Deck 16: Part B: Long-Run Macroeconomic Adjustments
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 16: Part B: Long-Run Macroeconomic Adjustments
1
In the long run, cost-push inflation results in a simultaneous decrease in the price level and real output.
False
2
Economists often recommend active monetary policy, and perhaps fiscal policy, to counteract the recessions.
True
3
The long-run Phillips Curve is vertical at the natural rate of unemployment.
True
4
Based on the long-run Phillips Curve, any particular rate of inflation is compatible in the long run with the natural rate of unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
When the economy is experiencing cost-push inflation, an increase in aggregate demand will likely result in less inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
If the government attempts to maintain full employment under conditions of cost-push inflation, deflation is likely to occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left when nominal wages rise in response to price level increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Many economists accept the idea of a short-run tradeoff between the unemployment and inflation rates, but they do not think that there is such a tradeoff in the long run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
In the short run, demand-pull inflation will drive up the price level and increase real output; in the long run, only the price level will rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Demand-pull inflation and cost-push inflation are identical concepts because both entail rising nominal wages and rising prices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The Phillips Curve suggests an inverse relationship between increases in the price level and the level of employment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
An ongoing economic growth causes continuous leftward shifts of the aggregate supply which, by themselves, would tend to cause an ongoing deflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
An upward shift of the Phillips Curve is consistent with the occurrence of stagflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
More inflation is likely to result when the government enacts policies to maintain full employment when there is cost-push inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
In the long-run firms respond to the lower profits by reducing their nominal wage increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Most economists reject the idea of a long-run tradeoff between unemployment and inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A shift in the Phillips Curve to the left will improve the "inflation-unemployment" choices available to society.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The characteristics of the long-run Phillips Curve suggest that the economy is generally stable at its natural rate of unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The long-run Phillips Curve is essentially a horizontal line at the economy's natural rate of unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
If there is sufficient time for wage contracts to expire and nominal wage adjustments to occur, then the:
A)economy is operating in the short run.
B)economy has entered the long run.
C)unemployment rate will increase.
D)inflation rate will decrease.
A)economy is operating in the short run.
B)economy has entered the long run.
C)unemployment rate will increase.
D)inflation rate will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The economy enters the long run once:
A)nominal wages become real wages.
B)real wages become nominal wages.
C)input prices start to change from being inflexible to fully flexible.
D)sufficient time has elapsed for real GDP to increase and unemployment to decrease.
A)nominal wages become real wages.
B)real wages become nominal wages.
C)input prices start to change from being inflexible to fully flexible.
D)sufficient time has elapsed for real GDP to increase and unemployment to decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
With demand-pull inflation in the long-run AD-AS model, there is:
A)a decrease in aggregate demand that eventually increases nominal wages and causes a decrease in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B)an increase in aggregate demand that eventually increases nominal wages and causes an increase in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C)an increase in aggregate demand that eventually increases nominal wages and causes a decrease in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)an increase in aggregate demand that eventually increases nominal wages and causes a decrease in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A)a decrease in aggregate demand that eventually increases nominal wages and causes a decrease in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B)an increase in aggregate demand that eventually increases nominal wages and causes an increase in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C)an increase in aggregate demand that eventually increases nominal wages and causes a decrease in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)an increase in aggregate demand that eventually increases nominal wages and causes a decrease in the short-run aggregate supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The long-run aggregate supply curve:
A)is downward sloping.
B)is vertical.
C)is horizontal.
D)is upward sloping.
A)is downward sloping.
B)is vertical.
C)is horizontal.
D)is upward sloping.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Long-run equilibrium occurs where:
A)real output is greater than potential output.
B)the vertical long-run aggregate supply curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve intersect.
C)the aggregate demand curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve intersect
D)the aggregate demand curve, vertical long-run aggregate supply curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve all intersect.
A)real output is greater than potential output.
B)the vertical long-run aggregate supply curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve intersect.
