Deck 31: Government Debt and Deficits
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 31: Government Debt and Deficits
1
If voters want to know how their tax dollars are being spent and how the federal government is managing its current spending,they should look at
A)federal/provincial tax transfers.
B)changes in the money supply.
C)the primary budget balance.
D)the overall budget balance.
E)the inflation adjusted deficit.
A)federal/provincial tax transfers.
B)changes in the money supply.
C)the primary budget balance.
D)the overall budget balance.
E)the inflation adjusted deficit.
the primary budget balance.
2
The governmentʹs primary budget deficit (or surplus)is the difference between the
A)non-interest expenditures and interest payments.
B)interest payments and revenues.
C)total budget deficit (or surplus)and debt-service payments.
D)total budget deficit (or surplus)between one year and the next.
E)total government expenditures and revenues.
A)non-interest expenditures and interest payments.
B)interest payments and revenues.
C)total budget deficit (or surplus)and debt-service payments.
D)total budget deficit (or surplus)between one year and the next.
E)total government expenditures and revenues.
total budget deficit (or surplus)and debt-service payments.
3
In any given year,the governmentʹs debt-service payments are
A)equal to the annual budget deficit.
B)equal to the annual primary budget deficit.
C)the interest payments on the outstanding stock of government debt.
D)not related to the government deficit.
E)not required unless the debt is held by foreigners.
A)equal to the annual budget deficit.
B)equal to the annual primary budget deficit.
C)the interest payments on the outstanding stock of government debt.
D)not related to the government deficit.
E)not required unless the debt is held by foreigners.
the interest payments on the outstanding stock of government debt.
4
The extent to which tax revenues are able to finance the discretionary part of total government expenditure is best measured by the
A)cyclically adjusted deficit/surplus.
B)governmentʹs current fiscal policy.
C)debt-to-GDP ratio.
D)governmentʹs primary budget deficit or surplus.
E)tax-to-GDP ratio.
A)cyclically adjusted deficit/surplus.
B)governmentʹs current fiscal policy.
C)debt-to-GDP ratio.
D)governmentʹs primary budget deficit or surplus.
E)tax-to-GDP ratio.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
When a government changes its fiscal policy,it is
A)changing the exchange rates to change national income.
B)increasing the money supply to increase national income.
C)changing government spending and/or tax rates to achieve some objective.
D)using government spending and taxes together with changing the money supply in order to achieve full employment.
E)buying and selling private bonds to increase or decrease the overnight lending rate.
A)changing the exchange rates to change national income.
B)increasing the money supply to increase national income.
C)changing government spending and/or tax rates to achieve some objective.
D)using government spending and taxes together with changing the money supply in order to achieve full employment.
E)buying and selling private bonds to increase or decrease the overnight lending rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The governmentʹs primary budget deficit (or surplus)is the
A)non-interest expenditures and interest payments.
B)sum of total government expenditures and revenues.
C)sum of interest payments and revenues.
D)total budget deficit between two fiscal years.
E)total budget deficit (or surplus)excluding debt-service payments.
A)non-interest expenditures and interest payments.
B)sum of total government expenditures and revenues.
C)sum of interest payments and revenues.
D)total budget deficit between two fiscal years.
E)total budget deficit (or surplus)excluding debt-service payments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Do we get a useful and meaningful statistic by dividing the national debt by the GDP?
A)No - we are essentially ʺdividing apples by oranges,ʺ which is unhelpful.
B)No - the GDP is not a meaningful measure of the well-being of the economy.
C)Yes - we can then see how much of the national debt is owed by each individual citizen.
D)Yes - we can see the burden of the debt in relation to the size of the economy.
E)No - dividing a stock by a flow can never be sensible.
A)No - we are essentially ʺdividing apples by oranges,ʺ which is unhelpful.
B)No - the GDP is not a meaningful measure of the well-being of the economy.
C)Yes - we can then see how much of the national debt is owed by each individual citizen.
D)Yes - we can see the burden of the debt in relation to the size of the economy.
E)No - dividing a stock by a flow can never be sensible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
If we want to know whether tax revenues are sufficient to finance the discretionary part of government expenditure,which of the following measures should we analyze?
A)the cyclically adjusted deficit/surplus
B)the governmentʹs budget constraint
C)the debt-to-GDP ratio
D)the governmentʹs primary deficit/surplus
E)the interest rate on government bonds compared to the growth rate of real GDP
A)the cyclically adjusted deficit/surplus
B)the governmentʹs budget constraint
C)the debt-to-GDP ratio
D)the governmentʹs primary deficit/surplus
E)the interest rate on government bonds compared to the growth rate of real GDP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The governmentʹs annual primary budget deficit is equal to the
A)accumulation of government borrowing.
B)decrease in the stock of government debt during the course of a year.
C)excess of governmentʹs program expenditures over tax revenues in a given fiscal year.
D)total amount of government spending on program expenses,personnel,and capital outlays.
E)excess of current revenue over current expenditure.
A)accumulation of government borrowing.
B)decrease in the stock of government debt during the course of a year.
C)excess of governmentʹs program expenditures over tax revenues in a given fiscal year.
D)total amount of government spending on program expenses,personnel,and capital outlays.
E)excess of current revenue over current expenditure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Consider the federal governmentʹs budget constraint.If the governmentʹs total budget deficit is $27 billion and its debt-service payments are $29 billion,then its
A)primary budget deficit is $2 billion.
B)primary budget deficit is $56 billion.
C)primary budget surplus is $2 billion.
D)primary budget surplus is $56 billion.
E)Not enough information to determine.
A)primary budget deficit is $2 billion.
B)primary budget deficit is $56 billion.
C)primary budget surplus is $2 billion.
D)primary budget surplus is $56 billion.
E)Not enough information to determine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Consider the governmentʹs budget constraint.The accumulated stock of government debt will begin to fall
A)if the governmentʹs debt-service payments are zero.
B)if the government does not borrow money.
C)if the growth rate of real GDP is higher than the real interest rate.
D)when the governmentʹs annual budget is in deficit.
E)when the governmentʹs annual budget is in surplus.
A)if the governmentʹs debt-service payments are zero.
