Deck 13: Reaction Rates Equilibrium
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Reaction Rates Equilibrium
1
In the diagram, the number 1 corresponds to the: 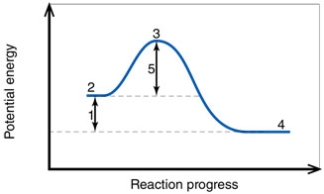
A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.
net energy change.
2
In the diagram, the activation energy of the FORWARD reaction is about: 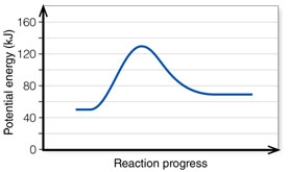
A) 60 kJ.
B) 130 kJ.
C) 80 kJ.
D) 20 kJ.

A) 60 kJ.
B) 130 kJ.
C) 80 kJ.
D) 20 kJ.
80 kJ.
3
In the diagram, the forward reaction will probably not proceed without an input of energy because the: 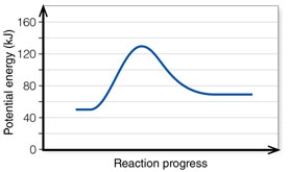
A) activation energy is too high.
B) net energy change is too low.
C) products are too far apart from the reactants.
D) reactant energy is too high to start with.

A) activation energy is too high.
B) net energy change is too low.
C) products are too far apart from the reactants.
D) reactant energy is too high to start with.
activation energy is too high.
4
In the diagram, the number 3 corresponds to the: 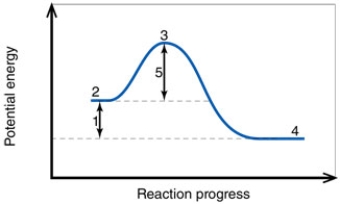
A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which factor tends to increase the rate of a reaction?
A) Decreasing the temperature
B) Decreasing the concentration of the reactants
C) Increasing the concentration of the reactants
D) Increasing the activation energy of the reaction
A) Decreasing the temperature
B) Decreasing the concentration of the reactants
C) Increasing the concentration of the reactants
D) Increasing the activation energy of the reaction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In the diagram, the energy of the transition state is about: 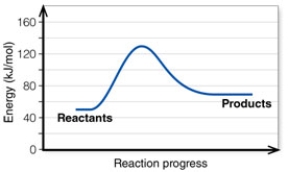
A) 50 kJ/mol.
B) 130 kJ/mol.
C) 80 kJ/mol.
D) 20 kJ/mol.

A) 50 kJ/mol.
B) 130 kJ/mol.
C) 80 kJ/mol.
D) 20 kJ/mol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
In the diagram, how do the concentrations of the reactants and products compare at equilibrium as a general rule? 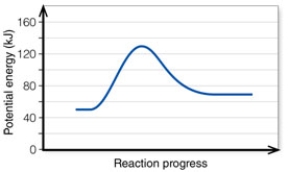
A) They are equal.
B) The reactant concentration is greater than that of the product.
C) The product concentration is greater than that of the reactant.

A) They are equal.
B) The reactant concentration is greater than that of the product.
C) The product concentration is greater than that of the reactant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Chemical reactions occur when molecules, atoms, or ions collide. However, not every collision results in a reaction. In order for a reaction to occur,
A) the molecules must be big enough.
B) the energy of the molecules is not important, but the molecules must collide at the correct orientation.
C) the molecules must have enough kinetic energy and collide at the correct orientation.
D) the molecules must be moving slowly enough to interact, and must be rotating in opposite directions.
A) the molecules must be big enough.
B) the energy of the molecules is not important, but the molecules must collide at the correct orientation.
C) the molecules must have enough kinetic energy and collide at the correct orientation.
D) the molecules must be moving slowly enough to interact, and must be rotating in opposite directions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In the diagram, the FORWARD reaction is: 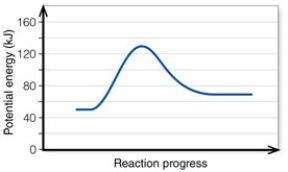
A) endothermic.
B) exothermic.
C) exergetic.
D) ergonomic.

