Deck 13: Passing on Lifes Information: Dna Structure and Replication
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Passing on Lifes Information: Dna Structure and Replication
1
Imagine that the DNA replication error rate for a strain of bacterium that has a defective repair mechanism is 1 in 10 million. If the cell's genome is 5 million nucleotide pairs, how often will the genome sustain a mutation in this strain, keeping in mind that both strands of a DNA molecule are replicated at once?
A) once every five cell divisions
B) once per cell division
C) twice per cell division
D) four times per cell division
E) once every ten cell divisions
A) once every five cell divisions
B) once per cell division
C) twice per cell division
D) four times per cell division
E) once every ten cell divisions
B
2
It was primarily the X-ray diffraction work on DNA done by ________ that allowed Watson and Crick to deduce the structure of DNA.
A) Louis Pasteur
B) Gregor Mendel
C) Rosalind Franklin
D) T.H. Morgan
A) Louis Pasteur
B) Gregor Mendel
C) Rosalind Franklin
D) T.H. Morgan
C
3
How many different types of bases are used to encode all the genetic information in a molecule of DNA?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 20
D) 10
E) 5
A) 2
B) 4
C) 20
D) 10
E) 5
B
4
What are the products of the replication of one DNA molecule?
A) four identical double-stranded DNA molecules
B) two strands joined into one double-stranded DNA molecule
C) two identical double-stranded DNA molecules
D) a set of four sister chromatids
E) a pair of homologous chromosomes
A) four identical double-stranded DNA molecules
B) two strands joined into one double-stranded DNA molecule
C) two identical double-stranded DNA molecules
D) a set of four sister chromatids
E) a pair of homologous chromosomes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
How is the information that specifies a protein stored in DNA?
A) in the arrangement of the sugar-phosphate chain
B) in the types of chemical bonds holding bases together
C) in the sequence of bases
D) in the orientation of the double strands
A) in the arrangement of the sugar-phosphate chain
B) in the types of chemical bonds holding bases together
C) in the sequence of bases
D) in the orientation of the double strands