B)if the government does not borrow money.
C)if the growth rate of real GDP is higher than the real interest rate.
D)when the governmentʹs annual budget is in deficit.
E)when the governmentʹs annual budget is in surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
What is the difference between the governmentʹs debt and the governmentʹs deficit?
A)The debt is the annual shortfall of revenues minus disbursements whereas the deficit is the accumulation of past debts.
B)The debt is the amount the government pays in interest payments whereas the deficit has not yet incurred interest charges.
C)The debt is the amount payable to the Bank of Canada whereas the deficit is the annual shortfall of revenue minus disbursements.
D)The debt is the accumulation of past deficits whereas the deficit is the annual shortfall between revenues and disbursements.
E)The debt is the difference between tax revenues and government expenditures whereas the deficit is the difference between tax revenues and borrowing.
A)The debt is the annual shortfall of revenues minus disbursements whereas the deficit is the accumulation of past debts.
B)The debt is the amount the government pays in interest payments whereas the deficit has not yet incurred interest charges.
C)The debt is the amount payable to the Bank of Canada whereas the deficit is the annual shortfall of revenue minus disbursements.
D)The debt is the accumulation of past deficits whereas the deficit is the annual shortfall between revenues and disbursements.
E)The debt is the difference between tax revenues and government expenditures whereas the deficit is the difference between tax revenues and borrowing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A simple equation describing the governmentʹs budget constraint is
A)government expenditure = tax revenue - borrowing.
B)government expenditure = tax revenue + borrowing.
C)government expenditure = tax revenue + debt-service payments.
D)tax revenue = government expenditure + borrowing.
E)tax revenue = borrowing - government expenditure.
A)government expenditure = tax revenue - borrowing.
B)government expenditure = tax revenue + borrowing.
C)government expenditure = tax revenue + debt-service payments.
D)tax revenue = government expenditure + borrowing.
E)tax revenue = borrowing - government expenditure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Suppose the stock of government debt in Canada at the end of one fiscal year is $475 billion.If the stock of debt falls to $461 billion by the end of the next fiscal year,and debt-service payments during that year were $38 billion,then we know that the government had
A)a primary budget surplus of $52 billion.
B)a primary budget surplus of $14 billion.
C)a primary budget surplus of $24 billion.
D)an annual budget surplus of $38 billion.
E)an annual budget deficit of $14 billion.
A)a primary budget surplus of $52 billion.
B)a primary budget surplus of $14 billion.
C)a primary budget surplus of $24 billion.
D)an annual budget surplus of $38 billion.
E)an annual budget deficit of $14 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Consider the following variables: G = government purchases
I = interest rate on government debt D = stock of government debt
T = net tax revenue
The governmentʹs budget deficit can be expressed as
A)ΔD = (G + iD)- T.
B)ΔD = (G - iD)+ T.
C)deficit = D - (G + iD)+ T.
D)deficit = D - T + (G + iD).
E)T = ΔD - (G + iD).
I = interest rate on government debt D = stock of government debt
T = net tax revenue
The governmentʹs budget deficit can be expressed as
A)ΔD = (G + iD)- T.
B)ΔD = (G - iD)+ T.
C)deficit = D - (G + iD)+ T.
D)deficit = D - T + (G + iD).
E)T = ΔD - (G + iD).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Suppose that in Year 2 there was a higher federal budget deficit than in Year 1.This could be explained by in ________ in Year 2.
A)lower real interest rates
B)higher real GDP (with fiscal policy constant)
C)lower real GDP (with fiscal policy constant)
D)lower government expenditure (with real GDP constant)
E)a lower primary budget surplus
A)lower real interest rates
B)higher real GDP (with fiscal policy constant)
C)lower real GDP (with fiscal policy constant)
D)lower government expenditure (with real GDP constant)
E)a lower primary budget surplus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
In any given year,the governmentʹs debt-service payments are equal to
A)(fiscal borrowing)× (the interest rate).
B)(government spending)× (the interest rate).
C)(government spending - tax revenue)× (the interest rate).
D)(total outstanding government debt)× (the interest rate).
E)(government spending + tax revenue)× (the interest rate).
A)(fiscal borrowing)× (the interest rate).
B)(government spending)× (the interest rate).
C)(government spending - tax revenue)× (the interest rate).
D)(total outstanding government debt)× (the interest rate).
E)(government spending + tax revenue)× (the interest rate).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Consider the following variables: G = government purchases
I = interest rate on government debt D = stock of government debt
T = net tax revenue
The governmentʹs budget constraint can be expressed as
A)(G + iD)= borrowing - T.
B)(G + iD)- T = borrowing.
C)(G + iD)+ T = borrowing.
D)G - T - (iD)= borrowing.
E)(G - iD)= borrowing + T.
I = interest rate on government debt D = stock of government debt
T = net tax revenue
The governmentʹs budget constraint can be expressed as
A)(G + iD)= borrowing - T.
B)(G + iD)- T = borrowing.
C)(G + iD)+ T = borrowing.
D)G - T - (iD)= borrowing.
E)(G - iD)= borrowing + T.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Suppose the stock of government debt in Canada at the end of one fiscal year is $475 billion.If the stock of debt falls to $461 billion by the end of the next fiscal year,then we know that in that year
A)the government had a primary budget surplus of $14 billion.
B)the government had a primary budget deficit of $14 billion.
C)tax revenues increased by $14 billion.
D)the government had an annual budget surplus of $14 billion.
E)debt-service payments fell by $14 billion.
A)the government had a primary budget surplus of $14 billion.
B)the government had a primary budget deficit of $14 billion.
C)tax revenues increased by $14 billion.
D)the government had an annual budget surplus of $14 billion.
E)debt-service payments fell by $14 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The federal governmentʹs ʺprimary budget deficitʺ
A)includes domestic borrowing but excludes foreign borrowing.
B)excludes debt-service payments.
C)is the amount of government borrowing in a fiscal year.
D)is the amount of tax revenue minus the amount of interest paid on the public debt.
E)is the most important indicator of the level of government spending.
A)includes domestic borrowing but excludes foreign borrowing.
B)excludes debt-service payments.
