Deck 23: Simulation
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 23: Simulation
1
Random number intervals are based on cumulative probability distributions.
True
2
Simulation allows managers to test the effects of major policy decisions on real-life systems without disturbing the real system.
True
3
The idea behind simulation is threefold: (1) to imitate a real-world situation mathematically, (2) then to study its properties and operating characteristics, and (3) finally to draw conclusions and make action decisions based on the results of the simulation.
True
4
Simulation models that are based on the generation of random numbers may fail to give the same solution in repeated use to any particular problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
By starting random number intervals at 01, not 00, the top of each range is the cumulative probability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Like mathematical and analytical models, simulation is restricted to using the standard probability distributions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A simulation is "Monte Carlo" when the elements of a system being simulated exhibit chance in their behavior.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Simulation is the attempt to duplicate the features, appearance, and characteristics of a real system, usually by means of a computerized model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In most real-world inventory problems, lead time and demand vary in ways that make simulation a necessity because mathematical modeling is extremely difficult.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Simulation models are inexpensive to design and use.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Simulation is usually capable of producing a more appropriate answer to a complex problem than can be obtained from a mathematical model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Simulation has numerous applications in modern business, but few of these are in the area of operations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Results of simulation experiments with large numbers of trials or long experimental runs will generally be better than those with fewer trials or shorter experimental runs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Simulation provides optimal solutions to problems.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
One effective use of simulation is to study problems for which the mathematical models of operations management are not realistic enough.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A simulation model is designed to arrive at a single specific numerical answer to a given problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A reason for the use of simulation in queuing is that the four standard queuing models do not allow for unusual arrival and service distributions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
One reason for using simulation rather than an analytical model in an inventory problem is that the simulation is able to handle probabilistic demand and lead times.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
All forms of simulation are based on probability or chance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Virtually all large-scale simulations take place on computers, but small simulations can be conducted by hand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The Las Vegas method is a simulation technique that uses random elements when chance exists in their behaviour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
One of the advantages of simulation is that
A) it is much less expensive than a mathematical solution.
B) it always generates a more accurate solution than a mathematical solution.
C) the policy changes may be tried out without disturbing the real-life system.
D) model development is less time consuming than for mathematical models.
E) model solutions are transferable to a wide variety of problems.
A) it is much less expensive than a mathematical solution.
B) it always generates a more accurate solution than a mathematical solution.
C) the policy changes may be tried out without disturbing the real-life system.
D) model development is less time consuming than for mathematical models.
E) model solutions are transferable to a wide variety of problems.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
One of the disadvantages of simulation is that it
A) does not allow for very complex problem solutions.
B) is not very flexible.
C) may be very expensive and time-consuming to develop.
D) is very limited in the type of probability distribution that can be used.
E) interferes with the production systems while the program is being run.
A) does not allow for very complex problem solutions.
B) is not very flexible.
C) may be very expensive and time-consuming to develop.
D) is very limited in the type of probability distribution that can be used.
E) interferes with the production systems while the program is being run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true regarding simulation?
A) Small problems can be done by hand.
B) Most simulations are computerized.
C) Real-world complications can be included in simulation models.
D) Simulation is most suitable where standard analytical models are too complex.
E) All of the above are true.
A) Small problems can be done by hand.
B) Most simulations are computerized.
C) Real-world complications can be included in simulation models.
D) Simulation is most suitable where standard analytical models are too complex.
E) All of the above are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
"Time compression" and the ability to pose "what-if" questions are elements of
A) setting up a probability distribution for important variables.
B) the disadvantages of simulation.
C) physical simulations but not mathematical simulations.
D) the advantages of simulation.
E) the broad threefold idea of simulation.
A) setting up a probability distribution for important variables.
B) the disadvantages of simulation.
C) physical simulations but not mathematical simulations.
D) the advantages of simulation.
E) the broad threefold idea of simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following is not a disadvantage to simulation?
A) Time compression
B) Expensive, can take months to develop
C) Trial and error approach
D) All input must be user generated.
E) All of these are disadvantages to simulation.
A) Time compression
B) Expensive, can take months to develop
C) Trial and error approach
D) All input must be user generated.
