Deck 21: The Expanding Universe
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/98
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 21: The Expanding Universe
1
Sailors could claim the distribution of islands in the ocean is both homogeneous and isotropic (as far as they can see) if
A) the only large islands are nearby, but small ones can be found near the horizon.
B) there are islands of varying sizes all around the horizon, but none near the sailors.
C) there are the same number of islands in every direction, but islands in one direction are bigger than in any other direction.
D) they can see islands in one direction, but not in other directions.
E) the average numbers, distances, and sizes of islands are the same in all directions.
A) the only large islands are nearby, but small ones can be found near the horizon.
B) there are islands of varying sizes all around the horizon, but none near the sailors.
C) there are the same number of islands in every direction, but islands in one direction are bigger than in any other direction.
D) they can see islands in one direction, but not in other directions.
E) the average numbers, distances, and sizes of islands are the same in all directions.
the average numbers, distances, and sizes of islands are the same in all directions.
2
If the distance of a galaxy at a redshift z = 0.05 is 220 Mpc, how many years back into the past are we looking when we observe this galaxy?
A) 5 million years
B) 220 million years
C) 720 million years
D) 6 billion years
E) 10 billion years
A) 5 million years
B) 220 million years
C) 720 million years
D) 6 billion years
E) 10 billion years
720 million years
3
One implication of Hubble's law is that
A) the Milky Way is at the center of the universe.
B) galaxies can have peculiar velocities that are greater than the speed of light.
C) the density and temperature of the universe must have been higher in the past.
D) it applies only to nearby galaxies within the Local Group.
E) more distant objects appear to be older than they actually are.
A) the Milky Way is at the center of the universe.
B) galaxies can have peculiar velocities that are greater than the speed of light.
C) the density and temperature of the universe must have been higher in the past.
D) it applies only to nearby galaxies within the Local Group.
E) more distant objects appear to be older than they actually are.
the density and temperature of the universe must have been higher in the past.
4
You measure the redshift of a distant galaxy and find, using Hubble's law and assuming a Hubble constant of 70 km/s/Mpc, that its distance is 1 billion ly (310 Mpc).Imagine that an observer in that galaxy is measuring the recession speed of the Milky Way at the same time as your measurement.What would be the speed that the remote alien observer would record?
A) 700 km/s
B) 21,500 km/s
C) 3,400 km/s
D) 10,700 km/s
E) 6,300 km/s
A) 700 km/s
B) 21,500 km/s
C) 3,400 km/s
D) 10,700 km/s
E) 6,300 km/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
An implication of the cosmological principle is that our location in the universe is
A) not special.
B) at the center of the universe.
C) stationary while everything else is moving.
D) near the edge of the universe.
E) something that cannot be determined.
A) not special.
B) at the center of the universe.
C) stationary while everything else is moving.
D) near the edge of the universe.
E) something that cannot be determined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Where in the universe did the Big Bang take place?
A) near the Milky Way Galaxy
B) near the Virgo Cluster
C) near some unknown location on the other side of the universe
D) everywhere in the universe
E) at the center of the universe, not too far from the center of the cosmic background radiation
A) near the Milky Way Galaxy
B) near the Virgo Cluster
C) near some unknown location on the other side of the universe
D) everywhere in the universe
E) at the center of the universe, not too far from the center of the cosmic background radiation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
What do astronomers mean when they say that the universe is isotropic?
A) Faraway parts of the universe look just like nearby parts.
B) All galaxies are spiral galaxies like our own.
C) Intergalactic gas has the same density everywhere in the universe.
D) The laws of physics are different in different places in the universe.
E) The universe looks the same no matter what direction you look.
A) Faraway parts of the universe look just like nearby parts.
B) All galaxies are spiral galaxies like our own.
C) Intergalactic gas has the same density everywhere in the universe.
D) The laws of physics are different in different places in the universe.
E) The universe looks the same no matter what direction you look.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What do astronomers mean when they say that the universe is homogeneous?
A) All stars in all galaxies have planetary systems just like ours.
B) The universe looks exactly the same no matter what direction you look.
C) Galaxies are generally distributed similarly throughout the universe.
D) Generally speaking, there is little difference between conditions on Earth, in the Sun, or in outer space.
E) The universe looks the same at all times in its history.
A) All stars in all galaxies have planetary systems just like ours.
B) The universe looks exactly the same no matter what direction you look.
C) Galaxies are generally distributed similarly throughout the universe.
D) Generally speaking, there is little difference between conditions on Earth, in the Sun, or in outer space.
E) The universe looks the same at all times in its history.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In an imaginary universe, astronomers find that there are thousands of galaxies within a few million light-years in all directions, but beyond those galaxies there is nothing but empty space.Such a universe would be
A) isotropic and homogeneous.
B) isotropic but not homogenous.
C) homogeneous but not isotropic.
D) neither homogeneous nor isotropic.
E) lacking any evidence for the Big Bang.
A) isotropic and homogeneous.
B) isotropic but not homogenous.
C) homogeneous but not isotropic.
D) neither homogeneous nor isotropic.
E) lacking any evidence for the Big Bang.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
If a scientist in the distant Andromeda Galaxy studies the hydrogen gas in that galaxy, they will measure ________ what a scientist in our galaxy would measure, studying hydrogen gas
In the Milky Way.
A) a larger mass per atom than
B) a smaller mass per atom than
C) a different set of spectral lines than
D) different possible chemical bonds with other elements than
E) the same properties as
In the Milky Way.
A) a larger mass per atom than
B) a smaller mass per atom than
C) a different set of spectral lines than
D) different possible chemical bonds with other elements than
E) the same properties as