A) endothermic.
B) exothermic.
C) exergetic.
D) ergonomic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which statement correctly describes reaction rates?
A) Decreasing the reactant concentration will increase reaction rate because, if there are fewer particles, there is more room to collide.
B) Decreasing the temperature will increase reaction rate because, if the particles are moving faster, there will be fewer collisions.
C) Both decreasing the reactant concentration and decreasing the temperature will increase reaction rate.
D) Neither decreasing the reactant concentration nor decreasing the temperature will increase reaction rate.
A) Decreasing the reactant concentration will increase reaction rate because, if there are fewer particles, there is more room to collide.
B) Decreasing the temperature will increase reaction rate because, if the particles are moving faster, there will be fewer collisions.
C) Both decreasing the reactant concentration and decreasing the temperature will increase reaction rate.
D) Neither decreasing the reactant concentration nor decreasing the temperature will increase reaction rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In the diagram, the net energy change is about: 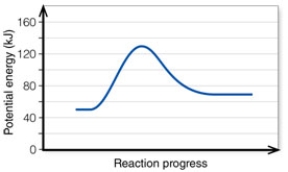
A) 60 kJ.
B) 130 kJ.
C) 80 kJ.
D) 20 kJ.

A) 60 kJ.
B) 130 kJ.
C) 80 kJ.
D) 20 kJ.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In the diagram, the reaction described is _____ and the equilibrium favors the _____. 
A) endothermic; reactants
B) endothermic; products
C) exothermic; reactants
D) exothermic; products

A) endothermic; reactants
B) endothermic; products
C) exothermic; reactants
D) exothermic; products

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In the diagram, the number 2 corresponds to the: 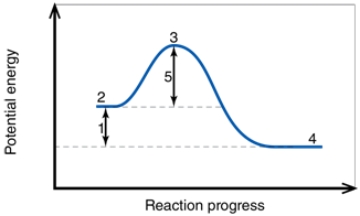
A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
In the diagram, the number 5 corresponds to the: 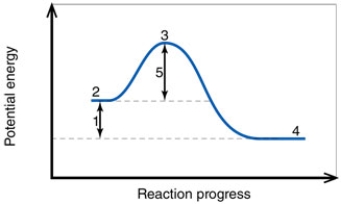
A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In the diagram, the activation energy of the REVERSE reaction is about: 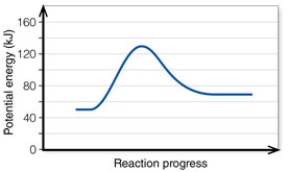
A) 50 kJ.
B) 130 kJ.
C) 80 kJ.
D) 60 kJ.

A) 50 kJ.
B) 130 kJ.
C) 80 kJ.
D) 60 kJ.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which statement correctly describes reaction rates?
A) Decreasing the reactant concentration will decrease reaction rate because, if there are fewer particles, there will be fewer collisions.
B) Increasing the temperature will decrease reaction rate because, if the particles are moving faster, there will be fewer collisions.
C) Both decreasing the reactant concentration and increasing the temperature will decrease reaction rate.
D) Neither decreasing the reactant concentration nor increasing the temperature will decrease reaction rate.
A) Decreasing the reactant concentration will decrease reaction rate because, if there are fewer particles, there will be fewer collisions.
B) Increasing the temperature will decrease reaction rate because, if the particles are moving faster, there will be fewer collisions.
C) Both decreasing the reactant concentration and increasing the temperature will decrease reaction rate.
D) Neither decreasing the reactant concentration nor increasing the temperature will decrease reaction rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which factor does NOT affect the rate of a reaction?
A) Temperature
B) Concentration
C) Activation energy
D) Formula mass
A) Temperature
B) Concentration
C) Activation energy
D) Formula mass

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In the diagram, the number 4 corresponds to the: 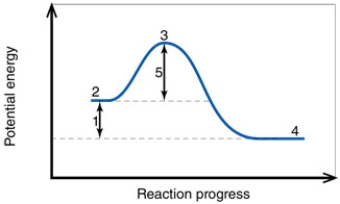
A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

A) reactants.
B) products.
C) activation energy.
D) transition state.
E) net energy change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which factor tends to increase rate of a reaction?
A) Increasing the temperature
B) Decreasing the concentration of the reactants
C) Increasing the concentration of the products
D) The presence of a noble gas
A) Increasing the temperature
B) Decreasing the concentration of the reactants
C) Increasing the concentration of the products
D) The presence of a noble gas