C)the aggregate demand curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve intersect
D)the aggregate demand curve, vertical long-run aggregate supply curve, and short-run aggregate supply curve all intersect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In the long-run aggregate demand-aggregate supply model:
A)long-run equilibrium occurs wherever the aggregate demand curve intersects the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B)the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
C)the price level is the same regardless of the location of the aggregate demand curve.
D)long-run equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve, the short-run aggregate supply curve, and the long-run aggregate supply curve.
A)long-run equilibrium occurs wherever the aggregate demand curve intersects the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B)the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
C)the price level is the same regardless of the location of the aggregate demand curve.
D)long-run equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve, the short-run aggregate supply curve, and the long-run aggregate supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping because:
A)higher prices discourage the producers to expand output.
B)higher price levels create incentives to expand output when resource prices remain constant.
C)lower prices encourage the producers to expand output.
D)higher price levels create an expectation among producers of still higher price levels.
A)higher prices discourage the producers to expand output.
B)higher price levels create incentives to expand output when resource prices remain constant.
C)lower prices encourage the producers to expand output.
D)higher price levels create an expectation among producers of still higher price levels.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
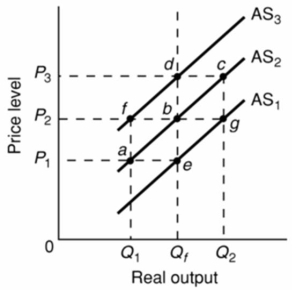 Refer to the above diagram.Assume that nominal wages initially are set on the basis of the price level P2 and that the economy initially is operating at its full-employment level of output Qf.In terms of this diagram, the long-run aggregate supply curve:
Refer to the above diagram.Assume that nominal wages initially are set on the basis of the price level P2 and that the economy initially is operating at its full-employment level of output Qf.In terms of this diagram, the long-run aggregate supply curve:A)is AS2.
B)is a vertical line extending from Qf upward through e, b, and d.
C)may be either AS1, AS2, or AS3 depending on whether the price level is P1, P2, or P3.
D)is a horizontal line extending from P2 rightward through f, b, and g.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The Laffer Curve suggests that lower tax rates will decrease saving and increase consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical:
A)because the rate of inflation is steady in the long run.
B)Input prices eventually rise in response to changes in output prices.
C)because product prices always increase at a faster rate than resource prices.
D)only when the money supply increases at the same rate as real GDP.
A)because the rate of inflation is steady in the long run.
B)Input prices eventually rise in response to changes in output prices.
C)because product prices always increase at a faster rate than resource prices.
D)only when the money supply increases at the same rate as real GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Other things equal, an increase in the price level will:
A)shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B)shift the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C)cause a movement up along a short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)cause a movement down a short run aggregate supply curve.
A)shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B)shift the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C)cause a movement up along a short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)cause a movement down a short run aggregate supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The Laffer Curve shows the real world tradeoff between the price level and tax rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The short run in macroeconomics is a period in which nominal wages:
A)remain fixed as the price level stays constant.
B)change as the price level stays constant.
C)remain fixed as the price level changes.
D)change as the price level changes.
A)remain fixed as the price level stays constant.
B)change as the price level stays constant.
C)remain fixed as the price level changes.
D)change as the price level changes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The Laffer Curve underlies the contention that lower tax rates need not reduce tax revenues.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Refer to the diagram given below. 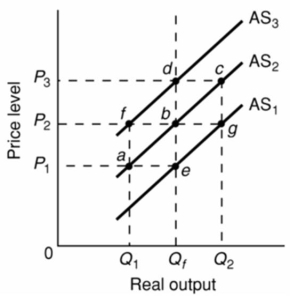 Assume that nominal wages are initially set on the basis of the price level P2 and that the economy is initially operating at the full-employment level of output Qf.In the short run, an increase in the price level from P2 to P3 will:
Assume that nominal wages are initially set on the basis of the price level P2 and that the economy is initially operating at the full-employment level of output Qf.In the short run, an increase in the price level from P2 to P3 will:
A)shift the aggregate supply curve from AS2 to AS3.
