Deck 12: Part A: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 12: Part A: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1
Suppose the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply schedules for a hypothetical economy are as shown below:
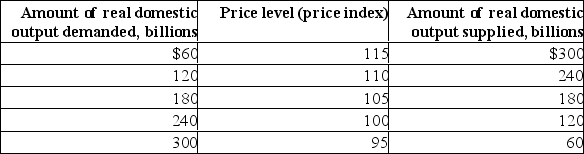 (a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 100 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 110 index be the equilibrium price level?
(a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 100 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 110 index be the equilibrium price level?
(c) Suppose aggregate demand increases by $120 billion at each price level.What will be the new equilibrium price and output levels?
(d) What factors might cause aggregate demand to increase?
(e) Suppose short-run aggregate supply increases by $120 billion at each price level.What will be the new equilibrium price and output levels?
 (a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 100 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 110 index be the equilibrium price level?
(a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 100 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 110 index be the equilibrium price level?(c) Suppose aggregate demand increases by $120 billion at each price level.What will be the new equilibrium price and output levels?
(d) What factors might cause aggregate demand to increase?
(e) Suppose short-run aggregate supply increases by $120 billion at each price level.What will be the new equilibrium price and output levels?
(a) The equilibrium real GDP is $180 billion and the equilibrium price level is 105.There is not enough information given to determine whether or not this is the full-employment level of real GDP.
(b) At a price level of 100, the aggregate demand would exceed short-run aggregate supply and prices would be bid up.At a price level of 110, aggregate supply would exceed aggregate demand and the resulting surpluses would cause prices to be bid downward toward the equilibrium level of 105.
(c) The new equilibrium price level is 110 and the new equilibrium real GDP is $120 billion.
(d) Aggregate demand would increase if any of the four basic determinants of aggregate demand-consumer spending, investment, government expenditures, and net export spending-increased.An increase in consumer wealth, increased expectations of future inflation, a decline in household indebtedness, or decreased personal taxes would increase the consumer spending component of aggregate demand.Investment spending would increase as a result of lower interest rates, increased expectations of improved profits in the future, a decline in business taxes, new and improved technology, or a decline in excess capacity.Government spending might increase for a variety of reasons.Net export spending would increase as a result of improved economic conditions abroad or a depreciation in the Canadian dollar.
(e) The new equilibrium price level is 100 and the new equilibrium real GDP is $240.
(b) At a price level of 100, the aggregate demand would exceed short-run aggregate supply and prices would be bid up.At a price level of 110, aggregate supply would exceed aggregate demand and the resulting surpluses would cause prices to be bid downward toward the equilibrium level of 105.
(c) The new equilibrium price level is 110 and the new equilibrium real GDP is $120 billion.
(d) Aggregate demand would increase if any of the four basic determinants of aggregate demand-consumer spending, investment, government expenditures, and net export spending-increased.An increase in consumer wealth, increased expectations of future inflation, a decline in household indebtedness, or decreased personal taxes would increase the consumer spending component of aggregate demand.Investment spending would increase as a result of lower interest rates, increased expectations of improved profits in the future, a decline in business taxes, new and improved technology, or a decline in excess capacity.Government spending might increase for a variety of reasons.Net export spending would increase as a result of improved economic conditions abroad or a depreciation in the Canadian dollar.
(e) The new equilibrium price level is 100 and the new equilibrium real GDP is $240.
2
What is the aggregate demand curve? What is the characteristic of its slope?
The aggregate demand curve shows the relationship between the price level and real GDP.It shows the amounts of real output that domestic consumers, businesses, government, and foreign buyers collectively desire to purchase at each price level.As the price level increases, the amount of real GDP purchased will decrease, so the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
3
In the below diagram assume that the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 in year 1 to AD2 in year 2, only to fall back to AD1 in year 3. 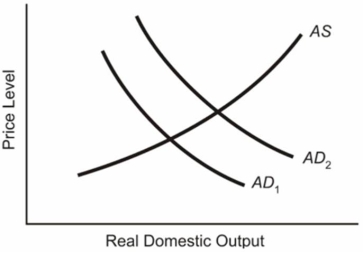 (a) Explain what will happen to the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP from year 1 to year 2.(b) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely flexible downward.Label this position, Pb and GDPb for the price level and real GDP respectively.(c) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely inflexible downward.Label this position, Pc and GDPc for the price level and real GDP respectively.
(a) Explain what will happen to the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP from year 1 to year 2.(b) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely flexible downward.Label this position, Pb and GDPb for the price level and real GDP respectively.(c) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely inflexible downward.Label this position, Pc and GDPc for the price level and real GDP respectively.