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The location of genetic information on chromosomes had been established beyond any doubt by:
A) 1880.
B) 1850.
C) 1890.
D) 1920.
E) 1900.
A) 1880.
B) 1850.
C) 1890.
D) 1920.
E) 1900.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Watson and Crick's model of the structure of DNA was published in:
A) 1953.
B) 1961.
C) 1923.
D) 1949.
E) 1975.
A) 1953.
B) 1961.
C) 1923.
D) 1949.
E) 1975.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The nucleotides in one strand of DNA are held together by:
A) bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the base of the next.
B) hydrogen bonds between phosphates.
C) bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the base of the next.
D) hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
E) links between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next.
A) bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the base of the next.
B) hydrogen bonds between phosphates.
C) bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the base of the next.
D) hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
E) links between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
What is meant by saying one strand of DNA is the template for the synthesis of another strand?
A) A strand of DNA is taken apart to supply nucleotides for synthesis of a new strand.
B) One strand of DNA acts as a wedge to separate other strands before replication.
C) The template specifies the order of bases of the strand being made.
D) The new strand will have exactly the same base sequence as the template strand.
E) A strand of DNA is the enzyme that connects nucleotides in replication.
A) A strand of DNA is taken apart to supply nucleotides for synthesis of a new strand.
B) One strand of DNA acts as a wedge to separate other strands before replication.
C) The template specifies the order of bases of the strand being made.
D) The new strand will have exactly the same base sequence as the template strand.
E) A strand of DNA is the enzyme that connects nucleotides in replication.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements about the two strands of a DNA molecule is true?
A) An A base on one strand always pairs with a G base on the other strand.
B) The strands are a pair of sister chromatids.
C) The strands are connected to each other by sugar-phosphate bonds.
D) A T base on one strand always pairs with an A base on the other strand.
E) The strands have identical base sequences.
A) An A base on one strand always pairs with a G base on the other strand.
B) The strands are a pair of sister chromatids.
C) The strands are connected to each other by sugar-phosphate bonds.
D) A T base on one strand always pairs with an A base on the other strand.
E) The strands have identical base sequences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
How are X rays used in the technique of X-ray diffraction?
A) The scattering of X rays by a purified form of a molecule reveals its structure.
B) DNA strands are separated by X-ray energy, revealing the order of bases.
C) Cells are broken open to release chromosomes by being bombarded with X rays.
D) The X rays are used to mutate DNA to determine the location of genes.
E) Enzymes are destroyed by X rays, revealing the order of steps in metabolism.
A) The scattering of X rays by a purified form of a molecule reveals its structure.
B) DNA strands are separated by X-ray energy, revealing the order of bases.
C) Cells are broken open to release chromosomes by being bombarded with X rays.
D) The X rays are used to mutate DNA to determine the location of genes.
E) Enzymes are destroyed by X rays, revealing the order of steps in metabolism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Why are the strands of DNA said to be complementary to each other?
A) The sugar-phosphate chains are running in opposite directions.
B) The sugar-phosphate chains of each strand are identical.
C) Both strands can have any of four possible bases attached.
D) All the bases of one strand are paired up with their complementary bases on the other strand.
A) The sugar-phosphate chains are running in opposite directions.
B) The sugar-phosphate chains of each strand are identical.
C) Both strands can have any of four possible bases attached.
D) All the bases of one strand are paired up with their complementary bases on the other strand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The building blocks of DNA are:
A) amino acids.
B) enzymes.
C) phosphate groups.
D) nucleotides.
E) bases.
A) amino acids.
B) enzymes.
C) phosphate groups.
D) nucleotides.
E) bases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which information was determined about DNA based on X-ray diffraction data?
A) Each gene encodes one enzyme.
B) There are four different bases on the nucleotides.
C) Point mutations change a single location in the genome.
D) DNA has a helical structure.
E) Chromosomes are made of DNA.
A) Each gene encodes one enzyme.
B) There are four different bases on the nucleotides.
C) Point mutations change a single location in the genome.
D) DNA has a helical structure.
E) Chromosomes are made of DNA.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What is the relationship between DNA and proteins?
A) Genes are made of proteins that encode the base sequence of DNA.
B) DNA stores the information needed to make proteins.
C) DNA makes up the individual sugar-phosphate-base units of a protein.
D) DNA molecules are the enzymes that synthesize proteins.
E) Proteins store the information needed to make DNA.
A) Genes are made of proteins that encode the base sequence of DNA.
B) DNA stores the information needed to make proteins.
C) DNA makes up the individual sugar-phosphate-base units of a protein.
D) DNA molecules are the enzymes that synthesize proteins.
E) Proteins store the information needed to make DNA.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What is the function of DNA polymerase?
A) synthesizing nucleotides from free sugars, phosphates, and bases
B) halting DNA replication if a cell becomes cancerous
C) breaking sugar-phosphate bonds to release free nucleotides for DNA synthesis
D) introducing mutations into DNA for evolutionary adaptation
E) joining together nucleotides as they are base-paired during DNA replication
A) synthesizing nucleotides from free sugars, phosphates, and bases
B) halting DNA replication if a cell becomes cancerous
C) breaking sugar-phosphate bonds to release free nucleotides for DNA synthesis
D) introducing mutations into DNA for evolutionary adaptation
E) joining together nucleotides as they are base-paired during DNA replication

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Watson and Crick discovered:
A) the structure of DNA.
B) that DNA is the genetic material.
C) X-ray crystallography.
D) that genetic information resides on chromosomes.
A) the structure of DNA.
B) that DNA is the genetic material.
C) X-ray crystallography.
D) that genetic information resides on chromosomes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of these individuals are credited with the discovery of the structure of DNA?
A) Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
B) Gregor Mendel and T.H. Morgan
C) James Watson and Francis Crick
D) Louis Pasteur
A) Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
B) Gregor Mendel and T.H. Morgan
C) James Watson and Francis Crick
D) Louis Pasteur

