Deck 30: The Great Depression and World War Ii, 1929-1945
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 30: The Great Depression and World War Ii, 1929-1945
1
Historians believe that the concept of "totalitarianism" may have originated
A) in Bolshevik émigré circles before World War I.
B) in the German press during World War I.
C) with the total war efforts of World War I.
D) among American anticommunists after 1945.
A) in Bolshevik émigré circles before World War I.
B) in the German press during World War I.
C) with the total war efforts of World War I.
D) among American anticommunists after 1945.
with the total war efforts of World War I.
2
How did Britain respond to the Great Depression?
A) It worked to encourage production and increase exports.
B) It instituted large-scale deficit spending policies.
C) It followed orthodox economic theory and concentrated increasingly on domestic markets.
D) It increased investments in its colonies.
A) It worked to encourage production and increase exports.
B) It instituted large-scale deficit spending policies.
C) It followed orthodox economic theory and concentrated increasingly on domestic markets.
D) It increased investments in its colonies.
It followed orthodox economic theory and concentrated increasingly on domestic markets.
3
When and why did the Great Depression start?
A) It began in 1923 when Germany defaulted on its reparations.
B) It began in 1935 when the WPA was established.
C) It began in 1929 when the U.S. stock market crashed.
D) It began in 1931 when Japan invaded Manchuria.
A) It began in 1923 when Germany defaulted on its reparations.
B) It began in 1935 when the WPA was established.
C) It began in 1929 when the U.S. stock market crashed.
D) It began in 1931 when Japan invaded Manchuria.
It began in 1929 when the U.S. stock market crashed.
4
During the Great Depression, what happened to the price of rice in Asia?
A) It fell by two-thirds between 1929 and 1932.
B) It tripled by 1932.
C) It exceeded the average income by 20 percent.
D) It remained the same, but yields decreased.
A) It fell by two-thirds between 1929 and 1932.
B) It tripled by 1932.
C) It exceeded the average income by 20 percent.
D) It remained the same, but yields decreased.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The slogan on this billboard, when juxtaposed against the socioeconomic status of many African Americans during the Great Depression, including these flood victims, does what? 
A) Highlights the racial and economic gaps that prevailed in many parts of America
B) Highlights the unwavering belief of white and black Americans in the American dream
C) Indicates that by 1937 many sectors of the American economy were on the road to recovery
D) Demonstrates that the average American during this period had attained middle-class status

A) Highlights the racial and economic gaps that prevailed in many parts of America
B) Highlights the unwavering belief of white and black Americans in the American dream
C) Indicates that by 1937 many sectors of the American economy were on the road to recovery
D) Demonstrates that the average American during this period had attained middle-class status

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Stalin's five-year plans were designed to be what kind of a revolution?
A) A revolution by the people
B) A revolution for the state
C) A nonviolent revolution
D) A revolution from above
A) A revolution by the people
B) A revolution for the state
C) A nonviolent revolution
D) A revolution from above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
What can be deduced from this picture about Hitler's view of German youth?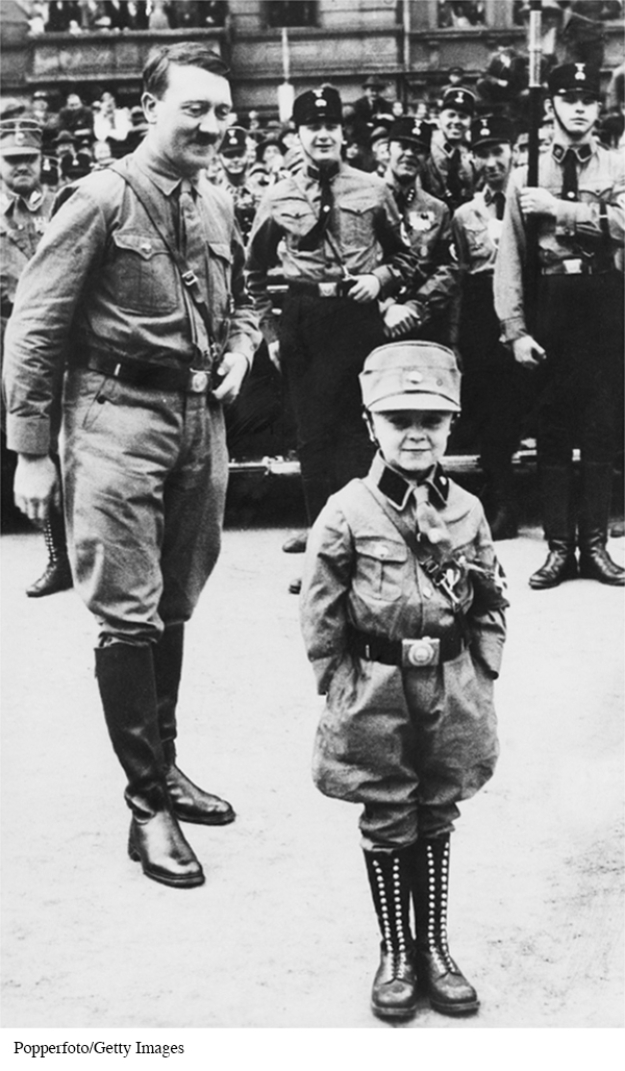 
A) He believed most children were too young to understand Nazi ideology.
B) He viewed German youth as the future of the Nazi Party.
C) He believed paramilitary organizations would be the downfall of the Nazi Party.
D) He had no appreciation for the role children could play in the growth of Nazism.

