issuance of money, taxes, environmental regulations, and foreign affairs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A competitive equilibrium is a state of affairs in which
A) markets clear, and output is maximized.
B) output is maximized, and all agents are equally well-off.
C) all agents are equally well-off and agents are price-takers.
D) economic agents are price takers and markets clear.
A) markets clear, and output is maximized.
B) output is maximized, and all agents are equally well-off.
C) all agents are equally well-off and agents are price-takers.
D) economic agents are price takers and markets clear.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A relationship that shows the technological possibilities for an economy as a whole is called a
A) production function.
B) utility possibilities frontier.
C) production possibilities frontier.
D) budget constraint.
A) production function.
B) utility possibilities frontier.
C) production possibilities frontier.
D) budget constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In the one-period competitive model we have been studying
A) both consumption and total factor productivity are exogenous.
B) consumption is exogenous and total factor productivity is endogenous.
C) consumption is endogenous and total factor productivity is exogenous.
D) both consumption and total factor productivity are endogenous.
A) both consumption and total factor productivity are exogenous.
B) consumption is exogenous and total factor productivity is endogenous.
C) consumption is endogenous and total factor productivity is exogenous.
D) both consumption and total factor productivity are endogenous.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
An externality is any activity for which an individual firm or consumer does not take into account all
A) of the ramifications of its actions on others.
B) associated costs.
C) associated benefits.
D) associated costs and benefits.
A) of the ramifications of its actions on others.
B) associated costs.
C) associated benefits.
D) associated costs and benefits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The PPF determines
A) all possible outcomes for a given wage.
B) the set of feasible outcomes.
C) given leisure, how much consumption a household wants.
D) the share of consumption in output.
A) all possible outcomes for a given wage.
B) the set of feasible outcomes.
C) given leisure, how much consumption a household wants.
D) the share of consumption in output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
PPF is the
A) price parity formula.
B) possible production function.
C) producer's preferred frontier.
D) production possibilities frontier.
A) price parity formula.
B) possible production function.
C) producer's preferred frontier.
D) production possibilities frontier.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A competitive equilibrium is Pareto optimal if there is no way to rearrange or to reallocate goods so that
A) anyone can be made better off.
B) no one can be made worse off.
C) someone can be made better off without making someone else worse off.
D) someone can be made better off without making everyone else worse off.
A) anyone can be made better off.
B) no one can be made worse off.
C) someone can be made better off without making someone else worse off.
D) someone can be made better off without making everyone else worse off.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The rate at which one good can be converted technologically into another is called
A) the marginal rate of transformation.
B) the marginal rate of substitution.
C) the marginal product of labor.
D) the rate of conversion.
A) the marginal rate of transformation.
B) the marginal rate of substitution.
C) the marginal product of labor.
D) the rate of conversion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The concept of Pareto optimality is a
A) utopian concept.
B) useful concept because it guarantees economic equality.
C) useful concept because it defines economic efficiency.
D) useful concept that carefully balances a society's desires for equality and efficiency.
A) utopian concept.
B) useful concept because it guarantees economic equality.
C) useful concept because it defines economic efficiency.
D) useful concept that carefully balances a society's desires for equality and efficiency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The second fundamental theorem of welfare economics states that
A) under certain conditions, a competitive equilibrium is Pareto optimal.
B) a competitive equilibrium is always Pareto optimal.
C) under certain conditions, a Pareto optimum is a competitive equilibrium.
D) a Pareto optimum is always a competitive equilibrium.
A) under certain conditions, a competitive equilibrium is Pareto optimal.
B) a competitive equilibrium is always Pareto optimal.
C) under certain conditions, a Pareto optimum is a competitive equilibrium.
D) a Pareto optimum is always a competitive equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A competitive equilibrium has all of the following properties except
A) MPN = slope of PFF.
B) MRS?,C = MRT?,C.
C) MRT?,C = MPN.
D) MPN = w.
A) MPN = slope of PFF.
B) MRS?,C = MRT?,C.
C) MRT?,C = MPN.
D) MPN = w.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The presence of a distorting tax on wage income can result in
A) MPN < MRT?,C.
B) MRT?,C < MRS?,C.
C) MPN < w.
D) MRS?,C < MPN
A) MPN < MRT?,C.
B) MRT?,C < MRS?,C.
C) MPN < w.
D) MRS?,C < MPN

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A Pareto optimum is a point that
A) a malevolent dictator would choose.
B) a cooperative coalition of some altruistic consumers would choose.
C) a cooperative coalition of some socially responsible firms would choose.
D) a social planner would choose.
A) a malevolent dictator would choose.
B) a cooperative coalition of some altruistic consumers would choose.
C) a cooperative coalition of some socially responsible firms would choose.
D) a social planner would choose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A competitive equilibrium
A) is always economically efficient.