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
What is one way that incorrect nucleotides are removed from a newly synthesized molecule of DNA?
A) Crossing over replaces regions with DNA errors with new segments of DNA.
B) DNA ligases both remove and replace incorrectly positioned nucleotides.
C) Any DNA strand with an error is destroyed, and an entire new strand is synthesized.
D) DNA polymerases remove incorrect nucleotides and replace them with correct ones.
E) DNA ligases remove incorrect nucleotides for replacement by DNA polymerases.
A) Crossing over replaces regions with DNA errors with new segments of DNA.
B) DNA ligases both remove and replace incorrectly positioned nucleotides.
C) Any DNA strand with an error is destroyed, and an entire new strand is synthesized.
D) DNA polymerases remove incorrect nucleotides and replace them with correct ones.
E) DNA ligases remove incorrect nucleotides for replacement by DNA polymerases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not a component of DNA nucleotides?
A) deoxyribose
B) a phosphate group
C) adenine
D) arginine
E) guanine
A) deoxyribose
B) a phosphate group
C) adenine
D) arginine
E) guanine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
What is a point mutation?
A) a mutation that affects a single cell
B) a mutation in which one chromosome is lost
C) an error in DNA that is caused by malfunctioning of DNA ligase
D) a mutation found at a single base pair in the genome
E) a mutation that affects only one metabolic pathway
A) a mutation that affects a single cell
B) a mutation in which one chromosome is lost
C) an error in DNA that is caused by malfunctioning of DNA ligase
D) a mutation found at a single base pair in the genome
E) a mutation that affects only one metabolic pathway

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In DNA, A, C, G, and T are abbreviations for the:
A) different types of bases on the nucleotides.
B) different types of sugars on the nucleotides.
C) types of genes found on DNA chromosomes.
D) different types of bonds that form between nucleotides.
E) different types of phosphates on the nucleotides.
A) different types of bases on the nucleotides.
B) different types of sugars on the nucleotides.
C) types of genes found on DNA chromosomes.
D) different types of bonds that form between nucleotides.
E) different types of phosphates on the nucleotides.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The DNA of a cell is analyzed and found to contain 28 percent thymine. What percent of the DNA would by cytosine?
A) 22 percent
B) 28 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 25 percent
A) 22 percent
B) 28 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 25 percent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The average mutation rate for DNA replication is 1 mutation for every 10 billion (10,000,000,000) nucleotides of DNA replicated. Yet DNA polymerase makes a mistake during replication at an average of 1 in 100,000 nucleotides. What does this say about DNA replication?
A) Most errors in DNA replication become mutations.
B) The base-pairing rules (A pairs with T and G pairs with
C) Cells are extraordinarily proficient at repairing errors made during DNA replication.
C) prevent any mutations.
D) Cells recognize that a small fraction of mutations are beneficial to organisms and do not repair those.
A) Most errors in DNA replication become mutations.
B) The base-pairing rules (A pairs with T and G pairs with
C) Cells are extraordinarily proficient at repairing errors made during DNA replication.
C) prevent any mutations.
D) Cells recognize that a small fraction of mutations are beneficial to organisms and do not repair those.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The three components of a DNA nucleotide are:
A) amino acids, phosphates, and deoxyribose.
B) bases, deoxyribose, and polymerases.
C) genes, sugars, and bases.
D) phosphates, sugars, and bases.
E) polymerases, ligases, and sugars.
A) amino acids, phosphates, and deoxyribose.
B) bases, deoxyribose, and polymerases.
C) genes, sugars, and bases.
D) phosphates, sugars, and bases.
E) polymerases, ligases, and sugars.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Cancer is a disease caused by mutations. Yet in most instances if one of your parents tragically died from cancer, this does not put you at greater risk than a person whose parents do not develop cancer. How can cancer be caused by mutations and yet not be heritable?
A) The mutations that cause cancer are special and cannot be passed on regardless of what type of cell they occur in.
B) Most cancers arise from mutations in germ-line cells.
C) Most cancers arise from mutations in somatic cells.
D) Cancer-causing mutations are repaired in offspring but not in parents.
A) The mutations that cause cancer are special and cannot be passed on regardless of what type of cell they occur in.
B) Most cancers arise from mutations in germ-line cells.
C) Most cancers arise from mutations in somatic cells.
D) Cancer-causing mutations are repaired in offspring but not in parents.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A key part of DNA's function is to encode information. In considering how information-rich a particular molecule might be, a question is how many different sequences are possible in a particular length of the molecule. In the case of DNA the four different nucleotides can be arranged in any order. How many different sequences are possible for a DNA strand three nucleotides long?
A) 4
B) 32
C) 16
D) 64
E) 3
A) 4
B) 32
C) 16
D) 64
E) 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What is the complementary sequence for a segment of DNA with the sequence ACGGCT?
A) TCGGCA
B) AGCCGT
C) TGCCGA
D) ACGGCT
E) GTAATC
A) TCGGCA
B) AGCCGT
C) TGCCGA
D) ACGGCT
E) GTAATC

