Deck 6: Economic Growth
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/95
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 6: Economic Growth
1
A movement _______ illustrates a return to full employment in a business cycle expansion.
A)from a point inside the PPF to a point on the PPF
B)down along the PPF
C)from a point outside the PPF to a point inside the PPF
D)up along the PPF
E)from a point on the PPF to the origin
A)from a point inside the PPF to a point on the PPF
B)down along the PPF
C)from a point outside the PPF to a point inside the PPF
D)up along the PPF
E)from a point on the PPF to the origin
from a point inside the PPF to a point on the PPF
2
During 2016, the country of Economia had real GDP of $115 billion and the population was 0.9 billion.In 2017, real GDP was $105 billion and the population was 0.85 billion.In 2016, real GDP per person was
A)$12,778.
B)$124.
C)$135.
D)$128.
E)$103.50.
A)$12,778.
B)$124.
C)$135.
D)$128.
E)$103.50.
$128.
3
In which of the following decades did Canada experience the slowest economic growth?
A)1960s
B)1970s
C)1980s
D)1940s
E)1990s
A)1960s
B)1970s
C)1980s
D)1940s
E)1990s
1980s
4
Economic growth is
A)a sustained expansion of consumption expenditure over a given period.
B)a sustained expansion of the population.
C)the expansion of production possibilities.
D)equal to real GDP per person multiplied by 70.
E)always accompanied by a rising price level.
A)a sustained expansion of consumption expenditure over a given period.
B)a sustained expansion of the population.
C)the expansion of production possibilities.
D)equal to real GDP per person multiplied by 70.
E)always accompanied by a rising price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If real GDP per person is growing at 4 percent per year, it will double in
A)8 years.
B)25 years.
C)17.5 years.
D)4 years.
E)56 years.
A)8 years.
B)25 years.
C)17.5 years.
D)4 years.
E)56 years.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Real GDP per person in the country of Flip is $10,000, and the growth rate is 10 percent a year.Real GDP per person in the country of Flap is $20,000 and the growth rate is 5 percent a year.When will real GDP per person be greater in Flip than in Flap?
A)in 2 years
B)in 15 years
C)never
D)in 7 years
E)in 10 years
A)in 2 years
B)in 15 years
C)never
D)in 7 years
E)in 10 years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Growthland's real GDP per person was $112,000 in 2016 and $117,000 in 2017.What is the growth rate of Growthland's real GDP per person in 2017?
A)4.3 percent
B)12 percent
C)4.5 percent
D)5 percent
E)17 percent
A)4.3 percent
B)12 percent
C)4.5 percent
D)5 percent
E)17 percent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
In 2016, Northland had real GDP of $4.21 billion and a population of 2.98 million.In 2017, real GDP was $4.59 billion and population was 2.97 million.What was Northland's growth rate of real GDP in 2017?
A)3.8 percent
B)0.38 percent
C)8.3 percent
D)11.1 percent
E)9.0 percent
A)3.8 percent
B)0.38 percent
C)8.3 percent
D)11.1 percent
E)9.0 percent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The current growth rate of real GDP per person is 2 percent a year.How long will it take for real GDP per person to double?
A)half a year
B)35 years
C)approximately 10 years
D)2 years
E)28.6 years
A)half a year
B)35 years
C)approximately 10 years
D)2 years
E)28.6 years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The current growth rate of real GDP per person is 1 percent a year.How long will it take for real GDP per person to double?
A)10 years
B)100 years
C)70 years
D)35 years
E)Real GDP per person will never double
A)10 years
B)100 years
C)70 years
D)35 years
E)Real GDP per person will never double

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
During 2016, the country of Economia had real GDP of $115 billion and the population was 0.9 billion.In 2017, real GDP was $105 billion and the population was 0.85 billion.In 2017, real GDP per person was
A)$124.
B)$1,235.
C)$135.
D)$80.95.
E)$128.
A)$124.
B)$1,235.
C)$135.
D)$80.95.
E)$128.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In 2016, Northland had real GDP of $4.21 billion and a population of 2.98 million.In 2017, real GDP was $4.59 billion and population was 2.97 million.Northland's real GDP per person in 2017 was
A)$1,413.
B)$64.70.
C)$1,545.
D)$6,470.
E)$1.55.
A)$1,413.
B)$64.70.
C)$1,545.
D)$6,470.
E)$1.55.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
If the current growth rate of real GDP per person is 10 percent a year, how long will it take for real GDP per person to double?
A)49 years
B)0.7 years
C)10 years
D)7 years
E)1 year
A)49 years
B)0.7 years
C)10 years
D)7 years
E)1 year