B)increase the real output from Q1 to Q2.
C)shift the aggregate supply curve from AS2 to AS1.
D)increase the real output from Qf to Q2.
 Assume that nominal wages are initially set on the basis of the price level P2 and that the economy is initially operating at the full-employment level of output Qf.In the short run, an increase in the price level from P2 to P3 will:
Assume that nominal wages are initially set on the basis of the price level P2 and that the economy is initially operating at the full-employment level of output Qf.In the short run, an increase in the price level from P2 to P3 will:A)shift the aggregate supply curve from AS2 to AS3.
B)increase the real output from Q1 to Q2.
C)shift the aggregate supply curve from AS2 to AS1.
D)increase the real output from Qf to Q2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
In terms of aggregate supply, the difference between the long run and the short run is that in the long run:
A)the price level is variable.
B)employment is variable.
C)real output is variable.
D)nominal wages and other input prices are variable.
A)the price level is variable.
B)employment is variable.
C)real output is variable.
D)nominal wages and other input prices are variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Other things equal, a decrease in the price level will:
A)shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the left.
B)shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)cause a movement up a short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)cause a movement down a short run aggregate supply curve.
A)shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the left.
B)shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)cause a movement up a short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)cause a movement down a short run aggregate supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
In terms of aggregate supply, the short run is a period in which:
A)the price level is constant.
B)employment is constant.
C)real GDP is constant.
D)nominal wages and other input prices are constant.
A)the price level is constant.
B)employment is constant.
C)real GDP is constant.
D)nominal wages and other input prices are constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The equilibrium price level and level of real output occur where:
A)real output is at its highest possible level.
B)exports equal imports.
C)price is at its lowest level.
D)the aggregate demand and supply curves intersect.
A)real output is at its highest possible level.
B)exports equal imports.
C)price is at its lowest level.
D)the aggregate demand and supply curves intersect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
In the short run, demand-pull inflation increases:
A)real wages, but in the long run only nominal wages.
B)nominal wages, but in the long run only real wages.
C)real output and the price level, but in the long-run only real output.
D)real output and the price level, but in the long-run only the price level.
A)real wages, but in the long run only nominal wages.
B)nominal wages, but in the long run only real wages.
C)real output and the price level, but in the long-run only real output.
D)real output and the price level, but in the long-run only the price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Refer to the graph below.Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AS1 intersects AD1.Then a supply shock occurs that shifts AS1 to AS2.If the government counters with an expansionary fiscal policy that shifts AD1 to AD2, then it is most likely that: 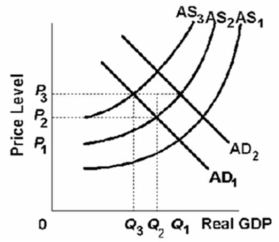
A)AD2 will shift to AD1.
B)AS2 will shift to AS1.
C)AS2 will shift to AS3.
D)AS2 will shift to AS3 and AD2 will shift to AD1.

A)AD2 will shift to AD1.
B)AS2 will shift to AS1.
C)AS2 will shift to AS3.
D)AS2 will shift to AS3 and AD2 will shift to AD1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
One policy dilemma posed by cost-push inflation is that:
A)an increase in aggregate demand will increase inflation and the unemployment rate simultaneously.
B)tax rates can be reduced without lowering tax revenues.
C)the reduction of aggregate demand to restrain inflation will cause a further reduction in the real GDP.
D)the adjustment of aggregate demand can neither increase real GDP nor reduce inflation.
A)an increase in aggregate demand will increase inflation and the unemployment rate simultaneously.
B)tax rates can be reduced without lowering tax revenues.
C)the reduction of aggregate demand to restrain inflation will cause a further reduction in the real GDP.
