Deck 13: Perfect Competition
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/137
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Perfect Competition
1
In a perfectly competitive market, many firms produce many different varieties of the same product.
False
2
The existence of positive economic profits in an industry attracts new entrants into the industry.
True
3
In the short run when the number of firms in the market is fixed, the market supply curve is just the horizontal sum of all the firms' marginal cost curves.
True
4
A firm will continue to operate in the long run as long as price exceeds long-run average variable cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The marginal cost curve is a competitive firm's supply curve; it shows how many units of output a firm will be willing to sell at different prices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Firms continue to produce (illegally) counterfeit computer software and documentation. Some of the illegal copies are Microsoft products, though Microsoft still has a large share of the market for its products. The presence of enforced copyright protection laws indicates that the market for Microsoft software cannot be considered a competitive market because:
A) the products of pirates are not identical to those of Microsoft.
B) pirate producers are not profit-maximizing entrepreneurial firms.
C) buyers are not price takers.
D) there are significant barriers to entry.
A) the products of pirates are not identical to those of Microsoft.
B) pirate producers are not profit-maximizing entrepreneurial firms.
C) buyers are not price takers.
D) there are significant barriers to entry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Each firm in perfect competition:
A) sets quantity based on market price.
B) follows the pricing decisions of other firms.
C) follows the output of other firms.
D) follows the reactions of competitors.
A) sets quantity based on market price.
B) follows the pricing decisions of other firms.
C) follows the output of other firms.
D) follows the reactions of competitors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
In a perfectly competitive market, firms set:
A) prices and quantities.
B) prices but not quantities.
C) quantities but not prices.
D) neither prices nor quantities.
A) prices and quantities.
B) prices but not quantities.
C) quantities but not prices.
D) neither prices nor quantities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In a perfectly competitive market, economic forces are controlled by government policy makers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following is one of the necessary conditions for perfect competition?
A) Diminishing utility
B) No barriers to entry
C) Differentiated products
D) Indivisible setup costs
A) Diminishing utility
B) No barriers to entry
C) Differentiated products
D) Indivisible setup costs

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In a perfectly competitive market, market prices are determined by:
A) individual producers.
B) market supply and market demand.
C) the entrepreneur.
D) individual consumers.
A) individual producers.
B) market supply and market demand.
C) the entrepreneur.
D) individual consumers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
If long-run average total cost exceeds marginal revenue, a perfectly competitive firm will incur losses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In perfect competition, price is equal to marginal revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The profit-maximizing output level minimizes average total cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Because only competitive firms are price takers, only competitive firms have supply curves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
For a perfectly competitive firm, the profit-maximizing output level occurs where marginal cost equals price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
An increase in market price, given a fixed number of firms, causes market supply to shift to the right.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Perfectly competitive firms:
A) are price takers, since they are not large enough to influence the market price.
B) are individually able to influence the market price.
C) will succeed by charging a price higher than that charged by the rest of the market.
D) can influence the prices of other firms in the same industry by altering their own prices.
A) are price takers, since they are not large enough to influence the market price.
B) are individually able to influence the market price.
C) will succeed by charging a price higher than that charged by the rest of the market.
D) can influence the prices of other firms in the same industry by altering their own prices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Barriers to entry:
A) do not affect the number of firms in an industry.
B) exist only in perfectly competitive markets.
C) restrict the number of firms in an industry.
D) limit output in an industry.
A) do not affect the number of firms in an industry.
B) exist only in perfectly competitive markets.
C) restrict the number of firms in an industry.
D) limit output in an industry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
An assumption of a competitive market is that both buyers and sellers are price takers. When we go to the mall to shop for clothing or to the grocery to buy food, what do we usually observe?
A) Both buyers and sellers are usually price takers.
B) Buyers are often price takers, but sellers are usually price makers.
C) Buyers are often price makers, but sellers are usually price takers.
D) Both buyers and sellers are usually price makers.
A) Both buyers and sellers are usually price takers.
B) Buyers are often price takers, but sellers are usually price makers.
C) Buyers are often price makers, but sellers are usually price takers.
D) Both buyers and sellers are usually price makers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
If the marginal revenue of the next unit a firm produces is $50 and its marginal cost is $35, a firm should:
A) reconsider past production decisions.
B) decrease production.
C) increase production.
D) hold production constant.
A) reconsider past production decisions.
B) decrease production.
C) increase production.
D) hold production constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In a perfectly competitive market, the demand curve faced by an individual firm is:
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) relatively inelastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) relatively elastic.
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) relatively inelastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) relatively elastic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Suppose a perfectly competitive firm can increase its profits by increasing its output. Then it must be true that the firm's:
A) marginal revenue is less than its marginal cost.
B) price exceeds its marginal revenue.
C) price exceeds its marginal cost.
D) marginal cost exceeds its marginal revenue.
A) marginal revenue is less than its marginal cost.
B) price exceeds its marginal revenue.
C) price exceeds its marginal cost.
D) marginal cost exceeds its marginal revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Refer to the graph shown. To maximize profit, this perfectly competitive firm should produce: 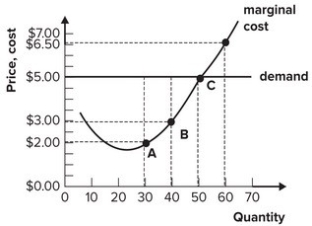
A) 30 units of output.
B) 40 units of output.
C) 50 units of output.
D) 60 units of output.