C)is the amount of government borrowing in a fiscal year.
D)is the amount of tax revenue minus the amount of interest paid on the public debt.
E)is the most important indicator of the level of government spending.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Consider the governmentʹs budget deficit function.Other things being equal,an autonomous increase in government purchases causes the budget deficit function.
A)an upward movement along
B)a downward movement along
C)an upward shift of
D)a downward shift of
E)no change in
A)an upward movement along
B)a downward movement along
C)an upward shift of
D)a downward shift of
E)no change in

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The diagram below shows the budget deficit function for a government in a hypothetical economy.
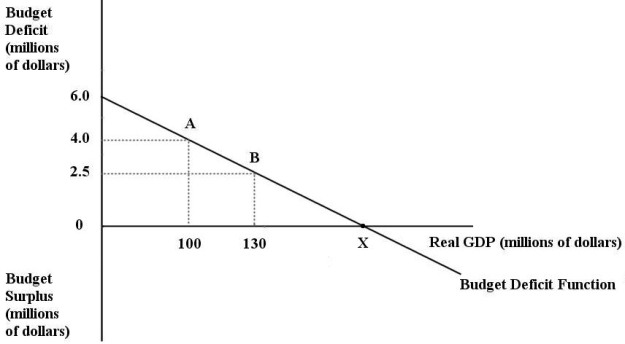 FIGURE 31-1
FIGURE 31-1
Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A.If the government implements an expansionary fiscal policy by increasing its purchases of goods and services,then
A)the budget deficit function would shift down.
B)the budget deficit function would become steeper.
C)the budget deficit function would become flatter.
D)the budget deficit function would shift up.
E)the size of the budget deficit would decrease as we move from point A to point B.
 FIGURE 31-1
FIGURE 31-1Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A.If the government implements an expansionary fiscal policy by increasing its purchases of goods and services,then
A)the budget deficit function would shift down.
B)the budget deficit function would become steeper.
C)the budget deficit function would become flatter.
D)the budget deficit function would shift up.
E)the size of the budget deficit would decrease as we move from point A to point B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Consider the governmentʹs budget deficit function over a two-year time span - Years 1 and 2.Suppose in Year 2 there was a lower federal budget deficit than in Year 1.This could be explained by ________ in Year 2.
A)higher government expenditures (with constant real GDP)
B)higher real GDP (with constant fiscal policy)
C)lower real GDP (with constant fiscal policy)
D)a higher stock of government debt
E)an upward shift of the budget deficit function
A)higher government expenditures (with constant real GDP)
B)higher real GDP (with constant fiscal policy)
C)lower real GDP (with constant fiscal policy)
D)a higher stock of government debt
E)an upward shift of the budget deficit function

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The diagram below shows the budget deficit function for a government in a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-1
FIGURE 31-1
Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A.If the government implements an expansionary fiscal policy by decreasing lump -sum taxes,then
A)the budget deficit function would shift up.
B)the budget deficit function would shift down.
C)the budget deficit function would become steeper.
D)the budget deficit function would become flatter.
E)the size of the budget deficit would decrease as we move from point A to point B.
 FIGURE 31-1
FIGURE 31-1Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A.If the government implements an expansionary fiscal policy by decreasing lump -sum taxes,then
A)the budget deficit function would shift up.
B)the budget deficit function would shift down.
C)the budget deficit function would become steeper.
D)the budget deficit function would become flatter.
E)the size of the budget deficit would decrease as we move from point A to point B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Suppose during one fiscal year,government purchases are $195 billion,debt-service payments are $22 billion and net tax revenues are $208 billion.What is the governmentʹs primary budget deficit/surplus?
A)primary budget surplus of $22 billion
B)primary budget deficit of $13 billion
C)primary budget surplus of $13 billion
D)primary budget deficit of $9 billion
E)primary budget surplus of $9 billion
A)primary budget surplus of $22 billion
B)primary budget deficit of $13 billion
C)primary budget surplus of $13 billion
D)primary budget deficit of $9 billion
E)primary budget surplus of $9 billion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The Canadian federal government had a budget surplus each year from________ until 2008.
A)1945
B)1967
C)1987
D)1998
E)2000
A)1945
B)1967
C)1987
D)1998
E)2000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Consider the governmentʹs budget deficit function.With an unchanged fiscal policy by government,an increase in GDP tends to net tax revenues and thus the budget deficit.
A)raise; raise
B)raise; lower
C)lower; raise
D)lower; lower
E)lower; leave unchanged
A)raise; raise
B)raise; lower
C)lower; raise
D)lower; lower
E)lower; leave unchanged

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Suppose during one fiscal year,government purchases are $195 billion,debt-service payments are $22 billion and net tax revenues are $208 billion.What is the annual budget deficit/surplus?
A)budget surplus of $22 billion
B)budget deficit of $13 billion
C)budget surplus of $13 billion
D)budget deficit of $9 billion
E)budget surplus of $9 billion
A)budget surplus of $22 billion
B)budget deficit of $13 billion
C)budget surplus of $13 billion
D)budget deficit of $9 billion
E)budget surplus of $9 billion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The diagram below shows the budget deficit function for a government in a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-1
FIGURE 31-1
Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A on the graph.Which of the following is consistent with a move from point A to point B?
A)implementation of an expansionary fiscal policy
B)implementation of a contractionary fiscal policy
C)implementation of a contractionary monetary policy
D)the economy entering into a recession
E)the economy entering into a boom
 FIGURE 31-1
FIGURE 31-1Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A on the graph.Which of the following is consistent with a move from point A to point B?
A)implementation of an expansionary fiscal policy
B)implementation of a contractionary fiscal policy
C)implementation of a contractionary monetary policy
D)the economy entering into a recession
E)the economy entering into a boom

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
If the governmentʹs total budget deficit is $24 billion and its debt -service payments are $20 billion,then its ________ is $4 billion.
A)cyclically adjusted deficit
B)primary budget deficit
C)primary budget surplus
D)government expenditure
E)total tax revenue
A)cyclically adjusted deficit
B)primary budget deficit
C)primary budget surplus
D)government expenditure
E)total tax revenue

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Consider the governmentʹs budget deficit function,graphed with the budget deficit on the vertical axis and real GDP on the horizontal axis.The vertical position (or height)of the budget deficit function is determined by
A)the governmentʹs fiscal policies.