A) He believed most children were too young to understand Nazi ideology.
B) He viewed German youth as the future of the Nazi Party.
C) He believed paramilitary organizations would be the downfall of the Nazi Party.
D) He had no appreciation for the role children could play in the growth of Nazism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
One of the first measures the United States took to deal with the financial panic was to raise which of the following?
A) Tariffs
B) Income tax
C) Wages
D) The national debt
A) Tariffs
B) Income tax
C) Wages
D) The national debt

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
What did the economist John Maynard Keynes believe that governments should do during economic depressions?
A) Spend less and save cash
B) Cut services and raise taxes
C) Spend more and stimulate the economy
D) Suspend stock trading for one year
A) Spend less and save cash
B) Cut services and raise taxes
C) Spend more and stimulate the economy
D) Suspend stock trading for one year

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
By the end of 1927, Stalin had
A) abolished all political offices but his own.
B) achieved absolute power in the Soviet Union.
C) negotiated a compromise with moderates to win their political support.
D) installed Trotsky as a figurehead premier while he held the real power.
A) abolished all political offices but his own.
B) achieved absolute power in the Soviet Union.
C) negotiated a compromise with moderates to win their political support.
D) installed Trotsky as a figurehead premier while he held the real power.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Why was it Stalin who assumed the leadership of the Soviet Union following the death of Lenin?
A) He had done most of the planning of the 1917 revolution.
B) There were no other serious contenders for the leadership position.
C) He had the support of the Communist Party.
D) The Red Army was fiercely loyal to Stalin.
A) He had done most of the planning of the 1917 revolution.
B) There were no other serious contenders for the leadership position.
C) He had the support of the Communist Party.
D) The Red Army was fiercely loyal to Stalin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
What was thought to be the fundamental goal of Franklin Delano Roosevelt's New Deal?
A) To preserve capitalism by reforming it
B) To have the federal government dictate the national economy
C) To create a socialist economy
D) To reduce public regulation of the economy
A) To preserve capitalism by reforming it
B) To have the federal government dictate the national economy
C) To create a socialist economy
D) To reduce public regulation of the economy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The formation of the Popular Front in France was a response to which of the following?
A) The occupation of the Ruhr
B) U.S. isolationism
C) The growth of communism
D) The growth of fascism
A) The occupation of the Ruhr
B) U.S. isolationism
C) The growth of communism
D) The growth of fascism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of these best characterizes the impact of the New Deal?
A) It had little or no effect on the U.S. economy.
B) It ended the Great Depression.
C) It drove the United States deeper into depression.
D) It was partly successful, but it did not pull the United States out of the Great Depression.
A) It had little or no effect on the U.S. economy.
B) It ended the Great Depression.
C) It drove the United States deeper into depression.
D) It was partly successful, but it did not pull the United States out of the Great Depression.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What could be thought of as the main interest of most conservative authoritarian regimes?
A) Maintaining the status quo
B) Territorial expansion
C) Engaging in war
D) Forcing society into rapid change
A) Maintaining the status quo
B) Territorial expansion
C) Engaging in war
D) Forcing society into rapid change

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Vladimir Lenin's New Economic Policy was a political compromise with what group?
A) Urban industrial workers
B) Rural peasants
C) White counter-revolutionaries
D) Foreign capitalists
A) Urban industrial workers
B) Rural peasants
C) White counter-revolutionaries
D) Foreign capitalists

