Deck 5: Probability and Probability Distributions
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/132
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 5: Probability and Probability Distributions
1
Given that events A and B are independent and that P(A)= 0.8 and P(B/A)= 0.4,then P(A and B)= 0.32.
True
2
Two or more events are said to be exhaustive if one of them must occur.
True
3
If P(A and B)= 1,then A and B must be collectively exhaustive.
True
4
If P(A and B)= 0,then A and B must be collectively exhaustive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Two events are said to be independent when knowledge of one event is of no value when assessing the probability of the other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The relative frequency of an event is the number of times the event occurs out of the total number of times the random experiment is run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Suppose that after graduation,you will either buy a new car (event A)or take a trip to Europe (event B).In this case,events A and B are mutually exclusive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Two or more events are said to be exhaustive if at most one of them can occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Conditional probability is the probability that an event will occur,with no other events taken into consideration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
You think you have a 90% chance of passing your statistics class.This is an example of subjective probability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Probability is a number between 0 and 1,inclusive,which measures the likelihood that some event will occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Two or more events are said to be mutually exclusive if at most one of them can occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
If A and B are independent events with P(A)= 0.40 and P(B)= 0.50,then P(A/B)is 0.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Two events A and B are said to mutually be exclusive if P(A and B)= 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The law of large numbers states that subjective probabilities can be estimated based on the long run relative frequencies of events.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
If A and B are two independent events with P(A)= 0.20 and P(B)= 0.60,then P(A and B)= 0.80.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Suppose A and B are mutually exclusive events where P(A)= 0.3 and P(B)= 0.4.Then,P(A and B)= 0.12.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The multiplication rule for two events A and B is: P(A and B)= P(A|B)P(A).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
If events A and B have nonzero probabilities,then they can be both independent and mutually exclusive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Suppose A and B are two events where P(A)= 0.5,P(B)= 0.4,and P(A and B)= 0.2,then P(B/A)= 0.5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A random variable X is standardized when each value of X has the mean of X subtracted from it,and the difference is divided by the standard deviation of X.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
If the random variable X is normally distributed with mean 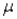 and standard deviation
and standard deviation 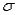 ,then the random variable Z defined by
,then the random variable Z defined by 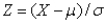 is also normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
is also normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
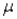 and standard deviation
and standard deviation 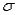 ,then the random variable Z defined by
,then the random variable Z defined by 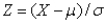 is also normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
is also normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Using the standard normal distribution,the Z-score representing the 5th percentile is 1.645.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The mean and standard deviation of a normally distributed random variable that has been "standardized" are zero and one,respectively.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A probability tree is a graphical representation of how events occur through time,which is useful for calculating probabilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Subjective probability is the probability that a given event will occur,given that another event has already occurred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Football teams toss a coin to see who will get their choice of kicking or receiving to begin a game.The probability that given team will win the toss three games in a row is 0.125.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Two events A and B are said to be independent if P(A and B)= P(A)+ P(B).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Suppose A and B are mutually exclusive events where P(A)= 0.2 and P(B)= 0.5,then P(A or B)= 0.70.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
When we wish to determine the probability that at least one of several events will occur,we would use the addition rule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The number of car insurance policy holders is an example of a discrete random variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Using the standard normal distribution,the Z- score representing the 99th percentile is 2.326.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The number of people entering a shopping mall on a given day is an example of a discrete random variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The time students spend in a computer lab during one day is an example of a continuous random variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
When two events are independent,they are also mutually exclusive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The number of cars produced by GM during a given quarter is a continuous random variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The total area under the normal distribution curve is equal to one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The temperature of the room in which you are writing this test is a continuous random variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The probability that event A will not occur is denoted as 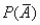 .
.
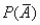 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A random variable is a function that associates a numerical value with each possible outcome of a random phenomenon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The variance of a binomial distribution is given by the formula 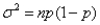 ,where n is the number of trials,and p is the probability of success in any trial.
,where n is the number of trials,and p is the probability of success in any trial.
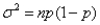 ,where n is the number of trials,and p is the probability of success in any trial.
,where n is the number of trials,and p is the probability of success in any trial.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The Poisson random variable is a discrete random variable with infinitely many possible values.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The number of loan defaults per month at a bank is Poisson distributed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Using the standard normal curve,the Z- score representing the 75th percentile is 0.674.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
An exponential distribution with parameter 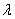 = 0.2 has mean and standard deviation both equal to 5.
= 0.2 has mean and standard deviation both equal to 5.
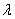 = 0.2 has mean and standard deviation both equal to 5.