 (a) Explain what will happen to the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP from year 1 to year 2.(b) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely flexible downward.Label this position, Pb and GDPb for the price level and real GDP respectively.(c) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely inflexible downward.Label this position, Pc and GDPc for the price level and real GDP respectively.
(a) Explain what will happen to the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP from year 1 to year 2.(b) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely flexible downward.Label this position, Pb and GDPb for the price level and real GDP respectively.(c) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely inflexible downward.Label this position, Pc and GDPc for the price level and real GDP respectively.(a) Equilibrium price and quantity will rise from Pb to Pc and GDPb to GDP2.
4
List four government tax or spending policy options that would shift the short-run aggregate supply curve rightward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Suppose the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply schedules for a hypothetical economy are as shown below:
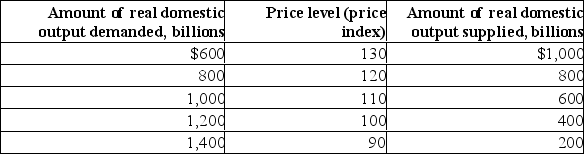 (a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 110 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 130 index be the equilibrium price level?
(a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 110 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 130 index be the equilibrium price level?
(c) Suppose aggregate demand increases by $400 billion at each price level.What will be the new equilibrium price and output levels?
(d) What factors might cause aggregate demand to increase?
 (a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 110 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 130 index be the equilibrium price level?
(a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 110 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 130 index be the equilibrium price level?(c) Suppose aggregate demand increases by $400 billion at each price level.What will be the new equilibrium price and output levels?
(d) What factors might cause aggregate demand to increase?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Identify the ways in which each of the following determinants would have to change to cause a decrease in aggregate demand: consumer wealth, consumer expectations, business taxes, national income in countries abroad, exchange rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
List the three major determinants that can cause a shift in the short-run aggregate supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What is the effect on the multiplier when an increase in aggregate demand also causes the price level to rise?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Economists think of three different aggregate supply curves based upon the time frame of observation.Briefly describe each.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The determinants of aggregate demand "determine" the location of the aggregate demand curve.Explain the four basic determinants of aggregate demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
List three events that would shift the short-run aggregate supply curve leftward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
How is the immediate short-run aggregate supply curve sloped? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Describe the change in short-run aggregate supply that should result from each of the following changes in determinants.Assume that nothing else is changing besides the identified change.(Use "Decrease" or "Increase.")
(a) A rise in the average price of inputs;
(b) An increase in worker productivity;
(c) Government antipollution regulations become stricter;
(d) A new subsidy program is enacted for new business investment in productive equipment;
(e) Energy prices decline.
(a) A rise in the average price of inputs;
(b) An increase in worker productivity;
(c) Government antipollution regulations become stricter;
(d) A new subsidy program is enacted for new business investment in productive equipment;
(e) Energy prices decline.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What is the difference in the explanation of the shape of the aggregate demand curve and a single product demand curve? After all, both demand curves show an inverse relationship between price and quantity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
How is the long-run aggregate supply curve sloped? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What determines the equilibrium price level and the level of real GDP in the aggregate demand-aggregate supply (short-run) model?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Explain the three reasons given for the downward slope of the aggregate demand curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
How is the short-run aggregate supply curve sloped and why is it sloped this way?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In the table below are aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules. 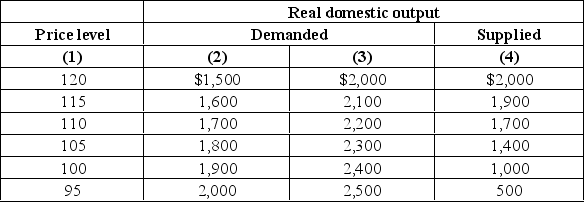 (a) Suppose in Year 1, aggregate demand is shown in columns (1) and (2) in the above table and short-run aggregate supply is shown in columns (1) and (4) in the above table.What will be the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level?
(a) Suppose in Year 1, aggregate demand is shown in columns (1) and (2) in the above table and short-run aggregate supply is shown in columns (1) and (4) in the above table.What will be the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level?
(b) Suppose in Year 2, aggregate demand changes and is now shown in columns (1) and (3).What will be the new equilibrium level of real GDP and the new equilibrium price level?
(c) Suppose in Year 3, aggregate demand changes and is now shown again in columns (1) and (2).What will be the new level of real GDP and the new price level if prices and wages are completely flexible downward?
(d) Suppose in Year 3, aggregate demand changes and is now shown again in columns (1) and (2).What will be the new level of real GDP and the new price level if prices and wages are completely inflexible downward?