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Why did Japan invade Manchuria in 1931?
A) Japan was after Manchuria's industrial complexes.
B) Control of Manchuria would provide Japan with better access to China.
C) Japan wanted the mainland territory for Japanese settlers.
D) Manchuria was rich in raw materials.
A) Japan was after Manchuria's industrial complexes.
B) Control of Manchuria would provide Japan with better access to China.
C) Japan wanted the mainland territory for Japanese settlers.
D) Manchuria was rich in raw materials.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
President Roosevelt's Works Progress Administration was established to do which of the following?
A) Dictate how many employees every business should have
B) Stabilize the nation's banks
C) Create unemployment insurance that paid the jobless
D) Solve the problem of unemployment
A) Dictate how many employees every business should have
B) Stabilize the nation's banks
C) Create unemployment insurance that paid the jobless
D) Solve the problem of unemployment

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
How did the Scandinavian countries under socialist leadership respond to the Great Depression?
A) They raised tariffs to isolate the countries economically.
B) They used large-scale deficits to finance public works projects and maintain production.
C) They created the Scandinavian Economic Union and pooled resources.
D) They borrowed money from the United States to fund unemployment insurance.
A) They raised tariffs to isolate the countries economically.
B) They used large-scale deficits to finance public works projects and maintain production.
C) They created the Scandinavian Economic Union and pooled resources.
D) They borrowed money from the United States to fund unemployment insurance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
How much lower was global industrial output in 1933 than it had been in 1929?
A) 13 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 38 percent
D) 50 percent
A) 13 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 38 percent
D) 50 percent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Many of Stalin's new factories were built by engineers from what country?
A) China
B) Japan
C) Britain
D) The United States
A) China
B) Japan
C) Britain
D) The United States

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What can be deduced about the trade policies of the British Conservative Party from this poster? 
A) They were anti-tariff.
B) Trade relations with Asia were lagging.
C) They were pro-tariff.
D) The Great Depression was doing little to hurt British trade.

A) They were anti-tariff.
B) Trade relations with Asia were lagging.
C) They were pro-tariff.
D) The Great Depression was doing little to hurt British trade.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Whose support did Mussolini gain with the Lateran Agreement?
A) The pope and the Catholic Church
B) Italian labor unions
C) Nazi Germany
D) The military officer class
A) The pope and the Catholic Church
B) Italian labor unions
C) Nazi Germany
D) The military officer class

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
By 1941, what group made up one-half of all Communist Party members in the Soviet Union?
A) American expatriates
B) Women
C) New members who had joined since the purges
D) Enemies of Stalin
A) American expatriates
B) Women
C) New members who had joined since the purges
D) Enemies of Stalin

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
By 1950, 75 percent of all Soviet doctors were what?
A) Retired army officers
B) Jews
C) Women
D) Former kulaks
A) Retired army officers
B) Jews
C) Women
D) Former kulaks

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In Mein Kampf, Hitler presents his basic anti-Semitic ideas and his conviction that Germany needed more land for what purpose?
A) Large-scale factories
B) Expansion
C) Exiling Jews
D) Collectivized farming
A) Large-scale factories
B) Expansion
C) Exiling Jews
D) Collectivized farming

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The Nuremberg Laws
A) ordered all professional Jews to leave Germany.
B) created the secret police, the Gestapo.
C) deprived German Communists of the right of citizenship.
D) stated that anyone with three or more Jewish grandparents was Jewish.
A) ordered all professional Jews to leave Germany.
B) created the secret police, the Gestapo.
C) deprived German Communists of the right of citizenship.
D) stated that anyone with three or more Jewish grandparents was Jewish.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The most impressive accomplishments of Stalin's five-year plans can be regarded to have occurred in what area?
A) Collectivized agriculture
B) Heavy industry
C) Consumer goods
D) Foreign trade
A) Collectivized agriculture
B) Heavy industry
C) Consumer goods
D) Foreign trade

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
What characterized Mussolini's policies for women?
A) They were more far-reaching than those in the Soviet Union.
B) He liberalized divorce laws.
C) He required that women be given 20 percent of all higher-level jobs in industry.
D) He favored a return to traditional roles and encouraged women to have many children.
A) They were more far-reaching than those in the Soviet Union.
B) He liberalized divorce laws.
C) He required that women be given 20 percent of all higher-level jobs in industry.
D) He favored a return to traditional roles and encouraged women to have many children.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Hitler acquired absolute dictatorial power as a result of what event?
A) The passage of the Enabling Act
B) A wave of strikes by German labor unions
C) The death of President Hindenburg
D) The assassination of a German diplomat by a Jew
A) The passage of the Enabling Act
B) A wave of strikes by German labor unions
C) The death of President Hindenburg
D) The assassination of a German diplomat by a Jew