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If Hubble expansion was due to an explosion throwing galaxies into space, instead of space expanding everywhere, which of the following would be true?
A) The Hubble constant would be zero.
B) The universe would have a measurable center.
C) We would not measure a redshift for distant galaxies.
D) The rate of expansion could not change with time.
E) There would be no new star formation in the modern universe.
A) The Hubble constant would be zero.
B) The universe would have a measurable center.
C) We would not measure a redshift for distant galaxies.
D) The rate of expansion could not change with time.
E) There would be no new star formation in the modern universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
If we lived in a galaxy 1 billion light-years from our own, what would we see?
A) a universe 1 billion years younger than ours
B) a universe 1 billion years older than ours
C) much the same universe as we see here
D) a universe expanding at a slower rate than we see from Earth
E) a universe expanding at a faster rate than we see from Earth
A) a universe 1 billion years younger than ours
B) a universe 1 billion years older than ours
C) much the same universe as we see here
D) a universe expanding at a slower rate than we see from Earth
E) a universe expanding at a faster rate than we see from Earth

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
According to Hubble's law, as the distance of a galaxy ________ its ________ increases.
A) increases; luminosity
B) increases; recessional velocity
C) decreases; luminosity
D) decreases; recessional velocity
E) decreases; peculiar velocity
A) increases; luminosity
B) increases; recessional velocity
C) decreases; luminosity
D) decreases; recessional velocity
E) decreases; peculiar velocity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
All distant galaxies appear to be moving away from us.Does this mean we are in a special place, and why?
A) Yes, it means we are at the center of the universe.
B) Yes, because we are in the newest part of the universe.
C) No, because science does not allow for special places.
D) No, because all observers will see the same phenomenon.
E) Yes, because all other possibilities have been disproven.
A) Yes, it means we are at the center of the universe.
B) Yes, because we are in the newest part of the universe.
C) No, because science does not allow for special places.
D) No, because all observers will see the same phenomenon.
E) Yes, because all other possibilities have been disproven.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Distant Galaxy A has a larger redshift than distant, but otherwise identical, Galaxy B.This means that Galaxy A
A) has a larger look-back time than Galaxy B.
B) appears to be bluer than Galaxy B.
C) appears to be brighter than Galaxy B.
D) is nearer to us than Galaxy B.
E) must be an elliptical-type galaxy if Galaxy B is also an elliptical-type galaxy.
A) has a larger look-back time than Galaxy B.
B) appears to be bluer than Galaxy B.
C) appears to be brighter than Galaxy B.
D) is nearer to us than Galaxy B.
E) must be an elliptical-type galaxy if Galaxy B is also an elliptical-type galaxy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
That "the physical laws and the properties of the universe are the same everywhere and in all directions" is a statement of
A) Hubble's law.
B) the Doppler shift.
C) Big Bang nucleosynthesis.
D) the cosmological principle.
E) Occam's razor.
A) Hubble's law.
B) the Doppler shift.
C) Big Bang nucleosynthesis.
D) the cosmological principle.
E) Occam's razor.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Galaxies move away from us in all directions because
A) the force of gravity increases with distance.
B) the force of gravity weakens with distance.
C) space is expanding, and there is no center to the universe.
D) space is expanding, and we are near (but not at) the center of the universe.
E) we are at the center of the expansion of the universe.
A) the force of gravity increases with distance.
B) the force of gravity weakens with distance.
C) space is expanding, and there is no center to the universe.
D) space is expanding, and we are near (but not at) the center of the universe.
E) we are at the center of the expansion of the universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
As measured from Earth, the spectrum of the galaxy NGC 7512 reveals a receding velocity of about 7,000 km/s.If an observer in that galaxy takes a spectrum of the Milky Way they would
Measure ________.
A) the same 7,000 km/s receding speed
B) only 1,000 km/s, because for that observer the Hubble expansion is a lot slower
C) something that we cannot possibly know, because the known laws of physics apply only within the Milky Way
D) 23,000 km/s, because the speed of light has a different value for that observer
E) no relative motion, because we are in fact measuring Earth's motion about the Sun.
Measure ________.
A) the same 7,000 km/s receding speed
B) only 1,000 km/s, because for that observer the Hubble expansion is a lot slower
C) something that we cannot possibly know, because the known laws of physics apply only within the Milky Way
D) 23,000 km/s, because the speed of light has a different value for that observer
E) no relative motion, because we are in fact measuring Earth's motion about the Sun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Astronomers use galactic redshift as a measure of
A) gravity.
B) luminosity.
C) rotation curves.
D) mass.
E) distance.
A) gravity.
B) luminosity.
C) rotation curves.
D) mass.
E) distance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Hubble's constant, H0, represents the
A) rate of expansion of the universe.
B) speed at which galaxies are moving away from us.
C) time it takes a galaxy to move twice as far away from us.
D) size of the universe.
E) amount of time since the Solar System formed.
A) rate of expansion of the universe.
B) speed at which galaxies are moving away from us.
C) time it takes a galaxy to move twice as far away from us.
D) size of the universe.
E) amount of time since the Solar System formed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Galaxy peculiar velocities are typically about 300 km/s.How far away do you have to look in order to see recessional velocities that are 10 times this peculiar velocity? Note that the Hubble constant has a value of 70 km/s/Mpc.
A) 12 Mpc
B) 25 Mly
C) 37 Mpc
D) 43 Mpc
E) 52 Mpc
A) 12 Mpc
B) 25 Mly
C) 37 Mpc
D) 43 Mpc
E) 52 Mpc