E) All of these are disadvantages to simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The seven steps in the use of simulation include all but which of the following?
A) define the problem
B) construct a mathematical model
C) introduce important variables associated with the problem
D) find the optimal solution
E) run the experiment
A) define the problem
B) construct a mathematical model
C) introduce important variables associated with the problem
D) find the optimal solution
E) run the experiment

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following is true regarding the use of simulation?
A) It is always very easy to build a simulation model.
B) It is very inexpensive to use a simulation model.
C) It always yields optimum solutions.
D) It allows time-compression in testing major policy decisions.
E) Few constraints, if any, have to be considered.
A) It is always very easy to build a simulation model.
B) It is very inexpensive to use a simulation model.
C) It always yields optimum solutions.
D) It allows time-compression in testing major policy decisions.
E) Few constraints, if any, have to be considered.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements regarding simulation is true?
A) Simulation can be physical or mathematical.
B) Simulation has numerous areas of application in operations.
C) Simulation attempts to duplicate a real system.
D) Monte Carlo simulation is a chance-based mathematical model of a real system.
E) All of these are true.
A) Simulation can be physical or mathematical.
B) Simulation has numerous areas of application in operations.
C) Simulation attempts to duplicate a real system.
D) Monte Carlo simulation is a chance-based mathematical model of a real system.
E) All of these are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not an idea behind simulation?
A) to imitate a real-world situation mathematically
B) study the properties and operating characteristics
C) draw conclusions and make decisions based on the results
D) both A and B
E) A, B, and C are all ideas behind simulation.
A) to imitate a real-world situation mathematically
B) study the properties and operating characteristics
C) draw conclusions and make decisions based on the results
D) both A and B
E) A, B, and C are all ideas behind simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Simulation can use any probability distribution that the user defines.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Simulation is used for several reasons, including
A) model development is a fast process.
B) it is inexpensive.
C) the models are usually simple.
D) it can handle large and complex real-world problems.
E) it always generates optimal solutions.
A) model development is a fast process.
B) it is inexpensive.
C) the models are usually simple.
D) it can handle large and complex real-world problems.
E) it always generates optimal solutions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not an application of simulation in the area of operations?
A) personnel scheduling
B) truck dispatching
C) plant (or facility) layout
D) inventory management using EOQ principles
E) inventory planning and control
A) personnel scheduling
B) truck dispatching
C) plant (or facility) layout
D) inventory management using EOQ principles
E) inventory planning and control

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
One of the advantages of simulation is that
A) it is much less expensive than a mathematical solution.
B) it always generates a more accurate solution than a mathematical solution.
C) it can study the interactive effects of individual components or variables.
D) model development is less time consuming than for mathematical models.
E) model solutions are transferable to a wide variety of problems.
A) it is much less expensive than a mathematical solution.
B) it always generates a more accurate solution than a mathematical solution.
C) it can study the interactive effects of individual components or variables.
D) model development is less time consuming than for mathematical models.
E) model solutions are transferable to a wide variety of problems.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
One of the advantages of simulation is that
A) real-world complications can be included that most OM models cannot permit.
B) it always generates a more accurate solution than a mathematical solution.
C) it is a trial-and-error approach that may produce different solutions in repeated runs.
D) model development is less time consuming than for mathematical models.
E) model solutions are transferable to a wide variety of problems.
A) real-world complications can be included that most OM models cannot permit.
B) it always generates a more accurate solution than a mathematical solution.
C) it is a trial-and-error approach that may produce different solutions in repeated runs.
D) model development is less time consuming than for mathematical models.
E) model solutions are transferable to a wide variety of problems.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
One of the disadvantages of simulation is that it
A) does not allow for very complex problem solutions.
B) is not very flexible.
C) is a trial-and-error approach that may produce different solutions in different runs.
D) is very limited in the type of probability distribution that can be used.
E) interferes with the production systems while the program is being run.
A) does not allow for very complex problem solutions.
B) is not very flexible.
C) is a trial-and-error approach that may produce different solutions in different runs.
D) is very limited in the type of probability distribution that can be used.
E) interferes with the production systems while the program is being run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
One of the disadvantages of simulation is that it
A) does not allow for very complex problem solutions.