= 0.2 has mean and standard deviation both equal to 5.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The Poisson distribution is characterized by a single parameter 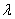 ,which must be positive.
,which must be positive.
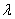 ,which must be positive.
,which must be positive.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A binomial distribution with n number of trials,and probability of success p can be approximated well by a normal distribution with mean np and variance 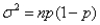 if np > 5 and n(1-p)> 5.
if np > 5 and n(1-p)> 5.
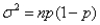 if np > 5 and n(1-p)> 5.
if np > 5 and n(1-p)> 5.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The binomial distribution is a discrete distribution that deals with a sequence of identical trials,each of which have only two possible outcomes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The variance of a binomial distribution for which n = 50 and p = 0.20 is 8.0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Using the standard normal curve,the Z- score representing the 10th percentile is 1.28.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
A Poisson distribution is appropriate to determine the probability of a given number of defective items in a shipment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Much of the study of probabilistic inventory models,queuing models,and reliability models relies heavily on the Poisson and exponential distributions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The binomial random variable represents the number of successes that occur in a specific period of time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
A random variable X is normally distributed with a mean of 175 and a standard deviation of 50.Given that X = 150,its corresponding Z- score is -0.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The Poisson probability distribution is one of the most commonly used continuous probability distributions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
For a given probability of success p that is not too close to 0 or 1,the binomial distribution takes on more of a symmetric bell shape as the number of trials n increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The density function specifies the probability distribution of a continuous random variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The binomial distribution deals with consecutive trials,each of which has two possible outcomes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The Poisson distribution is applied to events for which the probability of occurrence over a given span of time,space,or distance is very small.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The binomial distribution is a continuous distribution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A function that associates a numerical value with each possible outcome of an uncertain event is called a _____ variable.
A)conditional
B)random
C)population
D)sample
A)conditional
B)random
C)population
D)sample

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The probabilities shown in a table with two rows, 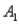 and
and 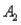 and two columns,
and two columns, 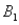 and
and 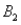 ,are as follows: P(
,are as follows: P( 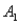 and
and 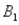 )= 0.10,P(
)= 0.10,P( 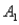 and
and  )= 0.30,P(
)= 0.30,P( 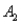 and
and 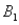 )= 0.05,and P(
)= 0.05,and P( 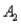 and
and 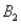 )= 0.55.Then P(
)= 0.55.Then P( 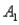 |
| 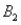 )is
)is
A)0.33.
B)0.35.
C)0.65.
D)0.67.
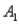 and
and 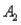 and two columns,
and two columns, 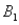 and
and 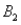 ,are as follows: P(
,are as follows: P( 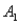 and
and 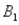 )= 0.10,P(
)= 0.10,P( 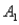 and
and  )= 0.30,P(
)= 0.30,P( 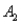 and
and 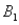 )= 0.05,and P(
)= 0.05,and P( 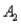 and
and 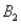 )= 0.55.Then P(
)= 0.55.Then P( 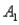 |
| 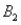 )is
)isA)0.33.
B)0.35.
C)0.65.
D)0.67.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Probabilities that can be estimated from long-run relative frequencies of events are called _____ probabilities.
A)objective
B)subjective
C)complementary
D)joint
A)objective
B)subjective
C)complementary
D)joint

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The probability of an event and the probability of its complement always sum to
A)1.
B)0.
C)any value between 0 and 1.
D)any positive value.
A)1.
B)0.
C)any value between 0 and 1.
D)any positive value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
If A and B are mutually exclusive events with P(A)= 0.70,then P(B)
A)can be any value between 0 and 1.
B)can be any value between 0 and 0.70.
C)cannot be larger than 0.30.
D)can be any value between 0.30 and 0.70.
A)can be any value between 0 and 1.
B)can be any value between 0 and 0.70.
C)cannot be larger than 0.30.
D)can be any value between 0.30 and 0.70.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Probabilities must be negative.
B)Probabilities must be greater than 1.
C)The sum of all probabilities for a random variable must be equal to 1.
D)The sum of all probabilities for a random variable must be equal to 0.
A)Probabilities must be negative.
B)Probabilities must be greater than 1.
C)The sum of all probabilities for a random variable must be equal to 1.
D)The sum of all probabilities for a random variable must be equal to 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
If two events are independent,what is the probability that they both occur?
A)0
B)0.50
C)1.00
D)This cannot be determined from the information given.
A)0
B)0.50
C)1.00
D)This cannot be determined from the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
A discrete probability distribution
A)is a set of possible values and a corresponding set of probabilities that sum to 1.
