Deck 13: International Trade
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/165
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: International Trade
1
In the mind of Adam Smith, what is true if person A voluntarily sells a good or service and person B voluntarily buys it?
A) A will benefit but B may or may not benefit.
B) B will benefit but A may or may not benefit.
C) Both A and B would benefit.
D) It is possible that both will benefit or that neither will benefit.
A) A will benefit but B may or may not benefit.
B) B will benefit but A may or may not benefit.
C) Both A and B would benefit.
D) It is possible that both will benefit or that neither will benefit.
C
2
Why doesn't Canada grow its own bananas?
A) It is not possible to grow bananas in Canada.
B) Canada's factor endowments suggest that it can better produce many other goods besides bananas.
C) It is cheaper to buy bananas from countries that have different factor endowments which are much better suited to growing bananas.
D) Both b) and c).
A) It is not possible to grow bananas in Canada.
B) Canada's factor endowments suggest that it can better produce many other goods besides bananas.
C) It is cheaper to buy bananas from countries that have different factor endowments which are much better suited to growing bananas.
D) Both b) and c).
D
3
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the output per worker in Mexico in the rye and bean industries respectively?
A) 10 and 20.
B) 2 and 4.
C) 3 and 0.5.
D) 0.5 and 3.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the output per worker in Mexico in the rye and bean industries respectively?
A) 10 and 20.
B) 2 and 4.
C) 3 and 0.5.
D) 0.5 and 3.
2 and 4.
4
Below is the productivity per worker in the beef and pork industries of two countries: Cholesterol and Fat.
(Output in kilos per day)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that a single worker in each country is transferred from the less to the more productive industry. What will be the total gains from specialization?
A) Beef + 6 and pork + 2.
B) Beef + 6 and pork - 2.
C) Beef + 2 and pork + 6.
D) Beef - 2 and pork + 6.
(Output in kilos per day)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that a single worker in each country is transferred from the less to the more productive industry. What will be the total gains from specialization?
A) Beef + 6 and pork + 2.
B) Beef + 6 and pork - 2.
C) Beef + 2 and pork + 6.
D) Beef - 2 and pork + 6.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Below is the productivity per worker in the beef and pork industries of two countries: Cholesterol and Fat.
(Output in kilos per day)
-What is comparative advantage?
A) The advantage gained from producing something at a lower opportunity cost than other producers are able to.
B) An advantage in production as a result of possessing better skills, or equipment or resources in comparison to other individuals or countries.
C) An econoMac policy of protecting domestic producers by restricting the importation of foreign products.
D) A government regulation which controls how much of a single product can be sold or produced in a competitive market.
(Output in kilos per day)
-What is comparative advantage?
A) The advantage gained from producing something at a lower opportunity cost than other producers are able to.
B) An advantage in production as a result of possessing better skills, or equipment or resources in comparison to other individuals or countries.
C) An econoMac policy of protecting domestic producers by restricting the importation of foreign products.
D) A government regulation which controls how much of a single product can be sold or produced in a competitive market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the rice and beer industries of Catalonia and Granada. The working population in each country is 12 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. Suppose that each country allocates 5 million of its population to the rice industry, the rest being employed in the beer industry. What is their (joint) total production?
A) 20 rice and 10 beer.
B) 48 rice and 24 beer.
C) 35 rice and 35 beer.
D) 21 rice and 21 beer.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. Suppose that each country allocates 5 million of its population to the rice industry, the rest being employed in the beer industry. What is their (joint) total production?
A) 20 rice and 10 beer.
B) 48 rice and 24 beer.
C) 35 rice and 35 beer.
D) 21 rice and 21 beer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the rice and beer industries of Catalonia and Granada. The working population in each country is 12 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. In which product does Catalonia have a comparative advantage?
A) Rice.
B) Beer.
C) Both rice and beer.
D) Neither rice nor beer.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. In which product does Catalonia have a comparative advantage?
A) Rice.
B) Beer.
C) Both rice and beer.
D) Neither rice nor beer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What is the cornerstone of trade?
A) The fact that countries have different factor endowments.
B) Specialization.
C) The presence of economies of scale.
D) Monopoly power.
A) The fact that countries have different factor endowments.
B) Specialization.
C) The presence of economies of scale.
D) Monopoly power.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the output per worker in Canada in the rye and bean industries respectively?
A) 30 and 20.
B) 15 and 10.
C) 75 and 50.
D) 50 and 75.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the output per worker in Canada in the rye and bean industries respectively?
A) 30 and 20.
B) 15 and 10.
C) 75 and 50.
D) 50 and 75.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Who was the originator of the Theory of Absolute Advantage?
A) Adam Smith.
B) David Ricardo.
C) John Maynard Keynes.
D) Arthur Laffer.
A) Adam Smith.
B) David Ricardo.
C) John Maynard Keynes.
D) Arthur Laffer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the wheat and bean industries of Caledonia and Ibrox. The working population in each country is 16 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. What is the cost of a kilo of beans in Ibrox?
A) 0.5 wheat.
B) 6 wheat.
C) 3 beans.
D) 2 wheat.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. What is the cost of a kilo of beans in Ibrox?
A) 0.5 wheat.
B) 6 wheat.
C) 3 beans.