B) produces solutions and inferences that are not usually transferable to other problems.
C) cannot study the interactive effects of individual components or variables.
D) is very limited in the type of probability distribution that can be used.
E) interferes with the production systems while the program is being run.
A) does not allow for very complex problem solutions.
B) produces solutions and inferences that are not usually transferable to other problems.
C) cannot study the interactive effects of individual components or variables.
D) is very limited in the type of probability distribution that can be used.
E) interferes with the production systems while the program is being run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The effects of OM policies over many months or years can be obtained by computer simulation in a short time. This phenomenon is referred to as
A) time suppression.
B) time suspension.
C) time compression.
D) time inversion.
E) time conversion.
A) time suppression.
B) time suspension.
C) time compression.
D) time inversion.
E) time conversion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following is true regarding simulation?
A) If an analytical model can't solve a problem, neither can a simulation.
B) Simulation can only be done by computer.
C) Monte Carlo simulation requires the use of random numbers.
D) Simulation models are inexpensive.
E) It cannot handle large and complex problems.
A) If an analytical model can't solve a problem, neither can a simulation.
B) Simulation can only be done by computer.
C) Monte Carlo simulation requires the use of random numbers.
D) Simulation models are inexpensive.
E) It cannot handle large and complex problems.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following are advantages to simulation? I. Time compression
II) What-if questions are possible
III) Flexibility
IV) Trial and Error approach
V) Input must be user generated
A) I, III, V
B) I, II, V
C) II, III, IV, V
D) I, II, IV, V
E) I, II, III
II) What-if questions are possible
III) Flexibility
IV) Trial and Error approach
V) Input must be user generated
A) I, III, V
B) I, II, V
C) II, III, IV, V
D) I, II, IV, V
E) I, II, III

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
A distribution of service times at a waiting line shows that service takes 6 minutes 30% of the time, 7 minutes 40% of the time, 8 minutes 20% of the time, and 9 minutes 10% of the time. This distribution has been prepared for Monte Carlo analysis. The first two random numbers drawn are 53 and 74. The simulated service times are ________ minutes, then ________ minutes.
A) 6; 7
B) 7; 7
C) 7; 8
D) 8; 9
E) Cannot determine, because no service time probability is that large.
A) 6; 7
B) 7; 7
C) 7; 8
D) 8; 9
E) Cannot determine, because no service time probability is that large.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A distribution of service times at a waiting line indicates that service takes 12 minutes 30% of the time and 14 minutes 70% of the time. This distribution has been prepared for Monte Carlo analysis. The first four random numbers drawn are 07, 60, 77, and 49. The average service time of this simulation is
A) 12 minutes.
B) 13 minutes.
C) 13.5 minutes.
D) 14 minutes.
E) 16 minutes.
A) 12 minutes.
B) 13 minutes.
C) 13.5 minutes.
D) 14 minutes.
E) 16 minutes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
A(n) ________ is a series of digits that have been selected by a totally random process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
From a portion of a probability distribution, you read that P(demand = 0) is 0.25, and P(demand = 1) is 0.30. The random number intervals for this distribution beginning with 01 are
A) 01 through 25, and 26 through 30.
B) 01 through 25, and 01 through 30.
C) 01 through 25, and 26 through 55.
D) 00 through 25, and 26 through 55.
E) 00 through 25, and 26 through 30.
A) 01 through 25, and 26 through 30.
B) 01 through 25, and 01 through 30.
C) 01 through 25, and 26 through 55.
D) 00 through 25, and 26 through 55.
E) 00 through 25, and 26 through 30.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
From a portion of a probability distribution, you read that P(demand = 1) is 0.05, P(demand = 2) is 0.15, and P(demand = 3) is .20. The cumulative probability for demand 3 would be
A) 0.133.
B) 0.200.
C) 0.400.
D) 0.600.
E) cannot be determined from the information given.
A) 0.133.
B) 0.200.
C) 0.400.
D) 0.600.
E) cannot be determined from the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
From a portion of a probability distribution, you read that P(demand = 0) is 0.05, P(demand = 1) is 0.10, and P(demand = 2) is 0.20. The two-digit random number intervals for this distribution beginning with 01 are
A) 01 through 05, 01 through 10, and 01 through 20.