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Cosmological redshift is redshift due to
A) the true velocity of a receding galaxy.
B) the cosmic microwave background radiation.
C) the expansion of the space that light travels through.
D) the higher abundance of hydrogen present in older galaxies.
E) light interacting with dark matter.
A) the true velocity of a receding galaxy.
B) the cosmic microwave background radiation.
C) the expansion of the space that light travels through.
D) the higher abundance of hydrogen present in older galaxies.
E) light interacting with dark matter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
If the distance of a galaxy is 5 Mpc, what is its recessional velocity if the Hubble constant is 70 km/s/Mpc?
A) 70 km/s
B) 100 km/s
C) 350 km/s
D) 500 km/s
E) 700 km/s
A) 70 km/s
B) 100 km/s
C) 350 km/s
D) 500 km/s
E) 700 km/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The inverse of the value of H0 gives a measurement in a unit of
A) time.
B) mass.
C) density.
D) size.
E) luminosity.
A) time.
B) mass.
C) density.
D) size.
E) luminosity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
You observe the following three galaxies and measure their respective recession velocities: A, 2,100 km/s; B, 4,400 km/s; and C, 3,050 km/s.Which of the following must be true about these galaxies?
A) A is smaller than B.
B) A has more star formation than C.
C) B has more stars than C.
D) B is farther away from us than A.
E) They are all members of the Local Group.
A) A is smaller than B.
B) A has more star formation than C.
C) B has more stars than C.
D) B is farther away from us than A.
E) They are all members of the Local Group.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The figure below uses a rubber sheet as an analogy for Hubble expansion, with coins representing galaxies.The illustration demonstrates that 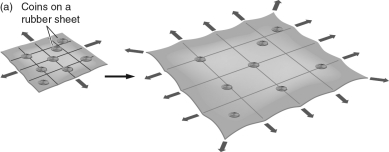
A) galaxies may be sitting still, but will move farther apart as space expands.
B) galaxies stand still, and distances are unchanged by the expanding universe.
C) galaxies are repelled from each other, causing them to move away from each other.
D) space is expanding in two dimensions only.
E) galaxies are being flung outward by the Big Bang.