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Italian workers felt cheated by World War I because they had been promised what in exchange for fighting?
A) New labor unions
B) Secularization of the state
C) Tax cuts
D) Social and land reforms
A) New labor unions
B) Secularization of the state
C) Tax cuts
D) Social and land reforms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
What was one of Stalin's rationales for the "second revolution"?
A) He thought that the Soviet Union's survival depended on catching up with the West.
B) He wanted to finish what Lenin had started.
C) He wanted to keep the peasants distracted and prevent them from revolting.
D) He was attempting to move agriculture to south Russia.
A) He thought that the Soviet Union's survival depended on catching up with the West.
B) He wanted to finish what Lenin had started.
C) He wanted to keep the peasants distracted and prevent them from revolting.
D) He was attempting to move agriculture to south Russia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
As a young man, Adolf Hitler formed many of his anti-Semitic beliefs while living where?
A) Munich
B) Berlin
C) Vienna
D) Linz
A) Munich
B) Berlin
C) Vienna
D) Linz

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Benito Mussolini's private army was known as what?
A) The Cheka
B) The Brown Shirts
C) The Black Shirts
D) The Stasi
A) The Cheka
B) The Brown Shirts
C) The Black Shirts
D) The Stasi

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The term fascist comes from the Italian word for what?
A) "A union of forces"
B) "Strength"
C) "Fist"
D) "National authority"
A) "A union of forces"
B) "Strength"
C) "Fist"
D) "National authority"

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
What was one of Hitler's beliefs about Jews?
A) They were misunderstood
B) They were republicans
C) They were liberals
D) They were Marxist socialists
A) They were misunderstood
B) They were republicans
C) They were liberals
D) They were Marxist socialists

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
What did many Russian peasants do to their crops in order to protest collectivization?
A) They traded them.
B) They sold them.
C) They burned them.
D) They hid them.
A) They traded them.
B) They sold them.
C) They burned them.
D) They hid them.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of the following characterized Nazi culture under Hitler?
A) It was antiwar.
B) It was pro-multicultural.
C) It was anti-intellectual.
D) It was pro-free market.
A) It was antiwar.
B) It was pro-multicultural.
C) It was anti-intellectual.
D) It was pro-free market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Based on Map 30.2, "World War II in Europe and Africa, 1939-1945," which was the only European member of the Allies not occupied by the Axis powers? 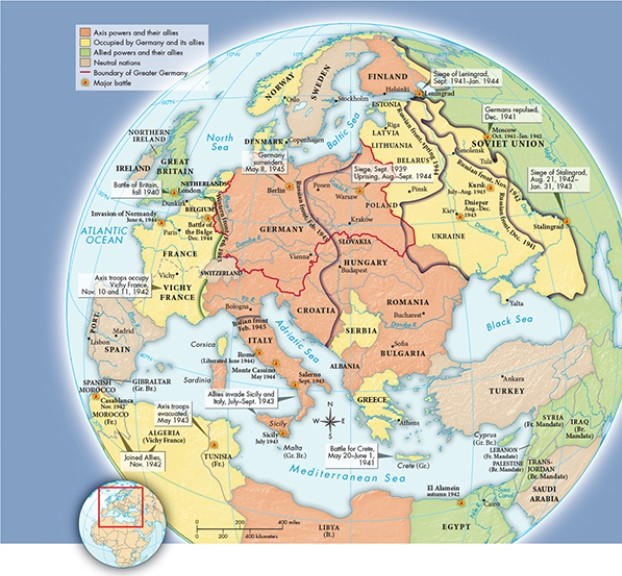
A) France
B) Norway
C) Denmark
D) Great Britain

A) France
B) Norway
C) Denmark
D) Great Britain

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Stalin ordered what group to be obliterated as a class?
A) Kulaks
B) Intellectuals
C) Nobles
D) Artists
A) Kulaks
B) Intellectuals
C) Nobles
D) Artists