D) 2 wheat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the rice and beer industries of Catalonia and Granada. The working population in each country is 12 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. Suppose that initially each country allocated 5 million of its population to the rice industry, the rest being employed in the beer industry. If they now decide to totally specialize in the products in which each has a comparative advantage, what will be the resulting gains from trade?
A) 0 rice and 25 beer.
B) 1 rice and 1 beer.
C) 35 rice and 35 beer.
D) 21 rice and 0 beer.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. Suppose that initially each country allocated 5 million of its population to the rice industry, the rest being employed in the beer industry. If they now decide to totally specialize in the products in which each has a comparative advantage, what will be the resulting gains from trade?
A) 0 rice and 25 beer.
B) 1 rice and 1 beer.
C) 35 rice and 35 beer.
D) 21 rice and 0 beer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the wheat and bean industries of Caledonia and Ibrox. The working population in each country is 16 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. Suppose that initially each country was self-sufficient in the two products and employed half of their working populations in each industry. If subsequently each country were to totally specialize in the product in which it has a comparative advantage, what would be the subsequent gains from trade?
A) 16 wheat and 16 beans.
B) 16 wheat and 32 beans.
C) 0 wheat and 64 beans.
D) 48 wheat and 32 beans.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. Suppose that initially each country was self-sufficient in the two products and employed half of their working populations in each industry. If subsequently each country were to totally specialize in the product in which it has a comparative advantage, what would be the subsequent gains from trade?
A) 16 wheat and 16 beans.
B) 16 wheat and 32 beans.
C) 0 wheat and 64 beans.
D) 48 wheat and 32 beans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the rice and beer industries of Catalonia and Granada. The working population in each country is 12 million people.
-What term describes the ability to produce something at a lower opportunity cost than others are able to?
A) Increased production possibilities.
B) Factor endowments.
C) Increasing returns to scale.
D) Comparative advantage.
-What term describes the ability to produce something at a lower opportunity cost than others are able to?
A) Increased production possibilities.
B) Factor endowments.
C) Increasing returns to scale.
D) Comparative advantage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the wheat and bean industries of Caledonia and Ibrox. The working population in each country is 16 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. If each country totally specializes in the product in which it has a comparative advantage, what is the total combined output that they are capable of producing?
A) 80 wheat and 96 beans.
B) 160 wheat and 192 beans.
C) 48 wheat and 32 beans.
D) 128 wheat and 128 beans.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. If each country totally specializes in the product in which it has a comparative advantage, what is the total combined output that they are capable of producing?
A) 80 wheat and 96 beans.
B) 160 wheat and 192 beans.
C) 48 wheat and 32 beans.
D) 128 wheat and 128 beans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the wheat and bean industries of Caledonia and Ibrox. The working population in each country is 16 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. What is the cost of a kilo of wheat in Caledonia?
A) 0.4 beans.
B) 2 beans.
C) 0.4 wheat.
D) 2.5 beans.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. What is the cost of a kilo of wheat in Caledonia?
A) 0.4 beans.
B) 2 beans.
C) 0.4 wheat.
D) 2.5 beans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the wheat and bean industries of Caledonia and Ibrox. The working population in each country is 16 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Caledonia should specialize and export wheat.
B) Ibrox should specialize and export wheat.
C) Caledonia should specialize and export beans.
D) Ibrox should specialize in beans but export wheat.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Caledonia should specialize and export wheat.
B) Ibrox should specialize and export wheat.
C) Caledonia should specialize and export beans.
D) Ibrox should specialize in beans but export wheat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Below is the productivity per worker (kilos per day) in the wheat and bean industries of Caledonia and Ibrox. The working population in each country is 16 million people.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. If each country is self-sufficient in the two products and each employs half of its working population in each industry, what is the total combined output that they are capable of producing?
A) 128 wheat and 0 beans.
B) 0 wheat and 128 beans.
C) 128 wheat and 128 beans.
D) 64 wheat and 64 beans.
-Refer to the data above to answer this question. If each country is self-sufficient in the two products and each employs half of its working population in each industry, what is the total combined output that they are capable of producing?
A) 128 wheat and 0 beans.
B) 0 wheat and 128 beans.
C) 128 wheat and 128 beans.
D) 64 wheat and 64 beans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Below is the productivity per worker in the beef and pork industries of two countries: Cholesterol and Fat.
(Output in kilos per day)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Which of the following is true?
A) Cholesterol has an absolute advantage in pork and Fat has an absolute advantage in beef.
B) Cholesterol has an absolute advantage in beef and Fat has an absolute advantage in pork.
C) Cholesterol has a comparative advantage in pork and Fat has a comparative advantage in beef.
D) Cholesterol has a comparative advantage in pork and Fat has an absolute advantage in beef.
(Output in kilos per day)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Which of the following is true?
A) Cholesterol has an absolute advantage in pork and Fat has an absolute advantage in beef.
B) Cholesterol has an absolute advantage in beef and Fat has an absolute advantage in pork.
C) Cholesterol has a comparative advantage in pork and Fat has a comparative advantage in beef.
D) Cholesterol has a comparative advantage in pork and Fat has an absolute advantage in beef.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In 2012, approximately what percentage of Canada's merchandize exports were petroleum and other fuels?