A) 30 units of output.
B) 40 units of output.
C) 50 units of output.
D) 60 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Refer to the graph shown. If the firm increases output from 30 to 40, total revenue will increase: 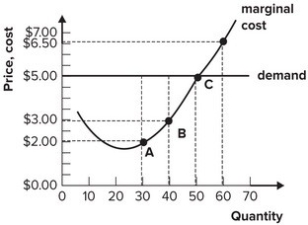
A) more than total cost, and so profit will increase.
B) more than total cost, and so profit will decrease.
C) less than total cost, and so profit will increase.
D) less than total cost, and so profit will decrease.

A) more than total cost, and so profit will increase.
B) more than total cost, and so profit will decrease.
C) less than total cost, and so profit will increase.
D) less than total cost, and so profit will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
To maximize profits, a perfectly competitive firm should produce where marginal:
A) cost equals total revenue.
B) cost exceeds marginal revenue.
C) cost equals marginal revenue.
D) revenue exceeds marginal cost.
A) cost equals total revenue.
B) cost exceeds marginal revenue.
C) cost equals marginal revenue.
D) revenue exceeds marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Suppose a perfectly competitive firm can increase its profits by reducing its output. Then it must be the case that the firm's:
A) marginal revenue equals its marginal cost.
B) price exceeds its marginal cost.
C) price exceeds its marginal revenue.
D) marginal cost exceeds its marginal revenue.
A) marginal revenue equals its marginal cost.
B) price exceeds its marginal cost.
C) price exceeds its marginal revenue.
D) marginal cost exceeds its marginal revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The demand curve for a firm in perfect competition is equal to its:
A) marginal cost curve.
B) marginal revenue curve.
C) average total cost curve.
D) average fixed cost curve.
A) marginal cost curve.
B) marginal revenue curve.
C) average total cost curve.
D) average fixed cost curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Suppose a perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue is $10 and its marginal cost is $11. Under these circumstances the firm:
A) is maximizing profit and should not change output.
B) is not maximizing profit and should increase output.
C) is not maximizing profit and should reduce output.
D) needs to know the market price before it can determine whether it is maximizing profit.
A) is maximizing profit and should not change output.
B) is not maximizing profit and should increase output.
C) is not maximizing profit and should reduce output.
D) needs to know the market price before it can determine whether it is maximizing profit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Refer to the graph shown. If the firm increases output from 50 to 60, total revenue will increase: 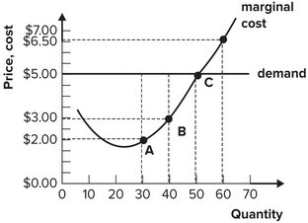
A) more than total cost, and so profit will increase.
B) more than total cost, and so profit will decrease.
C) less than total cost, and so profit will increase.
D) less than total cost, and so profit will decrease.