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Suppose a country's population grows by 2 percent a year and, at the same time, its real GDP grows by 5 percent a year.Real GDP per person is increasing by _______ a year.
A)3 percent
B)2 percent
C)10 percent
D)5 percent
E)7 percent
A)3 percent
B)2 percent
C)10 percent
D)5 percent
E)7 percent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Canada's economic growth rate was highest in which of the following decades?
A)the 1930s
B)the 1960s
C)the 1970s
D)the 1980s
E)the 1990s
A)the 1930s
B)the 1960s
C)the 1970s
D)the 1980s
E)the 1990s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Real GDP is $20 million.If the economy grows at 10 percent per year, approximately how many years will it take for real GDP to grow to $80 million?
A)4
B)30
C)7
D)14
E)3.5
A)4
B)30
C)7
D)14
E)3.5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
If the current growth rate of real GDP per person is 7 percent a year, how long will it take for real GDP per person to double?
A)2 years
B)1 year
C)49 years
D)10 years
E)7 years
A)2 years
B)1 year
C)49 years
D)10 years
E)7 years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Choose the statement that is incorrect.
A)The standard of living depends on real GDP per person.
B)The growth rate of real GDP per person can be calculated approximately by subtracting the population growth rate from the real GDP growth rate.
C)Real GDP per person grows only if real GDP grows faster than the population grows.
D)Real GDP increases when the economy returns to full employment in an expansion phase of the business cycle.
E)The return to full employment in an expansion phase of the business cycle is economic growth.
A)The standard of living depends on real GDP per person.
B)The growth rate of real GDP per person can be calculated approximately by subtracting the population growth rate from the real GDP growth rate.
C)Real GDP per person grows only if real GDP grows faster than the population grows.
D)Real GDP increases when the economy returns to full employment in an expansion phase of the business cycle.
E)The return to full employment in an expansion phase of the business cycle is economic growth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The Rule of 70 is used to
A)calculate the economy's growth rate.
B)estimate how much of an economy's growth rate is attributable to increases in capital per hour of labour.
C)estimate how long it will take the level of any variable to double.
D)calculate the standard of living.
E)estimate how much of an economy's growth rate is attributable to technological advance.
A)calculate the economy's growth rate.
B)estimate how much of an economy's growth rate is attributable to increases in capital per hour of labour.
C)estimate how long it will take the level of any variable to double.
D)calculate the standard of living.
E)estimate how much of an economy's growth rate is attributable to technological advance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In 2016, Northland had real GDP of $4.21 billion and a population of 2.98 million.In 2017, real GDP was $4.59 billion and population was 2.97 million.Between 2016 and 2017, Northland's standard of living
A)did not change.
B)increased.
C)might have increased, decreased, or remained unchanged.
D)decreased.
E)doubled.
A)did not change.
B)increased.
C)might have increased, decreased, or remained unchanged.
D)decreased.
E)doubled.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
According to the law of diminishing returns, along the aggregate production function, an additional unit of
A)labour produces more output than the previous unit.
B)labour increases the real wage rate.
C)labour decreases output.
D)labour produces less output than the previous unit.
E)capital produces more output than an additional unit of labour.
A)labour produces more output than the previous unit.
B)labour increases the real wage rate.
C)labour decreases output.
D)labour produces less output than the previous unit.
E)capital produces more output than an additional unit of labour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Use the information below to answer the following questions.
Fact 6.2.1
China was the largest economy for centuries because everyone had the same type of economy-subsistence-and so the country the most people would be economically biggest.Then the Industrial Revolution sent the West on a more prosperous path.No world is returning to a common economy, this time technology- and information- based, so once again population triumphs.
Consider Fact 6.2.1.Following the Industrial Revolution, the United States surpassed China to become the world's largest economy because
A)the U.S.population growth rate was much lower than China's population growth rate.
B)China began to import a significant portion of life- sustaining goods and services.
C)the benefits of the Industrial Revolution were greater in the United States than in China.
D)the U.S.population exceeded China's population.
E)the United States was a strong, united country following the Civil War and reconstruction.
Fact 6.2.1
China was the largest economy for centuries because everyone had the same type of economy-subsistence-and so the country the most people would be economically biggest.Then the Industrial Revolution sent the West on a more prosperous path.No world is returning to a common economy, this time technology- and information- based, so once again population triumphs.
Consider Fact 6.2.1.Following the Industrial Revolution, the United States surpassed China to become the world's largest economy because
A)the U.S.population growth rate was much lower than China's population growth rate.
B)China began to import a significant portion of life- sustaining goods and services.
C)the benefits of the Industrial Revolution were greater in the United States than in China.
D)the U.S.population exceeded China's population.
E)the United States was a strong, united country following the Civil War and reconstruction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
When the quantity of labour demanded exceeds the quantity of labour supplied, the real wage rate
A)does not change, but the money wage rate rises to eliminate the labour market shortage.
B)rises to eliminate the labour market surplus.
C)falls to eliminate the labour market shortage.
D)rises to eliminate the labour market shortage.
E)falls to eliminate the labour market surplus.
A)does not change, but the money wage rate rises to eliminate the labour market shortage.
B)rises to eliminate the labour market surplus.
C)falls to eliminate the labour market shortage.
D)rises to eliminate the labour market shortage.
E)falls to eliminate the labour market surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
If the money wage rate is $15.00 an hour and the price level is 120, the real wage rate is
A)$15.00 an hour.
B)$8.50 an hour.
C)$12.50 an hour.
D)$10.75 an hour.
E)$18 an hour.
A)$15.00 an hour.
B)$8.50 an hour.
C)$12.50 an hour.
D)$10.75 an hour.
E)$18 an hour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
If the money wage rate is $10.00 an hour and the price level is 60, the real wage rate is
A)$16.67 an hour.
B)$6.00 an hour.
C)$10.00 an hour.
D)$18.75 an hour.
E)$12.50 an hour.
A)$16.67 an hour.
B)$6.00 an hour.
C)$10.00 an hour.
D)$18.75 an hour.
E)$12.50 an hour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Convergence between real GDP per person in Canada and Japan was relatively _______ during the 1980s; During the 1990s, Japan's economy _______ .
A)rapid; grew at an even faster rate
B)slow; stagnated
C)rapidly; continued at the 1980s pace
D)slow; grew rapidly
E)rapid; stagnated
A)rapid; grew at an even faster rate
B)slow; stagnated
C)rapidly; continued at the 1980s pace
D)slow; grew rapidly
E)rapid; stagnated