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
If the sequence TCGTA was used as a template in DNA replication, what would be the sequence of bases on the newly synthesized strand?
A) ATGCT
B) CTACG
C) AGCAT
D) GCATC
E) TCGTA
A) ATGCT
B) CTACG
C) AGCAT
D) GCATC
E) TCGTA

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
What happens to the two original strands of a DNA molecule after the DNA has replicated?
A) After serving as replication templates, the two original strands are rejoined.
B) After serving as replication templates, the two original strands are destroyed.
C) Nucleotides from the original strands are randomly incorporated into the new strands.
D) Incomplete segments of the original strands end up in each newly synthesized strand.
E) Each original strand ends up paired with a newly synthesized strand.
A) After serving as replication templates, the two original strands are rejoined.
B) After serving as replication templates, the two original strands are destroyed.
C) Nucleotides from the original strands are randomly incorporated into the new strands.
D) Incomplete segments of the original strands end up in each newly synthesized strand.
E) Each original strand ends up paired with a newly synthesized strand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A base pair is a unit of DNA that consists of:
A) one sugar bonded to one phosphate.
B) a single chromosome.
C) one nucleotide.
D) two nucleotides, one on each complementary strand of a DNA molecule.
E) two identical chromosomes.
A) one sugar bonded to one phosphate.
B) a single chromosome.
C) one nucleotide.
D) two nucleotides, one on each complementary strand of a DNA molecule.
E) two identical chromosomes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The two strands of a double helix of DNA are linked by what kind of bond?
A) sugar-phosphate linkages
B) hydrogen bonds between bases
C) hydrogen bonds between sugars and phosphates
D) sugar-base linkages
E) base-phosphate linkages
A) sugar-phosphate linkages
B) hydrogen bonds between bases
C) hydrogen bonds between sugars and phosphates
D) sugar-base linkages
E) base-phosphate linkages