A) more than total cost, and so profit will increase.
B) more than total cost, and so profit will decrease.
C) less than total cost, and so profit will increase.
D) less than total cost, and so profit will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Marginal revenue is equal to:
A) total revenue divided by its output.
B) marginal cost.
C) the change in total revenue associated with a change in quantity.
D) the change in total profits associated with a change in quantity.
A) total revenue divided by its output.
B) marginal cost.
C) the change in total revenue associated with a change in quantity.
D) the change in total profits associated with a change in quantity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The profit-maximizing condition for a perfectly competitive firm is:
A) MR = P.
B) MR = AVC.
C) P = MC.
D) P = AVC.
A) MR = P.
B) MR = AVC.
C) P = MC.
D) P = AVC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A perfectly competitive firm facing a price of $50 decides to produce 500 widgets. Its marginal cost of producing the last widget is $50. If the firm's goal is maximize profit, it should:
A) produce more widgets.
B) produce fewer widgets.
C) continue producing 500 widgets.
D) shut down.
A) produce more widgets.
B) produce fewer widgets.
C) continue producing 500 widgets.
D) shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue is:
A) less than the selling price.
B) greater than the selling price.
C) equal to the selling price.
D) sometimes below and sometimes above the selling price.
A) less than the selling price.
B) greater than the selling price.
C) equal to the selling price.
D) sometimes below and sometimes above the selling price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The market demand curve for a product produced in a perfectly competitive industry is normally:
A) a vertical line.
B) upward sloping.
C) a horizontal line.
D) downward sloping.
A) a vertical line.
B) upward sloping.
C) a horizontal line.
D) downward sloping.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Refer to the graph shown. Currently, if this perfectly competitive firm is maximizing profit, the market price is: 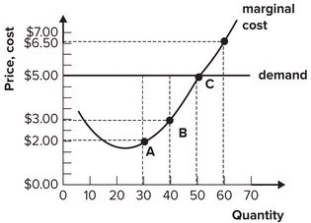
A) $6.50 and marginal revenue for the firm is $5.00
B) $5.00 and marginal revenue for the firm is $3.00
C) $5.00 and marginal revenue for the firm is $5.00
D) $6.50 and marginal revenue for the firm is $6.50

A) $6.50 and marginal revenue for the firm is $5.00
B) $5.00 and marginal revenue for the firm is $3.00
C) $5.00 and marginal revenue for the firm is $5.00
D) $6.50 and marginal revenue for the firm is $6.50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Refer to the graph shown. The marginal cost of producing the 60th unit is: 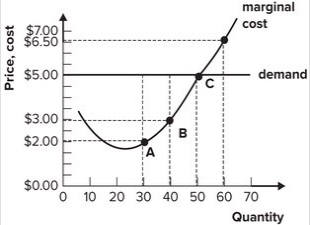
A) $6.50.
B) $5.00.
C) $3.00.
D) $3.50.

A) $6.50.
B) $5.00.
C) $3.00.
D) $3.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
As long as marginal cost is below marginal revenue, a perfectly competitive firm should:
A) increase production.
B) hold production constant.
C) decrease production.
D) reconsider past production decisions.
A) increase production.
B) hold production constant.
C) decrease production.
D) reconsider past production decisions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A perfectly competitive firm facing a price of $10 decides to produce 100 units. If its marginal cost of producing the last unit is $12 and it is seeking to maximize profit, the firm should:
A) produce more units.
B) produce fewer units.
C) continue producing 100 units.
D) shut down.
A) produce more units.
B) produce fewer units.
C) continue producing 100 units.
D) shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Refer to the graph shown. If the firm increases output from 40 to 50, total revenue will increase: 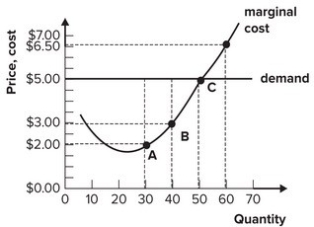
A) more than total cost, and so profit will increase.
B) more than total cost, and so profit will decrease.
C) less than total cost, and so profit will increase.
D) less than total cost, and so profit will decrease.