A) 5%
B) 12%
C) 26%
D) 30%
E) 35%
A) 5%
B) 12%
C) 26%
D) 30%
E) 35%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that each country was producing combination D before trade but then specializes in the product in which it has a comparative advantage. What would be the total gains from trade?
A) 40 million units of rice cakes.
B) 100 million units of rice cakes.
C) 60 million units of soya milk and 40 million units of rice cakes.
D) 40 million units of soya milk and 60 million units of rice cakes.
E) 20 million units of soya milk.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that each country was producing combination D before trade but then specializes in the product in which it has a comparative advantage. What would be the total gains from trade?
A) 40 million units of rice cakes.
B) 100 million units of rice cakes.
C) 60 million units of soya milk and 40 million units of rice cakes.
D) 40 million units of soya milk and 60 million units of rice cakes.
E) 20 million units of soya milk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Below is a graph illustrating rice and flax production in the countries of Cardassia and Bajor.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 100 tons of rice in Cardassia?
A) 80 tons of flax.
B) 100 tons of flax.
C) 125 tons of flax.
D) 200 tons of flax.
E) 500 tons of flax.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 100 tons of rice in Cardassia?
A) 80 tons of flax.
B) 100 tons of flax.
C) 125 tons of flax.
D) 200 tons of flax.
E) 500 tons of flax.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. If both countries produce combination D what will be the combined outputs?
A) 50 million units of soya milk and 130 million units of rice cakes.
B) 60 million units of soya milk and 120 million units of rice cakes.
C) 60 million units of soya milk and 130 million units of rice cakes.
D) 120 million units of soya milk and 100 million units of rice cakes.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. If both countries produce combination D what will be the combined outputs?
A) 50 million units of soya milk and 130 million units of rice cakes.
B) 60 million units of soya milk and 120 million units of rice cakes.
C) 60 million units of soya milk and 130 million units of rice cakes.
D) 120 million units of soya milk and 100 million units of rice cakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. If each country totally specializes according to its comparative advantage and the terms of trade are 1 bushel of beans for 1.25 bushels of rye, what will be the gains from trade?
A) 60 bushels of rye and 100 bushels of beans.
B) 25 bushels of rye and 10 bushels of beans.
C) 45 bushels of rye and 10 bushels of beans.
D) There are no gains from trade.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. If each country totally specializes according to its comparative advantage and the terms of trade are 1 bushel of beans for 1.25 bushels of rye, what will be the gains from trade?
A) 60 bushels of rye and 100 bushels of beans.
B) 25 bushels of rye and 10 bushels of beans.
C) 45 bushels of rye and 10 bushels of beans.
D) There are no gains from trade.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that each country specializes in the product in which it has a comparative advantage. What will be the total output of each product?
A) 40 million units of rice cakes and 160 million units of soya milk.
B) 80 million units of rice cakes and 120 million units of soya milk.
C) 80 million units of soya milk and 120 million units of rice cakes.
D) 40 million units of soya milk and 160 million units of rice cakes.
E) 160 million units of soya milk and 80 million units of rice cakes.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that each country specializes in the product in which it has a comparative advantage. What will be the total output of each product?
A) 40 million units of rice cakes and 160 million units of soya milk.
B) 80 million units of rice cakes and 120 million units of soya milk.
C) 80 million units of soya milk and 120 million units of rice cakes.
D) 40 million units of soya milk and 160 million units of rice cakes.
E) 160 million units of soya milk and 80 million units of rice cakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of one unit of rice cakes in Mental?
A) 0.25 units of soya milk.
B) 0.5 units of soya milk.
C) 2 units of soya milk.
D) 10 units of soya milk.
E) 20 units of soya milk.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of one unit of rice cakes in Mental?
A) 0.25 units of soya milk.
B) 0.5 units of soya milk.
C) 2 units of soya milk.
D) 10 units of soya milk.
E) 20 units of soya milk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of beans in Canada?
A) 0.67 bushels of rye.
B) 1.5 bushels of rye.
C) 6 bushels of rye.
D) 12 bushels of rye.
E) 75 bushels of rye.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of beans in Canada?
A) 0.67 bushels of rye.
B) 1.5 bushels of rye.
C) 6 bushels of rye.
D) 12 bushels of rye.
E) 75 bushels of rye.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of rye in Canada?
A) 0.67 bushels of beans.
B) 1.5 bushels of beans.
C) 2 bushels of beans.
D) 3 bushels of beans.
E) 75 bushels of beans.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of rye in Canada?
A) 0.67 bushels of beans.
B) 1.5 bushels of beans.
C) 2 bushels of beans.
D) 3 bushels of beans.
E) 75 bushels of beans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Which of the following would be feasible terms of trade between the two countries?
A) 1 bushel of beans = 2 bushels of rye.
B) 1 bushel of beans = 0.4 bushels of rye.
C) 1 bushel of beans = 1.25 bushels of rye.
D) 1 bushel of beans = 4 bushels of rye.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Which of the following would be feasible terms of trade between the two countries?
A) 1 bushel of beans = 2 bushels of rye.
B) 1 bushel of beans = 0.4 bushels of rye.
C) 1 bushel of beans = 1.25 bushels of rye.
D) 1 bushel of beans = 4 bushels of rye.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Below is a graph illustrating rice and flax production in the countries of Cardassia and Bajor.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 100 tons of rice in Bajor?