A) galaxies may be sitting still, but will move farther apart as space expands.
B) galaxies stand still, and distances are unchanged by the expanding universe.
C) galaxies are repelled from each other, causing them to move away from each other.
D) space is expanding in two dimensions only.
E) galaxies are being flung outward by the Big Bang.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Will the increasing scale factor of the universe cause the Sun to get larger over time?
A) Yes, because the scale factor will change the rate of fusion in the Sun's core.
B) Yes, because the atoms within the Sun will all expand individually.
C) No, because Earth is at center of the universe's expansion.
D) Yes, because the expansion of the universe will directly cause the Sun to expand.
E) No, because the Sun's self-gravity locally dominates over the expansion of the universe.
A) Yes, because the scale factor will change the rate of fusion in the Sun's core.
B) Yes, because the atoms within the Sun will all expand individually.
C) No, because Earth is at center of the universe's expansion.
D) Yes, because the expansion of the universe will directly cause the Sun to expand.
E) No, because the Sun's self-gravity locally dominates over the expansion of the universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The majority of the redshift that we measure from the most distant galaxies is due to
A) excess hydrogen emission.
B) most of these galaxies being old, elliptical-type galaxies.
C) the expansion of the universe "stretching" the wavelengths of photons.
D) the cosmic microwave background.
E) the actual velocity of that galaxy.
A) excess hydrogen emission.
B) most of these galaxies being old, elliptical-type galaxies.
C) the expansion of the universe "stretching" the wavelengths of photons.
D) the cosmic microwave background.
E) the actual velocity of that galaxy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
What would you predict for the recession velocity of a galaxy whose distance (measured with the help of Type Ia supernovae) is 42 Mpc? Note that the Hubble constant has a value of
70 km/s/Mpc.
A) 2,940 km/s
B) 1.42 km/s
C) 205,800 km/s
D) 25,000 km/s
E) 386 km/s
70 km/s/Mpc.
A) 2,940 km/s
B) 1.42 km/s
C) 205,800 km/s
D) 25,000 km/s
E) 386 km/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The apparent recessional velocities of galaxies at large distances are due mainly to
A) the actual motions of the galaxies through space.
B) the motion of our Sun around the galactic center.
C) a continuously increasing scaling factor of the universe.
D) the relativistic jets launched by supermassive black holes.
E) incorrect interpretation of spectra from galaxies.
A) the actual motions of the galaxies through space.
B) the motion of our Sun around the galactic center.
C) a continuously increasing scaling factor of the universe.
D) the relativistic jets launched by supermassive black holes.
E) incorrect interpretation of spectra from galaxies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Two galaxies are currently separated by 55 Mpc.Roughly how long did it take for them to reach this separation?
A) 13.7 billion years
B) 250 million years
C) 4.6 billion years
D) less than a second
E) 27 billion years
A) 13.7 billion years
B) 250 million years
C) 4.6 billion years
D) less than a second
E) 27 billion years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
If we "reverse" Hubble expansion, we see that the universe should have been very dense in the distant past, and so it must have been ________ than it is today, and we should be able to
Observe ________ as a result.
A) much colder; cosmological redshift
B) much colder; the cosmic microwave background
C) much hotter; gravitational redshift
D) much hotter; the cosmic microwave background
E) much hotter; black holes
Observe ________ as a result.
A) much colder; cosmological redshift
B) much colder; the cosmic microwave background
C) much hotter; gravitational redshift
D) much hotter; the cosmic microwave background
E) much hotter; black holes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If a galaxy has an apparent velocity of 700 km/s, what is its distance if the Hubble constant is 70 km/s/Mpc?
A) 1 Mpc
B) 7 Mpc
C) 10 Mpc
D) 70 Mpc
E) 100 Mpc
A) 1 Mpc
B) 7 Mpc
C) 10 Mpc
D) 70 Mpc
E) 100 Mpc

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
In the figure below, three identical photons were each emitted when their local scale factor was RU =0.5.Each is then measured after the scale factor of the universe changes to a different amount, as shown.Which photon will be measured to have the greatest energy? 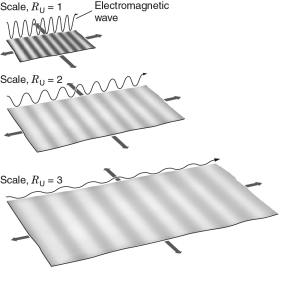
A) the one at RU =1
B) the one at RU = 2
C) the one at RU =3
D) The photons at RU= 2 and 3 will have identical energy.
E) All three will have the same energy.

A) the one at RU =1
B) the one at RU = 2
C) the one at RU =3
D) The photons at RU= 2 and 3 will have identical energy.
E) All three will have the same energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
If the slope of the graph v vs.D is Ho, the slope of the D vs.v graph is the
A) age of the universe.
B) cosmological constant.
C) scaling factor of the universe.
D) temperature of the CMB.
E) amount of dark energy in the universe.
A) age of the universe.
B) cosmological constant.
C) scaling factor of the universe.
D) temperature of the CMB.
E) amount of dark energy in the universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Hubble originally estimated the "Hubble constant" to be about 500 km/s/Mpc.What age of the universe would such a number imply?
A) 2 billion years
B) 13.8 billion years
C) 16 billion years
D) 250 million years
E) 500 million years
A) 2 billion years
B) 13.8 billion years
C) 16 billion years
D) 250 million years
E) 500 million years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
In the figure below, three identical photons were each emitted when their local scale factor was RU = 0.5.Each is then measured after the scale factor of the universe changes to a different amount, as shown.Which photon will be measured to have the greatest cosmological redshift? 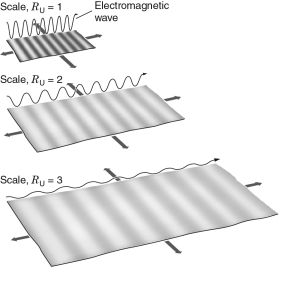
A) the one at RU =1
B) the one at RU = 2
C) the one at RU = 3
D) The photons at RU = 2 and 3 will be identical, and have the greatest redshift.
E) All three will have the same cosmological redshift.