 (a) Suppose in Year 1, aggregate demand is shown in columns (1) and (2) in the above table and short-run aggregate supply is shown in columns (1) and (4) in the above table.What will be the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level?
(a) Suppose in Year 1, aggregate demand is shown in columns (1) and (2) in the above table and short-run aggregate supply is shown in columns (1) and (4) in the above table.What will be the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level?(b) Suppose in Year 2, aggregate demand changes and is now shown in columns (1) and (3).What will be the new equilibrium level of real GDP and the new equilibrium price level?
(c) Suppose in Year 3, aggregate demand changes and is now shown again in columns (1) and (2).What will be the new level of real GDP and the new price level if prices and wages are completely flexible downward?
(d) Suppose in Year 3, aggregate demand changes and is now shown again in columns (1) and (2).What will be the new level of real GDP and the new price level if prices and wages are completely inflexible downward?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Suppose that a hypothetical economy has the following relationship between its real domestic output and the input quantities necessary for producing that level of output. 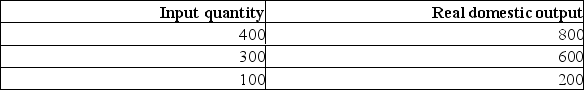 (a) What is the level of productivity in this economy?
(a) What is the level of productivity in this economy?
(b) What is the unit cost of production if the price of each input is $2.00?
(c) If the input price decreases from $2 to $1.50, what is the new per unit cost of production? What impact would this have on the short-run aggregate supply curve?
(d) Suppose that instead of the input price decreasing, the productivity had increased by 25%.What will be the new unit cost of production? What impact would this change have on the short-run aggregate supply curve?
 (a) What is the level of productivity in this economy?
(a) What is the level of productivity in this economy?(b) What is the unit cost of production if the price of each input is $2.00?
(c) If the input price decreases from $2 to $1.50, what is the new per unit cost of production? What impact would this have on the short-run aggregate supply curve?
(d) Suppose that instead of the input price decreasing, the productivity had increased by 25%.What will be the new unit cost of production? What impact would this change have on the short-run aggregate supply curve?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
What are five reasons for the downward price-level inflexibility, especially as it pertains to wages and prices?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply (short-run) model, explain the impact of the public's expectations of severe inflation on real GDP and the price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Why does aggregate demand shift outward by a greater amount than the initial change in spending?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Explain the relationship between the aggregate expenditures model in graph (A) below and the aggregate demand model in graph (B) below where aggregate demand is shifting. 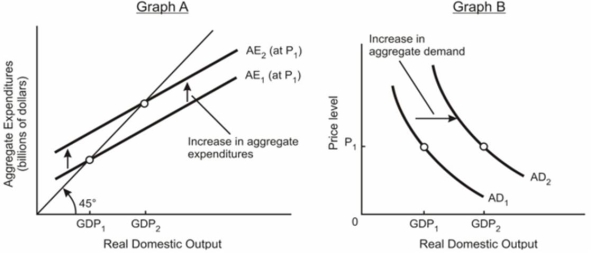


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply (short-run) model, explain how a reduction in business taxes would affect the economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Is the downward price inflexibility applicable to today's economy? Why or why not?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
How can the aggregate demand curve be derived from the aggregate expenditures model?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Explain the relationship between the aggregate expenditures model in graph (A) below and the aggregate demand model in graph (B) below.In other words, explain how points 1, 2, and 3 are related to points 1', 2', and 3'. 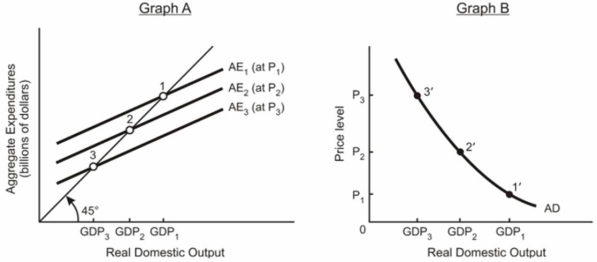


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Differentiate between "demand-pull" and "cost-push" inflation using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply (short-run) model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Describe and explain what is meant by the ratchet effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Some economists argue that it is easier to resolve demand-pull inflation than cost-push inflation.Use the aggregate demand-aggregate supply (short-run) model to explain this assertion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Would increased downward price flexibility lead to less severe or more severe recessions? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply (short-run) model, explain how the depreciation of the Canadian dollar in terms of foreign currencies would affect the economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Suppose an economic advisor to the Prime Minister recommended a personal income tax increase.Indicate the expected effects on aggregate demand and on short-run aggregate supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
How can an economy already at full-employment expand without igniting inflation? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 35 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