D)the adjustment of aggregate demand can neither increase real GDP nor reduce inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
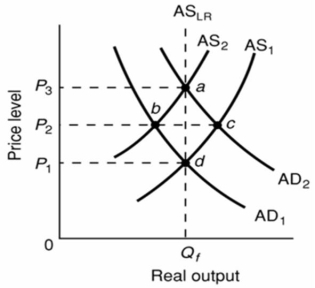 The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.In the long run, the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the diagram because:
The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.In the long run, the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the diagram because:A)nominal wages and other input prices are assumed to be fixed.
B)real output level Qf is the potential level of output.
C)price level increases produce perfectly offsetting changes in nominal wages and other input prices.
D)higher than expected rates of actual inflation reduce real output only temporarily.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
What will occur in the short run if there is cost-push inflation and if the government adopts a hands-off approach to it?
A)an increase in long-run aggregate supply
B)a decrease in long-run aggregate supply
C)low unemployment and a loss of real output
D)high unemployment and a loss of real output
A)an increase in long-run aggregate supply
B)a decrease in long-run aggregate supply
C)low unemployment and a loss of real output
D)high unemployment and a loss of real output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
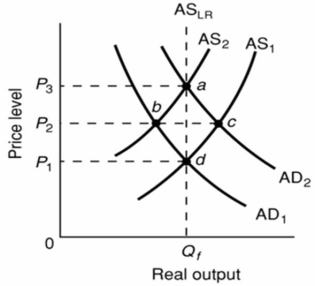 Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.If government offsets the decline in real output resulting from short-run cost-push inflation by increasing aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2:
Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.If government offsets the decline in real output resulting from short-run cost-push inflation by increasing aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2:A)real output will rise above Qf.
B)the price level will rise from P1 to P2.
C)it is possible that aggregate supply will shift rightward from AS2 because nominal wage demands will rise.
D)the price level will rise from P2 to P3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
If prices and wages are flexible, a recession arising from a decrease in aggregate demand will:
A)decrease the price level.
B)increase the price level.
C)increase the interest rate.
D)increase net exports.
A)decrease the price level.
B)increase the price level.
C)increase the interest rate.
D)increase net exports.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Cost-push inflation results directly from a(n):
A)decrease in per unit production costs that shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B)increase in per unit production costs that shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left
C)increase in government spending.
D)decrease in government regulation.
A)decrease in per unit production costs that shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B)increase in per unit production costs that shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left
C)increase in government spending.
D)decrease in government regulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
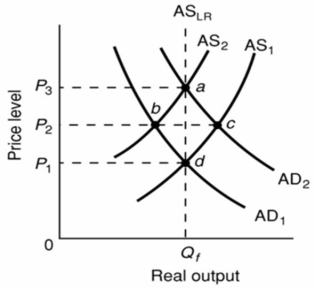 Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.Demand-pull inflation in the short run is best shown as:
Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.Demand-pull inflation in the short run is best shown as:A)a shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2.
B)a move from d to b to a.
C)a move directly from d to a.
D)a shift of the aggregate supply curve from AS1 to AS2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
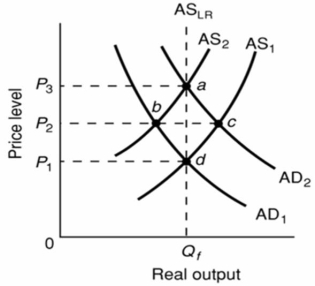 Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.Cost-push inflation in the short run is best represented as a:
Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.Cost-push inflation in the short run is best represented as a:A)leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve from AS1 to AS2.
B)rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2.
C)move from d to b to a.
