Deck 13: The Deaths of Stars
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: The Deaths of Stars
1
A white dwarf is composed of
A) hydrogen nuclei and degenerate electrons.
B) helium nuclei and normal electrons.
C) carbon and oxygen nuclei and degenerate electrons.
D) degenerate iron nuclei.
E) a helium burning core and a hydrogen burning shell.
A) hydrogen nuclei and degenerate electrons.
B) helium nuclei and normal electrons.
C) carbon and oxygen nuclei and degenerate electrons.
D) degenerate iron nuclei.
E) a helium burning core and a hydrogen burning shell.
carbon and oxygen nuclei and degenerate electrons.
2
The Algol paradox is explained by considering
A) the degenerate nature of the hydrogen on the surface of the white dwarf.
B) that iron is the most tightly bound of all atomic nuclei.
C) the rate of expansion of the shock wave inside the supernova.
D) the rotation rate of a neutron star.
E) mass transfer between the two stars in a binary system.
A) the degenerate nature of the hydrogen on the surface of the white dwarf.
B) that iron is the most tightly bound of all atomic nuclei.
C) the rate of expansion of the shock wave inside the supernova.
D) the rotation rate of a neutron star.
E) mass transfer between the two stars in a binary system.
mass transfer between the two stars in a binary system.
3
In A.D.1054,Chinese astronomers observed the appearance of a new star,whose location is now occupied by
A) a globular cluster.
B) a planetary nebulae.
C) a white dwarf.
D) a young massive star.
E) a supernova remnant.
A) a globular cluster.
B) a planetary nebulae.
C) a white dwarf.
D) a young massive star.
E) a supernova remnant.
a supernova remnant.
4
A Type I supernova is believed to occur when
A) the core of a massive star collapses.
B) carbon detonation occurs.
C) a white dwarf exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit.
D) the cores of massive stars collapse.
E) neutrinos in a massive star become degenerate and form a shock wave that explodes the star.
A) the core of a massive star collapses.
B) carbon detonation occurs.
C) a white dwarf exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit.
D) the cores of massive stars collapse.
E) neutrinos in a massive star become degenerate and form a shock wave that explodes the star.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A nova is almost always associated with
A) a very massive star.
B) a very young star.
C) a star undergoing helium flash.
D) a white dwarf in a close binary system.
E) a solar like star that has exhausted its hydrogen and helium.
A) a very massive star.
B) a very young star.
C) a star undergoing helium flash.
D) a white dwarf in a close binary system.
E) a solar like star that has exhausted its hydrogen and helium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A planetary nebula is
A) the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star.
B) produced by a supernova explosion.
C) produced by a nova explosion.
D) a nebula within which planets are forming.
E) a cloud of hot gas surrounding a planet.
A) the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star.
B) produced by a supernova explosion.
C) produced by a nova explosion.
D) a nebula within which planets are forming.
E) a cloud of hot gas surrounding a planet.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A typical planetary nebula will be visible for about
A) 50 years.
B) 500 years.
C) 50,000 years.
D) 5,000,000 years.
E) 5 billion years.
A) 50 years.
B) 500 years.
C) 50,000 years.
D) 5,000,000 years.
E) 5 billion years.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
As material leaves an expanding star and begins to fall into a white dwarf
A) an accretion disk will form around the white dwarf.
B) the material will cool off because it begins to move at high velocities.
C) the material will fall directly onto the surface of the white dwarf.
D) the white dwarf will produce a type-II supernova.
E) the white dwarf's radius will increase.
A) an accretion disk will form around the white dwarf.
B) the material will cool off because it begins to move at high velocities.
C) the material will fall directly onto the surface of the white dwarf.
D) the white dwarf will produce a type-II supernova.
E) the white dwarf's radius will increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A main sequence star of 8.5 solar masses can become a white dwarf by
A) exceeding the Chandrasekhar limit.
B) losing mass.
C) gaining mass.
D) remaining at 8.5 solar masses.
A) exceeding the Chandrasekhar limit.
B) losing mass.
C) gaining mass.
D) remaining at 8.5 solar masses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The energy a white dwarf emits into space is
A) replaced by fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium.
B) replaced by fusion of helium atoms into carbon.
C) not replaced.
A) replaced by fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium.
B) replaced by fusion of helium atoms into carbon.
C) not replaced.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
We know that the central object in a planetary nebula has a surface temperature of at least ____ because the nebula contains large amounts of ionized hydrogen.
A) 5000 K
B) 10,000 K
C) 15,000 K
D) 20,000 K
E) 25,000 K
A) 5000 K
B) 10,000 K
C) 15,000 K
D) 20,000 K
E) 25,000 K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The Chandrasekhar limit is ____ solar masses.
A) 0.014
B) 0.14
C) 1.4
D) 14
A) 0.014
B) 0.14
C) 1.4
D) 14