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Use the information below to answer the following questions.
Fact 6.2.1
China was the largest economy for centuries because everyone had the same type of economy-subsistence-and so the country the most people would be economically biggest.Then the Industrial Revolution sent the West on a more prosperous path.No world is returning to a common economy, this time technology- and information- based, so once again population triumphs.
Consider Fact 6.2.1.China's was the world's largest economy until the Industrial Revolution because
A)it was a large exporter of goods and services.
B)the Industrial Revolution gave the greatest growth to the countries with the largest populations.
C)it had a diverse climate.
D)it was the country with the largest land mass.
E)people in all countries had approximately the same subsistence level of income.
Fact 6.2.1
China was the largest economy for centuries because everyone had the same type of economy-subsistence-and so the country the most people would be economically biggest.Then the Industrial Revolution sent the West on a more prosperous path.No world is returning to a common economy, this time technology- and information- based, so once again population triumphs.
Consider Fact 6.2.1.China's was the world's largest economy until the Industrial Revolution because
A)it was a large exporter of goods and services.
B)the Industrial Revolution gave the greatest growth to the countries with the largest populations.
C)it had a diverse climate.
D)it was the country with the largest land mass.
E)people in all countries had approximately the same subsistence level of income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The gap between real GDP per person in Canada and Hong Kong has _______ since 1980.During this period, the growth rate of real GDP per person in Canada has been _______ than in Hong Kong.
A)reversed; slower
B)remained constant; equal
C)decreased; faster
D)increased; faster
E)reversed; faster
A)reversed; slower
B)remained constant; equal
C)decreased; faster
D)increased; faster
E)reversed; faster

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The decreasing slope of the aggregate production function reflects
A)increasing aggregate demand.
B)diminishing returns.
C)rising unemployment.
D)a decrease in potential GDP.
E)decreasing costs.
A)increasing aggregate demand.
B)diminishing returns.
C)rising unemployment.
D)a decrease in potential GDP.
E)decreasing costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Between 1980 and 2016, growth rates in real GDP per person in Hong Kong, Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, and China _______ the growth rate of real GDP per person in Canada.
Korea's real GDP per person in 2016 is approximately equal to real GDP per person in Hong Kong in _______.
A)exceeded; 2006
B)were approximately equal to; 2006
C)were less than; 2006
D)exceeded; 1980
E)were less than; 1980
Korea's real GDP per person in 2016 is approximately equal to real GDP per person in Hong Kong in _______.
A)exceeded; 2006
B)were approximately equal to; 2006
C)were less than; 2006
D)exceeded; 1980
E)were less than; 1980

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Between 1926 and 2016 real GDP per person in Canada grew at an average rate of
A)3.6 percent a year.
B)4.3 percent a year.
C)2.0 percent a year.
D)1.7 percent a year.
E)2.8 percent a year.
A)3.6 percent a year.
B)4.3 percent a year.
C)2.0 percent a year.
D)1.7 percent a year.
E)2.8 percent a year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
In the labour market, an increase in labour productivity _______ the real wage rate and _______ the level of employment.
A)lowers; decreases
B)raises; does not change
C)raises; decreases
D)raises; increases
E)lowers; increases
A)lowers; decreases
B)raises; does not change
C)raises; decreases
D)raises; increases
E)lowers; increases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The aggregate production function is graphed as
A)an upward- sloping line that becomes flatter as the quantity of labour increases.
B)a downward- sloping curve.
C)an upward- sloping line that becomes steeper as the quantity of labour increases.
D)an upward- sloping straight line.
E)a production possibilities frontier.
A)an upward- sloping line that becomes flatter as the quantity of labour increases.
B)a downward- sloping curve.
C)an upward- sloping line that becomes steeper as the quantity of labour increases.
D)an upward- sloping straight line.
E)a production possibilities frontier.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
During the last 10 years, which of the following had the lowest level of real GDP per person?
A)Russia
B)Japan
C)Mexico
D)Nigeria
E)China
A)Russia
B)Japan
C)Mexico
D)Nigeria
E)China