B)nominal GDP.
C)the interest rate times taxes.
D)the purchase and sale of government securities on the open market.
E)the stock of government debt minus government spending.
A)the governmentʹs fiscal policies.
B)nominal GDP.
C)the interest rate times taxes.
D)the purchase and sale of government securities on the open market.
E)the stock of government debt minus government spending.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Consider the governmentʹs budget deficit function.If the economy goes into a recession,a government budget deficit is most likely to
A)increase,because government expenditures and tax revenues will both rise.
B)increase,because government expenditures will rise and tax revenues will decline.
C)remain unchanged,although there will be a primary budget surplus.
D)remain unchanged,because changes in government expenditures and tax revenues will balance each other out.
E)decrease,because government expenditures will decrease and tax revenues will rise.
A)increase,because government expenditures and tax revenues will both rise.
B)increase,because government expenditures will rise and tax revenues will decline.
C)remain unchanged,although there will be a primary budget surplus.
D)remain unchanged,because changes in government expenditures and tax revenues will balance each other out.
E)decrease,because government expenditures will decrease and tax revenues will rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The diagram below shows the budget deficit function for a government in a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-1
FIGURE 31-1
Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A.If the government implements a contractionary fiscal policy by decreasing its purchases of goods and services,then
A)the budget deficit function would shift up.
B)the budget deficit function would shift down.
C)the budget deficit function would become steeper.
D)the budget deficit function would become flatter.
E)the size of the budget deficit would decrease as we move from point A to point B.
 FIGURE 31-1
FIGURE 31-1Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A.If the government implements a contractionary fiscal policy by decreasing its purchases of goods and services,then
A)the budget deficit function would shift up.
B)the budget deficit function would shift down.
C)the budget deficit function would become steeper.
D)the budget deficit function would become flatter.
E)the size of the budget deficit would decrease as we move from point A to point B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Suppose the governmentʹs budget deficit falls from one year to the next,but there has been no change in the governmentʹs fiscal policy.The change in the budget deficit can be explained by
A)a rising real interest rate.
B)a change in the stance of fiscal policy.
C)a rising real GDP.
D)a rise in the cyclically adjusted deficit.
E)a rise in the primary budget deficit.
A)a rising real interest rate.
B)a change in the stance of fiscal policy.
C)a rising real GDP.
D)a rise in the cyclically adjusted deficit.
E)a rise in the primary budget deficit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Consider the governmentʹs budget deficit function,graphed with dollars on the vertical axis and real GDP on the horizontal axis.This function is downward sloping because as real GDP
A)falls,the budget deficit function shifts down.
B)falls,tax revenues rise,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
C)rises,tax revenues rise,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
D)rises,tax revenues fall,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
E)rises,it leads to increasing debt-service payments.
A)falls,the budget deficit function shifts down.
B)falls,tax revenues rise,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
C)rises,tax revenues rise,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
D)rises,tax revenues fall,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
E)rises,it leads to increasing debt-service payments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The budget deficit function is graphed with the budget deficit on the vertical axis and ________ on the horizontal axis, and is ________.
A)real GDP; downward sloping
B)real GDP; upward sloping
C)the interest rate; downward sloping
D)the interest rate; upward sloping
E)the interest rate; horizontal
A)real GDP; downward sloping
B)real GDP; upward sloping
C)the interest rate; downward sloping
D)the interest rate; upward sloping
E)the interest rate; horizontal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If the governmentʹs total budget surplus is $10 billion and its debt-service payments are $8 billion,then its primary budget surplus is
A)$2 billion.
B)$8 billion.
C)$10 billion.
D)$18 billion.
E)-$2 billion.
A)$2 billion.
B)$8 billion.
C)$10 billion.
D)$18 billion.
E)-$2 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Consider the budget deficit function.With an unchanged fiscal policy by government,an increase in national income causes ________ the budget deficit function.
A)an upward movement along
B)a downward movement along
C)an upward shift of
D)a downward shift of
E)a downward rotation in
A)an upward movement along
B)a downward movement along
C)an upward shift of
D)a downward shift of
E)a downward rotation in

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Suppose the stock of government debt in Canada at the end of one fiscal year (Year 1)is $475 billion.During the following year (Year 2),government purchases were $180 billion,debt -service payments were $25 billion,and net tax revenues were $208 billion.What is the stock of debt at the end of Year 2?
A)$422 billion
B)$457 billion
C)$472 billion
D)$475 billion
E)$478 billion
A)$422 billion
B)$457 billion
C)$472 billion
D)$475 billion
E)$478 billion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Suppose the stock of government debt in Canada at the end of one fiscal year is $475 billion.If the stock of debt rises to $482 billion by the end of the next fiscal year,then we know that in that year
A)debt-service payments rose by $7 billion.
B)the government had a primary budget surplus of $7 billion.
C)the government had an annual budget deficit of $7 billion.
D)the government had a primary budget deficit of $7 billion.
E)tax revenues decreased by $7 billion.
A)debt-service payments rose by $7 billion.
B)the government had a primary budget surplus of $7 billion.
C)the government had an annual budget deficit of $7 billion.
D)the government had a primary budget deficit of $7 billion.
E)tax revenues decreased by $7 billion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If the economy goes into a recession,the structural budget deficit is most likely to
A)increase,because government expenditures and tax revenues will both rise.
B)increase,because government expenditures will rise and tax revenues will decline.
C)remain unchanged,although there will be a primary budget surplus.
D)remain unchanged,unless government actively changes its fiscal policy.
E)decrease,because government expenditures will decrease and tax revenues will rise.
A)increase,because government expenditures and tax revenues will both rise.
B)increase,because government expenditures will rise and tax revenues will decline.
C)remain unchanged,although there will be a primary budget surplus.
D)remain unchanged,unless government actively changes its fiscal policy.
