Deck 17: Gibbs Energy and Thermodynamics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/134
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 17: Gibbs Energy and Thermodynamics
1
Identify the change in state that does not have an increase in entropy.
A) water freezing
B) water boiling
C) ice melting
D) dry ice subliming
E) water evaporating
A) water freezing
B) water boiling
C) ice melting
D) dry ice subliming
E) water evaporating
water freezing
2
Which of the following processes have a ΔrS > 0?
A) CH3OH(l) → CH3OH(s)
B) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
C) CH4(g) + H2O (g) → CO(g) + 3H2(g)
D) Na2CO3(s) + H2O(g) + CO2(g) → 2NaHCO3(s)
E) H2O(g) → H2O(l)
A) CH3OH(l) → CH3OH(s)
B) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
C) CH4(g) + H2O (g) → CO(g) + 3H2(g)
D) Na2CO3(s) + H2O(g) + CO2(g) → 2NaHCO3(s)
E) H2O(g) → H2O(l)
CH4(g) + H2O (g) → CO(g) + 3H2(g)
3
Consider a reaction that has a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at low temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at low temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at low temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at low temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).
This reaction will be spontaneous only at low temperatures.
4
In which of the following processes do the molecules become more ordered?
A) water freezing
B) ice melting
C) water evaporating
D) salt dissolving in water
E) dry ice subliming
A) water freezing
B) ice melting
C) water evaporating
D) salt dissolving in water
E) dry ice subliming

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
For the following example, what is true about ΔrH and ΔrS? 2N2O(g) → 2N2(g) + O2(g)
A) a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
B) a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
C) a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
D) a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
E) ΔrH = 0 and a positive ΔrS
A) a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
B) a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
C) a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
D) a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
E) ΔrH = 0 and a positive ΔrS

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following processes have a ΔrS > 0?
A) 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) → NH2CONH2(aq) + H2O(l)
B) lithium fluoride forms from Li and F2
C) 2HBr(g) → H2(g) + Br2(l)
D) sodium chloride dissolves in pure water
E) Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)
A) 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) → NH2CONH2(aq) + H2O(l)
B) lithium fluoride forms from Li and F2
C) 2HBr(g) → H2(g) + Br2(l)
D) sodium chloride dissolves in pure water
E) Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Consider a reaction that has a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Consider the following reaction at constant pressure. Use the information here to determine the value of ΔSsurr at 398 K. Predict whether or not this reaction will be spontaneous at this temperature. 4NH3(g) + 3O2(g) → 2N2(g) + 6H2O(g) ΔrH = -1267 kJ
A) ΔSsurr = +12.67 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
B) ΔSsurr = -12.67 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
C) ΔSsurr = +50.4 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
D) ΔSsurr = +3.18 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
E) ΔSsurr = -3.18 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
A) ΔSsurr = +12.67 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
B) ΔSsurr = -12.67 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
C) ΔSsurr = +50.4 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
D) ΔSsurr = +3.18 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
E) ΔSsurr = -3.18 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Entropy is not a state function.
B) Endothermic processes decrease the entropy of the surroundings, at constant T and P.
C) Endothermic processes are never spontaneous.
D) Exothermic processes are always spontaneous.
E) Entropy of the universe is a constant value.
A) Entropy is not a state function.
B) Endothermic processes decrease the entropy of the surroundings, at constant T and P.
C) Endothermic processes are never spontaneous.
D) Exothermic processes are always spontaneous.
E) Entropy of the universe is a constant value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Consider the following reaction at constant pressure. Use the information here to determine the value of ΔSsurr at 298 K. Predict whether or not this reaction will be spontaneous at this temperature. N2(g) + 2O2(g) → 2NO2(g) ΔrH = +66.4 kJ
A) ΔSsurr = +223 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
B) ΔSsurr = -223J K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
C) ΔSsurr = -66.4 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
D) ΔSsurr = +66.4 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
E) ΔSsurr = -66.4 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
A) ΔSsurr = +223 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
B) ΔSsurr = -223J K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
C) ΔSsurr = -66.4 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
D) ΔSsurr = +66.4 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
E) ΔSsurr = -66.4 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which of the following relationships is correct at constant T and P?
A) ΔrG is proportional to -ΔSuniv.
B) ΔrG > 0 represents a spontaneous process.
C) ΔrG > 0 represents an increase in kinetic energy.
D) ΔrG < 0 represents a nonspontaneous process.
E) ΔrG is not a function of temperature.
A) ΔrG is proportional to -ΔSuniv.
B) ΔrG > 0 represents a spontaneous process.
C) ΔrG > 0 represents an increase in kinetic energy.
D) ΔrG < 0 represents a nonspontaneous process.
E) ΔrG is not a function of temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following processes shows a decrease in entropy of the system?
A) 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
B) COCl2(g) → CO(g) + Cl2(g)
C) CH3OH(l) → CO(g) + 2H2(g)
D) NaClO3(s) → Na+(aq) + ClO3-(aq)
E) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
A) 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
B) COCl2(g) → CO(g) + Cl2(g)
C) CH3OH(l) → CO(g) + 2H2(g)
D) NaClO3(s) → Na+(aq) + ClO3-(aq)
E) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Consider a reaction that has a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following processes have a ΔrS = 0?