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
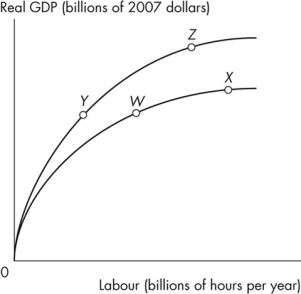 Figure 6.3.1
Figure 6.3.1
Refer to Figure 6.3.1.The country of Kemper is on its aggregate production function at point W.If the population increases with no change in capital or technology, the economy
A)moves to point such as X.
B)moves to point such as Y.
C)remains at point W.
D)moves to point such as Z.
E)either remains at point W or moves to point X.
 Figure 6.3.1
Figure 6.3.1Refer to Figure 6.3.1.The country of Kemper is on its aggregate production function at point W.If the population increases with no change in capital or technology, the economy
A)moves to point such as X.
B)moves to point such as Y.
C)remains at point W.
D)moves to point such as Z.
E)either remains at point W or moves to point X.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
An increase in labour hours will lead to
A)both a movement along and an upward shift of the aggregate production function.
B)an upward shift of the aggregate production function.
C)a movement along the aggregate production function.
D)neither a movement along nor a shift of the aggregate production function.
E)a downward shift of the aggregate production function.
A)both a movement along and an upward shift of the aggregate production function.
B)an upward shift of the aggregate production function.
C)a movement along the aggregate production function.
D)neither a movement along nor a shift of the aggregate production function.
E)a downward shift of the aggregate production function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Compared to growth in other countries, between 1980 and 2016 Canada
A)dramatically caught up to and passed other countries.
B)did as well or better than most countries except certain Asian countries.
C)caught up to the United States.
D)fell behind most other countries.
E)worsened dramatically versus the United States, but did better versus other countries.
A)dramatically caught up to and passed other countries.
B)did as well or better than most countries except certain Asian countries.
C)caught up to the United States.
D)fell behind most other countries.
E)worsened dramatically versus the United States, but did better versus other countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
If the real wage rate is $10.00 an hour and the price level is 60, the money wage rate is
A)$18.50 an hour.
B)$16.67 an hour.
C)$6.00 an hour.
D)$16.75 an hour.
E)$10.00 an hour.
A)$18.50 an hour.
B)$16.67 an hour.
C)$6.00 an hour.
D)$16.75 an hour.
E)$10.00 an hour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Of the following countries, which has the lowest level of real GDP per person?
A)China
B)Singapore
C)Korea
D)Hong Kong
E)Canada
A)China
B)Singapore
C)Korea
D)Hong Kong
E)Canada