E)decrease,because government expenditures will decrease and tax revenues will rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
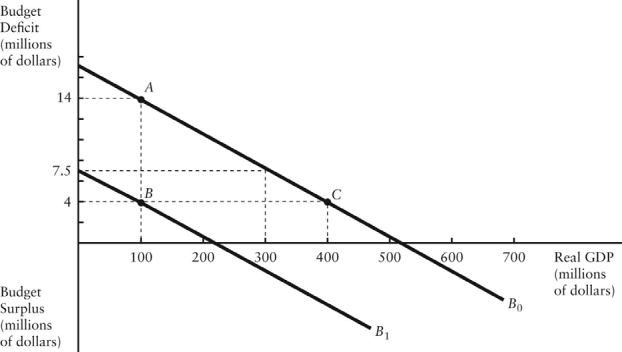 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the government implements a fiscal policy that causes the budget deficit function to shift to B1,we can conclude that the policy was ________ and the structural deficit will be ________ than previously.
A)expansionary; smaller
B)expansionary; larger
C)contractionary; larger
D)contractionary; smaller
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the government implements a fiscal policy that causes the budget deficit function to shift to B1,we can conclude that the policy was ________ and the structural deficit will be ________ than previously.
A)expansionary; smaller
B)expansionary; larger
C)contractionary; larger
D)contractionary; smaller

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The best measure of the change in the stance of a governmentʹs fiscal policy is
A)the actual budget deficit.
B)the cyclically adjusted deficit.
C)the change in the structural budget deficit.
D)the change in the actual budget deficit.
E)the change in the primary budget deficit.
A)the actual budget deficit.
B)the cyclically adjusted deficit.
C)the change in the structural budget deficit.
D)the change in the actual budget deficit.
E)the change in the primary budget deficit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $300 million,the structural budget deficit would be
A)$2 million.
B)$14 million.
C)measured by the vertical distance between the horizontal axis and B0 (at real GDP = 300).
D)measured by the vertical distance between point A and the budget deficit that would exist at real GDP = 300 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $300 million,the structural budget deficit would be
A)$2 million.
B)$14 million.
C)measured by the vertical distance between the horizontal axis and B0 (at real GDP = 300).
D)measured by the vertical distance between point A and the budget deficit that would exist at real GDP = 300 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $400 million,the structural budget deficit would be
A)$14 million.
B)$4 million.
C)negative.
D)-$10 million.
E)$0.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $400 million,the structural budget deficit would be
A)$14 million.
B)$4 million.
C)negative.
D)-$10 million.
E)$0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $300 million,how much of the actual budget deficit is due to the underlying structure of fiscal policy and is therefore independent of the current level of GDP?
A)$4 million.
B)$6.5 million.
C)$7.5 million.
D)$14 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $300 million,how much of the actual budget deficit is due to the underlying structure of fiscal policy and is therefore independent of the current level of GDP?
A)$4 million.
B)$6.5 million.
C)$7.5 million.
D)$14 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What economists call ʺgovernment savingʺ,or ʺpublic savingʺ is the same as the
A)governmentʹs actual budget surplus.
B)difference between household saving and business saving.
C)difference between household saving and private saving.
D)dollar amount of bonds that the government holds at any given time.
E)sum of the budget surplus and national saving.
A)governmentʹs actual budget surplus.
B)difference between household saving and business saving.
C)difference between household saving and private saving.
D)dollar amount of bonds that the government holds at any given time.
E)sum of the budget surplus and national saving.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Suppose the governmentʹs actual budget deficit is equal to the structural budget deficit.Then it must be the case that
A)the primary budget deficit is zero.
B)the overall government budget is balanced.
C)the debt-to-GDP ratio is stable.
D)real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
E)the government is not reporting all of its expenses.
A)the primary budget deficit is zero.
B)the overall government budget is balanced.
C)the debt-to-GDP ratio is stable.
D)real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
E)the government is not reporting all of its expenses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Consider a closed-economy AD/AS macro model.A policy-induced increase in the governmentʹs budget deficit is most likely to crowd-out private investment if
A)interest rates decrease sharply as a result of the deficit.
B)interest rates rise sharply as a result of the deficit.
C)rising income increases the volume of saving and interest rates rise very little.
D)there is a very large output gap.
E)consumers reduce consumption as a result of the deficit.
A)interest rates decrease sharply as a result of the deficit.
B)interest rates rise sharply as a result of the deficit.
C)rising income increases the volume of saving and interest rates rise very little.
D)there is a very large output gap.
E)consumers reduce consumption as a result of the deficit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $14 million,as shown by point A.Which of the following events could result in a move from point A to point C?
A)a fiscal expansion and an increase in GDP
B)a fiscal contraction and an increase in GDP
C)a fiscal expansion and a decrease in GDP
D)a fiscal contraction and a decrease in GDP
E)an increase in GDP with no change in fiscal policy
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $14 million,as shown by point A.Which of the following events could result in a move from point A to point C?
A)a fiscal expansion and an increase in GDP
B)a fiscal contraction and an increase in GDP
C)a fiscal expansion and a decrease in GDP
D)a fiscal contraction and a decrease in GDP
E)an increase in GDP with no change in fiscal policy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A.If the government were to then implement a fiscal expansion,the structural budget deficit would be
A)$4 million.
B)$6 million.
C)$7 million.
D)$10 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A.If the government were to then implement a fiscal expansion,the structural budget deficit would be
A)$4 million.
B)$6 million.
C)$7 million.
D)$10 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $300 million,the cyclical component of the actual budget deficit would be
A)$4 million.
B)$6.5 million.
C)$7.5 million.
D)$14 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $300 million,the cyclical component of the actual budget deficit would be
A)$4 million.
B)$6.5 million.
C)$7.5 million.
D)$14 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Consider an open-economy AD/AS macro model.An expansionary fiscal policy will generally increase the governmentʹs budget and also tends to and thus net exports.
A)deficit; appreciate the currency; decrease
B)surplus; depreciate the currency; increase
C)deficit; appreciate the currency; increase
D)surplus; appreciate the currency; decrease
E)deficit; depreciate the currency; decrease
A)deficit; appreciate the currency; decrease
B)surplus; depreciate the currency; increase
C)deficit; appreciate the currency; increase
D)surplus; appreciate the currency; decrease
E)deficit; depreciate the currency; decrease

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
An illustration of ʺcrowding outʺ in macroeconomics is best provided by
A)a decrease in government subsidies for low-cost housing causes an increase in private spending on housing.