A) water freezes
B) isopropyl alcohol vapour condenses
C) methanol (g, at 555 K) → methanol (g, at 400 K)
D) carbon dioxide(g) → carbon dioxide(s)
E) H2(g) + F2(g) → 2HF(g)
A) water freezes
B) isopropyl alcohol vapour condenses
C) methanol (g, at 555 K) → methanol (g, at 400 K)
D) carbon dioxide(g) → carbon dioxide(s)
E) H2(g) + F2(g) → 2HF(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that takes place without any outside intervention.
B) Thermodynamics is a study of reaction rates.
C) A nonspontaneous reaction is a reaction that does not take place under any conditions.
D) Chemical kinetics is a discipline that studies the spontaneity of chemical reactions.
E) Every spontaneous reaction is a very rapid reaction.
A) A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that takes place without any outside intervention.
B) Thermodynamics is a study of reaction rates.
C) A nonspontaneous reaction is a reaction that does not take place under any conditions.
D) Chemical kinetics is a discipline that studies the spontaneity of chemical reactions.
E) Every spontaneous reaction is a very rapid reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Consider the following reaction at constant pressure. Use the information here to determine the value of ?Ssurr at 355 K. Predict whether or not this reaction will be spontaneous at this temperature. 2NO(g) + O2(g) ? 2NO2(g) ?rH = -114 kJ
A) ?Ssurr = +114 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
B) ?Ssurr = +114 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
C) ?Ssurr = +321 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
D) ?Ssurr = -321 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
E) ?Ssurr = +321 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
A) ?Ssurr = +114 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
B) ?Ssurr = +114 kJ K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
C) ?Ssurr = +321 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is spontaneous
D) ?Ssurr = -321 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous
E) ?Ssurr = +321 J K-1 mol-1, reaction is not spontaneous

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
What is the sign of ΔSuniv for a biological system?
A) positive
B) negative
C) zero
D) It depends on the biological system.
A) positive
B) negative
C) zero
D) It depends on the biological system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Consider a reaction that has a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at low temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at low temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at low temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at low temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Consider a reaction that has a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at very low temperatures.
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at very low temperatures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Consider a reaction that has a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).
A) This reaction will be spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) This reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
D) This reaction will be nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
E) This reaction will be spontaneous only at absolute zero (0 Kelvin).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Use the following thermodynamic values to calculate Δr NEWLINE 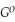 .
.
Δr
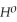 = -95 kJ
= -95 kJ 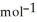 , Δr
, Δr
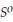 = -157 J
= -157 J 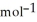 , T = 855 K
, T = 855 K
A) -48 kJ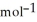
B) -68 kJ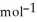
C) +39 kJ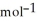
D) -157 kJ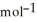
E) +142 kJ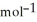
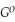 .
.Δr
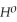 = -95 kJ
= -95 kJ 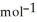 , Δr
, Δr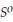 = -157 J
= -157 J 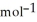 , T = 855 K
, T = 855 KA) -48 kJ
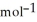
B) -68 kJ
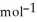
C) +39 kJ
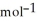
D) -157 kJ
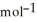
E) +142 kJ
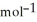

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Identify the statement that is TRUE.
A) The entropy of a gas is lower than the entropy of a liquid.
B) Entropy generally decreases with increasing molecular complexity.
C) Free atoms have lower entropy than molecules.
D) Entropy decreases with dissolution.
E) For noble gases, entropy decreases with increase in atomic size.
A) The entropy of a gas is lower than the entropy of a liquid.
B) Entropy generally decreases with increasing molecular complexity.
C) Free atoms have lower entropy than molecules.
D) Entropy decreases with dissolution.
E) For noble gases, entropy decreases with increase in atomic size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Place the following in order of increasing molar entropy at 298 K. CO2 C3H8 SO
A) CO2 < C3H8 < SO
B) C3H8 < CO2 < SO
C) SO < CO2 < C3H8
D) C3H8 < SO < CO2
E) CO2 < SO < C3H8
A) CO2 < C3H8 < SO
B) C3H8 < CO2 < SO
C) SO < CO2 < C3H8
D) C3H8 < SO < CO2
E) CO2 < SO < C3H8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Place the following in order of decreasing molar entropy at 298 K. HCl N2H4 Ar
A) Ar > N2H4 > HCl
B) Ar > HCl > N2H4
C) N2H4 > Ar > HCl
D) N2H4 > HCl > Ar
E) HCl > N2H4 > Ar
A) Ar > N2H4 > HCl
B) Ar > HCl > N2H4
C) N2H4 > Ar > HCl
D) N2H4 > HCl > Ar
E) HCl > N2H4 > Ar

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Above what temperature does the following reaction become nonspontaneous? 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) → 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ΔrH = -1036 kJ; ΔrS = -153.2 J K-1 mol-1
A) 6.762 × 103 K
B) 158.7 K
C) 298 K
D) 67.62 K
E) 1.587 × 103 K
A) 6.762 × 103 K
B) 158.7 K
C) 298 K
D) 67.62 K
E) 1.587 × 103 K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
For the following example, what is true about ΔrH and ΔrS? H2O(l) → H2O(s)
A) a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
B) a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
C) a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
D) a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
E) ΔrH = 0 and a positive ΔrS
A) a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
B) a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
C) a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
D) a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
E) ΔrH = 0 and a positive ΔrS

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Use the following thermodynamic values to calculate Δr 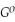 .