D)move from d directly to a.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
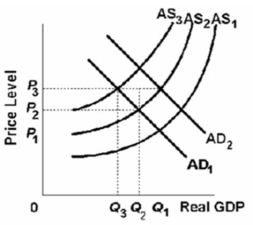 Refer to the above graph.Given that the economy is at an initial equilibrium where the AD1 and AS1 curves intersect, demand-pull inflation in the short run can best be represented by a shift from:
Refer to the above graph.Given that the economy is at an initial equilibrium where the AD1 and AS1 curves intersect, demand-pull inflation in the short run can best be represented by a shift from:A)AS1 to AS3.
B)AD1 to AD2.
C)AS1 to AS2.
D)AD2 to AD1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If government fiscal policy is used to restrain cost-push inflation, we can expect:
A)the unemployment rate to rise.
B)the unemployment rate to fall.
C)the aggregate demand curve to shift rightward.
D)tax-rate declines and increases in government spending.
A)the unemployment rate to rise.
B)the unemployment rate to fall.
C)the aggregate demand curve to shift rightward.
D)tax-rate declines and increases in government spending.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
In the long run, demand-pull inflation:
A)increases unemployment.
B)decreases nominal wages.
C)decreases real output.
D)increases the price level.
A)increases unemployment.
B)decreases nominal wages.
C)decreases real output.
D)increases the price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Demand-pull inflation in the short run increases the price level and:
A)real wages.
B)real output.
C)unemployment.
D)nominal wages.
A)real wages.
B)real output.
C)unemployment.
D)nominal wages.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
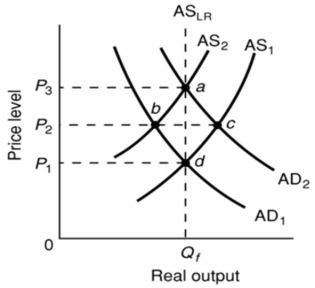 Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.In the long run, demand-pull inflation is best shown as:
Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.In the long run, demand-pull inflation is best shown as:A)a shift of aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 followed by a shift of aggregate supply from AS1 to AS2.
B)a move from d to b to a.
C)a shift of aggregate supply from AS1 to AS2 followed by a shift of aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2.
D)a move from a to d.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
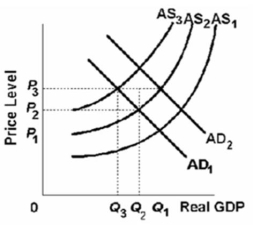 Refer to the above graph.Assume that the economy is at equilibrium at AD1 and AS1 and then is hit with both demand-pull and cost-push inflation.If this occurs, then, in the short run:
Refer to the above graph.Assume that the economy is at equilibrium at AD1 and AS1 and then is hit with both demand-pull and cost-push inflation.If this occurs, then, in the short run:A)AD1 will shift to AD2, AS2 will shift to AS3, the price level will be at P2, and output will be at Q2.
B)AS1 will shift to AS3, AD2 will shift to AD1, the price level will be at P3, and output will be at Q3.
C)AD1 will shift to AD2, AS1 will shift to AS2, the price level will be at P2, and output will be at Q2.
D)AD1 will shift to AD2, AS1 will shift to AS2, the price level will be at P3, and output will be at Q1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
If government uses its stabilization policies to maintain full employment under conditions of cost-push inflation:
A)a deflationary spiral is likely to occur.
B)an inflationary spiral is likely to occur.
C)stagflation is likely to occur.
D)the Phillips Curve is likely to shift inward.
A)a deflationary spiral is likely to occur.
B)an inflationary spiral is likely to occur.
C)stagflation is likely to occur.
D)the Phillips Curve is likely to shift inward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
An increase in inflation is likely to occur when government:
A)counters cost-push inflation with a stimulative fiscal policy or monetary policy.
B)adopts a hands-off approach to cost-push inflation.
C)increases aggregate supply by lowering nominal wages.
D)increases aggregate demand by raising nominal wages.
A)counters cost-push inflation with a stimulative fiscal policy or monetary policy.
B)adopts a hands-off approach to cost-push inflation.
C)increases aggregate supply by lowering nominal wages.