A) the one at RU =1
B) the one at RU = 2
C) the one at RU = 3
D) The photons at RU = 2 and 3 will be identical, and have the greatest redshift.
E) All three will have the same cosmological redshift.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The high temperature and density of the early universe are directly responsible for
A) the expansion of the universe.
B) the cosmic microwave background.
C) star formation.
D) cosmological redshift.
E) nucleosynthesis of the heaviest elements.
A) the expansion of the universe.
B) the cosmic microwave background.
C) star formation.
D) cosmological redshift.
E) nucleosynthesis of the heaviest elements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If you measured the distances and recessional velocities for a sample of galaxies and plotted the data to get the figure shown below, what value would you derive for the Hubble constant? 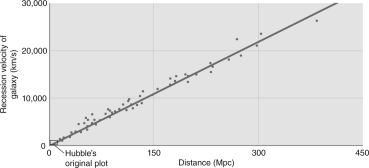
A) 10 km/s/Mpc
B) 50 km/s/Mpc
C) 70 km/s/Mpc
D) 100 km/s/Mpc
E) 500 km/s/Mpc

A) 10 km/s/Mpc
B) 50 km/s/Mpc
C) 70 km/s/Mpc
D) 100 km/s/Mpc
E) 500 km/s/Mpc

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
If the Hubble constant had a value that was half of its current measured value of 70 km/s/Mpc, the age of the universe would be about
A) 7 billion years.
B) 14 billion years.
C) 22 billion years.
D) 28 billion years.
E) 33 billion years.
A) 7 billion years.
B) 14 billion years.
C) 22 billion years.
D) 28 billion years.
E) 33 billion years.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The CMB can be regarded as a "wall" beyond which we cannot see light because
A) photons couldn't leave the hot plasma before the recombination period.
B) we haven't discovered the technology to detect light from earlier epochs.
C) galaxies absorb all the photons from earliest times, closer to the Big Bang.
D) there existed only massive particles within the universe in the first 380,000 years of existence; there were no photons.
E) behind the CMB "wall" there is a huge black hole that doesn't allow light to escape.
A) photons couldn't leave the hot plasma before the recombination period.
B) we haven't discovered the technology to detect light from earlier epochs.
C) galaxies absorb all the photons from earliest times, closer to the Big Bang.
D) there existed only massive particles within the universe in the first 380,000 years of existence; there were no photons.
E) behind the CMB "wall" there is a huge black hole that doesn't allow light to escape.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
If the wavelength of the background radiation peaked at 1 µm at the time of recombination, how old was the universe then compared with its age today?
A) one second old
B) 1/100th of a second old
C) 1/1,000th of a year old
D) 3,000 years old
E) several hundred thousand years old
A) one second old
B) 1/100th of a second old
C) 1/1,000th of a year old
D) 3,000 years old
E) several hundred thousand years old

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In the early 1960s, physicists Penzias and Wilson detected a persistent noise at a wavelength of about 1 mm in their radio telescope that came from all directions in the sky due to
A) synchrotron emission from the Crab Nebula.
B) emission from newly formed stars in the Orion Nebula.
C) cellphone usage.
D) photons left over from the Big Bang.
E) television and radio broadcasting.
A) synchrotron emission from the Crab Nebula.
B) emission from newly formed stars in the Orion Nebula.
C) cellphone usage.
D) photons left over from the Big Bang.
E) television and radio broadcasting.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
What is the correct interpretation of a redshift larger than 1?
A) The object is moving faster than the speed of light.
B) The universe's scale factor universe has more than doubled in size since the light from that object was emitted.
C) The object has an extremely large peculiar velocity.
D) The light was shifted to longer wavelengths from gravitational radiation.
E) The rate of expansion of the universe is increasing.
A) The object is moving faster than the speed of light.
B) The universe's scale factor universe has more than doubled in size since the light from that object was emitted.
C) The object has an extremely large peculiar velocity.
D) The light was shifted to longer wavelengths from gravitational radiation.
E) The rate of expansion of the universe is increasing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The CMB fluctuations seen in the WMAP temperature distribution measures are of crucial importance in that
A) they prove that the cosmological principle is incorrect; the universe is in fact anisotropic.
B) they reveal the signatures of the large mass concentrations where subsequent galaxies and clusters of galaxies formed.
C) they reveal the technical limitation of the detectors on board the WMAP satellite.
D) they give us clues about the black-hole evaporation happening in the early universe.
E) they emphasize the limited value of general relativity.
A) they prove that the cosmological principle is incorrect; the universe is in fact anisotropic.
B) they reveal the signatures of the large mass concentrations where subsequent galaxies and clusters of galaxies formed.
C) they reveal the technical limitation of the detectors on board the WMAP satellite.
D) they give us clues about the black-hole evaporation happening in the early universe.
E) they emphasize the limited value of general relativity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A galaxy is measured to have a redshift of z = 5.0.This galaxy is
A) filled with very cold gas.
B) moving at 5 times the speed of light.
C) dominated by gravitational redshift due to its supermassive black hole.
D) dominated by older, redder stars.
E) so far away that cosmological redshift dominates our observation.
A) filled with very cold gas.
B) moving at 5 times the speed of light.
C) dominated by gravitational redshift due to its supermassive black hole.
D) dominated by older, redder stars.
E) so far away that cosmological redshift dominates our observation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The COBE microwave map shown in the figure below seems to indicate that one part of the sky is 0.003 K warmer than the other.What is the cause of such an apparent anisotropy? 
A) Earth and the Sun are moving at 368 km/s relative to the CMB reference frame.
B) The map was obtained when the Sun was at its peak of activity within a given 11-year cycle.
C) It is due to interference from the many microwave ovens people use in homes.
D) The boundaries between the warmer and cooler areas are sites of strong supernova activity.
E) It indicates that galaxies could form in only half of the universe.