.
Δr
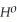 = +95 kJ
= +95 kJ 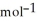 , Δr
, Δr
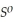 = -157 J
= -157 J 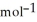 , T = 398 K
, T = 398 K
A) -48 kJ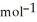
B) -68 kJ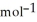
C) +39 kJ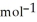
D) +157 kJ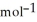
E) +142 kJ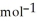
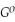 .
.Δr
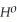 = +95 kJ
= +95 kJ 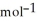 , Δr
, Δr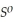 = -157 J
= -157 J 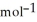 , T = 398 K
, T = 398 KA) -48 kJ
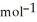
B) -68 kJ
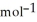
C) +39 kJ
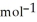
D) +157 kJ
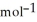
E) +142 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Entropy is an extensive property.
B) Entropy is not temperature dependent.
C) Exothermic processes decrease the entropy of the surroundings.
D) ΔSuniv is always greater than zero for a nonspontaneous process.
E) Just like enthalpy, entropy has no absolute zero value.
A) Entropy is an extensive property.
B) Entropy is not temperature dependent.
C) Exothermic processes decrease the entropy of the surroundings.
D) ΔSuniv is always greater than zero for a nonspontaneous process.
E) Just like enthalpy, entropy has no absolute zero value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
For the following example, what is true about ΔrH and ΔrS? H2O(l) → H2O(g)
A) a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
B) a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
C) a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
D) a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
E) ΔrH = 0 and a positive ΔrS
A) a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
B) a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
C) a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
D) a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
E) ΔrH = 0 and a positive ΔrS

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Place the following in order of decreasing standard molar entropy. NaCl(s) Na3PO4(aq) NaCl(aq)
A) NaCl(s) > NaCl(aq) > Na3PO4(aq)
B) NaCl(aq) > NaCl(s) > Na3PO4(aq)
C) Na3PO4(aq) > NaCl(aq) > NaCl(s)
D) NaCl(s) > Na3PO4(aq) > NaCl(aq)
E) NaCl(aq) > Na3PO4(aq) > NaCl(s)
A) NaCl(s) > NaCl(aq) > Na3PO4(aq)
B) NaCl(aq) > NaCl(s) > Na3PO4(aq)
C) Na3PO4(aq) > NaCl(aq) > NaCl(s)
D) NaCl(s) > Na3PO4(aq) > NaCl(aq)
E) NaCl(aq) > Na3PO4(aq) > NaCl(s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Place the following in order of increasing molar entropy at 298 K. Ne Xe He Ar Kr
A) He < Kr < Ne < Ar < Xe
B) Xe < Kr < Ar < Ne < He
C) Ar < He < Ar < Ne < Kr
D) Ar < Ne < Xe < Kr < He
E) He < Ne < Ar < Kr < Xe
A) He < Kr < Ne < Ar < Xe
B) Xe < Kr < Ar < Ne < He
C) Ar < He < Ar < Ne < Kr
D) Ar < Ne < Xe < Kr < He
E) He < Ne < Ar < Kr < Xe

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Above what temperature does the following reaction become nonspontaneous? FeO(s) + CO(g) → CO2(g) + Fe(s) ΔrH = -11.0 kJ; ΔrS = -17.4 J K-1 mol-1
A) 632 K
B) 298 K
C) 191 K
D) 6.32 × 103 K
E) 0 K
A) 632 K
B) 298 K
C) 191 K
D) 6.32 × 103 K
E) 0 K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Below what temperature does the following reaction become nonspontaneous? 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g) → 3NO2(g) + H2O(l) ΔrH = +136.5 kJ; ΔrS = +287.5 J K-1 mol-1
A) 39.2 K
B) 151 K
C) 475 K
D) 4.75 × 103 K
E) 298.17 K
A) 39.2 K
B) 151 K
C) 475 K
D) 4.75 × 103 K
E) 298.17 K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Place the following in order of increasing molar entropy at 298 K. NO CO SO
A) NO < CO < SO
B) SO < CO < NO
C) SO < NO < CO
D) CO < SO < NO
E) CO < NO < SO
A) NO < CO < SO
B) SO < CO < NO
C) SO < NO < CO
D) CO < SO < NO
E) CO < NO < SO

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Place the following in order of decreasing molar entropy at 298 K. H2 Cl2 F2
A) H2 > Cl2 > F2
B) Cl2 > H2 > F2
C) F2 > Cl2 > H2
D) H2 > F2 > Cl2
E) Cl2 > F2 > H2
A) H2 > Cl2 > F2
B) Cl2 > H2 > F2
C) F2 > Cl2 > H2
D) H2 > F2 > Cl2
E) Cl2 > F2 > H2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Use the following thermodynamic values to calculate Δr 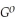 .