B) is efficient only if there is an externality.
C) is economically efficient only given some special conditions.
D) does not exist without government taxation.
A) is always economically efficient.
B) is efficient only if there is an externality.
C) is economically efficient only given some special conditions.
D) does not exist without government taxation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Relative to the social optimum,monopoly power tends to lead to
A) underproduction.
B) overproduction.
C) too much leisure.
D) too little leisure.
A) underproduction.
B) overproduction.
C) too much leisure.
D) too little leisure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not equal to the others in equilibrium?
A) the real wage
B) the marginal rate of substitution between leisure and consumption
C) the marginal product of labor
D) the price of consumption
A) the real wage
B) the marginal rate of substitution between leisure and consumption
C) the marginal product of labor
D) the price of consumption

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The first fundamental theorem of welfare economics states that
A) under certain conditions, a competitive equilibrium is Pareto optimal.
B) a competitive equilibrium is always Pareto optimal.
C) under certain conditions, a Pareto optimum is a competitive equilibrium.
D) a Pareto optimum is always a competitive equilibrium.
A) under certain conditions, a competitive equilibrium is Pareto optimal.
B) a competitive equilibrium is always Pareto optimal.
C) under certain conditions, a Pareto optimum is a competitive equilibrium.
D) a Pareto optimum is always a competitive equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A competitive equilibrium fails to be a Pareto Optimum with a distorting tax because
A) the consumer's budget constraint has an additional kink.
B) the firm is no longer maximizing profits.
C) the government wastes its revenue.
D) the consumer faces a different effective wage than the firm.
A) the consumer's budget constraint has an additional kink.
B) the firm is no longer maximizing profits.
C) the government wastes its revenue.
D) the consumer faces a different effective wage than the firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Points on the production possibilities frontier have the property that they
A) are inherently unattainable.
B) show the maximum amount of leisure that can be consumed for given amounts of goods consumed.
C) show the maximum amount of goods that can be consumed for given amounts of government spending.
D) show the maximum amount of leisure that can be consumed for given amounts of hours worked.
A) are inherently unattainable.
B) show the maximum amount of leisure that can be consumed for given amounts of goods consumed.
C) show the maximum amount of goods that can be consumed for given amounts of government spending.
D) show the maximum amount of leisure that can be consumed for given amounts of hours worked.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Under a Pareto Optimum
A) it is always possible to improve someone's welfare.
B) it is never possible to improve someone's welfare.
C) one can only reduce someone's welfare.
D) it is impossible to reduce someone's welfare.
A) it is always possible to improve someone's welfare.
B) it is never possible to improve someone's welfare.
C) one can only reduce someone's welfare.
D) it is impossible to reduce someone's welfare.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A competitive equilibrium may fail to be Pareto optimal due to all of the following except
A) inequality.
B) externalities.
C) distorting taxes.
D) non-price-taking firms.
A) inequality.
B) externalities.
C) distorting taxes.
D) non-price-taking firms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Much of the writings of Adam Smith are in close agreement with
A) the necessity of trade restrictions.
B) the first fundamental theorem of welfare economics.
C) the second theorem of welfare economics.
D) both B and C above.
A) the necessity of trade restrictions.
B) the first fundamental theorem of welfare economics.
C) the second theorem of welfare economics.
D) both B and C above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A Pareto optimum requires all of the following except
A)MPN= -slope of PPF.
B) MRS?,C = MRT?,C.
C) MRS?,C ? MPN.
D) MPN = w.
A)MPN= -slope of PPF.
B) MRS?,C = MRT?,C.
C) MRS?,C ? MPN.
D) MPN = w.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If the government replaces a lump sum tax with a proportional labor income tax,then
A) employment and output increase.
B) employment increases and output decreases.
C) employment decreases and output increases.
D) employment and output decrease.
A) employment and output increase.
B) employment increases and output decreases.
C) employment decreases and output increases.
D) employment and output decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
With a linear production function in labor only,which of the following must be true?
A) The representative household works as much as possible.
B) The representative firm makes large profits.
C) The real wage equals total factor productivity.
D) The marginal product of labor exceeds the real wage.
A) The representative household works as much as possible.
B) The representative firm makes large profits.
C) The real wage equals total factor productivity.
D) The marginal product of labor exceeds the real wage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The variable G considered in the model encompasses
A) government expenses on goods.
B) government expenses on goods and services.
C) government expenses on goods and services as well as transfers.
D) government expenses on goods and services as well as transfers and public debt service.
A) government expenses on goods.
B) government expenses on goods and services.
C) government expenses on goods and services as well as transfers.
D) government expenses on goods and services as well as transfers and public debt service.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
How does an increase in the proportional labor income tax modify the consumer's budget constraint?