A) more than total cost, and so profit will increase.
B) more than total cost, and so profit will decrease.
C) less than total cost, and so profit will increase.
D) less than total cost, and so profit will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Refer to the graph shown. What area represents total economic profits? 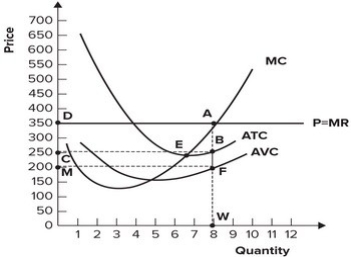
A) DAFM
B) CBWT
C) MFWT
D) DABC

A) DAFM
B) CBWT
C) MFWT
D) DABC

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Refer to the graph shown. What distance represents average profits? 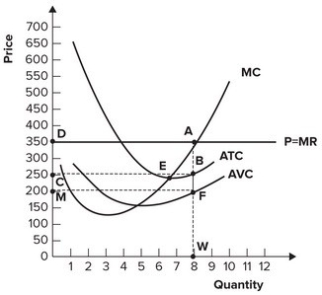
A) AB
B) BF
C) AF
D) FW

A) AB
B) BF
C) AF
D) FW

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Refer to the graph shown. If market price is currently $7.00 per unit, this perfectly competitive firm will maximize profit by producing: 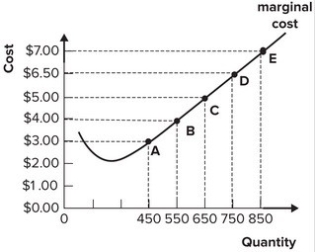
A) 450 units of output.
B) 650 units of output.
C) 850 units of output.
D) between 550 and 650 units of output.

A) 450 units of output.
B) 650 units of output.
C) 850 units of output.
D) between 550 and 650 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Refer to the table shown. If the market price is $6, a perfectly competitive profit-maximizing firm will produce:
A) 1 unit of output.
B) 2 units of output.
C) 3 units of output.
D) 4 units of output.
A) 1 unit of output.
B) 2 units of output.
C) 3 units of output.
D) 4 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Refer to the table shown. If the market price is $8, a perfectly competitive profit-maximizing firm will produce:
A) 1 unit of output.
B) 2 units of output.
C) 3 units of output.
D) 4 units of output.
A) 1 unit of output.
B) 2 units of output.
C) 3 units of output.
D) 4 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Refer to the graph shown depicting a perfectly competitive firm. If average variable cost is $3 at quantity 450, points A through E represent the: 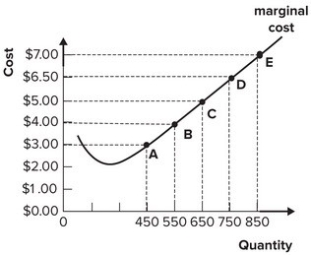
A) firm's total cost curve.
B) firm's total revenue curve.
C) demand for the firm's product.
D) firm's supply curve.

A) firm's total cost curve.
B) firm's total revenue curve.
C) demand for the firm's product.
D) firm's supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Refer to the graph shown. If market price increases from $5.00 per unit to $6.00 per unit, a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm will: 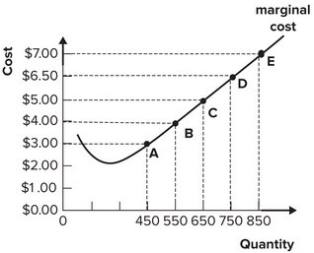
A) increase output from 650 to 750.
B) decrease output from 750 to 650.
C) continue to produce 650 units.
D) produce 850 units of output.

A) increase output from 650 to 750.
B) decrease output from 750 to 650.
C) continue to produce 650 units.
D) produce 850 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Refer to the graph shown. What level of output should the perfectly competitive firm produce to maximize profits? 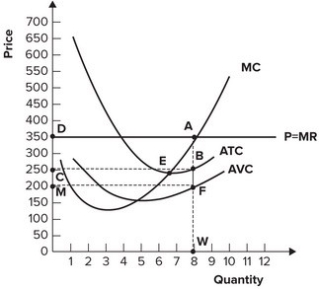
A) 7.
B) 8.
C) 6.
D) 4.