A) 50 tons of flax.
B) 100 tons of flax.
C) 125 tons of flax.
D) 200 tons of flax.
E) 225 tons of flax.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 100 tons of rice in Bajor?
A) 50 tons of flax.
B) 100 tons of flax.
C) 125 tons of flax.
D) 200 tons of flax.
E) 225 tons of flax.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of beans in Mexico?
A) 0.5 bushels of rye.
B) 1 bushels of rye.
C) 2 bushels of rye.
D) 6 bushels of rye.
E) 10 bushels of rye.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of beans in Mexico?
A) 0.5 bushels of rye.
B) 1 bushels of rye.
C) 2 bushels of rye.
D) 6 bushels of rye.
E) 10 bushels of rye.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of one unit of soya milk in Mental?
A) 0.5 units of rice cakes.
B) 0.75 units of rice cakes.
C) 2 units of rice cakes.
D) 5 units of rice cakes.
E) 10 units of rice cakes.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of one unit of soya milk in Mental?
A) 0.5 units of rice cakes.
B) 0.75 units of rice cakes.
C) 2 units of rice cakes.
D) 5 units of rice cakes.
E) 10 units of rice cakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Below is a graph illustrating rice and flax production in the countries of Cardassia and Bajor.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Cardassia has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in the production of rice.
B) Bajor has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in the production of rice.
C) Cardassia has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in the production of flax.
D) Bajor has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in the production of flax.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Cardassia has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in the production of rice.
B) Bajor has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in the production of rice.
C) Cardassia has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in the production of flax.
D) Bajor has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in the production of flax.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of one unit of rice cakes in Etheric?
A) 0.375 units of soya milk.
B) 1.33 units of soya milk.
C) 2.67 units of soya milk.
D) 20 units of rice cakes.
E) 40 units of rice cakes.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of one unit of rice cakes in Etheric?
A) 0.375 units of soya milk.
B) 1.33 units of soya milk.
C) 2.67 units of soya milk.
D) 20 units of rice cakes.
E) 40 units of rice cakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In which product should Mental specialize and export?
A) It should specialize in soya milk and export rice cakes.
B) It should specialize and export soya milk.
C) It should specialize and export rice cakes.
D) It should specialize in rice cakes and export soya milk.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In which product should Mental specialize and export?
A) It should specialize in soya milk and export rice cakes.
B) It should specialize and export soya milk.
C) It should specialize and export rice cakes.
D) It should specialize in rice cakes and export soya milk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In which product should Etheric specialize and export?
A) It should specialize in soya milk and export rice cakes.
B) It should specialize and export soya milk.
C) It should specialize and export rice cakes.
D) It should specialize in rice cakes and export soya milk.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In which product should Etheric specialize and export?
A) It should specialize in soya milk and export rice cakes.
B) It should specialize and export soya milk.
C) It should specialize and export rice cakes.
D) It should specialize in rice cakes and export soya milk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In what product does Canada and Mexico have a comparative advantage?
A) Neither country has a comparative advantage in either rye or beans.
B) Canada has a comparative advantage in rye but neither country has a comparative advantage in beans.
C) Canada has a comparative advantage in rye and Mexico has a comparative advantage in beans.
D) Canada has a comparative advantage in beans and Mexico has a comparative advantage in rye.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In what product does Canada and Mexico have a comparative advantage?
A) Neither country has a comparative advantage in either rye or beans.
B) Canada has a comparative advantage in rye but neither country has a comparative advantage in beans.
C) Canada has a comparative advantage in rye and Mexico has a comparative advantage in beans.
D) Canada has a comparative advantage in beans and Mexico has a comparative advantage in rye.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Suppose that a country has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat. Which of the following statements is true?
A) It must also have an absolute advantage in the production of wheat.
B) The purchasing power parity theory must also be in its favour.
C) Specialization is wise only up to a point because of the law of increasing costs.
D) Specialization is wise only if exchange rates are fixed.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Suppose that a country has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat. Which of the following statements is true?
A) It must also have an absolute advantage in the production of wheat.
B) The purchasing power parity theory must also be in its favour.
C) Specialization is wise only up to a point because of the law of increasing costs.
D) Specialization is wise only if exchange rates are fixed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Below is some hypothetical data for the countries of Canada and Mexico. (Assume that Canada has 10 million workers per month available and Mexico has 20 million.)
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of rye in Mexico?
A) 0.5 bushels of beans.
B) 1 bushel of beans.
C) 2 bushels of beans.
D) 15 bushels of beans.
E) 20 bushels of beans.
Canada's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Mexico's Production Possibilities
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
Output Before Trade
(Output in millions of bushels per month)
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of rye in Mexico?
A) 0.5 bushels of beans.
B) 1 bushel of beans.
C) 2 bushels of beans.
D) 15 bushels of beans.
E) 20 bushels of beans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of one unit of soya milk in Etheric?
A) 0.5 units of rice cakes.
B) 0.75 units of rice cakes.
C) 1.33 units of rice cakes.
D) 20 units of rice cakes.
E) 40 units of rice cakes.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the opportunity cost of one unit of soya milk in Etheric?
A) 0.5 units of rice cakes.
B) 0.75 units of rice cakes.
C) 1.33 units of rice cakes.