A) a parallel move up
B) a parallel move down
C) the slope decreases (constraint gets steeper)
D) the slope increases (constraint gets flatter)
A) a parallel move up
B) a parallel move down
C) the slope decreases (constraint gets steeper)
D) the slope increases (constraint gets flatter)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
An increase in total factor productivity
A) increases consumption, increases output, and increases the real wage.
B) reduces consumption, increases output, and increases the real wage.
C) reduces consumption, increases output and reduces the real wage.
D) reduces consumption, reduces output, and reduces the real wage.
A) increases consumption, increases output, and increases the real wage.
B) reduces consumption, increases output, and increases the real wage.
C) reduces consumption, increases output and reduces the real wage.
D) reduces consumption, reduces output, and reduces the real wage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
At the competitive equilibrium with a positive proportional labor income tax
A) the real wage after tax exceeds the marginal product of labor.
B) the real wage after tax equals the marginal product of labor.
C) the real wage after tax is lower than the marginal product of labor.
D) We cannot say.
A) the real wage after tax exceeds the marginal product of labor.
B) the real wage after tax equals the marginal product of labor.
C) the real wage after tax is lower than the marginal product of labor.
D) We cannot say.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Changes in total factor productivity are plausible causes of business cycles because productivity-induced business cycles correctly predict
A) real wages and total hours must be procyclical.
B) real wages and consumption must be procyclical.
C) total hours worked and consumption must be procyclical.
D) consumption and government spending must be procyclical.
A) real wages and total hours must be procyclical.
B) real wages and consumption must be procyclical.
C) total hours worked and consumption must be procyclical.
D) consumption and government spending must be procyclical.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
An increase in government spending
A) increases consumption and output.
B) increases consumption, decreases output.
C) decreases consumption, increases output.
D) decreases consumption and output.
A) increases consumption and output.
B) increases consumption, decreases output.
C) decreases consumption, increases output.
D) decreases consumption and output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
An increase in government spending shifts the PPF
A) upward, but does not change its slope.
B) upward, and also changes its slope.
C) downward, but does not change its slope.
D) downward, and also changes its slope.
A) upward, but does not change its slope.
B) upward, and also changes its slope.
C) downward, but does not change its slope.
D) downward, and also changes its slope.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In response to an increase in total factor productivity
A) both the substitution effect and the income effect suggest that hours worked should increase.
B) the substitution effect suggests that hours worked should increase, while the income effect suggests that hours worked should decrease.
C) the substitution effect suggests that hours worked should decrease, while the income effect suggests that hours worked should increase.
D) both the substitution effect and the income effect suggest that hours worked should decrease.
A) both the substitution effect and the income effect suggest that hours worked should increase.
B) the substitution effect suggests that hours worked should increase, while the income effect suggests that hours worked should decrease.
C) the substitution effect suggests that hours worked should decrease, while the income effect suggests that hours worked should increase.
D) both the substitution effect and the income effect suggest that hours worked should decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
An increase in government spending
A) increases consumption, increases hours worked, and increases the real wage.
B) reduces consumption, increases hours worked, and increases the real wage.
C) reduces consumption, increases hours worked, and reduces the real wage.
D) reduces consumption, reduces hours worked, and reduces the real wage.
A) increases consumption, increases hours worked, and increases the real wage.
B) reduces consumption, increases hours worked, and increases the real wage.
C) reduces consumption, increases hours worked, and reduces the real wage.
D) reduces consumption, reduces hours worked, and reduces the real wage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which feature of the business cycle does the one-period model replicate with shocks to government expenditures?
A) procyclical employment
B) procyclical consumption
C) procyclical real wages
D) countercyclical prices
A) procyclical employment
B) procyclical consumption
C) procyclical real wages
D) countercyclical prices

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Changes in government spending are not likely causes of business cycles because changes in government spending predict
A) countercyclical real wages.
B) procyclical real wages.
C) countercyclical employment.
D) procyclical employment.
A) countercyclical real wages.
B) procyclical real wages.
C) countercyclical employment.
D) procyclical employment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Proportional income taxation is distorting because
A) people do all they can to avoid paying taxes.
B) the competitive equilibrium is not Pareto optimal.
C) firms do all they can to avoid paying taxes.
D) the government budget constraint does not hold.
A) people do all they can to avoid paying taxes.
B) the competitive equilibrium is not Pareto optimal.
C) firms do all they can to avoid paying taxes.
D) the government budget constraint does not hold.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A one-unit increase in government expenditures should,according to the model,increase GDP by
A) 0.
B) between zero and one unit.
C) one unit.
D) more than one unit.
A) 0.
B) between zero and one unit.
C) one unit.
D) more than one unit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
An increase in total factor productivity shifts the PPF
A) upward, but does not change its slope.
B) upward, and also changes its slope.
C) downward, but does not change its slope.
D) downward, and also changes its slope.