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Between 1926 and 2016, the average growth rate of real GDP per person in Canada was _______ percent a year.During this period, _______ grew at a faster rate than the population.
A)1.0; inflation
B)3.0; real GDP
C)2.0; GDP;
D)2.0; real GDP
E)3.0; GDP
A)1.0; inflation
B)3.0; real GDP
C)2.0; GDP;
D)2.0; real GDP
E)3.0; GDP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
When labour productivity decreases, the
A)supply of labour curve shifts rightward and the real wage rate fall.
B)demand for labour curve shifts leftward and the real wage rate falls.
C)demand for labour decreases and the supply of labour decreases, and the real wage rate rises, falls, or remains unchanged.
D)supply of labour curve shifts leftward and the real wage rate rises.
E)demand for labour decreases and the supply of labour increases, and the real wage rate falls.
A)supply of labour curve shifts rightward and the real wage rate fall.
B)demand for labour curve shifts leftward and the real wage rate falls.
C)demand for labour decreases and the supply of labour decreases, and the real wage rate rises, falls, or remains unchanged.
D)supply of labour curve shifts leftward and the real wage rate rises.
E)demand for labour decreases and the supply of labour increases, and the real wage rate falls.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
When the population increases, potential GDP _______ and potential GDP per hour of labour _______.
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; does not change
C)decreases; decreases
D)increases; increases
E)increases; decreases
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; does not change
C)decreases; decreases
D)increases; increases
E)increases; decreases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
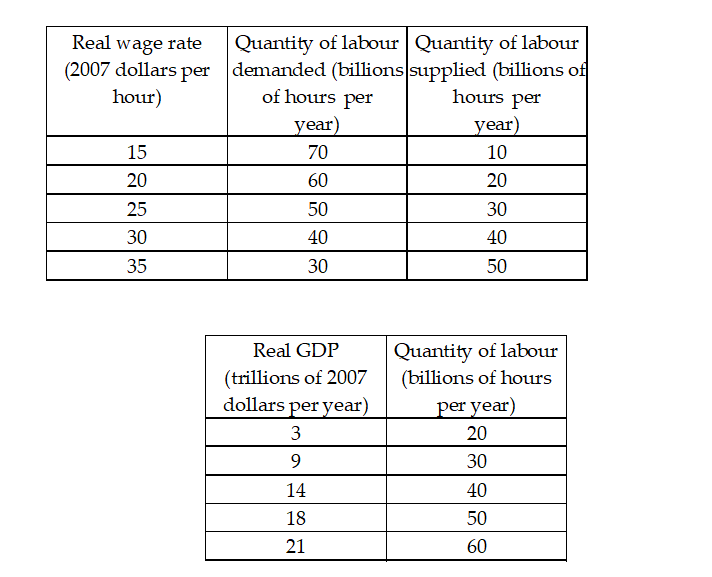
Refer to Table 6.3.1.The top table describes an economy's labour market.The second table describes its production function.Potential GDP is
A) $14 trillion.B) $40 trillion.C) $25 trillion.D) $6 trillion.E) $9 trillion.Answer: A
Refer to Table 6.3.1.The top table describes an economy's labour market.The second table describes its production function.An increase in population changes the quantity of labour supplied by 20 billion hours at each real wage rate.Potential GDP
A)does not change.
B)changes to $20 trillion.
C)changes to $50 trillion.
D)changes to $3 trillion.
E)changes to $18 trillion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
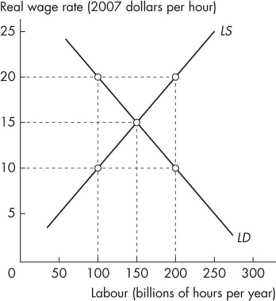 Figure 6.3.2
Figure 6.3.2
Refer to Figure 6.3.2.The equilibrium quantity of labour is
A)100 billion hours per year.
B)150 billion hours per year.
C)250 billion hours per year.
D)50 billion hours per year.
E)200 billion hours per year.
 Figure 6.3.2
Figure 6.3.2Refer to Figure 6.3.2.The equilibrium quantity of labour is
A)100 billion hours per year.
B)150 billion hours per year.
C)250 billion hours per year.
D)50 billion hours per year.
E)200 billion hours per year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
A movement along the aggregate production function occurs when _______ changes.
A)technology
B)capital
C)the inflation rate
D)the interest rate
E)the quantity of labour
A)technology
B)capital
C)the inflation rate
D)the interest rate
E)the quantity of labour

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
When labour productivity decreases, there is _______ the aggregate production function and _______ in potential GDP.
A)a movement down along; no change
B)a downward shift of; a decrease
C)a downward shift of; no change
D)a movement down along; a decrease
E)neither a movement along nor a shift of; no change
A)a movement down along; no change
B)a downward shift of; a decrease
C)a downward shift of; no change
D)a movement down along; a decrease
E)neither a movement along nor a shift of; no change

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The aggregate production function shows how _______changes as the quantity of _______ changes when all other influences on production remain the same.
A)labour; leisure
B)real GDP; capital
C)real GDP; leisure
D)real GDP; labour
E)labour; capital
A)labour; leisure
B)real GDP; capital
C)real GDP; leisure
D)real GDP; labour
E)labour; capital

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If an increase in capital increases labour productivity, the supply of labour _______ and the demand for labour _______.
A)decreases; stays the same
B)increases; decreases
C)stays the same; increases
D)increases; increases
E)increases; stays the same
A)decreases; stays the same
B)increases; decreases
C)stays the same; increases
D)increases; increases
E)increases; stays the same

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Ceteris paribus, an increase in labour productivity results in a
A)higher real wage rate and higher potential GDP per hour of labour.
B)higher real wage rate and lower potential GDP per hour of labour.
C)lower real wage rate and lower potential GDP per hour of labour.
D)constant real wage rate in the long run.
E)lower real wage rate and higher potential GDP per hour of labour.
A)higher real wage rate and higher potential GDP per hour of labour.
B)higher real wage rate and lower potential GDP per hour of labour.
C)lower real wage rate and lower potential GDP per hour of labour.
D)constant real wage rate in the long run.
E)lower real wage rate and higher potential GDP per hour of labour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
If real GDP is $12,150 billion and aggregate labour hours are 270 billion, labour productivity equals
A)$32.81 an hour.
B)$48 an hour.
C)$6.50 an hour.
D)$650 an hour.
E)$45 an hour.
A)$32.81 an hour.
B)$48 an hour.
C)$6.50 an hour.
D)$650 an hour.
E)$45 an hour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
When the population increases with no change in labour productivity, employment _______ and potential GDP _______.
A)increases; does not change
B)increases; increases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)increases; decreases
A)increases; does not change
B)increases; increases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)increases; decreases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
An increase in labour productivity _______ the real wage rate and an increase in population _______ the real wage rate.
A)raises; lowers
B)lowers; raises
C)lowers; lowers
D)raises; does not change
E)raises; raises
A)raises; lowers
B)lowers; raises
C)lowers; lowers
D)raises; does not change
E)raises; raises