.
Δr
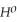 = -95 kJ
= -95 kJ  , Δr
, Δr
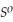 = -157 J
= -157 J 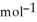 , T = 298 K
, T = 298 K
A) -48 kJ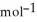
B) -68 kJ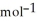
C) + 39 kJ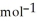
D) -157 kJ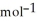
E) +142 kJ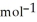
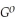 .
.Δr
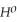 = -95 kJ
= -95 kJ 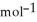 , Δr
, Δr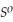 = -157 J
= -157 J 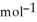 , T = 298 K
, T = 298 KA) -48 kJ
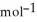
B) -68 kJ
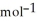
C) + 39 kJ
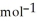
D) -157 kJ
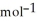
E) +142 kJ
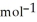

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Use the following thermodynamic values to calculate Δr 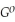 .
.
Δr
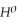 = +95 kJ
= +95 kJ 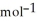 , Δr
, Δr
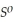 = -157 J
= -157 J 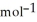 , T = 298 K
, T = 298 K
A) -48 kJ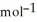
B) -68 kJ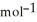
C) +39 kJ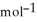
D) -157 kJ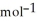
E) +142 kJ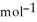
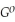 .
.Δr
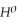 = +95 kJ
= +95 kJ 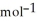 , Δr
, Δr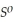 = -157 J
= -157 J 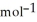 , T = 298 K
, T = 298 KA) -48 kJ
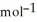
B) -68 kJ
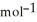
C) +39 kJ
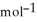
D) -157 kJ
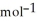
E) +142 kJ
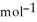

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Place the following in order of increasing standard molar entropy. H2O(l) H2O(g) H2O(s)
A) H2O(g) < H2O(l) < H2O(s)
B) H2O(s) < H2O(l) < H2O(g)
C) H2O(g) < H2O(s) < H2O(l)
D) H2O(l) < H2O(s) < H2O(g)
E) H2O(s) < H2O(g) < H2O(l)
A) H2O(g) < H2O(l) < H2O(s)
B) H2O(s) < H2O(l) < H2O(g)
C) H2O(g) < H2O(s) < H2O(l)
D) H2O(l) < H2O(s) < H2O(g)
E) H2O(s) < H2O(g) < H2O(l)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Place the following in order of decreasing standard molar entropy. N2O4 NO NO2
A) N2O4 > NO2 > NO
B) NO > NO2 > N2O4
C) N2O4 > NO > NO2
D) NO > N2O4 > NO2
E) NO2 > NO > N2O4
A) N2O4 > NO2 > NO
B) NO > NO2 > N2O4
C) N2O4 > NO > NO2
D) NO > N2O4 > NO2
E) NO2 > NO > N2O4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
For the following example, what is true about ΔrH and ΔrS? 3O2(g) → 2O3(g)
A) a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
B) a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
C) a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
D) a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
E) ΔrH = 0 and a positive ΔrS
A) a negative ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
B) a positive ΔrH and a negative ΔrS
C) a negative ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
D) a positive ΔrH and a positive ΔrS
E) ΔrH = 0 and a positive ΔrS

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Given the following equation, N2O(g) + NO2(g) → 3NO(g) ΔrG° = -23.0 kJ mol-1
Calculate ΔrG° for the following reaction:
3N2O(g) + 3NO2(g) → 9NO(g)
A) -23.0 kJ mol-1
B) 69.0 kJ mol-1
C) -69.0 kJ mol-1
D) -7.67 kJ mol-1
E) 23.0 kJ mol-1
Calculate ΔrG° for the following reaction:
3N2O(g) + 3NO2(g) → 9NO(g)
A) -23.0 kJ mol-1
B) 69.0 kJ mol-1
C) -69.0 kJ mol-1
D) -7.67 kJ mol-1
E) 23.0 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What is the change in Gibbs energy of a process?
A) It is a maximum amount of energy available to do work.
B) It is energy that is lost to the surroundings.
C) It is energy that is used to break chemical bonds.
D) It is energy that is converted to heat.
E) It is the total energy of a process.
A) It is a maximum amount of energy available to do work.
B) It is energy that is lost to the surroundings.
C) It is energy that is used to break chemical bonds.
D) It is energy that is converted to heat.
E) It is the total energy of a process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Identify the compound with the highest standard Gibbs energy of formation.