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
How do most mutations affect an organism?
A) Most mutations either are harmful, or they have no effect.
B) Most mutations will kill the organism.
C) Most mutations create cancerous cells.
D) Most mutations are beneficial and create a more adapted organism.
A) Most mutations either are harmful, or they have no effect.
B) Most mutations will kill the organism.
C) Most mutations create cancerous cells.
D) Most mutations are beneficial and create a more adapted organism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
There are two alleles for each gene in a cell. If each gene encodes for a particular protein, what would make two alleles different from each other?
A) The sequence of bases in the DNA for each allele would be slightly different and would lead to the production of slightly different proteins.
B) The sequence of bases in the DNA would be different for each allele, but they would result in the production of identical proteins.
C) The sequence of bases in the DNA would be identical for each allele, but they would produce very different proteins.
D) The sequence of bases in the DNA would be identical for each allele, but one would produce a protein and the other would not.
A) The sequence of bases in the DNA for each allele would be slightly different and would lead to the production of slightly different proteins.
B) The sequence of bases in the DNA would be different for each allele, but they would result in the production of identical proteins.
C) The sequence of bases in the DNA would be identical for each allele, but they would produce very different proteins.
D) The sequence of bases in the DNA would be identical for each allele, but one would produce a protein and the other would not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Mutations that occur in somatic cells are:
A) responsible for the appearance of human diseases such as sickle-cell anemia.
B) never harmful.
C) passed on to successive generations when they are incorporated into gametes.
D) not passed on to future generations.
E) always harmful.
A) responsible for the appearance of human diseases such as sickle-cell anemia.
B) never harmful.
C) passed on to successive generations when they are incorporated into gametes.
D) not passed on to future generations.
E) always harmful.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
On average, if you examine 1 million human cells looking at a single gene, you'll find one cell with a mutation in that gene. If you were looking at a gene that could lead to cancer when mutated, how many mutated copies of that gene would you find in a person? (Assume a person contains 100 trillion [100,000,000,000,000] cells.)
A) 100,000,000
B) 1,000
C) 1,000,000
D) 10,000,000,000
E) 100
A) 100,000,000
B) 1,000
C) 1,000,000
D) 10,000,000,000
E) 100

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A DNA molecule can be described as a twisted ladder. The ________ form the sides, and the ________ form the rungs.
A) base pairs; sugar-phosphate chains
B) sugars; phosphates
C) sugars; base pairs
D) sugar-phosphate chains; base pairs
A) base pairs; sugar-phosphate chains
B) sugars; phosphates
C) sugars; base pairs
D) sugar-phosphate chains; base pairs

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which process changes, adds, or removes information from the genome?
A) mutation
B) DNA replication
C) genetic recombination
D) crossing over
E) cancer
A) mutation
B) DNA replication
C) genetic recombination
D) crossing over
E) cancer

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Melanoma is a cancer that is frequently associated with a mutation in what gene?
A) in the IT15 gene
B) in the DNA polymerase gene
C) in the BRAF gene
D) in the Huntington gene
A) in the IT15 gene
B) in the DNA polymerase gene
C) in the BRAF gene
D) in the Huntington gene

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which type of mutation will have the most impact from an evolutionary point of view?
A) a mutation in a somatic cell
B) a mutation in a liver cell
C) a mutation in a germ-line cell
D) a mutation in a brain cell
A) a mutation in a somatic cell
B) a mutation in a liver cell
C) a mutation in a germ-line cell
D) a mutation in a brain cell

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
What is the cause of Huntington disease?
A) a somatic cell mutation that causes cells to proliferate without control
B) a mutation that results in defective DNA polymerase
C) loss of the chromosome with the gene for a blood protein
D) a mutation in which there are repeating groups of three nucleotides
E) a mutation that results in defective amino acid synthesis
A) a somatic cell mutation that causes cells to proliferate without control
B) a mutation that results in defective DNA polymerase
C) loss of the chromosome with the gene for a blood protein
D) a mutation in which there are repeating groups of three nucleotides
E) a mutation that results in defective amino acid synthesis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Any agent that can change the base sequence of DNA is known as a:
A) trinucleotide repeat.
B) free radical.
C) cancer.
D) mutagen.
E) spontaneous event.
A) trinucleotide repeat.
B) free radical.
C) cancer.
D) mutagen.
E) spontaneous event.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
What is the benefit of mutations?
A) They eliminate unneeded regions of chromosomes.
B) They increase the shuffling of existing genetic information.
C) They create cancerous cells, which grow faster than others.
D) They add new genetic information upon which evolution can act.
A) They eliminate unneeded regions of chromosomes.
B) They increase the shuffling of existing genetic information.
C) They create cancerous cells, which grow faster than others.
D) They add new genetic information upon which evolution can act.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
DNA polymerase cannot copy point mutations, so they are not passed on from parent cells to daughter cells in cell division.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Which of the following would be considered an environmental mutagen?
A) free radicals
B) ultraviolet light
C) spontaneous events
D) the collision of water molecules with DNA
E) DNA replication errors
A) free radicals
B) ultraviolet light
C) spontaneous events
D) the collision of water molecules with DNA
E) DNA replication errors