A) Earth and the Sun are moving at 368 km/s relative to the CMB reference frame.
B) The map was obtained when the Sun was at its peak of activity within a given 11-year cycle.
C) It is due to interference from the many microwave ovens people use in homes.
D) The boundaries between the warmer and cooler areas are sites of strong supernova activity.
E) It indicates that galaxies could form in only half of the universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The cosmic microwave background radiation was emitted when the universe had a size about 1/1,000 of today's value.What was the temperature of the microwave background radiation at the epoch of recombination?
A) 30 K
B) 300 K
C) 3000 K
D) 30,000 K
E) 300,000 K
A) 30 K
B) 300 K
C) 3000 K
D) 30,000 K
E) 300,000 K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Redshift z = vr/c, where vr is the apparent recessional velocity, and c is the speed of light.Is it possible to observe a redshift greater than 1.0, or lower than=1.0?
A) Neither is possible.
B) Yes, it is possible to measure both.
C) It is possible to measure z -1.0, but not z 1.0.
D) It is possible to measure z 1.0, but not z -1.0.
E) Redshifts greater than 1.0 and less than -1.0 are the only possible redshifts.
A) Neither is possible.
B) Yes, it is possible to measure both.
C) It is possible to measure z -1.0, but not z 1.0.
D) It is possible to measure z 1.0, but not z -1.0.
E) Redshifts greater than 1.0 and less than -1.0 are the only possible redshifts.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following would be the oldest?
A) a 4000 K white dwarf
B) the Sun
C) the CMB
D) a 20-solar mass main-sequence star
E) a halo star with 1/250 heavy-element abundance relative to the Sun's
A) a 4000 K white dwarf
B) the Sun
C) the CMB
D) a 20-solar mass main-sequence star
E) a halo star with 1/250 heavy-element abundance relative to the Sun's