A) NaCl(s)
B) N2(g)
C) NO(g)
D) O3(g)
E) Cl2(g)
A) NaCl(s)
B) N2(g)
C) NO(g)
D) O3(g)
E) Cl2(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Given the following equation, N2O(g) + NO2(g) → 3NO(g) ΔrG° = -23.0 kJ mol-1
Calculate ΔrGo for the following reaction:
3NO(g) → N2O(g) + NO2(g)
A) -23.0 kJ mol-1
B) 69.0 kJ mol-1
C) -69.0 kJ mol-1
D) -7.67 kJ mol-1
E) 23.0 kJ mol-1
Calculate ΔrGo for the following reaction:
3NO(g) → N2O(g) + NO2(g)
A) -23.0 kJ mol-1
B) 69.0 kJ mol-1
C) -69.0 kJ mol-1
D) -7.67 kJ mol-1
E) 23.0 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Calculate ΔrS° for the following reaction. The S° for each species is shown below the reaction. 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 192.8 205.2 210.8 188.8
A) +287.4 J K-1 mol-1
B) -401.2 J K-1 mol-1
C) +160.0 J K-1 mol-1
D) -336.6 J K-1 mol-1
E) +178.8 J K-1 mol-1
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 192.8 205.2 210.8 188.8
A) +287.4 J K-1 mol-1
B) -401.2 J K-1 mol-1
C) +160.0 J K-1 mol-1
D) -336.6 J K-1 mol-1
E) +178.8 J K-1 mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Identify the compound with the standard Gibbs energy of formation equal to zero.
A) NaCl(s)
B) N2(g)
C) NO(g)
D) O3(g)
E) HCl(g)
A) NaCl(s)
B) N2(g)
C) NO(g)
D) O3(g)
E) HCl(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What is the name of the reaction that achieves the theoretical limits with respect to the change in Gibbs energy in thermodynamics?
A) reversible reaction
B) forward reaction
C) reverse reaction
D) equilibrium reaction
E) irreversible reaction
A) reversible reaction
B) forward reaction
C) reverse reaction
D) equilibrium reaction
E) irreversible reaction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which one of the following has the highest standard molar entropy, S°, at 25 °C?
A) I2(s)
B) F2(g)
C) Br2(l)
D) N2(g)
E) Cl2(g)
A) I2(s)
B) F2(g)
C) Br2(l)
D) N2(g)
E) Cl2(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Calculate ΔrS° for the following reaction. The S° for each species is shown below the reaction. C2H2(g) + 2H2(g) → C2H6(g)
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 200.9 130.7 229.2
A) +303.3 J K-1 mol-1
B) +560.8 J K-1 mol-1
C) -102.4 J K-1 mol-1
D) -233.1 J K-1 mol-1
E) 229.2 J K-1 mol-1
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 200.9 130.7 229.2
A) +303.3 J K-1 mol-1
B) +560.8 J K-1 mol-1
C) -102.4 J K-1 mol-1
D) -233.1 J K-1 mol-1
E) 229.2 J K-1 mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Calculate ΔrS° for the following reaction. The S° for each species is shown below the reaction. N2H4(l) + H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
S° (J K-1 mol-1) 121.2 130.7 192.8
A) +133.7 J K-1 mol-1
B) -59.1 J K-1 mol-1
C) +118.2 J K-1 mol-1
D) -202.3 J K-1 mol-1
E) +178.9 J K-1 mol-1
S° (J K-1 mol-1) 121.2 130.7 192.8
A) +133.7 J K-1 mol-1
B) -59.1 J K-1 mol-1
C) +118.2 J K-1 mol-1
D) -202.3 J K-1 mol-1
E) +178.9 J K-1 mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Calculate ΔrS° for the following reaction. The S° for each species is shown below the reaction. C2H2(g) + H2(g) → C2H4(g)
S°(J J K-1 mol-1) 200.9 130.7 219.3
A) +112.3 J K-1 mol-1
B) +550.9 J K-1 mol-1
C) -112.3 J K-1 mol-1
D) +337.1 J K-1 mol-1
E) -550.9 J K-1 mol-1
S°(J J K-1 mol-1) 200.9 130.7 219.3
A) +112.3 J K-1 mol-1
B) +550.9 J K-1 mol-1
C) -112.3 J K-1 mol-1
D) +337.1 J K-1 mol-1
E) -550.9 J K-1 mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Identify the compound with the lowest standard Gibbs energy of formation.
A) NaCl(s)
B) N2(g)
C) NO(g)
D) O3(g)
E) Cl2(g)
A) NaCl(s)
B) N2(g)
C) NO(g)
D) O3(g)
E) Cl2(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which of the following is TRUE regarding allotropes?
A) Allotropes are different forms of the same element, but they have identical standard molar enthalpies.
B) Allotropes are different forms of the same element and have different standard molar enthalpies.
C) Allotropes are composed of different isotopes of the same element and have different standard molar enthalpies.
D) Allotropes are composed of different isotopes of the same element and identical standard molar enthalpies.
E) Allotropes are different elements with the same structure and have different standard molar enthalpies.
A) Allotropes are different forms of the same element, but they have identical standard molar enthalpies.
B) Allotropes are different forms of the same element and have different standard molar enthalpies.
C) Allotropes are composed of different isotopes of the same element and have different standard molar enthalpies.
D) Allotropes are composed of different isotopes of the same element and identical standard molar enthalpies.