B)a decrease in the money supply decreases nominal GDP.
C)an increase in tariffs causes a decrease in imports.
D)an increase in the money supply crowds out the issuance of privately held debt.
E)a fiscal expansion raises interest rates and thereby lowers private investment.
A)a decrease in government subsidies for low-cost housing causes an increase in private spending on housing.
B)a decrease in the money supply decreases nominal GDP.
C)an increase in tariffs causes a decrease in imports.
D)an increase in the money supply crowds out the issuance of privately held debt.
E)a fiscal expansion raises interest rates and thereby lowers private investment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $300 million,the structural budget deficit would be
A)$4 million.
B)$6.5 million.
C)$7.5 million.
D)$14 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function B0.Real GDP (Y)is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*)were $300 million,the structural budget deficit would be
A)$4 million.
B)$6.5 million.
C)$7.5 million.
D)$14 million.
E)Insufficient information to know.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The concept of ʺnational savingʺ refers to the
A)difference between private saving and government saving.
B)sum of private saving and government saving.
C)money supply measure,M3.
D)difference between the two measurements of the money supply,M3 - M2.
E)total saving of the private sector.
A)difference between private saving and government saving.
B)sum of private saving and government saving.
C)money supply measure,M3.
D)difference between the two measurements of the money supply,M3 - M2.
E)total saving of the private sector.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The governmentʹs structural budget deficit is the budget deficit that would exist
A)if real GDP were equal to potential GDP.
B)with taxes and expenditures measured at the equilibrium level of GDP.
C)if policy were changed to eliminate the business cycle.
D)if tax rates were set to maximize tax revenues.
E)if there were no discretionary fiscal interventions in the economy.
A)if real GDP were equal to potential GDP.
B)with taxes and expenditures measured at the equilibrium level of GDP.
C)if policy were changed to eliminate the business cycle.
D)if tax rates were set to maximize tax revenues.
E)if there were no discretionary fiscal interventions in the economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The governmentʹs structural budget deficit adjusts for
A)any primary budget surplus or deficit incurred by the federal government.
B)changes in investment to smooth fluctuations in national income.
C)changes in spending or tax revenues caused by deviations in national income from potential output.
D)increases in the money supply in excess of the real growth in the economy.
E)interest rate changes that affect the absolute amount of debt-service payments.
A)any primary budget surplus or deficit incurred by the federal government.
B)changes in investment to smooth fluctuations in national income.
C)changes in spending or tax revenues caused by deviations in national income from potential output.
D)increases in the money supply in excess of the real growth in the economy.
E)interest rate changes that affect the absolute amount of debt-service payments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Consider a closed-economy AD/AS macro model.An expansionary fiscal policy will generally increase the governmentʹs budget and also tends to and thus private investment.
A)deficit; raise interest rates; decrease
B)surplus; reduce interest rates; increase
C)deficit; raise interest rates; increase
D)surplus; reduce interest rates; decrease
E)deficit; reduce interest rates; increase
A)deficit; raise interest rates; decrease
B)surplus; reduce interest rates; increase
C)deficit; raise interest rates; increase
D)surplus; reduce interest rates; decrease
E)deficit; reduce interest rates; increase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy.
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2
Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $14 million,as shown by point A.Which of the following events could result in a move from point A to point B?
A)the implementation of an expansionary fiscal policy
B)the implementation of a contractionary fiscal policy
C)the implementation of an expansionary monetary policy
D)the implementation of a contractionary monetary policy
E)the economy entering into a boom
 FIGURE 31-2
FIGURE 31-2Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $14 million,as shown by point A.Which of the following events could result in a move from point A to point B?
A)the implementation of an expansionary fiscal policy
B)the implementation of a contractionary fiscal policy
C)the implementation of an expansionary monetary policy
D)the implementation of a contractionary monetary policy
E)the economy entering into a boom

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
If the Canadian federal government adopted a formal balanced budget rule,during times that GDP was rising it would have to
A)increase tax rates and/or increase spending which would destabilize the economy.
B)decrease spending and transfer payments while holding tax rates constant.
C)decrease tax rates and/or increase spending which would destabilize the economy.
D)decrease interest payments on the debt.
E)decrease tax rates and/or decrease spending which would destabilize the economy.
A)increase tax rates and/or increase spending which would destabilize the economy.
B)decrease spending and transfer payments while holding tax rates constant.
C)decrease tax rates and/or increase spending which would destabilize the economy.
D)decrease interest payments on the debt.
E)decrease tax rates and/or decrease spending which would destabilize the economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The concept of capital budgeting refers to the idea that
A)government budgets should be designed to be balanced,while fully recognizing that changing economic circumstances may prevent such balance.
B)if the debt-to-GDP ratio rises to unacceptable levels,the central bank can monetize portions of the government debt.
C)counter-cyclical fiscal policy is included in the government budget.
D)the government would classify all expenditures as either consumption (benefiting current generations)or investment (benefiting future generations).
E)the government would direct a fixed percentage of its budget toward investment expenditure that would benefit future generations.
A)government budgets should be designed to be balanced,while fully recognizing that changing economic circumstances may prevent such balance.
B)if the debt-to-GDP ratio rises to unacceptable levels,the central bank can monetize portions of the government debt.
C)counter-cyclical fiscal policy is included in the government budget.
D)the government would classify all expenditures as either consumption (benefiting current generations)or investment (benefiting future generations).
E)the government would direct a fixed percentage of its budget toward investment expenditure that would benefit future generations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Consider a closed-economy AD/AS model.If an increase in the governmentʹs budget deficit drives up market interest rates,
A)credit will become less expensive.
B)nothing - government borrowing cannot push up interest rates.
C)private expenditure will likely increase.
D)some private investment expenditure will probably be crowded out.
E)the money supply will increase.
A)credit will become less expensive.
B)nothing - government borrowing cannot push up interest rates.