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The existence of the cosmic background radiation tells us that the early universe was
A) much hotter than it is today.
B) much colder than it is today.
C) composed entirely of radiation at early times.
D) composed entirely of stars at early times.
E) about the same temperature as today but much more dense.
A) much hotter than it is today.
B) much colder than it is today.
C) composed entirely of radiation at early times.
D) composed entirely of stars at early times.
E) about the same temperature as today but much more dense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The oldest photons we detect in the universe come from
A) distant quasars.
B) the first generations of stars.
C) the most distant galaxies.
D) the epoch of recombination.
E) the first supernovae.
A) distant quasars.
B) the first generations of stars.
C) the most distant galaxies.
D) the epoch of recombination.
E) the first supernovae.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Why is it not possible to look all the way back to the Big Bang itself?
A) Photons are not produced until the stars begin to shine at a redshift of z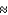 20.
20.
B) From redshifts of z=0 to 100, photons are gravitationally lensed by the dark matter in the universe.
C) At redshifts of z 1,000, most of the photons are blocked by large amounts of cold gas and dust.
D) For redshifts of z 1,000, photons cannot travel freely because they easily interact with individual protons and electrons in the universe.
E) Photons from the Big Bang would be so strongly redshifted that we could never detect them.
A) Photons are not produced until the stars begin to shine at a redshift of z
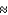 20.
20.B) From redshifts of z=0 to 100, photons are gravitationally lensed by the dark matter in the universe.
C) At redshifts of z 1,000, most of the photons are blocked by large amounts of cold gas and dust.
D) For redshifts of z 1,000, photons cannot travel freely because they easily interact with individual protons and electrons in the universe.
E) Photons from the Big Bang would be so strongly redshifted that we could never detect them.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The temperature of the CMB is hotter on one side of the sky than on the other by approximately 3 milliKelvin.What does this tell us?
A) The true center of the universe is in the direction of the hotter side of the CMB.
B) Earth is moving with respect to the CMB.
C) Earth is near the center of the universe's expansion but not exactly at the middle.
D) The universe is expanding faster on one side of us than on the other.
E) The universe is homogeneous but not isotropic.
A) The true center of the universe is in the direction of the hotter side of the CMB.
B) Earth is moving with respect to the CMB.
C) Earth is near the center of the universe's expansion but not exactly at the middle.
D) The universe is expanding faster on one side of us than on the other.
E) The universe is homogeneous but not isotropic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The current temperature of the cosmic background radiation of 2.73 K means that the peak of its spectrum occurs at a wavelength of
A) 0.1 µm.
B) 1 µm.
C) 10 µm.
D) 100 µm.
E) 1,000 µm.
A) 0.1 µm.
B) 1 µm.
C) 10 µm.
D) 100 µm.
E) 1,000 µm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The CMB fluctuations of 0.001 percent seen in the WMAP sky map are due to
A) gravitational redshifts.
B) technical artifacts.
C) faulty instrumentation.
D) Hubble expansion.
E) explosive supernovae.
A) gravitational redshifts.
B) technical artifacts.
C) faulty instrumentation.
D) Hubble expansion.
E) explosive supernovae.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
It is possible for a galaxy to have an apparent velocity greater than the speed of light.This means that the galaxy
A) has an active nucleus capable of producing relativistic jets.
B) is approaching us and the measured speed is a mere artifact of projecting its velocity along the line of sight.
C) has been ejected at tremendous speed by the Big Bang.
D) is being temporarily accelerated by large numbers of simultaneous supernovae blasts.
E) is being carried by the expansion of the universe.
A) has an active nucleus capable of producing relativistic jets.
B) is approaching us and the measured speed is a mere artifact of projecting its velocity along the line of sight.
C) has been ejected at tremendous speed by the Big Bang.
D) is being temporarily accelerated by large numbers of simultaneous supernovae blasts.
E) is being carried by the expansion of the universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
After the Big Bang, as the universe cooled and protons and electrons combined, what important consequence happened?
A) Protons and neutrons combined to form nuclei such as deuterium and helium.
B) Neutrinos ceased to interact with normal matter.
C) Dark matter ceased to interact with normal matter.
D) Photons began to travel freely through the universe.
E) Lithium and other light elements were formed by the fusion of hydrogen and helium.
A) Protons and neutrons combined to form nuclei such as deuterium and helium.
B) Neutrinos ceased to interact with normal matter.
C) Dark matter ceased to interact with normal matter.
D) Photons began to travel freely through the universe.
E) Lithium and other light elements were formed by the fusion of hydrogen and helium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The CMB spectrum shown in the figure below is 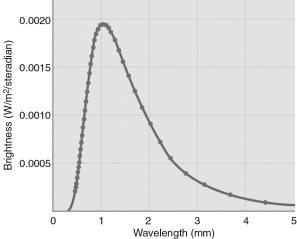
A) an absorption line spectrum.
B) an emission line spectrum.
C) a thermal spectrum.
D) identical to the spectrum of our Sun.
E) blueshifted into the microwaves domain.

A) an absorption line spectrum.
B) an emission line spectrum.
C) a thermal spectrum.
D) identical to the spectrum of our Sun.
E) blueshifted into the microwaves domain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The apparently "grainy" CMB distribution shown in the WMAP in the figure below represents temperature fluctuations of about 
A) 0.001 percent.
B) 0.1 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 50 percent.
E) 27.4 percent.

A) 0.001 percent.
B) 0.1 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 50 percent.
E) 27.4 percent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A recent record for the most distant galaxy yet discovered was held by a galaxy that has a redshift of z =8.68.Compared with the current scale factor of the universe, what was the scale factor when the light from that galaxy started its long journey to us?
A) about 10 times smaller
B) about 50 percent smaller
C) about 0.001 percent smaller
D) about 99 percent smaller
E) about 250 percent bigger
A) about 10 times smaller
B) about 50 percent smaller
C) about 0.001 percent smaller
D) about 99 percent smaller
E) about 250 percent bigger