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
What was the difference between totalitarianism in the Soviet Union and in Germany?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What was the New Deal? In what ways did it succeed, and in what ways did it fail?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In August 1939, Germany and what other country signed a ten-year nonaggression pact?
A) Poland
B) Japan
C) The Soviet Union
D) Great Britain
A) Poland
B) Japan
C) The Soviet Union
D) Great Britain

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
In September 1940, Japan signed a formal alliance with what country?
A) The United States
B) China
C) Germany
D) The Soviet Union
A) The United States
B) China
C) Germany
D) The Soviet Union

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
What was the goal of the British policy of appeasement?
A) To prepare the way for a German-British alliance
B) To lull Germany into a false sense of security
C) To buy time to rearm
D) To avoid another general war
A) To prepare the way for a German-British alliance
B) To lull Germany into a false sense of security
C) To buy time to rearm
D) To avoid another general war

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following was true of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor?
A) It destroyed the entire Pacific fleet of the United States.
B) It came only minutes after Japan had declared war on the United States.
C) It did not affect American aircraft carriers.
D) It was supported by German U-boats.
A) It destroyed the entire Pacific fleet of the United States.
B) It came only minutes after Japan had declared war on the United States.
C) It did not affect American aircraft carriers.
D) It was supported by German U-boats.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
How did Stalin's reforms of Soviet society transform the lives of Soviet women?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
At the onset of the Great Depression, what actions by nations worsened the economic conditions? What steps could these nations have taken to improve conditions?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
How did Hitler and the Nazi Party use propaganda to gather support? What kinds of propaganda did they use?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
What kinds of Germans were critical of Nazism?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What World War II battle was the turning point for the Allies in the Pacific in 1944?
A) Battle of Midway
B) Battle of Leyte Gulf
C) Battle of the Coral Sea
D) Battle of Guadalcanal
A) Battle of Midway
B) Battle of Leyte Gulf
C) Battle of the Coral Sea
D) Battle of Guadalcanal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Who had the more totalitarian government, Benito Mussolini or Joseph Stalin?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What were some of the problems Italy had to deal with before World War II? Did any of these problems change with the war?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
By 1938, Hitler's domestic policies had resulted in which of the following?
A) Heavy taxation to pay for his highways, sports stadiums, and rearmament programs
B) A steady drop in unemployment
C) Greater economic equality for women
D) Little improvement in the average standard of living
A) Heavy taxation to pay for his highways, sports stadiums, and rearmament programs
B) A steady drop in unemployment
C) Greater economic equality for women
D) Little improvement in the average standard of living

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Why did Japan lose the war in the Pacific? Was there a turning point in the fighting?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What action taken by the Nazis, as illustrated in Map 30.1, "The Growth of Nazi Germany, 1933-1939," was a direct violation of the Treaty of Versailles? 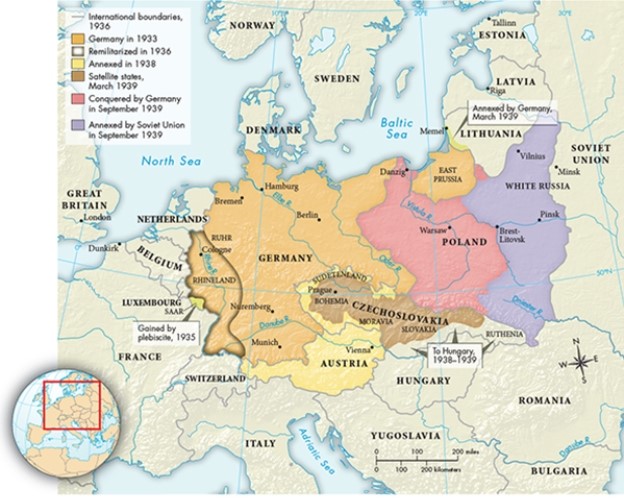
A) The remilitarization of the Rhineland
B) The invasion of Poland
C) The annexation of East Prussia
D) The remilitarization of the Sudetenland

A) The remilitarization of the Rhineland
B) The invasion of Poland
C) The annexation of East Prussia
D) The remilitarization of the Sudetenland

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
During the war, Japan claimed that it was freeing Asians from which of the following?
A) Communist hegemony
B) The threat of communism
C) Monarchical rule
D) Western imperialism
A) Communist hegemony
B) The threat of communism
C) Monarchical rule
D) Western imperialism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
In June 1941, Hitler ordered what military action?
A) An aerial "blitz" of London to break the will of England
B) An attack on the Soviet Union
C) The building of an atomic weapon
D) Establishment of the Vichy government in France
A) An aerial "blitz" of London to break the will of England
B) An attack on the Soviet Union
C) The building of an atomic weapon
D) Establishment of the Vichy government in France