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
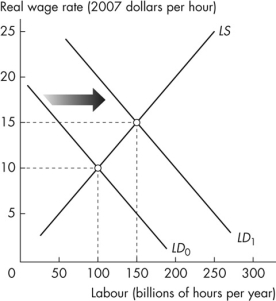 Figure 6.3.3
Figure 6.3.3
Refer to Figure 6.3.3.The graph shows the effect of _______ As a result _______.
A)an increase in the population; potential GDP increases and potential GDP per hour of labour decreases
B)a decrease in the population; potential GDP decreases and potential GDP per hour of labour increases
C)an increase in labour productivity; potential GDP increases and potential GDP per hour of labour does not change
D)an increase in labour productivity; potential GDP increases and potential GDP per hour of labour decreases
E)an increase in labour productivity; potential GDP and potential GDP per hour of labour increase
 Figure 6.3.3
Figure 6.3.3Refer to Figure 6.3.3.The graph shows the effect of _______ As a result _______.
A)an increase in the population; potential GDP increases and potential GDP per hour of labour decreases
B)a decrease in the population; potential GDP decreases and potential GDP per hour of labour increases
C)an increase in labour productivity; potential GDP increases and potential GDP per hour of labour does not change
D)an increase in labour productivity; potential GDP increases and potential GDP per hour of labour decreases
E)an increase in labour productivity; potential GDP and potential GDP per hour of labour increase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 6.3.2
Figure 6.3.2
Refer to Figure 6.3.2.If the real wage is $20 an hour, a labour
A)shortage occurs and the real wage falls.
B)surplus occurs and the real wage falls.
C)surplus occurs and the real wage rises.
D)surplus occurs and the demand for labour increases.
E)shortage occurs and the real wage rises.
 Figure 6.3.2
Figure 6.3.2Refer to Figure 6.3.2.If the real wage is $20 an hour, a labour
A)shortage occurs and the real wage falls.
B)surplus occurs and the real wage falls.
C)surplus occurs and the real wage rises.
D)surplus occurs and the demand for labour increases.
E)shortage occurs and the real wage rises.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Labour productivity is
A)shown as a movement along the production function.
B)the rate of change in real GDP per hour of labour.
C)the quantity of real GDP produced by an hour of labour.
D)real GDP per hour of labour times the hours of work.
E)real GDP per hour of labour times the population.
A)shown as a movement along the production function.
B)the rate of change in real GDP per hour of labour.
C)the quantity of real GDP produced by an hour of labour.
D)real GDP per hour of labour times the hours of work.
E)real GDP per hour of labour times the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
When labour productivity increases, the demand for labour curve _______ and the supply of labour curve _______.
A)shifts leftward; does not shift
B)shifts rightward; shifts rightward
C)shifts rightward; does not shift
D)shifts leftward; shifts rightward
E)shifts rightward; shifts leftward
A)shifts leftward; does not shift
B)shifts rightward; shifts rightward
C)shifts rightward; does not shift
D)shifts leftward; shifts rightward
E)shifts rightward; shifts leftward

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
An increase in population
A)creates a movement along the aggregate production function.
B)shifts the labour supply curve leftward.
C)shifts the labour demand curve rightward.
D)increases the real wage rate.
E)shifts the aggregate production function upward.
A)creates a movement along the aggregate production function.
B)shifts the labour supply curve leftward.
C)shifts the labour demand curve rightward.
D)increases the real wage rate.
E)shifts the aggregate production function upward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Ceteris paribus, an increase in the population results in a
A)higher equilibrium quantity of labour and lower potential GDP per hour of labour.
B)constant equilibrium quantity of labour and constant potential GDP per hour of labour.
C)lower equilibrium quantity of labour and higher potential GDP per hour of labour.
D)higher equilibrium quantity of labour and higher potential GDP per hour of labour.
E)lower equilibrium quantity of labour and lower potential GDP per hour of labour.
A)higher equilibrium quantity of labour and lower potential GDP per hour of labour.
B)constant equilibrium quantity of labour and constant potential GDP per hour of labour.
C)lower equilibrium quantity of labour and higher potential GDP per hour of labour.
D)higher equilibrium quantity of labour and higher potential GDP per hour of labour.
E)lower equilibrium quantity of labour and lower potential GDP per hour of labour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 6.3.2
Figure 6.3.2
Refer to Figure 6.3.2.The equilibrium real wage rate is
A)$15 an hour.
B)$20 an hour.
C)$10 an hour.
D)any wage rate above $15 an hour.
E)any wage rate below $15 an hour.
 Figure 6.3.2
Figure 6.3.2Refer to Figure 6.3.2.The equilibrium real wage rate is
A)$15 an hour.
B)$20 an hour.
C)$10 an hour.
D)any wage rate above $15 an hour.
E)any wage rate below $15 an hour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
If real GDP is $800 million and aggregate labour hours are 20 million, labour productivity is
A)$16 an hour.
B)$40 million.
C)$40 an hour.
D)$160 an hour.
E)$16,000 million.
A)$16 an hour.
B)$40 million.
C)$40 an hour.
D)$160 an hour.
E)$16,000 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Labour productivity rises when
A)the working- age population grows.
B)firms invest more in hiring workers than in replacing worn- out capital.
C)the real wage rate falls.
D)new full- time jobs are created.
E)the amount of capital per worker increases.
A)the working- age population grows.
B)firms invest more in hiring workers than in replacing worn- out capital.
C)the real wage rate falls.
D)new full- time jobs are created.
E)the amount of capital per worker increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
If capital per worker increases, labour productivity
A)does not change unless technology advances at the same time.
B)decreases for a given level of technology.
C)increases because the level of technology increases.
D)increases for a given level of technology.
E)decreases because the level of technology decreases.
A)does not change unless technology advances at the same time.
B)decreases for a given level of technology.
C)increases because the level of technology increases.
D)increases for a given level of technology.
E)decreases because the level of technology decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Which theory of economic growth argues that population growth lowers the real wage rate and stops economic growth?
A)classical growth theory
B)neoclassical growth theory
C)new growth theory
D)all of the theories
E)none of the theories
A)classical growth theory
B)neoclassical growth theory
C)new growth theory
D)all of the theories
E)none of the theories