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The natural abundances of various forms of the elements hydrogen, helium, and lithium are predicted by
A) Einstein's special theory of relativity.
B) Einstein's general theory of relativity.
C) the cosmological principle.
D) Hubble expansion.
E) the Big Bang theory.
A) Einstein's special theory of relativity.
B) Einstein's general theory of relativity.
C) the cosmological principle.
D) Hubble expansion.
E) the Big Bang theory.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Describe the two assumptions regarding the universe that are made by the cosmological principle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The CMB is a snapshot of the radiation in the universe at a redshift of z 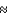 1,000 when the universe was about
1,000 when the universe was about
A) 1,000 times smaller than it is today.
B) 10 times smaller than it is today.
C) 2 times smaller than it is today.
D) the same size as it is today.
E) 10 times larger than it is today.
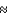 1,000 when the universe was about
1,000 when the universe was aboutA) 1,000 times smaller than it is today.
B) 10 times smaller than it is today.
C) 2 times smaller than it is today.
D) the same size as it is today.
E) 10 times larger than it is today.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Provide an example of something that is homogenous but not isotropic.You may use an imaginary (but clear) situation, if desired.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Employing Hubble's law, calculate the distance to the Andromeda Galaxy, which is approaching at
110 km/s.The directly measured distance to Andromeda is 2.5 million light-years.How do the two numbers agree or disagree? Explain.
110 km/s.The directly measured distance to Andromeda is 2.5 million light-years.How do the two numbers agree or disagree? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Where did the Big Bang occur? Explain your reasoning.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
We see the universe around us expanding at 70 km/s/Mpc, a rate given by the Hubble constant.If you were an astronomer living today in a galaxy that was located 1 billion light-years from the Milky Way, what would you measure for your Hubble constant?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Imagine a balloon that you can inflate to visualize the expansion of the universe.Space is symbolized by the surface of the balloon.You use a marker to draw galaxies on its outside surface, and you start inflating the balloon.Name at least one aspect of this model that is analogous to the real expansion of the universe, and at least one aspect that is not analogous.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Explain how Hubble's law can be used to infer the temperatures and densities of the universe in the past.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Scientists indicate that the first stars probably formed at a redshift z ~ 20.At that time the universe was about
A) 5 percent its current size.
B) 50 percent of Earth's size.
C) as big as an atom.
D) about 100 AU across.
E) the size of a grapefruit.
A) 5 percent its current size.
B) 50 percent of Earth's size.
C) as big as an atom.
D) about 100 AU across.
E) the size of a grapefruit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Does the expansion of the universe make the Sun bigger? What about the Milky Way? Why or why not?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Explain the difference between the universe and the observable universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Does Hubble's law imply that our galaxy is sitting at the center of the universe? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Why did Big Bang nucleosynthesis only produce elements less massive than beryllium?
A) The laws of physics do not allow the formation of massive nuclei outside stars.
B) The universe was never hot enough for nucleosynthesis by fusion before stars formed.
C) There was no black hole to provide sufficient energy for advanced nucleosynthesis.
D) The universe expanded and cooled rapidly.
E) More massive elements did form, but they decayed very rapidly into lighter ones.
A) The laws of physics do not allow the formation of massive nuclei outside stars.
B) The universe was never hot enough for nucleosynthesis by fusion before stars formed.
C) There was no black hole to provide sufficient energy for advanced nucleosynthesis.
D) The universe expanded and cooled rapidly.
E) More massive elements did form, but they decayed very rapidly into lighter ones.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Distant galaxies we can see today with a redshift of z 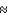 6 emitted their light when the universe was
6 emitted their light when the universe was
A) 5 times smaller than it is today.
B) 6 times smaller than it is today.
C) 7 times smaller than it is today.
D) 8 times smaller than it is today.
E) the same size as it is today.
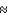 6 emitted their light when the universe was
6 emitted their light when the universe wasA) 5 times smaller than it is today.
B) 6 times smaller than it is today.
C) 7 times smaller than it is today.
D) 8 times smaller than it is today.
E) the same size as it is today.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
When we look at galaxies in the universe and measure their star formation rates, we find that galaxies at redshifts z 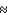 1 have higher star formation rates than they do now.At that time, the universe was ________ times the size it is today.
1 have higher star formation rates than they do now.At that time, the universe was ________ times the size it is today.
A) 0.1
B) 0.2
C) 0.5
D) 0.7
E) 0.9
 1 have higher star formation rates than they do now.At that time, the universe was ________ times the size it is today.
1 have higher star formation rates than they do now.At that time, the universe was ________ times the size it is today.A) 0.1
B) 0.2
C) 0.5
D) 0.7
E) 0.9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Movies and television shows often portray the Big Bang as a tiny bright spot that loudly explodes to fill the screen.Why is this depiction inaccurate?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Prior to detailed studies of the cosmic microwave background, the age of the universe was poorly known.The age of the universe was thought to be around 16 billion years.If the universe were 16 billion years old, what would be the value of the Hubble constant, assuming constant expansion? Note that 1 Mpc = 3.086 * 1019 km and 1 year= 3.154 *107 s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Galaxies with redshifts greater than 1 ________ moving greater than the speed of light due to ________.
A) appear to be; cosmological redshift
B) appear to be; hydrogen absorption
C) appear to be; gravitational redshift
D) are actually; leftover inertia from the Big Bang
E) are actually; a poorly understood repulsive force
A) appear to be; cosmological redshift
B) appear to be; hydrogen absorption
C) appear to be; gravitational redshift
D) are actually; leftover inertia from the Big Bang
E) are actually; a poorly understood repulsive force

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 98 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