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
As a white dwarf cools its radius does not change because
A) pressure due to nuclear reactions in a shell just below the surface keeps it from collapsing.
B) pressure does not depend on temperature for a white dwarf because the electrons are degenerate.
C) pressure does not depend on temperature because the white dwarf is too hot.
D) pressure does not depend on temperature because the star has exhausted all its nuclear fuels.
E) material accreting onto it from a companion maintains a constant radius.
A) pressure due to nuclear reactions in a shell just below the surface keeps it from collapsing.
B) pressure does not depend on temperature for a white dwarf because the electrons are degenerate.
C) pressure does not depend on temperature because the white dwarf is too hot.
D) pressure does not depend on temperature because the star has exhausted all its nuclear fuels.
E) material accreting onto it from a companion maintains a constant radius.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
If the theory that novae occur in close binary systems is correct,then novae should
A) produce synchrotron radiation.
B) occur in regions of star formation.
C) not occur in old star clusters.
D) all be visual binaries.
E) repeat after some interval.
A) produce synchrotron radiation.
B) occur in regions of star formation.
C) not occur in old star clusters.
D) all be visual binaries.
E) repeat after some interval.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The Helix and Egg nebulae are
A) supernova remnants.
B) planetary nebulae.
C) the result of carbon detonation.
D) the result of the collapse of the iron core of each star.
E) nebulae associated with Herbig-Haro objects.
A) supernova remnants.
B) planetary nebulae.
C) the result of carbon detonation.
D) the result of the collapse of the iron core of each star.
E) nebulae associated with Herbig-Haro objects.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
When material expanding away from a star in a binary system reaches the Roche surface
A) the material will start to fall back toward the star.
B) all of the material will accrete onto the companion.
C) the material is no longer gravitationally bound to the star.
D) the material will increase in temperature and eventually undergo thermonuclear fusion.
E) c and d
A) the material will start to fall back toward the star.
B) all of the material will accrete onto the companion.
C) the material is no longer gravitationally bound to the star.
D) the material will increase in temperature and eventually undergo thermonuclear fusion.
E) c and d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Suppose that a planetary nebula is 0.5 parsecs in diameter and expanding at 20 km/s.How old is it? (Hint: 1 pc = 3.1*1013 km.)
A) 25,000 years
B) 12,000 years
C) 6,000 years
D) 49,000 years
E) 100,000 years
A) 25,000 years
B) 12,000 years
C) 6,000 years
D) 49,000 years
E) 100,000 years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that
A) accretion disks can grow hot through friction.
B) neutron stars of more than 3 solar masses are not stable.
C) white dwarfs must contain more than 1.4 solar masses.
D) not all stars will end up as white dwarfs.
E) stars with a mass less than 0.5 solar masses will not go through helium flash.
A) accretion disks can grow hot through friction.
B) neutron stars of more than 3 solar masses are not stable.
C) white dwarfs must contain more than 1.4 solar masses.
D) not all stars will end up as white dwarfs.
E) stars with a mass less than 0.5 solar masses will not go through helium flash.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The lowest-mass stars cannot become giants because
A) they do not contain helium.
B) they rotate too slowly.
C) they cannot heat their centers hot enough.
D) they contain strong magnetic fields.
E) they never use up their hydrogen.
A) they do not contain helium.
B) they rotate too slowly.
C) they cannot heat their centers hot enough.
D) they contain strong magnetic fields.
E) they never use up their hydrogen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A planetary nebula
A) produces an absorption spectrum.
B) produces an emission spectrum.
C) is contracting to form planets.
D) is contracting to form the star.
E) is the result of carbon detonation in a 1.
A) produces an absorption spectrum.
B) produces an emission spectrum.
C) is contracting to form planets.
D) is contracting to form the star.
E) is the result of carbon detonation in a 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A supernova remnant is expanding in radius at the rate of 0.5 seconds of arc per year.Doppler shifts show that the velocity of expansion is 5700 km/sec.How far away is the supernova remnant?
A) 1140 pc
B) 11,400 km
C) 5700 pc
D) 24 pc
E) 2400 pc
A) 1140 pc
B) 11,400 km
C) 5700 pc
D) 24 pc
E) 2400 pc