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What is the difference between whole-chromosome aberrations and point mutations?
A) Point mutations are not permanent changes in the DNA; aberrations are permanent.
B) Aberrations are not permanent changes in the DNA; point mutations are permanent.
C) Point mutations are the loss of parts of chromosomes; aberrations are the loss of whole chromosomes.
D) Point mutations affect a single base pair in the genome; aberrations affect a large section.
A) Point mutations are not permanent changes in the DNA; aberrations are permanent.
B) Aberrations are not permanent changes in the DNA; point mutations are permanent.
C) Point mutations are the loss of parts of chromosomes; aberrations are the loss of whole chromosomes.
D) Point mutations affect a single base pair in the genome; aberrations affect a large section.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Watson and Crick's experiments involved isolating DNA, generating X-ray diffraction images of the DNA, and building a model of its structure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In a normal DNA molecule, adenine always pairs with ________, and cytosine always pairs with ________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
What is the relationship between mutations and cancer?
A) Cells do not require mutations to become cancerous but acquire them as they divide.
B) Cells lose the ability to mutate their DNA and evolve once they become cancerous.
C) Some mutations cause cells to lose control over cell division, resulting in cancer.
D) Any point mutation will cause a cell to start proliferating without control, resulting in cancer.
E) Only a mutation can stop a cell once it becomes cancerous.
A) Cells do not require mutations to become cancerous but acquire them as they divide.
B) Cells lose the ability to mutate their DNA and evolve once they become cancerous.
C) Some mutations cause cells to lose control over cell division, resulting in cancer.
D) Any point mutation will cause a cell to start proliferating without control, resulting in cancer.
E) Only a mutation can stop a cell once it becomes cancerous.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The structure of a molecule can be revealed by bombarding it with X rays.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The bases of each strand of a double helix are paired with bases on the other strand, so each strand of DNA is said to be ________ to the other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The structure of DNA allows repair of simple damage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Most point mutations have immediate, drastic effects on an organism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The structure of DNA allows the molecule to store information.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
What happens if an incorrect nucleotide is not removed and replaced by the cell's DNA-correcting machinery?
A) A point mutation has occurred.
B) The result is a chromosomal aberration.
C) The effect will be lethal, and the cell will die.
D) The cell will become cancerous.
E) The entire chromosome must be destroyed.
A) A point mutation has occurred.
B) The result is a chromosomal aberration.
C) The effect will be lethal, and the cell will die.
D) The cell will become cancerous.
E) The entire chromosome must be destroyed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A trinucleotide repeat refers to:
A) a nucleotide that is made of three subunits: a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
B) a sequence of three nucleotides that repeats and can be involved in genetic diseases.
C) the same nucleotide repeating three times in a row.
D) a nucleotide that contains three bases.
A) a nucleotide that is made of three subunits: a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
B) a sequence of three nucleotides that repeats and can be involved in genetic diseases.
C) the same nucleotide repeating three times in a row.
D) a nucleotide that contains three bases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The structure of DNA allows the molecule to replicate itself.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Base-pairing rules apply from one DNA strand to its partner, but not along the sugar-phosphate "handrails" of a DNA strand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
What is one mechanism by which a mutation can cause melanoma?
A) by causing the accumulation of Huntington protein in melanocytes, which keeps them moving through the cell cycle
B) by causing the accumulation of altered BRAF protein in germ-line cells
C) by the production of an altered BRAF protein that keeps melanocytes moving through the cell cycle
D) by preventing the BRAF protein from being able to repair damaged DNA
A) by causing the accumulation of Huntington protein in melanocytes, which keeps them moving through the cell cycle
B) by causing the accumulation of altered BRAF protein in germ-line cells
C) by the production of an altered BRAF protein that keeps melanocytes moving through the cell cycle
D) by preventing the BRAF protein from being able to repair damaged DNA