D) 20 units of rice cakes.
E) 40 units of rice cakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Below are the production possibilities (without trade) and the trading possibilities (with free trade) for Canada.
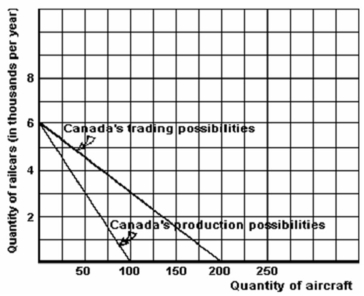
Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming free trade, what is the opportunity cost of 1 more aircraft?
A) 0.033 railcars.
B) 33.33 railcars.
C) 30 railcars.
D) 50 railcars.
E) 3,000 railcars

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming free trade, what is the opportunity cost of 1 more aircraft?
A) 0.033 railcars.
B) 33.33 railcars.
C) 30 railcars.
D) 50 railcars.
E) 3,000 railcars

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What is the formula for the terms of trade?
A) Total volume of exports/total volume of imports x 100.
B) Average price of imports/average price of exports x 100.
C) Average price of exports/average price of imports x 100.
D) Total volume of exports minus total volume of imports.
A) Total volume of exports/total volume of imports x 100.
B) Average price of imports/average price of exports x 100.
C) Average price of exports/average price of imports x 100.
D) Total volume of exports minus total volume of imports.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Below are the production possibilities (without trade) and the trading possibilities (with free trade) for Canada.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming no trade, what is the opportunity cost of 1 more railcar?
A) 0.0167 aircraft.
B) 1.67 aircraft.
C) 16.67 aircraft.
D) 20 aircraft.
E) 100 aircraft.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming no trade, what is the opportunity cost of 1 more railcar?
A) 0.0167 aircraft.
B) 1.67 aircraft.
C) 16.67 aircraft.
D) 20 aircraft.
E) 100 aircraft.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Below is some data on the output of kumquats in Smith Island.
-Refer to information above to answer this question. If the world price (free trade) price prevailed, how many kumquats per month would Smith Island import?
A) 10.
B) 30.
C) 40.
D) 60.
E) 90.
-Refer to information above to answer this question. If the world price (free trade) price prevailed, how many kumquats per month would Smith Island import?
A) 10.
B) 30.
C) 40.
D) 60.
E) 90.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that the two countries, who were producing at combination D before trade, now specialize and engage in free trade and establish the terms of trade at 1 unit of rice cake = 1.5 units of soya milk. If Etheric exports 30 million units of rice cakes to Mental, what will be the gains from trade for each country?
A) Mental gains 30 million units of rice cakes and Etheric gains 45 million units of soya milk.
B) Mental gains 45 million units of rice cakes and Etheric gains 30 million units of soya milk.
C) Mental gains 15 million units of soya milk and Etheric gains 45 million units of soya milk.
D) Mental gains 15 million units of soya milk and Etheric gains 5 million units of soya milk.
E) Mental gains 15 million units of soya milk and Etheric gains 5 million units of rice cakes.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that the two countries, who were producing at combination D before trade, now specialize and engage in free trade and establish the terms of trade at 1 unit of rice cake = 1.5 units of soya milk. If Etheric exports 30 million units of rice cakes to Mental, what will be the gains from trade for each country?
A) Mental gains 30 million units of rice cakes and Etheric gains 45 million units of soya milk.
B) Mental gains 45 million units of rice cakes and Etheric gains 30 million units of soya milk.
C) Mental gains 15 million units of soya milk and Etheric gains 45 million units of soya milk.
D) Mental gains 15 million units of soya milk and Etheric gains 5 million units of soya milk.
E) Mental gains 15 million units of soya milk and Etheric gains 5 million units of rice cakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The chart below refers to the economy of Smith Island.
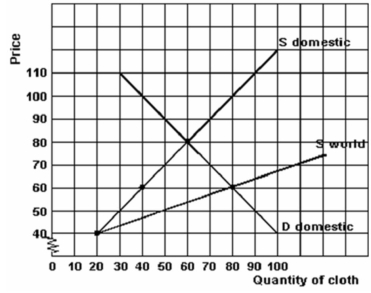
Refer to the graph above to answer this question. How much is Smith Island producing at the world (free trade) price of cloth?
A) 0 units.
B) 20 units.
C) 40 units.
D) 80 units.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. How much is Smith Island producing at the world (free trade) price of cloth?
A) 0 units.
B) 20 units.
C) 40 units.
D) 80 units.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Below are the production possibilities (without trade) and the trading possibilities (with free trade) for Canada.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming free trade, what is the opportunity cost of 1 more railcar?
A) 0.00835 aircraft.
B) 0.033 aircraft.
C) 3.33 aircraft.
D) 8.33 aircraft.
E) 10 aircraft.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming free trade, what is the opportunity cost of 1 more railcar?
A) 0.00835 aircraft.
B) 0.033 aircraft.
C) 3.33 aircraft.
D) 8.33 aircraft.
E) 10 aircraft.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
All of the following, except one, are benefits of free trade. Which is the exception?
A) Products will be produced at lower cost and in higher volumes.
B) There will be an increase in the variety of products available.
C) There will be increased competition.
D) The world exchange rates will approach parity.