A) upward, but does not change its slope.
B) upward, and also changes its slope.
C) downward, but does not change its slope.
D) downward, and also changes its slope.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Changes in total factor productivity are plausible causes of business cycles because
A) of the welfare theorems.
B) the U.S. government is following supply-side economic policy.
C) the model matches many stylized facts.
D) prices are countercyclical.
A) of the welfare theorems.
B) the U.S. government is following supply-side economic policy.
C) the model matches many stylized facts.
D) prices are countercyclical.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Changes in government spending are not likely causes of business cycles because changes in government spending predict
A) countercyclical consumption.
B) procyclical consumption.
C) countercyclical employment.
D) procyclical employment.
A) countercyclical consumption.
B) procyclical consumption.
C) countercyclical employment.
D) procyclical employment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Real business cycle theory argues that the primary cause of business cycles is fluctuations in
A) preferences.
B) government spending.
C) the importance of externalities.
D) total factor productivity.
A) preferences.
B) government spending.
C) the importance of externalities.
D) total factor productivity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Suppose total factor productivity increases. Which of the following is incorrect?
A) Households are better off.
B) Consumption goes up.
C) The real wage goes down.
D) Output goes up.
A) Households are better off.
B) Consumption goes up.
C) The real wage goes down.
D) Output goes up.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
In the model of public goods
A) government spending is pure waste
B) private consumption and government spending are equal.
C) consumers benefit from private goods and public goods.
D) the government provides goods at no cost to the public.
A) government spending is pure waste
B) private consumption and government spending are equal.
C) consumers benefit from private goods and public goods.
D) the government provides goods at no cost to the public.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
If public goods can be produced more efficiently,then
A) public goods increase, and private goods may increase or decrease.
B) public goods production stays the same, and private goods increase.
C) public goods and private goods both increase.
D) public goods production falls, and private goods production rises.
A) public goods increase, and private goods may increase or decrease.
B) public goods production stays the same, and private goods increase.
C) public goods and private goods both increase.
D) public goods production falls, and private goods production rises.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
In the model of public goods
A) GDP is fixed.
B) there is a production function.
C) labor supply matters.
D) public goods production is proportional to labor input.
A) GDP is fixed.
B) there is a production function.
C) labor supply matters.
D) public goods production is proportional to labor input.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The Laffer curve is a curve showing
A) output as a function of the tax rate.
B) tax revenue as a function of the tax rate.
C) government expenses as a function of how liberal the government is.
D) the tax rate as a function of government expenses.
A) output as a function of the tax rate.
B) tax revenue as a function of the tax rate.
C) government expenses as a function of how liberal the government is.
D) the tax rate as a function of government expenses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
When the tax rate increases,the tax revenue
A) always increases.
B) does not change.
C) always decreases.
D) may increase or decrease.
A) always increases.
B) does not change.
C) always decreases.
D) may increase or decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Supply-side economists argue that
A) one should get rid of all taxes.
B) tax rates should not be progressive.
C) increasing tax rates always hurts tax revenue.
D) one can increase tax revenue by decreasing the tax rate.
A) one should get rid of all taxes.
B) tax rates should not be progressive.
C) increasing tax rates always hurts tax revenue.
D) one can increase tax revenue by decreasing the tax rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The tax base is
A) the average tax rate.
B) the tax rate for the base year.
C) the object being taxed.
D) the lowest tax rate.
A) the average tax rate.
B) the tax rate for the base year.
C) the object being taxed.
D) the lowest tax rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If GDP increases in the model of public goods
A) people are richer, so they need less public goods.
B) there is substitution from private goods to public goods.
C) if the government provides public goods optimally, public and private goods production both increase.
D) all of the increase in GDP goes into public goods.
A) people are richer, so they need less public goods.
B) there is substitution from private goods to public goods.
C) if the government provides public goods optimally, public and private goods production both increase.
D) all of the increase in GDP goes into public goods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
At the competitive equilibrium with a positive proportional labor income tax
A) the real wage before tax exceeds the marginal product of labor.
B) the real wage before tax equals the marginal product of labor.
C) the real wage before tax is lower than the marginal product of labor.
D) We cannot say.
A) the real wage before tax exceeds the marginal product of labor.
B) the real wage before tax equals the marginal product of labor.
C) the real wage before tax is lower than the marginal product of labor.
D) We cannot say.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
In the model of public goods,when the government chooses public goods provision optimally
A) there is no public goods production.
B) public goods are provided in an amount equal to private goods.
C) the marginal rate of substitution of private goods for public goods equals the marginal rate of transformation.
D) GDP is maximized.
A) there is no public goods production.
B) public goods are provided in an amount equal to private goods.
C) the marginal rate of substitution of private goods for public goods equals the marginal rate of transformation.
D) GDP is maximized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 70 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