D)increases aggregate demand by raising nominal wages.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Refer to the diagram below.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.Assuming no change in aggregate demand, the long-run response to a recession caused by cost-push inflation is best depicted as a: 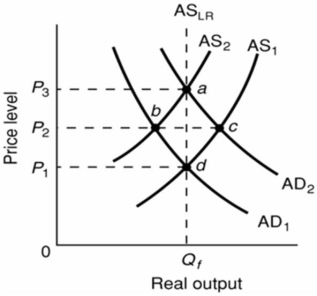
A)move from a to d along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B)rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve from AS2 to AS1.
C)move from a to c to d.
D)leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve from AS1 to AS2.

A)move from a to d along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B)rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve from AS2 to AS1.
C)move from a to c to d.
D)leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve from AS1 to AS2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
In the long-run, the attempt to correct slow economic growth or the unemployment caused by cost-push inflation by implementing an expansionary fiscal policy will most likely produce:
A)disinflation.
B)a recession.
C)a price level surprise.
D)inflation
A)disinflation.
B)a recession.
C)a price level surprise.
D)inflation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Assuming prices and wages are flexible, a recession will decrease the price level, which:
A)raises nominal wages, and which eventually decreases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus decreasing real output to its original level.
B)raises nominal wages, and which eventually increases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus increasing real output to its original level.
C)reduces nominal wages, and which eventually decreases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus decreasing real output to its original level.
D)reduces nominal wages, and which eventually increases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus increasing real output to its original level.
A)raises nominal wages, and which eventually decreases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus decreasing real output to its original level.
B)raises nominal wages, and which eventually increases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus increasing real output to its original level.
C)reduces nominal wages, and which eventually decreases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus decreasing real output to its original level.
D)reduces nominal wages, and which eventually increases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus increasing real output to its original level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The Phillips Curve suggests a tradeoff between:
A)price level stability and income equality.
B)the level of unemployment and price level stability.
C)unemployment and income equality.
D)economic growth and full employment.
A)price level stability and income equality.
B)the level of unemployment and price level stability.
C)unemployment and income equality.
D)economic growth and full employment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Adverse aggregate supply shocks would result in:
A)a lower rate of inflation and a higher rate of unemployment.
B)a higher rate of inflation and a lower rate of unemployment.
C)a lower rate of inflation and a lower rate of unemployment.
D)a higher rate of inflation and a higher rate of unemployment.
A)a lower rate of inflation and a higher rate of unemployment.
B)a higher rate of inflation and a lower rate of unemployment.
C)a lower rate of inflation and a lower rate of unemployment.
D)a higher rate of inflation and a higher rate of unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
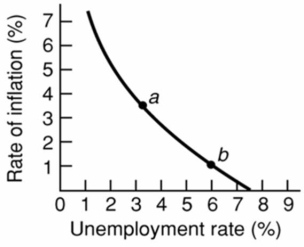 Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Which of the following best describes the relationship shown by this curve?
Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Which of the following best describes the relationship shown by this curve?A)The demand for labor is large when the rate of inflation is small.
B)When the rate of unemployment is high, the rate of inflation is high.
C)The rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment are inversely related.
D)The rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment are directly related.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
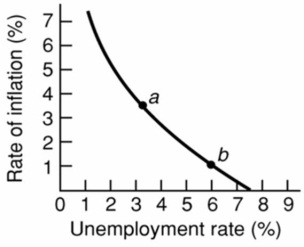 Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.The curve on this graph is known as a:
Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.The curve on this graph is known as a:A)Laffer Curve.
B)Phillips Curve.
C)labor demand curve.
D)production possibilities curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Aggregate supply shocks will:
A)move the economy along the Phillips Curve toward less unemployment.
B)move the economy along the Phillips Curve toward less inflation.
C)shift the Phillips Curve to the left.
D)shift the Phillips Curve to the right.
A)move the economy along the Phillips Curve toward less unemployment.
B)move the economy along the Phillips Curve toward less inflation.