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The new growth theory holds that growth can persist indefinitely based on the major assumption that
A)discoveries bring profit.
B)knowledge capital does not experience diminishing returns.
C)knowledge destroys profit.
D)discoveries result from regulations.
E)knowledge is a public capital good.
A)discoveries bring profit.
B)knowledge capital does not experience diminishing returns.
C)knowledge destroys profit.
D)discoveries result from regulations.
E)knowledge is a public capital good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
If capital per worker decreases, real GDP per hour of labour
A)decreases for a given level of technology.
B)increases because the level of technology increases.
C)increases for a given level of technology.
D)decreases because the level of technology decreases.
E)does not change.
A)decreases for a given level of technology.
B)increases because the level of technology increases.
C)increases for a given level of technology.
D)decreases because the level of technology decreases.
E)does not change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements regarding human capital is incorrect?
A)The accumulation of human capital is the source of both increased labour productivity and technological advance.
B)Education is the only vehicle for the creation of human capital because training simply reinforces what has already been learned.
C)Human capital is the accumulated skill and knowledge of human beings.
D)Human capital is the fundamental source of labour productivity growth.
E)Writing and mathematics, the most basic of human skills, are crucial elements in economic progress.
A)The accumulation of human capital is the source of both increased labour productivity and technological advance.
B)Education is the only vehicle for the creation of human capital because training simply reinforces what has already been learned.
C)Human capital is the accumulated skill and knowledge of human beings.
D)Human capital is the fundamental source of labour productivity growth.
E)Writing and mathematics, the most basic of human skills, are crucial elements in economic progress.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Factors that influence labour productivity include
A)physical capital, the real wage rate, and technology.
B)physical capital, human capital, and technology.
C)the demand for labour, the real wage rate, and technology.
D)the inflation rate, the real wage rate, and the exchange rate.
E)the population growth rate, human capital, and markets.
A)physical capital, the real wage rate, and technology.
B)physical capital, human capital, and technology.
C)the demand for labour, the real wage rate, and technology.
D)the inflation rate, the real wage rate, and the exchange rate.
E)the population growth rate, human capital, and markets.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
_______ is the accumulated skill and knowledge of human beings.
A)Technology
B)Human investment
C)Capital
D)Labour productivity
E)Human capital
A)Technology
B)Human investment
C)Capital
D)Labour productivity
E)Human capital

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
In the classical growth theory, economic growth eventually stops due to
A)knowledge capital being easily replicated.
B)the real rate of interest falling back down to its target rate.
C)diminishing returns.
D)high population growth resulting from the increase in real GDP per person.
E)real GDP per person becoming too high.
A)knowledge capital being easily replicated.
B)the real rate of interest falling back down to its target rate.
C)diminishing returns.
D)high population growth resulting from the increase in real GDP per person.
E)real GDP per person becoming too high.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Which theory of economic growth argues that growth does not automatically slow down?
A)classical growth theory
B)neoclassical growth theory
C)new growth theory
D)all of the theories
E)none of the theories
A)classical growth theory
B)neoclassical growth theory
C)new growth theory
D)all of the theories
E)none of the theories