A) 7.
B) 8.
C) 6.
D) 4.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Refer to the graph shown. A perfectly competitive firm would never operate if the price dropped to which segment of the marginal cost curve? 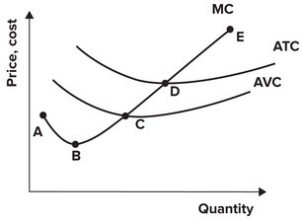
A) AC.
B) CD.
C) DE.
D) CE.

A) AC.
B) CD.
C) DE.
D) CE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Refer to the table shown. The maximum profit that the perfectly competitive firm represented by the above data could earn is:
A) $25.
B) $35.
C) $45.
D) $55.
A) $25.
B) $35.
C) $45.
D) $55.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Refer to the graph shown. If market price is currently $5.00 per unit, this perfectly competitive firm will maximize profit by producing: 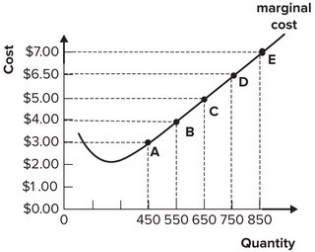
A) 450 units of output.
B) 650 units of output.
C) 850 units of output.
D) between 550 and 650 units of output.

A) 450 units of output.
B) 650 units of output.
C) 850 units of output.
D) between 550 and 650 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
To maximize profits, a perfectly competitive firm should do all the following except:
A) produce until economic profits are maximized.
B) produce until marginal cost equals price.
C) produce until marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) produce until per-unit profits are maximized.
A) produce until economic profits are maximized.
B) produce until marginal cost equals price.
C) produce until marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) produce until per-unit profits are maximized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
A perfectly competitive firm will be profitable if price at the profit-maximizing quantity is above:
A) MC.
B) AVC.
C) ATC.
D) AFC.
A) MC.
B) AVC.
C) ATC.
D) AFC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Based on the information shown, a perfectly competitive profit-maximizing firm would produce:
A) 10 units of output.
B) 20 units of output.
C) 30 units of output.
D) 40 units of output.
A) 10 units of output.
B) 20 units of output.
C) 30 units of output.
D) 40 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Refer to the graph shown. If market price is currently $3.00 per unit, this perfectly competitive firm will maximize profit by producing: 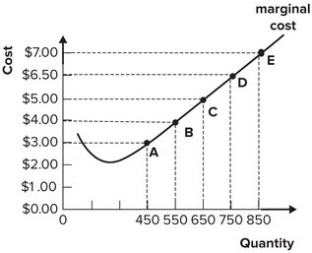
A) 450 units of output.
B) 650 units of output.
C) 850 units of output.
D) between 550 and 650 units of output.

A) 450 units of output.
B) 650 units of output.
C) 850 units of output.
D) between 550 and 650 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
To maximize profits, a perfectly competitive firm should produce until:
A) price is greater than average total cost.
B) marginal cost is equal to price.
C) average total cost is minimized.
D) per unit profits are maximized.
A) price is greater than average total cost.
B) marginal cost is equal to price.
C) average total cost is minimized.
D) per unit profits are maximized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm is:
A) the marginal cost curve only if price exceeds average variable cost.
B) the marginal cost curve only if price exceeds average total cost.
C) the average total cost curve only if price exceeds average variable cost.
D) nonexistent.
A) the marginal cost curve only if price exceeds average variable cost.
B) the marginal cost curve only if price exceeds average total cost.
C) the average total cost curve only if price exceeds average variable cost.
D) nonexistent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Refer to the graph shown. The supply curve for the perfectly competitive firm is best represented by the segment: 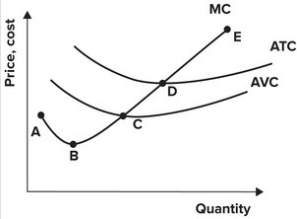
A) AB.
B) BD.
C) CE.
D) DE.