C)shift the Phillips Curve to the left.
D)shift the Phillips Curve to the right.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
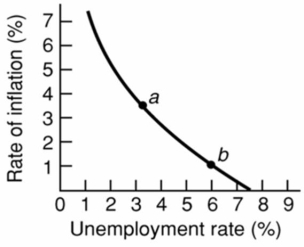 Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.An increase in aggregate demand will:
Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.An increase in aggregate demand will:A)shift this curve to the right.
B)shift this curve to the left.
C)move this economy southeast along the curve.
D)move this economy northwest along the curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Economic growth driven by supply factors causes:
A)continuous leftward shifts of aggregate supply.
B)a rightward shift of an economy's long-run aggregate supply.
C)one time shift in aggregate supply.
D)no shift in aggregate supply.
A)continuous leftward shifts of aggregate supply.
B)a rightward shift of an economy's long-run aggregate supply.
C)one time shift in aggregate supply.
D)no shift in aggregate supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
A rightward shift of the Phillips Curve suggests that:
A)a higher rate of unemployment is associated with each inflation rate.
B)a lower rate of unemployment is associated with each inflation rate.
C)the aggregate supply curve has shifted to the right.
D)the aggregate demand curve has shifted to the left.
A)a higher rate of unemployment is associated with each inflation rate.
B)a lower rate of unemployment is associated with each inflation rate.
C)the aggregate supply curve has shifted to the right.
D)the aggregate demand curve has shifted to the left.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The basic problem portrayed by the Phillips Curve is:
A)that a level of aggregate demand sufficiently high to result in full employment may also cause inflation.
B)that changes in the composition of total labor demand tend to be deflationary.
C)that unemployment rises at the same time the general price level is rising.
D)the possibility that automation will increase the level of noncyclical unemployment.
A)that a level of aggregate demand sufficiently high to result in full employment may also cause inflation.
B)that changes in the composition of total labor demand tend to be deflationary.
C)that unemployment rises at the same time the general price level is rising.
D)the possibility that automation will increase the level of noncyclical unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
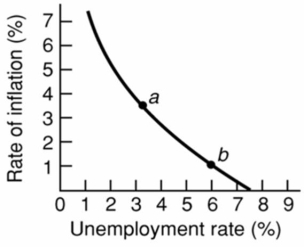 Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Stagflation will:
Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Stagflation will:A)shift this curve outward.
B)shift this curve inward.
C)move this economy southeast along the curve.
D)move this economy northwest along the curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The Phillips Curve is based on the idea that with a constant short-run aggregate supply curve, a greater increase in aggregate demand is associated with a:
A)smaller increase in price level.
B)smaller increase in nominal wage rates.
C)greater increase in the unemployment rate.
D)greater increase in the rate of inflation.
A)smaller increase in price level.
B)smaller increase in nominal wage rates.
C)greater increase in the unemployment rate.
D)greater increase in the rate of inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
An adverse aggregate supply shock:
A)automatically shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B)causes the Phillips Curve to shift leftward and downward.
C)can be caused by a boost in the rate of growth of productivity.
D)can cause stagflation.
A)automatically shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B)causes the Phillips Curve to shift leftward and downward.
C)can be caused by a boost in the rate of growth of productivity.
D)can cause stagflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Although the increase in long-run aggregate supply (other things equal), would expand real GDP and lower the price level, the declines in the price level has not been part of Canada's growth experience.This is because:
A)the Bank of Canada has taken no action to change the nation's money supply.
B)the Bank of Canada has increased the money supply much less than the increase in aggregate supply.
C)the increase in the money supply by Bank of Canada has matched the increase in aggregate supply.
D)the Bank of Canada usually engineers inflationary rightward shifts of the aggregate demand curve that are faster than the deflationary rightward shifts of the aggregate supply curve.
A)the Bank of Canada has taken no action to change the nation's money supply.
B)the Bank of Canada has increased the money supply much less than the increase in aggregate supply.