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
When a chemical reaction is at equilibrium, which statement is TRUE, by definition?
A) The concentrations of the reactants and of the products are equal.
B) The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
C) All reactants have been converted to products.
D) Both the forward and reverse reactions cease.
A) The concentrations of the reactants and of the products are equal.
B) The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
C) All reactants have been converted to products.
D) Both the forward and reverse reactions cease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Given the following equation and equilibrium concentrations, determine the value of the equilibrium constant.
PCl5 (g) PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
[PCl5] = 5.30 M; [PCl3] = 0.406 M; [Cl2] = 0.406 M
A) 32.2
B) 0.0311
C) 6.52
D) 0.153
PCl5 (g) PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
[PCl5] = 5.30 M; [PCl3] = 0.406 M; [Cl2] = 0.406 M
A) 32.2
B) 0.0311
C) 6.52
D) 0.153

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The equilibrium expression of the following reaction is represented by:
2 CO2 (g) 2 CO (g) + O2 (g)
A)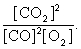
B)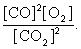
C)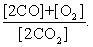
D)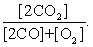
2 CO2 (g) 2 CO (g) + O2 (g)
A)
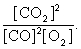
B)
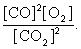
C)
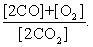
D)
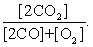

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The symbol used to represent the equilibrium solubility of a slightly soluble compound in water is:
A) Ka.
B) Kb.
C) Ks.
D) Ksp.
A) Ka.
B) Kb.
C) Ks.
D) Ksp.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Cyanic acid, HOCN, ionizes in water to produce the hydronium ion, H3O+, and the cyanate ion, OCN-: HOCN (aq) + H2O (l) H3O+ (aq) + OCN- (aq) K = 3.5 × 10-4
If [H3O+] = 7.3 × 10-4 M and [OCN-] = 7.3 × 10-4 M, what is the value of the acid concentration, [HOCN]?
A) 1.5 × 10-3 M
B) 660 M
C) 0.48 M
D) 2.1 M
If [H3O+] = 7.3 × 10-4 M and [OCN-] = 7.3 × 10-4 M, what is the value of the acid concentration, [HOCN]?
A) 1.5 × 10-3 M
B) 660 M
C) 0.48 M
D) 2.1 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
In a saturated solution of cobalt(II) carbonate, CoCO3, both [Co2+] and [CO32-] = 3.7 × 10-7 M. Calculate the value of the solubility product for this compound.
A) 1.4 × 10-13
B) 6.1 × 10-4
C) 7.4 × 10-7
D) 1.9 × 10-7
A) 1.4 × 10-13
B) 6.1 × 10-4
C) 7.4 × 10-7
D) 1.9 × 10-7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Given the following equation and equilibrium concentrations, determine the value of the equilibrium constant.
2 NO2 N2O4 (g)
[NO2] = 0.579 M; [N2O4] = 0.234 M
A) 0.698
B) 1.43
C) 0.404
D) 2.47
2 NO2 N2O4 (g)
[NO2] = 0.579 M; [N2O4] = 0.234 M
A) 0.698
B) 1.43
C) 0.404
D) 2.47

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Write the solubility product expression for the following solubility equilibrium: BaSO4 (s) Ba2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq)
A)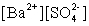
B)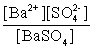
C)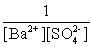
D)
A)
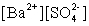
B)
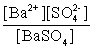
C)
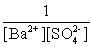
D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following K values indicates a reaction that most favors the reactants?
A) 1 × 10-2
B) 1 × 102
C) 1 × 10-11
D) 1 × 1011
A) 1 × 10-2
B) 1 × 102
C) 1 × 10-11
D) 1 × 1011