A) AB.
B) BD.
C) CE.
D) DE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Refer to the table shown. If the market price is $4, a perfectly competitive profit-maximizing firm will produce:
A) 1 unit of output.
B) 2 units of output.
C) 3 units of output.
D) 4 units of output.
A) 1 unit of output.
B) 2 units of output.
C) 3 units of output.
D) 4 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Refer to the graph shown. If market price decreases from $7.00 per unit to $6.00 per unit, a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm will: 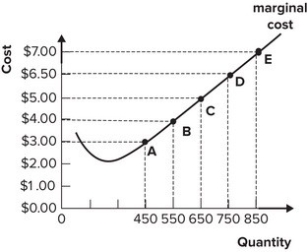
A) increase output from 650 to 750.
B) decrease output from 850 to 750.
C) continue to produce 850 units.
D) produce 850 units of output.

A) increase output from 650 to 750.
B) decrease output from 850 to 750.
C) continue to produce 850 units.
D) produce 850 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Refer to the graph shown, which depicts a perfectly competitive firm. To maximize profit, the firm represented will produce: 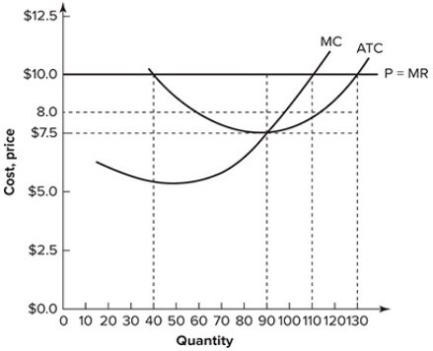
A) 40 units of output.
B) 90 units of output.
C) 110 units of output.
D) 130 units of output.

A) 40 units of output.
B) 90 units of output.
C) 110 units of output.
D) 130 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Refer to the graph shown. To maximize profit, this firm should produce: 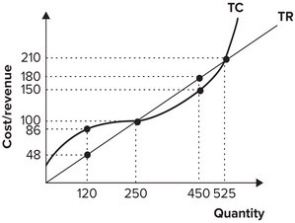
A) 120 units of output.
B) 250 units of output.
C) 450 units of output.
D) 525 units of output.

A) 120 units of output.
B) 250 units of output.
C) 450 units of output.
D) 525 units of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Refer to the graph shown. If the firm is producing 250 units of output, profit is equal to: 
A) $38.
B) -$38.
C) $0.
D) $30.

A) $38.
B) -$38.
C) $0.
D) $30.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Refer to the graph shown. If the firm is producing 120 units of output, profit is equal to: 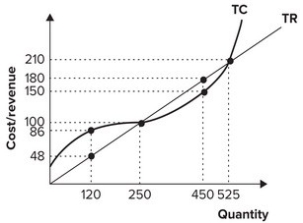
A) $38.
B) −$38.
C) $0.
D) $30.

A) $38.
B) −$38.
C) $0.
D) $30.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Refer to the graph shown. What price represents the shutdown price? 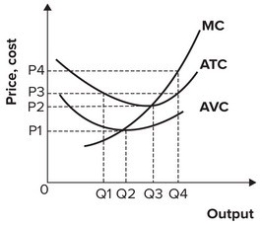
A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) P4

A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) P4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Refer to the graph shown. Suppose the market price is $4. At this price, a perfectly competitive firm should: 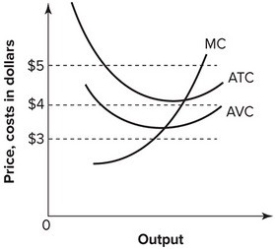
A) continue to produce in the short run but shut down in the long run.
B) continue to produce in both the short run and the long run.
C) shut down in the short run but continue production in the long run.
D) shut down immediately.