A) Products will be produced at lower cost and in higher volumes.
B) There will be an increase in the variety of products available.
C) There will be increased competition.
D) The world exchange rates will approach parity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
All of the following, except one, are reasons why complete free trade may not be possible. Which is the exception?
A) Transportation costs might exceed any cost differences between countries.
B) Higher taxes in one country than another might exceed any cost differences.
C) Free trade usually causes a reduction in international competition.
D) Differences in languages and cultures might restrict the amount of trade.
E) Cost differences between countries disappear as one country tries to totally specialize.
A) Transportation costs might exceed any cost differences between countries.
B) Higher taxes in one country than another might exceed any cost differences.
C) Free trade usually causes a reduction in international competition.
D) Differences in languages and cultures might restrict the amount of trade.
E) Cost differences between countries disappear as one country tries to totally specialize.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
All of the following except one are initials of international trade organizations. Which is the exception?
A) WTO.
B) RIF.
C) OECD.
D) EU.
E) APEC.
A) WTO.
B) RIF.
C) OECD.
D) EU.
E) APEC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Proponents of free trade suggest that all of the following, except one, are benefits of free trade. Which is the exception?
A) Free trade leads to lower prices.
B) Free trade leads to greater self-sufficiency.
C) Free trade leads to higher incomes.
D) Free trade leads to a greater variety of products.
E) Free trade increases competition.
A) Free trade leads to lower prices.
B) Free trade leads to greater self-sufficiency.
C) Free trade leads to higher incomes.
D) Free trade leads to a greater variety of products.
E) Free trade increases competition.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Below is some data on the output of kumquats in Smith Island.
-Refer to information above to answer this question. If Smith Island imposed a tariff on kumquats of $3 per kilo, what would be the equilibrium price and quantity traded?
A) $5 and 80.
B) $6 and 70.
C) $12 and 130.
D) $12 and 0.
E) $12 and 70.
-Refer to information above to answer this question. If Smith Island imposed a tariff on kumquats of $3 per kilo, what would be the equilibrium price and quantity traded?
A) $5 and 80.
B) $6 and 70.
C) $12 and 130.
D) $12 and 0.
E) $12 and 70.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Below is the total market demand and supply of wine for France and Germany. Quantities are in millions of litres per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assuming no trade, what are the equilibrium price and quantity of wine in France?
A) $4 and 24.
B) $5 and 14.
C) $6 and 15.
D) $7 and 14.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assuming no trade, what are the equilibrium price and quantity of wine in France?
A) $4 and 24.
B) $5 and 14.
C) $6 and 15.
D) $7 and 14.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Below are the production possibilities (without trade) and the trading possibilities (with free trade) for Canada.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming no trade, what is the opportunity cost of 1 more aircraft?
A) 0.0167 railcars.
B) 16.67 railcars.
C) 60 railcars.
D) 100 railcars.
E) 6,000 railcars.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming no trade, what is the opportunity cost of 1 more aircraft?
A) 0.0167 railcars.
B) 16.67 railcars.
C) 60 railcars.
D) 100 railcars.
E) 6,000 railcars.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
What term describes the average price of a country's exports compared with the price of its imports?
A) The trade deficit.
B) The gains from trade.
C) The terms of trade.
D) The factor endowment.
A) The trade deficit.
B) The gains from trade.
C) The terms of trade.
D) The factor endowment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that the two countries specialize and engage in free trade and establish the terms of trade at 1 unit of rice cake = 1.5 units of soya milk. If Etheric exports 30 million units of rice cakes to Mental, what will be the consumption combinations for Etheric?
A) 30 million units of soya milk and 55 million units of rice cakes.
B) 45 million units of soya milk and 90 million units of rice cakes.
C) 55 million units of soya milk and 30 million units of rice cakes.
D) 90 million units of soya milk and 45 million units of rice cakes.
E) 10 million units of soya milk and 30 million units of rice cakes.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that the two countries specialize and engage in free trade and establish the terms of trade at 1 unit of rice cake = 1.5 units of soya milk. If Etheric exports 30 million units of rice cakes to Mental, what will be the consumption combinations for Etheric?
A) 30 million units of soya milk and 55 million units of rice cakes.
B) 45 million units of soya milk and 90 million units of rice cakes.
C) 55 million units of soya milk and 30 million units of rice cakes.
D) 90 million units of soya milk and 45 million units of rice cakes.
E) 10 million units of soya milk and 30 million units of rice cakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
What could cause the terms of trade to move in a country's favour?
A) If the average price of its exports increases.
B) If the average price of its imports increases.
C) If the average price of its exports decreases.
D) If the costs of transport and insurance falls.
A) If the average price of its exports increases.
B) If the average price of its imports increases.
C) If the average price of its exports decreases.
D) If the costs of transport and insurance falls.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The chart below refers to the economy of Smith Island.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the world (free trade) price of cloth?
A) $40.
B) $50.
C) $60.
D) $80.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the world (free trade) price of cloth?
A) $40.
B) $50.
C) $60.
D) $80.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Which of the following would cause the terms of trade to move in favour of Canada?
A) If the prices of resources increased significantly.
B) If the volume of Canada's exports increased significantly.
C) If more Canadians travelled abroad.
D) If the price of imports increased.
E) If the volume of imports decreased.