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
What made the Grand Alliance such a powerful adversary against Hitler and Nazi Germany?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Many historians believe that the beginning of the Final Solution occurred with what event?
A) Kristallnacht
B) The failed coup of 1925
C) The publication of Mein Kampf
D) The 1934 purging of the Nazi Party
A) Kristallnacht
B) The failed coup of 1925
C) The publication of Mein Kampf
D) The 1934 purging of the Nazi Party

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer questions :
New Economic Policy (NEP)
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
New Economic Policy (NEP)
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The most horrifying aspect of Hitler's ideology and his regime was its anti-Semitism, culminating in the Final Solution, which claimed over 6 million lives including millions of Jews. Describe Nazi policies toward the Jews of Europe, being sure to indicate the basis of Hitler's anti-Semitism. Were ordinary Germans Hitler's willing accomplices?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
What factors contributed to the Grand Alliance's military success? What were the turning points in the Allies' march to victory?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions :
fascism
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
fascism
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions :
collectivization
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
collectivization
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer questions :
New Order
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
New Order
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer questions :
blitzkrieg
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
blitzkrieg
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions :
five-year plan
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
five-year plan
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the world suffered through the Great Depression. What were the causes of the economic collapse? How did the United States and the European states respond to this crisis? How effective were their responses? What were the consequences of the Great Depression?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions :
Holocaust
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
Holocaust
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions :
Popular Front
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
Popular Front
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Use the following to answer questions :
Lateran Agreement
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
Lateran Agreement
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Describe Stalin's "revolution from above." What factors prompted Stalin's actions, and what were his goals? How successful was the revolution?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Use the following to answer questions :
New Deal
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
New Deal
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer questions :
Black Shirts
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
Black Shirts
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Use the following to answer questions :
totalitarianism
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
totalitarianism
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Some have argued that strong actions by England and France in the mid-1930s would have prevented World War II and that appeasement merely whetted Hitler's appetite. How accurate is this statement?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Use the following to answer questions :
Enabling Act
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
Enabling Act
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Use the following to answer questions :
Nazism
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
Nazism
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Use the following to answer questions :
Europe first policy
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.
Europe first policy
A)Franklin Delano Roosevelt's plan to reform capitalism in the United States through forceful government intervention in the economy.
B)A party formed in 1936 in France that encouraged unions and launched a far-reaching New Deal-inspired program of social reform.
C)A radical dictatorship that exercises complete political power and control over all aspects of society and seeks to mobilize the masses for action.
D)A movement characterized by extreme, often expansionist nationalism, anti-socialism, a dynamic and violent leader, and glorification of war and the military.
E)Launched by Stalin in 1928 and termed the "revolution from above," its goal was to modernize the Soviet Union and generate a Communist society with new attitudes, new loyalties, and a new socialist humanity.
F)Lenin's 1921 policy re-establishing limited economic freedom in the Soviet Union in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration.
G)Stalin's forcible consolidation, beginning in 1929, of individual peasant farms in the Soviet Union into large, state-controlled enterprises.
H)A private army under Mussolini in Italy that destroyed Socialist newspapers, union halls, and local Socialist Party headquarters, eventually pushing Socialists out of the city governments of northern Italy.
I)A 1929 agreement in which Mussolini in Italy recognized the Vatican as an independent state and agreed to give the church heavy financial support in return for the pope's public support.
J)A movement born of extreme nationalism and racism and dominated by Adolf Hitler from 1933 until the end of World War II in 1945.
K)An act pushed through the Reichstag by the Nazis in 1933 that gave Hitler absolute dictatorial power for four years.
L)"Lightning war" using planes, tanks, and trucks, first used by Hitler to crush Poland in four weeks.
M)Hitler's program, based on the guiding principle of racial imperialism, which gave preferential treatment to the Nordic peoples above "inferior" Latin peoples and, at the bottom, "subhuman" Slavs and Jews.
N)The attempted systematic extermination of all European Jews and other "undesirables" by the Nazi state during World War II.
O)The military strategy, set forth by Churchill and adopted by Roosevelt, that called for the defeat of Hitler in Europe before the United States launched an all-out strike against Japan in the Pacific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