A) continue to produce in the short run but shut down in the long run.
B) continue to produce in both the short run and the long run.
C) shut down in the short run but continue production in the long run.
D) shut down immediately.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Refer to the graph shown, which depicts a perfectly competitive firm. When maximizing profit, the firm represented will earn per-unit profit roughly equal to: 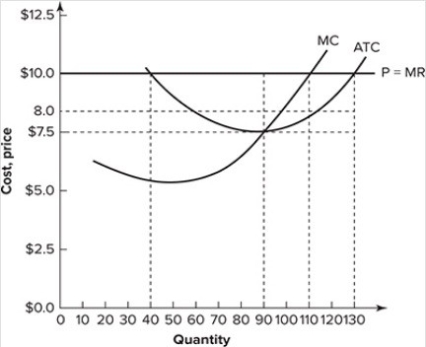
A) $2.00.
B) $5.
C) $7.50
D) $10.

A) $2.00.
B) $5.
C) $7.50
D) $10.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If a perfectly competitive firm finds that price is less than average variable cost, it should:
A) not adjust output if marginal cost equals price.
B) shut down immediately.
C) increase output until price equals marginal cost.
D) decrease output until price equals marginal cost.
A) not adjust output if marginal cost equals price.
B) shut down immediately.
C) increase output until price equals marginal cost.
D) decrease output until price equals marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Total profit is maximized at the output level at which the:
A) vertical distance between the total revenue curve and the total cost curve is maximized.
B) total cost and total revenue curves intersect.
C) area between the total revenue and total cost curves is greatest.
D) vertical distance between the total revenue and total cost curves is minimized.
A) vertical distance between the total revenue curve and the total cost curve is maximized.
B) total cost and total revenue curves intersect.
C) area between the total revenue and total cost curves is greatest.
D) vertical distance between the total revenue and total cost curves is minimized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Refer to the graph shown. If this perfectly competitive firm is producing 120 units of output, the market price is equal to: 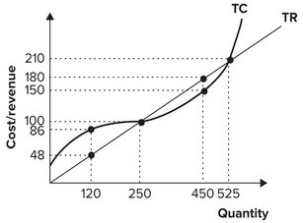
A) $48.
B) 2.50.
C) $0.40.
D) impossible to determine with the information given.

A) $48.
B) 2.50.
C) $0.40.
D) impossible to determine with the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Refer to the graph shown. If the market price is P2, the firm will produce: 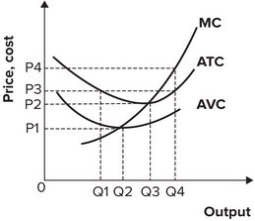
A) Q2 and incur a loss.
B) Q3 and earn a profit.
C) Q3 and break even.
D) Q4 and incur a loss.

A) Q2 and incur a loss.
B) Q3 and earn a profit.
C) Q3 and break even.
D) Q4 and incur a loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Refer to the graph shown. If the market price is P4, the firm will produce: 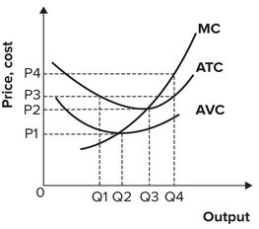
A) Q2 and incur a loss.
B) Q3 and break even.
C) Q3 and earn a profit.
D) Q4 and earn a profit.

A) Q2 and incur a loss.
B) Q3 and break even.
C) Q3 and earn a profit.
D) Q4 and earn a profit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Refer to the graph shown. Suppose that the market price is $5. At this price, a perfectly competitive firm should: 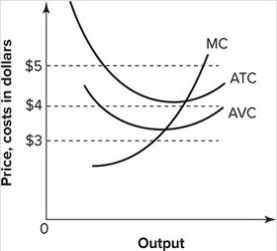
A) continue to produce in the short run but shut down in the long run.
B) continue to produce in both the short run and the long run.
C) shut down in the short run but continue production in the long run.
D) shut down immediately.

A) continue to produce in the short run but shut down in the long run.
B) continue to produce in both the short run and the long run.
C) shut down in the short run but continue production in the long run.
D) shut down immediately.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Refer to the graph shown. Suppose the market price is $3. At this price, a perfectly competitive firm should: 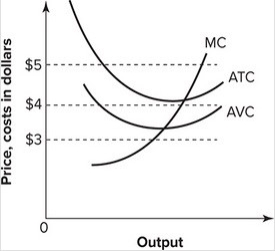
A) continue to produce in the short run but shut down in the long run.
B) continue to produce in both the short run and the long run.
C) shut down in the short run but continue production in the long run.
D) shut down immediately.