C)private expenditure will likely increase.
D)some private investment expenditure will probably be crowded out.
E)the money supply will increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The diagram below is for a closed economy which begins in long-run equilibrium at Y* and P0.
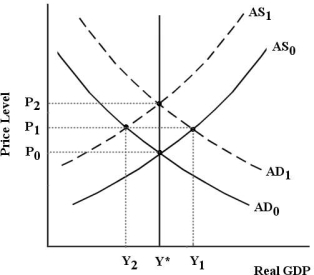 FIGURE 31-3
FIGURE 31-3
Refer to Figure 31-3.Suppose the government implements an expansionary fiscal policy,which increases the budget deficit.The economyʹs adjustment process returns real GDP to Y* in the long run.Since real GDP is not affected in the long run,how are future generations likely to be harmed by this government policy?
A)Investment in public infrastructure has been crowded out,which will harm future generations.
B)Private investment has been crowded out,which may lead to a lower future growth rate of potential GDP.
C)The inflationary gap is harmful to the economy and reduces real GDP in the future.
D)The budget deficit causes an appreciation in the domestic currency which reduces the income of future generations.
E)Future generations are definitely not harmed by this policy.
 FIGURE 31-3
FIGURE 31-3Refer to Figure 31-3.Suppose the government implements an expansionary fiscal policy,which increases the budget deficit.The economyʹs adjustment process returns real GDP to Y* in the long run.Since real GDP is not affected in the long run,how are future generations likely to be harmed by this government policy?
A)Investment in public infrastructure has been crowded out,which will harm future generations.
B)Private investment has been crowded out,which may lead to a lower future growth rate of potential GDP.
C)The inflationary gap is harmful to the economy and reduces real GDP in the future.
D)The budget deficit causes an appreciation in the domestic currency which reduces the income of future generations.
E)Future generations are definitely not harmed by this policy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
In an open economy with internationally mobile financial capital,we would expect a policy -induced increase in the governmentʹs budget deficit to crowd out
A)consumption more than investment.
B)consumption more than net exports.
C)investment more than net exports.
D)government purchases more than net exports.
E)net exports more than investment.
A)consumption more than investment.
B)consumption more than net exports.
C)investment more than net exports.
D)government purchases more than net exports.
E)net exports more than investment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
An annually balanced government budget is a difficult policy goal to achieve because
A)a significant portion of the governmentʹs budget is beyond the short-term discretion of the federal government.
B)government has little control over interest-rate charges on its debt during a fiscal year.
C)tax revenues automatically rise during economic booms and fall during recessions.
D)transfer payments rise during recessions and fall during economic booms.
E)all of the above are reasons why a balanced budget is difficult to achieve.
A)a significant portion of the governmentʹs budget is beyond the short-term discretion of the federal government.
B)government has little control over interest-rate charges on its debt during a fiscal year.
C)tax revenues automatically rise during economic booms and fall during recessions.
D)transfer payments rise during recessions and fall during economic booms.
E)all of the above are reasons why a balanced budget is difficult to achieve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
There is a long-term burden of government debt in a closed economy when
A)foreign owners of Canadian debt demand repayment.
B)it is no longer possible to find individuals in the private sector willing to finance the debt.
C)the burden of the debt is being borne by the current generation rather than future generations.
D)present consumption and government expenditure are not reduced because of future crowding-out.
E)the stock of physical productive capital is reduced because of crowding out.
A)foreign owners of Canadian debt demand repayment.
B)it is no longer possible to find individuals in the private sector willing to finance the debt.
C)the burden of the debt is being borne by the current generation rather than future generations.
D)present consumption and government expenditure are not reduced because of future crowding-out.
E)the stock of physical productive capital is reduced because of crowding out.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
An annually balanced government budget is a
A)destabilizer because fiscal policy is then pro-cyclical.
B)destabilizer because the fiscal year is longer than the business cycle.
C)stabilizer because it smooths out the peaks and troughs of the business cycle.
D)stabilizer because it allows greater flexibility in the design of fiscal policy.
E)stabilizer in most circumstances.
A)destabilizer because fiscal policy is then pro-cyclical.
B)destabilizer because the fiscal year is longer than the business cycle.
C)stabilizer because it smooths out the peaks and troughs of the business cycle.
D)stabilizer because it allows greater flexibility in the design of fiscal policy.
E)stabilizer in most circumstances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Financing a budget deficit by increasing the money supply will
A)allow more flexibility in the design of monetary policy.
B)increase investment over time.
C)create greater inflationary pressure.
D)have no short-run monetary effects on the economy.
E)reduce the burden of government debt.
A)allow more flexibility in the design of monetary policy.
B)increase investment over time.
C)create greater inflationary pressure.
D)have no short-run monetary effects on the economy.
E)reduce the burden of government debt.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
In general, the government will have ________ flexibility in implementing counter-cyclical fiscal policy when the outstanding stock of government debt is ________ relative to the size of GDP.
A)more; large
B)more; small
C)total; large
D)less; small
E)less; insignificant
A)more; large
B)more; small
C)total; large
D)less; small
E)less; insignificant

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Consider the governmentʹs debt-to-GDP ratio.A significant reason for a government to maintain a low debt-to-GDP ratio is so that
A)the real interest rate remains high,which leads to increased investment.
B)the Canadian dollar will appreciate and net exports will increase.
C)the government has the flexibility to use expansionary fiscal policy if the economy enters a recession.
D)the Bank of Canada has the flexibility to use contractionary policy.
E)there is no ʺcrowding inʺ of investment or net exports.
A)the real interest rate remains high,which leads to increased investment.
B)the Canadian dollar will appreciate and net exports will increase.
C)the government has the flexibility to use expansionary fiscal policy if the economy enters a recession.
D)the Bank of Canada has the flexibility to use contractionary policy.
E)there is no ʺcrowding inʺ of investment or net exports.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The policy objective of an annually balanced government budget
A)is feasible and would be stabilizing.
B)is easy to achieve but would be destabilizing.
C)would be stabilizing,but is difficult to achieve.
D)is difficult to achieve and would be destabilizing.
E)would eliminate the swings in real GDP.