E) Allotropes are different elements with the same structure and have different standard molar enthalpies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Calculate ΔρS° for the following reaction. The S° for each species is shown below the reaction. P4(g) + 10Cl2(g) → 4PCl5(g)
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 280.0 223.1 364.6
A) -138.5 J K-1 mol-1
B) -1052.6 J K-1 mol-1
C) +171.3 J K-1 mol-1
D) -583.6 J K-1 mol-1
E) +2334.6 J K-1 mol-1
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 280.0 223.1 364.6
A) -138.5 J K-1 mol-1
B) -1052.6 J K-1 mol-1
C) +171.3 J K-1 mol-1
D) -583.6 J K-1 mol-1
E) +2334.6 J K-1 mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which one of the following has the lowest standard molar entropy, S°, at 25 °C?
A) NH3(g)
B) Ne(g)
C) SO2(g)
D) CH3CH2OH(g)
E) He (g)
A) NH3(g)
B) Ne(g)
C) SO2(g)
D) CH3CH2OH(g)
E) He (g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What is the name of the reaction that does not achieve the theoretical limits with respect to the change in Gibbs energy in thermodynamics?
A) reversible reaction
B) forward reaction
C) reverse reaction
D) equilibrium reaction
E) irreversible reaction
A) reversible reaction
B) forward reaction
C) reverse reaction
D) equilibrium reaction
E) irreversible reaction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which one of the following has the highest standard molar entropy, S°, at 25 °C?
A) H2(g)
B) F2(g)
C) O2(g)
D) N2(g)
E) Cl2(g)
A) H2(g)
B) F2(g)
C) O2(g)
D) N2(g)
E) Cl2(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Which one of the following has the highest standard molar entropy, S°, at 25 °C?
A) NH3(g)
B) Ne(g)
C) SO2(g)
D) CH3CH2OH(g)
E) He (g)
A) NH3(g)
B) Ne(g)
C) SO2(g)
D) CH3CH2OH(g)
E) He (g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Given the following equation, N2O(g) + NO2(g) → 3 NO(g) ΔrG° = -23.0 kJ mol-1
Calculate ΔrG° for the following reaction:
9NO(g) → 3N2O(g) + 3NO2(g)
A) -23.0 kJ mol-1
B) 69.0 kJ mol-1
C) -69.0 kJ mol-1
D) -7.67 kJ mol-1
E) 23.0 kJ mol-1
Calculate ΔrG° for the following reaction:
9NO(g) → 3N2O(g) + 3NO2(g)
A) -23.0 kJ mol-1
B) 69.0 kJ mol-1
C) -69.0 kJ mol-1
D) -7.67 kJ mol-1
E) 23.0 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Which one of the following has the highest standard molar entropy, S°, at 25 °C?
A) N2O4(g)
B) H2(g)
C) N2(g)
D) H2O(g)
E) O2(g)
A) N2O4(g)
B) H2(g)
C) N2(g)
D) H2O(g)
E) O2(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Calculate ΔrG at 298 K under the conditions shown below for the following reaction: Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) ΔG° = -28.0 kJ mol-1
P(CO) = 1.4 atm, P(CO2) = 2.1 atm
A) +31.0 kJ mol-1
B) +2.99 kJ mol-1
C) -30.7 kJ mol-1
D) +17.5 kJ mol-1
E) -25.0 kJ mol-1
P(CO) = 1.4 atm, P(CO2) = 2.1 atm
A) +31.0 kJ mol-1
B) +2.99 kJ mol-1
C) -30.7 kJ mol-1
D) +17.5 kJ mol-1
E) -25.0 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Determine ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: 2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) ΔrH°= -77.6 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= +494.6 J K-1 mol-1
A) -225.0 kJ mol-1
B) +68.4 .0 kJ mol-1
C) -89.3 kJ mol-1
D) +131.5 kJ mol-1
E) +175.2 kJ mol-1
A) -225.0 kJ mol-1
B) +68.4 .0 kJ mol-1
C) -89.3 kJ mol-1
D) +131.5 kJ mol-1
E) +175.2 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Calculate ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g) → 3NO2(g) + H2O(l) ΔrG° = ?
ΔfG° (kJ mol-1) -110.9 87.6 51.3 -237.1
A) -162.5 kJ mol-1
B) +51.0 kJ mol-1
C) -54.5 kJ mol-1
D) +171.1 kJ mol-1
E) -87.6 kJ mol-1
ΔfG° (kJ mol-1) -110.9 87.6 51.3 -237.1
A) -162.5 kJ mol-1
B) +51.0 kJ mol-1
C) -54.5 kJ mol-1
D) +171.1 kJ mol-1
E) -87.6 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Calculate ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) → 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ΔrG° = ?
ΔfG°(kJ mol-1) -33.4 -300.1 -228.6
A) +112.4 kJ mol-1
B) -495.3 kJ mol-1
C) -528.7 kJ mol-1
D) +66.8 kJ mol-1
E) -990.6 kJ mol-1
ΔfG°(kJ mol-1) -33.4 -300.1 -228.6
A) +112.4 kJ mol-1
B) -495.3 kJ mol-1
C) -528.7 kJ mol-1
D) +66.8 kJ mol-1
E) -990.6 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Calculate ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g) → 3NO2(g) + H2O(l) ΔrG° = ?