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The key difference between the neoclassical growth theory and the new growth theory is that
A)the pace of technological advances are caused by chance in new growth theory.
B)knowledge is capital that is not subject to diminishing returns under new growth theory.
C)labour productivity grows indefinitely in neoclassical growth theory.
D)capital is subject to diminishing returns under new growth theory.
E)increases in population drive workers' incomes back down to the subsistence level in neoclassical growth theory.
A)the pace of technological advances are caused by chance in new growth theory.
B)knowledge is capital that is not subject to diminishing returns under new growth theory.
C)labour productivity grows indefinitely in neoclassical growth theory.
D)capital is subject to diminishing returns under new growth theory.
E)increases in population drive workers' incomes back down to the subsistence level in neoclassical growth theory.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Which of the following is not a source of economic growth?
A)better educated workers
B)increasing stock market prices
C)advances in technology
D)appropriate incentive system
E)growing physical capital
A)better educated workers
B)increasing stock market prices
C)advances in technology
D)appropriate incentive system
E)growing physical capital

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Which theory of economic growth argues that, in the long run, people do not benefit from growth?
A)classical growth theory
B)neoclassical growth theory
C)new growth theory
D)all of the theories
E)none of the theories
A)classical growth theory
B)neoclassical growth theory
C)new growth theory
D)all of the theories
E)none of the theories

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Human capital is the
A)skill and knowledge accumulated by humans.
B)plant and equipment produced by humans and not by machines.
C)technology used by humans to produce real GDP.
D)machinery used by humans to produce GDP.
E)technology used by humans to produce GDP.
A)skill and knowledge accumulated by humans.
B)plant and equipment produced by humans and not by machines.
C)technology used by humans to produce real GDP.
D)machinery used by humans to produce GDP.
E)technology used by humans to produce GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Labour productivity grows as
A)physical capital grows, human capital grows, and technology advances.
B)depreciation increases.
C)the population grows.
D)people work longer hours.
E)consumption expenditure increases.
A)physical capital grows, human capital grows, and technology advances.
B)depreciation increases.
C)the population grows.
D)people work longer hours.
E)consumption expenditure increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The Industrial Revolution in England was largely the result of
A)population growth.
B)the elimination of the patent system.
C)technological innovations that were financed mainly by government spending.
D)technological innovations encouraged by the patent system.
E)growth in human capital.
A)population growth.
B)the elimination of the patent system.
C)technological innovations that were financed mainly by government spending.
D)technological innovations encouraged by the patent system.
E)growth in human capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
For three years, there was no technological change in Longland but capital per hour of labour increased from $10 to $20 to $30 and real GDP per hour of labour increased from $3.80 to $5.70 to $7.13.Then in the fourth year, capital per hour of labour remained constant but real GDP per hour of labour increased to $10.Longland _______
Experience diminishing returns because _______ .
A)does; as capital per hour of labour increases, real GDP per hour of labour increases but by smaller amounts
B)does; all countries experience diminishing returns
C)does not; in the fourth year capital per hour of labour does not change
D)does; in the fourth year capital per hour of labour does not change
E)does not; as capital per hour of labour increases, real GDP per hour of labour also increases
Experience diminishing returns because _______ .
A)does; as capital per hour of labour increases, real GDP per hour of labour increases but by smaller amounts
B)does; all countries experience diminishing returns
C)does not; in the fourth year capital per hour of labour does not change
D)does; in the fourth year capital per hour of labour does not change
E)does not; as capital per hour of labour increases, real GDP per hour of labour also increases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The key difference between the neoclassical growth theory and the classical growth theory is that
A)growth in the neoclassical growth theory ends with a population explosion.
B)capital is not subject to diminishing returns under classical growth theory.
C)increases in population drive workers' incomes back down to the subsistence level in classical growth theory.
D)in classical growth theory, the pace of technological change influences the economic growth rate but economic growth does not influence the pace of technological change.
E)capital is subject to diminishing returns under classical growth theory.
A)growth in the neoclassical growth theory ends with a population explosion.
B)capital is not subject to diminishing returns under classical growth theory.
C)increases in population drive workers' incomes back down to the subsistence level in classical growth theory.
D)in classical growth theory, the pace of technological change influences the economic growth rate but economic growth does not influence the pace of technological change.
E)capital is subject to diminishing returns under classical growth theory.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Which one of the following quotations could be attributed to a supporter of the classical growth theory?
A)"Growth will last as long as knowledge accumulation continues."
B)"Growth will last only until the increase in population brings productivity down to the subsistence level."
C)"Growth will last as long as technology keeps advancing."
D)"Prosperity will last as long as technology keeps advancing."
E)"Prosperity will last as long as there is knowledge accumulation."
A)"Growth will last as long as knowledge accumulation continues."
B)"Growth will last only until the increase in population brings productivity down to the subsistence level."
C)"Growth will last as long as technology keeps advancing."
D)"Prosperity will last as long as technology keeps advancing."
E)"Prosperity will last as long as there is knowledge accumulation."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
An increase in education and training
A)decreases real GDP growth.
B)increases the hours worked per person.
C)increases labour productivity.
D)increases aggregate hours.
E)increases the employment rate.
A)decreases real GDP growth.
B)increases the hours worked per person.
C)increases labour productivity.
D)increases aggregate hours.
E)increases the employment rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 95 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