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Errors never occur in DNA replication because the DNA polymerases edit out mistakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Describe what happens to the two parent strands of DNA during DNA replication.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows. 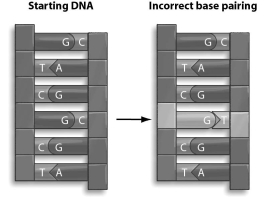
A mistake is made during DNA replication, so there is incorrect base pairing in the DNA. Depending on how the replication repair mechanism fixes this problem, a point mutation may or may not result. What might the replication repair mechanism do, and would it result in a point mutation?
A) The repair mechanism might replace the T with a C, which would result in a point mutation.
B) The repair mechanism might replace the G with an A, which would result in a point mutation.
C) The repair mechanism might replace the G with a C, which would result in a point mutation.
D) The repair mechanism might replace the T with a G, which would not result in a point mutation.

A mistake is made during DNA replication, so there is incorrect base pairing in the DNA. Depending on how the replication repair mechanism fixes this problem, a point mutation may or may not result. What might the replication repair mechanism do, and would it result in a point mutation?
A) The repair mechanism might replace the T with a C, which would result in a point mutation.
B) The repair mechanism might replace the G with an A, which would result in a point mutation.
C) The repair mechanism might replace the G with a C, which would result in a point mutation.
D) The repair mechanism might replace the T with a G, which would not result in a point mutation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
What mechanism can introduce new genetic information into a species?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
________ is the enzyme involved in joining nucleotides as they are paired up.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows. 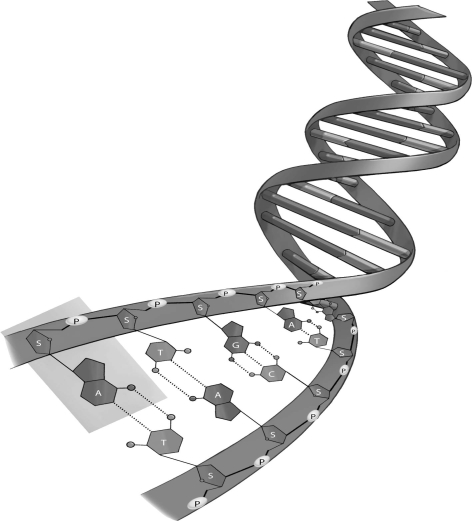
A G-C base pair holds the double helix together more strongly than an A-T base pair. Can you suggest a reason why?

A G-C base pair holds the double helix together more strongly than an A-T base pair. Can you suggest a reason why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Early in the twentieth century, many biologists believed that the genetic material of living organisms had to be made of protein-it seemed that only proteins had the complexity to store the vast amount of genetic information that organisms need. How is a relatively simple molecule such as DNA capable of storing large amounts of genetic information? Another requirement for genetic material is that it will sometimes need to be replicated. How does DNA satisfy this requirement?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Write the sequence of the DNA strand complementary to a strand with the sequence AAATGCC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
A mutation involving a single base pair in the genome is called a ________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Mutations will not be passed on to the next generation if they occur in ________ cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Individuals who have a disease such as melanoma do not necessarily have offspring with melanoma. However, individuals with Huntington disease often do pass it on to their offspring. What accounts for the difference in the heritability of the two diseases?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Suppose you are a biologist trying to discover the process by which DNA copies itself. You grow cells in a culture that contains a special isotope of nitrogen, N-15, which will become part of any new DNA the cell makes. After one generation, you analyze the DNA and find all the DNA has some N-15 in it. You then take those cells and grow them for another generation in a culture with the normal isotope of nitrogen, N-14, and find that half of the DNA has some N-15 in it and half of it has only N-14. From this information, what can you infer is the process by which DNA replicates?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