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A white dwarf star is prevented from collapsing by
A) nuclear energy it is generating
B) its gravitational force
C) Hubble's law of extragalactic redshifts
D) degenerate electron gas pressure
E) degenerate astronomers observing the star
A) nuclear energy it is generating
B) its gravitational force
C) Hubble's law of extragalactic redshifts
D) degenerate electron gas pressure
E) degenerate astronomers observing the star

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Massive stars cannot generate energy through iron fusion because
A) iron fusion requires very high density.
B) stars contain very little iron.
C) no star can get hot enough for iron fusion.
D) iron is the most tightly bound of all nuclei.
E) massive stars supernova before they create an iron core.
A) iron fusion requires very high density.
B) stars contain very little iron.
C) no star can get hot enough for iron fusion.
D) iron is the most tightly bound of all nuclei.
E) massive stars supernova before they create an iron core.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The diagram below shows a light curve from a supernova.How many days after maximum light did it take for the supernova to decrease in brightness by a factor of 100? 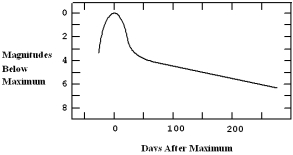
A) 25
B) 50
C) 100
D) 150
E) 250

A) 25
B) 50
C) 100
D) 150
E) 250

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Before it ejects a planetary nebula,a star is a
A) red giant
B) black hole
C) white dwarf
D) super nova
A) red giant
B) black hole
C) white dwarf
D) super nova

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
What are the two longest stages in the life of a one solar mass star?
A) Protostar,pre-main sequence.
B) Protostar,white dwarf.
C) Protostar,main-sequence.
D) Main-sequence,white dwarf.
A) Protostar,pre-main sequence.
B) Protostar,white dwarf.
C) Protostar,main-sequence.
D) Main-sequence,white dwarf.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
For a star of Sun-like mass,what is the last stage of the nuclear fusion?
A) Hydrogen to helium.
B) Helium to carbon and oxygen.
C) Carbon to magnesium.
D) Fusion goes all the way up to iron.
A) Hydrogen to helium.
B) Helium to carbon and oxygen.
C) Carbon to magnesium.
D) Fusion goes all the way up to iron.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A type-II supernova
A) occurs when a white dwarf's mass exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit.
B) is the result of helium flash.
C) is characterized by a spectrum that shows hydrogen lines.
D) occurs when the iron core of a massive star collapses.
E) c and d
A) occurs when a white dwarf's mass exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit.
B) is the result of helium flash.
C) is characterized by a spectrum that shows hydrogen lines.
D) occurs when the iron core of a massive star collapses.
E) c and d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Stars that have ejected a planetary nebula eventually become
A) protostars.
B) brown dwarfs.
C) white dwarfs.
D) red giants.
A) protostars.
B) brown dwarfs.
C) white dwarfs.
D) red giants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The central star in a planetary nebula ...
A) is a main sequence star
B) is a pre-main sequence proto-star
C) is a neutron star
D) will become a white dwarf
A) is a main sequence star
B) is a pre-main sequence proto-star
C) is a neutron star
D) will become a white dwarf