C)the increase in the money supply by Bank of Canada has matched the increase in aggregate supply.
D)the Bank of Canada usually engineers inflationary rightward shifts of the aggregate demand curve that are faster than the deflationary rightward shifts of the aggregate supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
In the long-run, any inflation that occurs in the economy is the result of:
A)the reduction in the rate of increase in money supply.
B)the growth of aggregate supply.
C)the growth of aggregate demand.
D)the growth of real GDP.
A)the reduction in the rate of increase in money supply.
B)the growth of aggregate supply.
C)the growth of aggregate demand.
D)the growth of real GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
An "adverse aggregate supply shock" could result from:
A)a sharp rise in productivity.
B)a rapid rise in oil prices.
C)a decline in wages.
D)an appreciation of the dollar.
A)a sharp rise in productivity.
B)a rapid rise in oil prices.
C)a decline in wages.
D)an appreciation of the dollar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
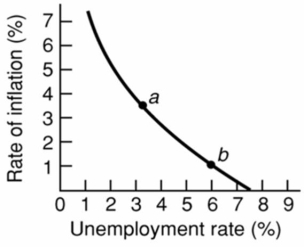 Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.The shape of this curve suggests that:
Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.The shape of this curve suggests that:A)the price level rises at a diminishing rate as the level of aggregate demand increases.
B)full employment and price stability are compatible goals only when aggregate demand is falling.
C)each successive unit of decline in the unemployment rate is accompanied by a smaller increase in the rate of inflation.
D)each successive unit of decline in the unemployment rate is accompanied by a larger increase in the rate of inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
A major adverse aggregate supply shock:
A)automatically shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B)causes the Phillips Curve to shift outward.
C)can be caused by rising productivity.
D)can be caused by falling wages.
A)automatically shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B)causes the Phillips Curve to shift outward.
C)can be caused by rising productivity.
D)can be caused by falling wages.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The Phillips Curve suggests that, if government uses an expansionary fiscal policy to stimulate output and employment:
A)unemployment may actually increase because of the crowding-out effect.
B)tax revenues may increase even though tax rates have been reduced.
C)inflation may result.
D)the natural rate of unemployment may fall.
A)unemployment may actually increase because of the crowding-out effect.
B)tax revenues may increase even though tax rates have been reduced.
C)inflation may result.
D)the natural rate of unemployment may fall.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
The Phillips Curve reveals that with a constant short-run aggregate supply curve, the larger the increase in aggregate demand:
A)the lesser the increase in real output and the higher the rate of inflation.
B)the greater the increase in real output and the higher the rate of inflation.
C)the greater the increase in real output and the lower the rate of inflation.
D)the lesser the increase in real output and the lower the rate of inflation.
A)the lesser the increase in real output and the higher the rate of inflation.
B)the greater the increase in real output and the higher the rate of inflation.
C)the greater the increase in real output and the lower the rate of inflation.
D)the lesser the increase in real output and the lower the rate of inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
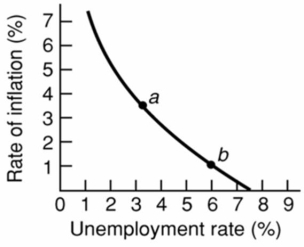 Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Which of the following best describes a decision by policymakers which moves this economy from point b to point a?
Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Which of the following best describes a decision by policymakers which moves this economy from point b to point a?A)Policymakers have instituted an expansionary money policy and/or a budgetary deficit, thereby accepting more unemployment to reduce the rate of inflation.
B)Policymakers have instituted a tight money policy and/or a budgetary surplus, thereby accepting a higher rate of inflation to reduce unemployment.
C)Policymakers have instituted an expansionary money and/or a budgetary deficit, thereby accepting a higher rate of inflation to reduce unemployment.
D)Policymakers have instituted a tight money policy and/or a budgetary surplus, thereby accepting more unemployment to reduce the rate of inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