A) continue to produce in the short run but shut down in the long run.
B) continue to produce in both the short run and the long run.
C) shut down in the short run but continue production in the long run.
D) shut down immediately.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Refer to the graph shown. If the market price is $4, a perfectly competitive firm: 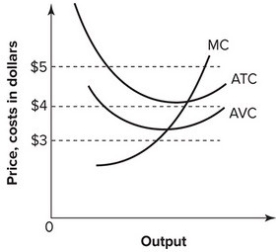
A) breaks even.
B) earns a profit.
C) incurs a loss but can still cover its variable costs and some of its fixed costs.
D) incurs a loss and cannot cover its variable costs.

A) breaks even.
B) earns a profit.
C) incurs a loss but can still cover its variable costs and some of its fixed costs.
D) incurs a loss and cannot cover its variable costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Refer to the graph shown. If the firm is producing 450 units of output, profit is equal to: 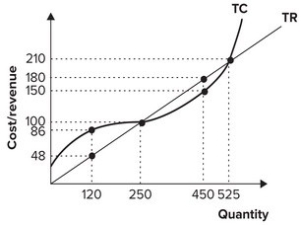
A) $38.
B) −$30.
C) $0.
D) $30.

A) $38.
B) −$30.
C) $0.
D) $30.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Refer to the graph shown. If the market price is $3, a perfectly competitive firm: 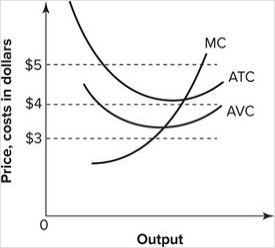
A) breaks even.
B) earns a profit.
C) incurs a loss but can still cover its variable costs and some of its fixed costs.
D) incurs a loss and cannot cover its variable costs.

A) breaks even.
B) earns a profit.
C) incurs a loss but can still cover its variable costs and some of its fixed costs.
D) incurs a loss and cannot cover its variable costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Refer to the graph shown. If the firm is producing 525 units of output, profit is equal to: 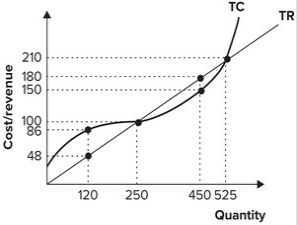
A) $38.
B) −$38.
C) $0.
D) $30.

A) $38.
B) −$38.
C) $0.
D) $30.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Refer to the graph shown, which depicts a perfectly competitive firm. When it is maximizing profit, the total profit earned by the firm represented is: 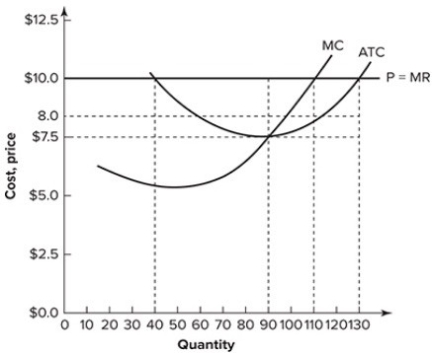
A) $220.
B) $275.
C) $330.
D) $605.

A) $220.
B) $275.
C) $330.
D) $605.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Refer to the graph shown. If the market price is P4, the maximum profit the firm can earn is: 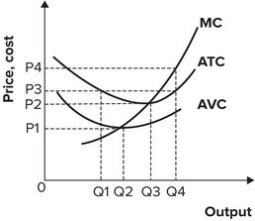
A) Q4 multiplied by P4.
B) Q3 multiplied by P3.
C) Q4 multiplied by the difference between P4 and P3.
D) Q3 multiplied by the difference between P3 and P2.

A) Q4 multiplied by P4.
B) Q3 multiplied by P3.
C) Q4 multiplied by the difference between P4 and P3.
D) Q3 multiplied by the difference between P3 and P2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 137 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