B) 00 through 04, 05 through 14, and 15 through 34.
C) 01 through 05, 06 through 15, and 16 through 35.
D) 00 through 04, 00 through 09, and 00 through 19.
E) 01 through 06, 07 through 16, and 17 through 36.
A) 01 through 05, 01 through 10, and 01 through 20.
B) 00 through 04, 05 through 14, and 15 through 34.
C) 01 through 05, 06 through 15, and 16 through 35.
D) 00 through 04, 00 through 09, and 00 through 19.
E) 01 through 06, 07 through 16, and 17 through 36.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A(n) ________ is the accumulation of individual probabilities of a distribution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which of the following is a necessity for common EOQ methodology but not simulations?
A) constant lead time
B) variable demand
C) variable holding costs
D) A and B
E) A, B and C
A) constant lead time
B) variable demand
C) variable holding costs
D) A and B
E) A, B and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Which of the following restrictions applies to queuing models but not Monte Carlo simulations?
A) Poisson distribution of arrivals
B) constant or exponential service times
C) average length of line
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
A) Poisson distribution of arrivals
B) constant or exponential service times
C) average length of line
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
A distribution of service times at a waiting line indicates that service takes 12 minutes 30% of the time and 14 minutes 70% of the time. In preparing this distribution for Monte Carlo analysis, the service time 13 minutes would be represented by the random number range
A) 00 through 29.
B) 01 through 30.
C) 30 through 99.
D) 31 through 00.
E) None of these; 13 minutes is not a possible outcome.
A) 00 through 29.
B) 01 through 30.
C) 30 through 99.
D) 31 through 00.
E) None of these; 13 minutes is not a possible outcome.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
________ is the attempt to duplicate the features, appearance, and characteristics of a real system, usually by means of a computerized model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Setting up a probability distribution, building a cumulative probability distribution, and generating random numbers are
A) necessary when the underlying probability distribution is normal.
B) three of the five steps in Monte Carlo analysis.
C) elements of physical simulation but not mathematical simulation.
D) the three steps involved in simulating a queuing problem.
E) advantages of simulation.
A) necessary when the underlying probability distribution is normal.
B) three of the five steps in Monte Carlo analysis.
C) elements of physical simulation but not mathematical simulation.
D) the three steps involved in simulating a queuing problem.
E) advantages of simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The number of tires sold at a car garage varies randomly between 0 and 4 each hour. What set of random numbers (on the 1-100 scale would tire sales of 2 be assigned?
A) 01 through 20
B) 21 through 40
C) 41 through 60
D) 61 through 80
E) 81 through 100
A) 01 through 20
B) 21 through 40
C) 41 through 60
D) 61 through 80
E) 81 through 100

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
What is the cumulative probability distribution of the following variable?
A) 1
B) .5
C) 10
D) .2
E) 15
A) 1
B) .5
C) 10
D) .2
E) 15

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which of the following is not a step in running a Monte Carlo simulation?
A) setting up a probability distribution for important variables
B) building a cumulative probability distribution for each variable
C) establishing an interval of random numbers for each variable
D) generating random numbers
E) All of the above are steps in running a Monte Carlo simulation.
A) setting up a probability distribution for important variables
B) building a cumulative probability distribution for each variable
C) establishing an interval of random numbers for each variable
D) generating random numbers
E) All of the above are steps in running a Monte Carlo simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A distribution of service times at a waiting line indicates that service takes 6 minutes 30% of the time, 7 minutes 40% of the time, 8 minutes 20% of the time, and 9 minutes 10% of the time. In preparing this distribution for Monte Carlo analysis, the service time 8 minutes would be represented by the random number range
A) 20 through 40.
B) 21 through 40.
C) 70 through 90.
D) 71 through 90.
E) 40 through 70.
A) 20 through 40.
B) 21 through 40.
C) 70 through 90.
D) 71 through 90.
E) 40 through 70.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A distribution of lead times in an inventory problem indicates that lead time was 1 day 20% of the time, 2 days 30% of the time, 3 days 30% of the time, and. 4 days 20% of the time. This distribution has been prepared for Monte Carlo analysis. The first four random numbers drawn are 06, 63, 57, and 02. The average lead time of this simulation is
A) 1.75 days.