B)is a modeling tool that can be used to incorporate uncertainty into models.
C)can be estimated from long-run proportions.
D)is the distribution of a single random variable.
A)is a set of possible values and a corresponding set of probabilities that sum to 1.
B)is a modeling tool that can be used to incorporate uncertainty into models.
C)can be estimated from long-run proportions.
D)is the distribution of a single random variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
If events A and B are mutually exclusive,then the probability of both events occurring simultaneously is equal to
A)0.0.
B)0.5.
C)1.0.
D)any value between 0.5 and 1.0.
A)0.0.
B)0.5.
C)1.0.
D)any value between 0.5 and 1.0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
There are two types of random variables,they are
A)discrete and continuous.
B)exhaustive and mutually exclusive.
C)complementary and cumulative.
D)real and unreal.
A)discrete and continuous.
B)exhaustive and mutually exclusive.
C)complementary and cumulative.
D)real and unreal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
If P(A)= P(A|B),then events A and B are said to be
A)mutually exclusive.
B)independent.
C)dependent.
D)complementary.
A)mutually exclusive.
B)independent.
C)dependent.
D)complementary.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The probabilities shown in a table with two rows, 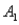 and
and 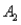 and two columns,
and two columns, 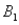 and
and 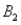 ,are as follows: P(
,are as follows: P( 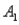 and
and 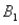 )= 0.10,P(
)= 0.10,P( 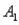 and
and 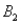 )= 0.30,P(
)= 0.30,P( 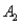 and
and 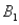 )= 0.05,and P(
)= 0.05,and P( 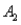 and
and 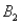 )= 0.55.Then P(
)= 0.55.Then P( 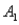 |
| 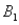 ),calculated up to two decimals,is
),calculated up to two decimals,is
A)0.33.
B)0.35.
C)0.65.
D)0.67.
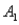 and
and 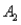 and two columns,
and two columns, 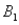 and
and 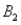 ,are as follows: P(
,are as follows: P( 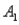 and
and 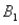 )= 0.10,P(
)= 0.10,P( 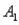 and
and 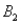 )= 0.30,P(
)= 0.30,P( 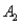 and
and 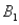 )= 0.05,and P(
)= 0.05,and P( 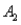 and
and 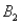 )= 0.55.Then P(
)= 0.55.Then P( 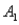 |
| 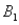 ),calculated up to two decimals,is
),calculated up to two decimals,isA)0.33.
B)0.35.
C)0.65.
D)0.67.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
If P(A)= 0.25 and P(B)= 0.65,then P(A and B)is
A)0.25.
B)0.40.
C)0.90.
D)This cannot be determined from the information given.
A)0.25.
B)0.40.
C)0.90.
D)This cannot be determined from the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
If two events are collectively exhaustive,what is the probability that both occur at the same time?
A)0.00
B)0.50
C)1.00
D)This cannot be determined from the information given.
A)0.00
B)0.50
C)1.00
D)This cannot be determined from the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The formal way to revise probabilities based on new information is to use _____ probabilities.
A)complementary
B)conditional
C)unilateral
D)common sense
A)complementary
B)conditional
C)unilateral
D)common sense

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Probabilities that cannot be estimated from long-run relative frequencies of events are called
A)objective probabilities.
B)subjective probabilities.
C)complementary probabilities.
D)joint probabilities.
A)objective probabilities.
B)subjective probabilities.
C)complementary probabilities.
D)joint probabilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
If two events are mutually exclusive,what is the probability that both occur at the same time?
A)0.0
B)0.5
C)1.0
D)This can be any probability between 0 and 1.
A)0.0
B)0.5
C)1.0
D)This can be any probability between 0 and 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The law of large numbers is relevant to the estimation of _____ probabilities.
A)objective
B)subjective
C)both objective and subjective
D)neither objective nor subjective
A)objective
B)subjective
C)both objective and subjective
D)neither objective nor subjective

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
If A and B are any two events with P(A)= 0.8 and P(B|A)= 0.4,then the joint probability of A and B is:
A)0.80
B)0.40
C)0.32
D)1.20
A)0.80
B)0.40
C)0.32
D)1.20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Which of the following best describes the concept of probability?
A)It is a measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur.
B)It is a measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur,given that another event has already occurred.
C)It is a measure of the likelihood of the simultaneous occurrence of two or more events.
D)None of these choices describe the concept of probability.
A)It is a measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur.
B)It is a measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur,given that another event has already occurred.
C)It is a measure of the likelihood of the simultaneous occurrence of two or more events.
D)None of these choices describe the concept of probability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 132 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