A)is feasible and would be stabilizing.
B)is easy to achieve but would be destabilizing.
C)would be stabilizing,but is difficult to achieve.
D)is difficult to achieve and would be destabilizing.
E)would eliminate the swings in real GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
The diagram below is for a closed economy which begins in long-run equilibrium at Y* and P0.
 FIGURE 31-3
FIGURE 31-3
Refer to Figure 31-3.Suppose the government implements an expansionary fiscal policy which increases the budget deficit.The initial effect of this policy is the opening of a(n) ________ gap, and a new short -run equilibrium with a price level of ________ and real GDP of ________.
A)recessionary; P1; Y2
B)inflationary; P1; Y*
C)inflationary; P2; Y*
D)inflationary; P1; Y1
E)recessionary; P0; Y*
 FIGURE 31-3
FIGURE 31-3Refer to Figure 31-3.Suppose the government implements an expansionary fiscal policy which increases the budget deficit.The initial effect of this policy is the opening of a(n) ________ gap, and a new short -run equilibrium with a price level of ________ and real GDP of ________.
A)recessionary; P1; Y2
B)inflationary; P1; Y*
C)inflationary; P2; Y*
D)inflationary; P1; Y1
E)recessionary; P0; Y*

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
In an open economy like Canadaʹs,a policy -induced increase in the governmentʹs budget deficit tends to
A)attract foreign capital and reduce interest rates.
B)crowd out public consumption.
C)crowd out net exports and reduce interest rates.
D)attract foreign capital and crowd out net exports.
E)depreciate the domestic currency.
A)attract foreign capital and reduce interest rates.
B)crowd out public consumption.
C)crowd out net exports and reduce interest rates.
D)attract foreign capital and crowd out net exports.
E)depreciate the domestic currency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The diagram below is for a closed economy which begins in long-run equilibrium at Y* and P0.
 FIGURE 31-3
FIGURE 31-3
Refer to Figure 31-3.Suppose the government in this closed economy implements an expansionary fiscal policy,which increases the budget deficit.When the economy reaches its new long -run equilibrium,how has the composition of national income changed?
A)net exports have fallen
B)investment has fallen
C)consumption has increased
D)net exports have risen
E)the composition of national income at Y* is unchanged
 FIGURE 31-3
FIGURE 31-3Refer to Figure 31-3.Suppose the government in this closed economy implements an expansionary fiscal policy,which increases the budget deficit.When the economy reaches its new long -run equilibrium,how has the composition of national income changed?
A)net exports have fallen
B)investment has fallen
C)consumption has increased
D)net exports have risen
E)the composition of national income at Y* is unchanged

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
In the long run,the government budget will add to sustained inflation if
A)they require decreases in the money supply.
B)continual deficits are financed by the continual creation of new money.
C)deficits are always accompanied by decreases in the money supply.
D)government borrowing lowers interest rates.
E)the government finances the deficit by borrowing from the private sector.
A)they require decreases in the money supply.
B)continual deficits are financed by the continual creation of new money.
C)deficits are always accompanied by decreases in the money supply.
D)government borrowing lowers interest rates.
E)the government finances the deficit by borrowing from the private sector.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The proposition that increases in government budget deficits in an open economy tend to crowd out net exports relies on the idea that
A)government demand for labour tends to create manpower shortages in export industries.
B)much government expenditure is typically directed towards imported goods and services.
C)the resulting increase in interest rates attracts an inflow of financial capital that causes the currency to appreciate.
D)the rise in private-sector wealth associated with the rising stock of bonds leads to a fall in the saving rate and therefore a current account deficit.
E)there is downward pressure on interest rates that causes the currency to depreciate.
A)government demand for labour tends to create manpower shortages in export industries.
B)much government expenditure is typically directed towards imported goods and services.
C)the resulting increase in interest rates attracts an inflow of financial capital that causes the currency to appreciate.
D)the rise in private-sector wealth associated with the rising stock of bonds leads to a fall in the saving rate and therefore a current account deficit.
E)there is downward pressure on interest rates that causes the currency to depreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
In an open economy like Canadaʹs,a fiscal expansion by the government tends to
A)reduce capital inflow,depreciate the currency,and increase net exports.
B)attract foreign capital and encourage increased investment.
C)crowd out net exports and encourage private investment.
D)attract foreign capital,appreciate the currency,and crowd out net exports.
E)attract foreign capital,depreciate the currency,and crowd out net exports.
A)reduce capital inflow,depreciate the currency,and increase net exports.
B)attract foreign capital and encourage increased investment.
C)crowd out net exports and encourage private investment.
D)attract foreign capital,appreciate the currency,and crowd out net exports.
E)attract foreign capital,depreciate the currency,and crowd out net exports.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
It can be argued that a government budget deficit,rather than being a burden for future generations,may provide net benefits to future generations.This view is correct if the current budget deficit is used to
A)pay transfers such as welfare and old age pensions in the present period.
B)finance projects that deliver long-term benefits to society.
C)invest in the purchasing of goods not available in the local economy.
D)ensure that all interest paid goes to residents rather than foreigners.
E)pay subsidies to Canadian firms to offset rising energy costs.
A)pay transfers such as welfare and old age pensions in the present period.
B)finance projects that deliver long-term benefits to society.
C)invest in the purchasing of goods not available in the local economy.
D)ensure that all interest paid goes to residents rather than foreigners.
E)pay subsidies to Canadian firms to offset rising energy costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Decreasing government expenditures in order to reduce the governmentʹs budget deficit can involve certain costs.An example of such a cost could be
A)larger school facilities to accommodate a growing population.
B)longer queues for essential government services such as health-care.
C)encouraging future generations to be more self-sufficient and less reliant on government to provide for them.
D)a lower portion of taxes being used to pay interest.
E)improving the flexibility to practice counter-cyclical fiscal policy.
A)larger school facilities to accommodate a growing population.
B)longer queues for essential government services such as health-care.
C)encouraging future generations to be more self-sufficient and less reliant on government to provide for them.
D)a lower portion of taxes being used to pay interest.
E)improving the flexibility to practice counter-cyclical fiscal policy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