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The explosion of a supernova typically leaves behind
A) a planetary nebula.
B) a shell of hot,expanding gas with a white dwarf at the center.
C) a shell of hot,expanding gas with a pulsar at the center.
D) nothing is ever left behind.
A) a planetary nebula.
B) a shell of hot,expanding gas with a white dwarf at the center.
C) a shell of hot,expanding gas with a pulsar at the center.
D) nothing is ever left behind.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The theory that the collapse of a massive star's iron core produces neutrinos was supported by
A) the size and structure of the Crab nebula.
B) laboratory measurements of the mass of the neutrino.
C) calculation of models of core collapse.
D) underground counts from solar neutrinos.
E) the detection of neutrinos from the supernova of 1987.
A) the size and structure of the Crab nebula.
B) laboratory measurements of the mass of the neutrino.
C) calculation of models of core collapse.
D) underground counts from solar neutrinos.
E) the detection of neutrinos from the supernova of 1987.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Synchrotron radiation is produced by
A) objects with temperatures below 10,000 K.
B) high-velocity electrons moving through a magnetic field.
C) cold hydrogen atoms in space.
D) the collapsing cores of massive stars.
E) helium flash.
A) objects with temperatures below 10,000 K.
B) high-velocity electrons moving through a magnetic field.
C) cold hydrogen atoms in space.
D) the collapsing cores of massive stars.
E) helium flash.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Stars with masses between 0.4 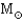 and 4
and 4 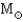
A) undergo thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen and helium,but never get hot enough to ignite carbon.
B) undergo thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen,but never get hot enough to ignite helium.
C) produce type-I supernovae after they exhaust their nuclear fuels.
D) produce type-II supernovae after they exhaust their nuclear fuels.
E) undergo carbon detonation.
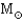 and 4
and 4 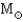
A) undergo thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen and helium,but never get hot enough to ignite carbon.
B) undergo thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen,but never get hot enough to ignite helium.
C) produce type-I supernovae after they exhaust their nuclear fuels.
D) produce type-II supernovae after they exhaust their nuclear fuels.
E) undergo carbon detonation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The image shows the Crab Nebula.The Crab Nebula is 
A) a planetary nebula
B) a name for the cloud of gas and dust which later became our solar system
C) a ejected cloud of gas from a super nova
D) in the constellation Orion,containing many bright young blue stars

A) a planetary nebula
B) a name for the cloud of gas and dust which later became our solar system
C) a ejected cloud of gas from a super nova
D) in the constellation Orion,containing many bright young blue stars

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
White dwarf stars are formed from
A) the most massive main sequence stars
B) lower mass main sequence stars
C) A main sequence star stays a main sequence star forever.
D) Main sequence stars are formed from white dwarf stars.
A) the most massive main sequence stars
B) lower mass main sequence stars
C) A main sequence star stays a main sequence star forever.
D) Main sequence stars are formed from white dwarf stars.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Where are elements heavier than iron primarily produced?
A) Brown dwarfs
B) White dwarfs
C) Supergiants
D) Supernovae
A) Brown dwarfs
B) White dwarfs
C) Supergiants
D) Supernovae

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Synchrotron radiation is produced
A) in planetary nebulae.
B) by red dwarfs.
C) by massive stars as their iron core collapses.
D) in supernova remnants.
E) by neutrinos.
A) in planetary nebulae.
B) by red dwarfs.
C) by massive stars as their iron core collapses.
D) in supernova remnants.
E) by neutrinos.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
After what evolutionary stage does a star become a white dwarf?
A) Protostar
B) Pre-main sequence
C) Main sequence
D) Giant
A) Protostar
B) Pre-main sequence
C) Main sequence
D) Giant

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
What mechanism does an isolated white dwarf use to generate energy?
A) Proton-proton chain
B) CNO cycle
C) Triple alpha process
D) White dwarfs don't generate their own energy.
A) Proton-proton chain
B) CNO cycle
C) Triple alpha process
D) White dwarfs don't generate their own energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Planetary nebulae are sites of planet formation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Stars less massive than 0.4 solar mass never become giant stars.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The sun will eventually become a supernova.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Because massive stars have more gravitational energy than the sun,they can fuse heavier nuclear fuels.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Synchrotron radiation occurs when high speed electrons move through a magnetic field.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A star begins fusing hydrogen to helium the moment it leaves the main sequence.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Electrons moving in a strong magnetic field emit ____________________ radiation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
A white dwarf whose red giant companion dumps hydrogen onto it may
A) show no effect.
B) explode recurrently as a nova.
C) blow up as a type I supernova.
D) answers b or
A) show no effect.
B) explode recurrently as a nova.
C) blow up as a type I supernova.
D) answers b or

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Mass can flow from one star in a binary system to its companion through the first ____________________ point.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
A(n)____________________ is the sudden expulsion of the outer layers of a moderate mass star that has a dormant carbon core.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
A(n)____________________ supernova is caused by the collapse of a massive star that has lost its outer envelope of hydrogen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
____________________ are caused by periodic eruptions in the helium fusion shell and may provide the energy to eject the material that forms a planetary nebula.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
No known white dwarf has a mass greater than the Chandrasekhar limit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
A nova destroys the star and leaves behind a white dwarf.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
An accretion disk can grow hot enough to radiate X-rays.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A Type II supernova produces a planetary nebula.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The average size of a white dwarf is about the same size as the Earth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Type II supernovae are believed to occur when the core of a massive star collapses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Once a star ejects a planetary nebula,it becomes a white dwarf.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