ΔfH° (kJ mol-1) -207.0 91.3 33.2 -285.8
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 146.0 210.8 240.1 70.0
A) -151 kJ mol-1
B) -85.5 kJ mol-1
C) +50.8 kJ mol-1
D) +222 kJ mol-1
E) -186 kJ mol-1
ΔfH° (kJ mol-1) -207.0 91.3 33.2 -285.8
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 146.0 210.8 240.1 70.0
A) -151 kJ mol-1
B) -85.5 kJ mol-1
C) +50.8 kJ mol-1
D) +222 kJ mol-1
E) -186 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Determine ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: H2(g) + CO(g) → CH2O(g) ΔrH°= +1.9 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= -109.6 J K-1 mol-1
A) +57.7 kJ mol-1
B) -30.8 kJ mol-1
C) +34.6 kJ mol-1
D) -41.5 kJ mol-1
E) +17.3 kJ mol-1
A) +57.7 kJ mol-1
B) -30.8 kJ mol-1
C) +34.6 kJ mol-1
D) -41.5 kJ mol-1
E) +17.3 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Use Hess's law to calculate ΔrG° using the following information: ClO(g) + O3(g) → Cl(g) + 2O2(g) ΔrG° = ?
2O3(g)→ 3O2(g) ΔrG° = +489.6 kJ mol-1
Cl(g) + O3(g) → ClO(g) + O2(g) ΔrG° = -34.5 kJ mol-1
A) -472.4 kJ mol-1
B) -210.3 kJ mol-1
C) +455.1 kJ mol-1
D) +262.1 kJ mol-1
E) +524.1 kJ mol-1
2O3(g)→ 3O2(g) ΔrG° = +489.6 kJ mol-1
Cl(g) + O3(g) → ClO(g) + O2(g) ΔrG° = -34.5 kJ mol-1
A) -472.4 kJ mol-1
B) -210.3 kJ mol-1
C) +455.1 kJ mol-1
D) +262.1 kJ mol-1
E) +524.1 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Estimate ΔrG° for the following reaction at 775 K. 2Hg(g) + O2(g) → 2HgO(s) ΔrH°= -304.2 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= -414.2 J K-1 mol-1
A) -625 kJ mol-1
B) -181 kJ mol-1
C) +17 kJ mol-1
D) +321 kJ mol-1
E) -110 kJ mol-1
A) -625 kJ mol-1
B) -181 kJ mol-1
C) +17 kJ mol-1
D) +321 kJ mol-1
E) -110 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Estimate ΔrG° for the following reaction at 387 K. HCN(g) + 2H2(g) → CH3NH2(g) ΔrH°= -158.0 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= -219.9 J K-1 mol-1
A) +243 kJ mol-1
B) -72.9 kJ mol-1
C) +84.9 kJ mol-1
D) -92.5 kJ mol-1
E) -188 kJ mol-1
A) +243 kJ mol-1
B) -72.9 kJ mol-1
C) +84.9 kJ mol-1
D) -92.5 kJ mol-1
E) -188 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Use Hess's law to calculate ΔrG° using the following information: CO(g) → C(s) + 1/2 O2(g) ΔrG° = ?
CO2(g) → C(s) + O2(g) ΔrG° = +394.4 kJ mol-1
CO(g) + 1/2 O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔrG° = -257.2 kJ mol-1
A) -60.0 kJ mol-1
B) +651.6 kJ mol-1
C) -265.8 kJ mol-1
D) +137.2 kJ mol-1
E) +523.0 kJ mol-1
CO2(g) → C(s) + O2(g) ΔrG° = +394.4 kJ mol-1
CO(g) + 1/2 O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔrG° = -257.2 kJ mol-1
A) -60.0 kJ mol-1
B) +651.6 kJ mol-1
C) -265.8 kJ mol-1
D) +137.2 kJ mol-1
E) +523.0 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Calculate ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: 4HNO3(g) + 5N2H4(l) → 7N2(g) + 12H2O(l) ΔrG° = ?
ΔfH° (kJ mol-1) -133.9 50.6 -285.8
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 266.9 121.2 191.6 70.0
A) +4.90 × 103 kJ mol-1
B) +3.90 × 103 kJ mol-1
C) -2.04 × 103 kJ mol-1
D) -3.15 × 103 kJ mol-1
E) -3.30 × 103 kJ mol-1
ΔfH° (kJ mol-1) -133.9 50.6 -285.8
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 266.9 121.2 191.6 70.0
A) +4.90 × 103 kJ mol-1
B) +3.90 × 103 kJ mol-1
C) -2.04 × 103 kJ mol-1
D) -3.15 × 103 kJ mol-1
E) -3.30 × 103 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Calculate ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) → 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ΔrG° = ?