B) 2 days.
C) 3 days.
D) 3.5 days.
E) 4 days.
A) 1.75 days.
B) 2 days.
C) 3 days.
D) 3.5 days.
E) 4 days.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Monte Carlo simulations applied to queuing problems have what advantage?
A) simpler
B) Arrival distribution does not need to be a Poisson distribution.
C) Unloading rates can vary randomly.
D) B and C
E) A, B, and C
A) simpler
B) Arrival distribution does not need to be a Poisson distribution.
C) Unloading rates can vary randomly.
D) B and C
E) A, B, and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
From a portion of a probability distribution, you read that P(demand = 0) is 0.05 and P(demand = 1) is 0.10. The cumulative probability for demand 1 would be
A) 0.05.
B) 0.075.
C) 0.10.
D) 0.15.
E) cannot be determined.
A) 0.05.
B) 0.075.
C) 0.10.
D) 0.15.
E) cannot be determined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The ________ method is a simulation technique that uses random elements when chance exists in their behaviour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Define simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Explain how Monte Carlo simulation uses random numbers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Explain what is meant by "simulation is not limited to using the standard probability distributions."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
What are the advantages and disadvantages of simulation models?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
State the three-fold idea behind simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
A distribution of service times at a waiting line shows that service takes 6 minutes 40% of the time, 7 minutes 30% of the time, 8 minutes 20% of the time, and 9 minutes 10% of the time. Prepare the probability distribution, the cumulative probability distribution, and the random number intervals for this problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
What is the Monte Carlo method?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Identify the seven steps involved in using simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Explain what is meant by the concept of "time compression" in simulation modeling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The effects of OM policies over many months or years can be obtained by computer simulation in a short time. This phenomenon is referred to as ________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Explain the difference between random numbers and random number intervals.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The numbers used to represent each possible value or outcome in a computer simulation are referred to as ________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
A distribution of service times at a waiting line shows that service takes 6 minutes 40% of the time, 7 minutes 30% of the time, 8 minutes 20% of the time, and 9 minutes 10% of the time. Prepare the probability distribution, the cumulative probability distribution, and the random number intervals for this problem. The first five random numbers are 37, 69, 53, 80, and 60. What is the average service time of this simulation run?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Identify, in order, the five steps required to implement the Monte Carlo simulation technique.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Identify five applications of simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Would you simulate a problem for which there is an exact mathematical model already?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
A waiting-line problem that cannot be modelled by standard distributions has been simulated. The table below shows the result of a Monte Carlo simulation. (Assume that the simulation began at 8:00 a.m. and there is only one server.
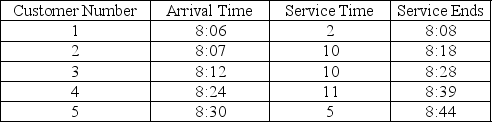 a. What is the average waiting time in line?
a. What is the average waiting time in line?
b. What is the average time in the system?
 a. What is the average waiting time in line?
a. What is the average waiting time in line?b. What is the average time in the system?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Provide a small example illustrating how random numbers are used in Monte Carlo simulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
A waiting-line problem that cannot be modelled by standard distributions has been simulated. The table below shows the result of a Monte Carlo simulation. (Assume that the simulation began at 8:00 a.m. and there is only one server.) Why do you think this problem does not fit the standard distribution for waiting lines? Explain briefly how a Monte Carlo simulation might work where analytical models cannot.
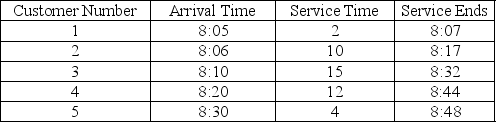


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
A warehouse manager needs to simulate the demand placed on a product that does not fit standard models. The concept being measured is "demand during lead time," where both lead time and daily demand are variable. The historical record for this product suggests the following probability distribution. Convert this distribution into random number intervals.
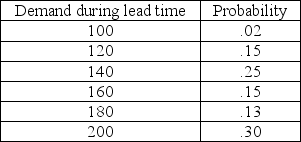


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 102 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