A) If the prices of resources increased significantly.
B) If the volume of Canada's exports increased significantly.
C) If more Canadians travelled abroad.
D) If the price of imports increased.
E) If the volume of imports decreased.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Below is production possibilities data for the countries of Mental and Etheric.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that the two countries specialize and trade in the products in which they have a comparative advantage and establish the terms of trade at 1 unit of rice cake = 1.5 units of soya milk. If Etheric exports 30 million units of rice cakes to Mental, what will be the consumption combinations for Mental?
A) 30 million units of soya milk and 55 million units of rice cakes.
B) 45 million units of soya milk and 90 million units of rice cakes.
C) 35 million units of soya milk and 30 million units of rice cakes.
D) 90 million units of soya milk and 45 million units of rice cakes.
E) 10 million units of soya milk and 30 million units of rice cakes.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Suppose that the two countries specialize and trade in the products in which they have a comparative advantage and establish the terms of trade at 1 unit of rice cake = 1.5 units of soya milk. If Etheric exports 30 million units of rice cakes to Mental, what will be the consumption combinations for Mental?
A) 30 million units of soya milk and 55 million units of rice cakes.
B) 45 million units of soya milk and 90 million units of rice cakes.
C) 35 million units of soya milk and 30 million units of rice cakes.
D) 90 million units of soya milk and 45 million units of rice cakes.
E) 10 million units of soya milk and 30 million units of rice cakes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
All the following, except one, are examples of trade restrictions. Which is the exception?
A) Import subsidies.
B) Quotas.
C) Tariffs.
D) Exchange controls.
E) Voluntary export restrictions.
A) Import subsidies.
B) Quotas.
C) Tariffs.
D) Exchange controls.
E) Voluntary export restrictions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
What is the term for a tax or duty levied on imported products?
A) Quota.
B) Tariff.
C) Dumping.
D) Trade barrier.
A) Quota.
B) Tariff.
C) Dumping.
D) Trade barrier.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Below is the total market demand and supply of wine for France and Germany. Quantities are in millions of litres per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assume that France and Germany enter into a free trade agreement (and there are no extra transportation costs, etc.) what will France do?
A) Export 4 million litres of wine per month.
B) Export 1 million litres of wine per month.
C) Import 4 million litres of wine per month.
D) Import 1 million litres of wine per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assume that France and Germany enter into a free trade agreement (and there are no extra transportation costs, etc.) what will France do?
A) Export 4 million litres of wine per month.
B) Export 1 million litres of wine per month.
C) Import 4 million litres of wine per month.
D) Import 1 million litres of wine per month.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Below is the total market demand and supply of wine for France and Germany. Quantities are in millions of litres per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assuming no trade, what are the equilibrium price and quantity of wine in Germany?
A) $6 and 10.
B) $7 and 5.
C) $8 and 7.
D) $9 and 7.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assuming no trade, what are the equilibrium price and quantity of wine in Germany?
A) $6 and 10.
B) $7 and 5.
C) $8 and 7.
D) $9 and 7.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Below is a graph illustrating the market for mustard seeds in Rysen III. (Sd is domestic supply, and Dd is domestic demand.). The world price of mustard seeds is $100.
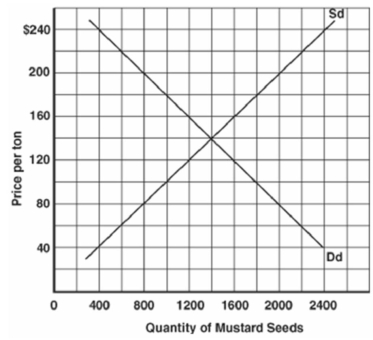
Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Suppose that the government introduces a tariff of $20 on mustard seeds. What will be the new price?
A) $100.
B) $120.
C) $130.
D) $140.
E) $150.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Suppose that the government introduces a tariff of $20 on mustard seeds. What will be the new price?
A) $100.
B) $120.
C) $130.
D) $140.
E) $150.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
What is the term for the policy of restricting the importation of foreign products?
A) Quota.
B) Protectionism.
C) Trade barriers.
D) Terms of trade.
A) Quota.
B) Protectionism.
C) Trade barriers.
D) Terms of trade.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Below is the total market demand and supply of wine for France and Germany. Quantities are in millions of litres per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Who loses from free trade in wine between France and Germany?
A) German wine producers and French wine drinkers.
B) German wine producers and German wine drinkers.
C) French wine producers and French wine drinkers.
D) French wine producers and German wine drinkers.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Who loses from free trade in wine between France and Germany?
A) German wine producers and French wine drinkers.
B) German wine producers and German wine drinkers.
C) French wine producers and French wine drinkers.
D) French wine producers and German wine drinkers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
What are voluntary export restrictions?
A) A restriction placed on the importation of foreign products.
B) An agreement by an exporting country to restrict the amount of exports to another country.
C) Government restrictions limiting the amount of foreign currency which can be obtained.
D) A limit imposed on the production or sale of a product.
A) A restriction placed on the importation of foreign products.
B) An agreement by an exporting country to restrict the amount of exports to another country.
C) Government restrictions limiting the amount of foreign currency which can be obtained.