ΔfH° (kJ mol-1) -20.6 -296.8 -241.8
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 205.8 205.2 248.2 188.8
A) -990.3 kJ mol-1
B) +108.2 kJ mol-1
C) -466.1 kJ mol-1
D) +676.2 kJ mol-1
E) -147.1 kJ mol-1
ΔfH° (kJ mol-1) -20.6 -296.8 -241.8
S°(J K-1 mol-1) 205.8 205.2 248.2 188.8
A) -990.3 kJ mol-1
B) +108.2 kJ mol-1
C) -466.1 kJ mol-1
D) +676.2 kJ mol-1
E) -147.1 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Estimate ΔrG° for the following reaction at 449.0 K. CH2O(g) + 2H2(g) → CH4(g) + H2O(g) ΔrH°= -94.9 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= -224.2 J K-1 mol-1
A) +5.8 kJ mol-1
B) +12.9 kJ mol-1
C) -101 kJ mol-1
D) +2.4 kJ mol-1
E) -4.2 kJ mol-1
A) +5.8 kJ mol-1
B) +12.9 kJ mol-1
C) -101 kJ mol-1
D) +2.4 kJ mol-1
E) -4.2 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Determine ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) ΔrH°= +179.2 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= +160.2 J K-1 mol-1
A) -607.0 kJ mol-1
B) +112 .0 kJ mol-1
C) -89.3 kJ mol-1
D) +131.5 kJ mol-1
E) +228.1 kJ mol-1
A) -607.0 kJ mol-1
B) +112 .0 kJ mol-1
C) -89.3 kJ mol-1
D) +131.5 kJ mol-1
E) +228.1 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Determine ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: 2CH4(g) → C2H6(g) + H2(g) ΔrH°= +64.6 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= -12.7 J K-1 mol-1
A) -225.0 kJ mol-1
B) +68.4 .0 kJ mol-1
C) -89.3 kJ mol-1
D) +131.5 kJ mol-1
E) +175.2 kJ mol-1
A) -225.0 kJ mol-1
B) +68.4 .0 kJ mol-1
C) -89.3 kJ mol-1
D) +131.5 kJ mol-1
E) +175.2 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Use Hess's law to calculate ΔrG° using the following information: NO(g) + O(g) → NO2(g) ΔrG° = ?
2O3(g) → 3O2(g) ΔrG° = +489.6 kJ mol-1
O2(g) → 2O(g) ΔrG° = +463.4 kJ mol-1
NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) ΔrG° = - 199.5 kJ mol-1
A) +753.5 kJ mol-1
B) +277.0 kJ mol-1
C) -676.0 kJ mol-1
D) -1152.5 kJ mol-1
E) -225.7 kJ mol-1
2O3(g) → 3O2(g) ΔrG° = +489.6 kJ mol-1
O2(g) → 2O(g) ΔrG° = +463.4 kJ mol-1
NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) ΔrG° = - 199.5 kJ mol-1
A) +753.5 kJ mol-1
B) +277.0 kJ mol-1
C) -676.0 kJ mol-1
D) -1152.5 kJ mol-1
E) -225.7 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Determine ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: FeO(s) + CO(g) → Fe(s) + CO2(g) ΔrH°= -11.0 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= -17.4 J K-1 mol-1
A) +191.0 kJ mol-1
B) -5.8 kJ mol-1
C) +1.6 kJ mol-1
D) -6.4 kJ mol-1
E) +89.5 kJ mol-1
A) +191.0 kJ mol-1
B) -5.8 kJ mol-1
C) +1.6 kJ mol-1
D) -6.4 kJ mol-1
E) +89.5 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Determine ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) ΔrH°= +182.6 kJ mol-1; ΔrS°= +24.8 J K-1 mol-1
A) -607.0 kJ mol-1
B) +68.4 .0 kJ mol-1
C) -89.3 kJ mol-1
D) +131.5 kJ mol-1
E) +175.2 kJ mol-1
A) -607.0 kJ mol-1
B) +68.4 .0 kJ mol-1
C) -89.3 kJ mol-1
D) +131.5 kJ mol-1
E) +175.2 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Calculate ΔrG at 298 K under the conditions shown below for the following reaction: SO3(g) + H2O(g) → H2SO4(l) ΔrG°= -90.5 kJ mol-1
P(SO3) = 0.20 atm, P(H2O) = 0.88 atm
A) +15.9 kJ mol-1
B) -90.5 kJ mol-1
C) +51.4 kJ mol-1
D) -86.2 kJ mol-1
E) -30.4 kJ mol-1
P(SO3) = 0.20 atm, P(H2O) = 0.88 atm
A) +15.9 kJ mol-1
B) -90.5 kJ mol-1
C) +51.4 kJ mol-1
D) -86.2 kJ mol-1
E) -30.4 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Calculate ΔrG° at 298 K using the following information: 4HNO3(g) + 5N2H4(l) → 7N2(g) + 12H2O(l) ΔrG° = ?
ΔfG° (kJ mol-1) -73.5 149.3 -237.1
A) -3.2977 × 103 kJ mol-1
B) -312.9 kJ mol-1
C) +2.845 × 103 kJ mol-1
D) +110.7 kJ mol-1
E) -954.7 kJ mol-1
ΔfG° (kJ mol-1) -73.5 149.3 -237.1
A) -3.2977 × 103 kJ mol-1
B) -312.9 kJ mol-1
C) +2.845 × 103 kJ mol-1
D) +110.7 kJ mol-1
E) -954.7 kJ mol-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 134 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