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
According to Le Châtelier's principle:
A) equilibrium cannot be established without a change in temperature or pressure.
B) equilibrium will be established quickly if there is no disturbance in temperature or pressure.
C) when a disturbance occurs to a system at equilibrium, a new equilibrium constant will be established.
D) when a disturbance occurs to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift to minimize the disturbance.
A) equilibrium cannot be established without a change in temperature or pressure.
B) equilibrium will be established quickly if there is no disturbance in temperature or pressure.
C) when a disturbance occurs to a system at equilibrium, a new equilibrium constant will be established.
D) when a disturbance occurs to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift to minimize the disturbance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Consider the equilibrium reaction between the gas phases of hydrogen and bromine: H2 (g) + Br2 (g) 2 HBr (g)
If the partial pressures of hydrogen and of bromine are 0.016 atm each, what is the partial pressure of HBr if K = 2.2 × 103?
A) 0.75 atm
B) 0.56 atm
C) 8.6 × 106 atm
D) 2.9 × 103 atm
If the partial pressures of hydrogen and of bromine are 0.016 atm each, what is the partial pressure of HBr if K = 2.2 × 103?
A) 0.75 atm
B) 0.56 atm
C) 8.6 × 106 atm
D) 2.9 × 103 atm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
In a saturated solution of aluminum phosphate, AlPO4, both [Al3+] and [PO43-] = 7.9 × 10-10 M. Calculate the value of the solubility product for this compound.
A) 6.2 × 10-19
B) 2.8 × 10-5
C) 1.6 × 10-9
D) 4.0 × 10-10
A) 6.2 × 10-19
B) 2.8 × 10-5
C) 1.6 × 10-9
D) 4.0 × 10-10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which K value indicates a reaction that MOST favors the products?
A) 1 × 10-2
B) 1 × 102
C) 1 × 10-11
D) 1 × 1011
A) 1 × 10-2
B) 1 × 102
C) 1 × 10-11
D) 1 × 1011

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The equilibrium expression of the following reaction is represented by:
2 CO (g) + O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g)
A)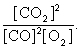
B)
C)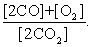
D)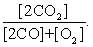
2 CO (g) + O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g)
A)
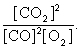
B)

C)
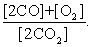
D)
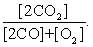

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Considering the solubility product values for the following carbonates, which is the MOST soluble?
A) CuCO3Ksp = 1.4 × 10-10
B) FeCO3 Ksp = 3.2 × 10-11
C) PbCO3Ksp = 7.4 × 10-14
D) MgCO3Ksp = 3.5 × 10-8
A) CuCO3Ksp = 1.4 × 10-10
B) FeCO3 Ksp = 3.2 × 10-11
C) PbCO3Ksp = 7.4 × 10-14
D) MgCO3Ksp = 3.5 × 10-8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Write the solubility product expression for the following solubility equilibrium: CuOH (s) Cu+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
A)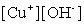
B)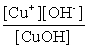
C)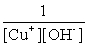
D)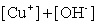
A)
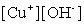
B)
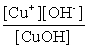
C)
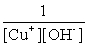
D)
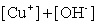

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Consider the equilibrium reaction between the gas phases of hydrogen and iodine: H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g)
If the partial pressures of hydrogen and of iodine are 0.42 atm each, what is the partial pressure of HI if K = 7.1 × 102?
A) 11 atm
B) 63 atm
C) 125 atm
D) 2.5 × 10-4 atm
If the partial pressures of hydrogen and of iodine are 0.42 atm each, what is the partial pressure of HI if K = 7.1 × 102?
A) 11 atm
B) 63 atm
C) 125 atm
D) 2.5 × 10-4 atm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Considering the solubility product values for the following carbonates, which is the LEAST soluble?
A) CuCO3Ksp = 1.4 × 10-10
B) FeCO3 Ksp = 3.2 × 10-11
C) PbCO3Ksp = 7.4 × 10-14
D) MgCO3Ksp = 3.5 × 10-8
A) CuCO3Ksp = 1.4 × 10-10
B) FeCO3 Ksp = 3.2 × 10-11
C) PbCO3Ksp = 7.4 × 10-14
D) MgCO3Ksp = 3.5 × 10-8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The equilibrium expression of the following reaction is represented by:
H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g)
A)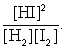
B)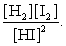
C)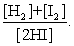
D)
H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g)
A)
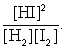
B)
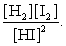
C)
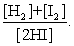
D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If an acetic acid, HC2H3O2, buffer solution contains [HC2H3O2] = 0.12 M and [C2H3O2-] = 0.15 M, what is the [H3O+] in the solution? HC2H3O2 (aq) + H2O (l) H3O+ (aq) + C2H3O2- (aq) K = 1.8 × 10-5
A) 1.4 × 10-5 M
B) 2.3 × 10-5 M
C) 1.0 × 10-3 M
D) 3.2 × 10-5 M
A) 1.4 × 10-5 M
B) 2.3 × 10-5 M
C) 1.0 × 10-3 M
D) 3.2 × 10-5 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which choice is NOT included in the equilibrium expression?
A) solids
B) gases
C) aqueous solutions
A) solids
B) gases
C) aqueous solutions

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