D) A limit imposed on the production or sale of a product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Below is the total market demand and supply of wine for France and Germany. Quantities are in millions of litres per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assume that France and Germany enter into a free trade agreement (and there are no extra transportation costs, etc.) what are the equilibrium price and quantity of wine?
A) $5 and 30.
B) $6 and 19.
C) $7 and 21.
D) $8 and 19.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assume that France and Germany enter into a free trade agreement (and there are no extra transportation costs, etc.) what are the equilibrium price and quantity of wine?
A) $5 and 30.
B) $6 and 19.
C) $7 and 21.
D) $8 and 19.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
What is the term for restrictions imposed by a government limiting the amount of foreign currencies which can be obtained?
A) Tariffs.
B) Taxes.
C) Quotas.
D) Exchange controls.
A) Tariffs.
B) Taxes.
C) Quotas.
D) Exchange controls.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
What are currency exchange controls?
A) Government restrictions limiting the amount of foreign currency which can be obtained.
B) A limit imposed on the production or sale of a product.
C) A government regulation which controls how much of a single product can be sold or produced in a competitive market.
D) A restriction placed on the importation of foreign products.
A) Government restrictions limiting the amount of foreign currency which can be obtained.
B) A limit imposed on the production or sale of a product.
C) A government regulation which controls how much of a single product can be sold or produced in a competitive market.
D) A restriction placed on the importation of foreign products.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Below is a graph illustrating the market for mustard seeds in Rysen III. (Sd is domestic supply, and Dd is domestic demand.). The world price of mustard seeds is $100.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming there is free trade, what quantity of mustard seeds will be imported?
A) 0.
B) 800
C) 1,000.
D) 1,200.
E) 1,400.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Assuming there is free trade, what quantity of mustard seeds will be imported?
A) 0.
B) 800
C) 1,000.
D) 1,200.
E) 1,400.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
What is a quota?
A) A limit imposed on the production or sale of a product.
B) A restriction placed on the importation of foreign products.
C) A tax levied on imports.
D) A maximum or minimum price placed on a product by government regulation.
A) A limit imposed on the production or sale of a product.
B) A restriction placed on the importation of foreign products.
C) A tax levied on imports.
D) A maximum or minimum price placed on a product by government regulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
What is a tariff?
A) A restriction placed on the importation of foreign products.
B) A maximum or minimum price placed on a product by government regulation.
C) A limit imposed on the production or sale of a product.
D) A tax or duty levied on imports.
A) A restriction placed on the importation of foreign products.
B) A maximum or minimum price placed on a product by government regulation.
C) A limit imposed on the production or sale of a product.
D) A tax or duty levied on imports.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
What is the term for an agreement by an exporting country to restrict the amount of exports to another country?
A) Tariff.
B) Trade agreement.
C) Voluntary export restrictions.
D) Quota.
A) Tariff.
B) Trade agreement.
C) Voluntary export restrictions.
D) Quota.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
What is the term for a limit which is imposed on the production or sale of a product?
A) Protectionism.
B) Trade barrier.
C) Quota.
D) Tariff.
A) Protectionism.
B) Trade barrier.
C) Quota.
D) Tariff.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Below is the total market demand and supply of wine for France and Germany. Quantities are in millions of litres per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Who gains from free trade in wine between France and Germany?
A) German wine producers and French wine drinkers.
B) German wine producers and German wine drinkers.
C) French wine producers and French wine drinkers.
D) French wine producers and German wine drinkers.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Who gains from free trade in wine between France and Germany?
A) German wine producers and French wine drinkers.
B) German wine producers and German wine drinkers.
C) French wine producers and French wine drinkers.
D) French wine producers and German wine drinkers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Below is a graph illustrating the market for mustard seeds in Rysen III. (Sd is domestic supply, and Dd is domestic demand.). The world price of mustard seeds is $100.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Suppose that the government introduces a quota of 400 on imports of mustard seeds, what will be the new price?
A) $40.
B) $100.
C) $120.
D) $140.
E) Cannot be determined.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Suppose that the government introduces a quota of 400 on imports of mustard seeds, what will be the new price?
A) $40.
B) $100.
C) $120.
D) $140.
E) Cannot be determined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Below is the total market demand and supply of wine for France and Germany. Quantities are in millions of litres per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assume that France and Germany enter into a free trade agreement (and there are no extra transportation costs, etc.) what will Germany do?
A) Export 4 million litres of wine per month.
B) Export 1 million litres of wine per month.
C) Import 4 million litres of wine per month.
D) Import 1 million litres of wine per month.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Assume that France and Germany enter into a free trade agreement (and there are no extra transportation costs, etc.) what will Germany do?
A) Export 4 million litres of wine per month.
B) Export 1 million litres of wine per month.
C) Import 4 million litres of wine per month.
D) Import 1 million litres of wine per month.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
What does protectionism mean?
A) Policies designed to limit the amount of exports leaving a country.
B) A form of insurance on exported goods in case of loss during transportation.
C) Subsidies give in order to keep the prices of imported goods low.
D) Policies designed to limit the amount of imports entering a country.
A) Policies designed to limit the amount of exports leaving a country.
B) A form of insurance on exported goods in case of loss during transportation.
C) Subsidies give in order to keep the prices of imported goods low.
D) Policies designed to limit the amount of imports entering a country.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 165 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








