Deck 24: Ideologies of Change in Europe, 1815-1914
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 24: Ideologies of Change in Europe, 1815-1914
1
Who co-wrote The Communist Manifesto with Karl Marx?
A) Henri de Saint-Simon
B) Charles Fourier
C) Friedrich Engels
D) Robert Owen
A) Henri de Saint-Simon
B) Charles Fourier
C) Friedrich Engels
D) Robert Owen
Friedrich Engels
2
Which of the following was a primary cause of the French Revolution of 1848?
A) The landed aristocracy was dissatisfied over questions of property ownership.
B) Workers in France's silk factories were upset over factory wages.
C) Women in the major cities were angry over high bread prices.
D) The French government refused to consider electoral reforms.
A) The landed aristocracy was dissatisfied over questions of property ownership.
B) Workers in France's silk factories were upset over factory wages.
C) Women in the major cities were angry over high bread prices.
D) The French government refused to consider electoral reforms.
The French government refused to consider electoral reforms.
3
What did the members of the Quadruple Alliance have in common?
A) They wanted to take advantage of France's defeat to gain land.
B) All were conservative monarchies and wanted to keep France in check.
C) They were more concerned with their colonial reforms than European stability.
D) They had been allies of Napoleon until they changed sides.
A) They wanted to take advantage of France's defeat to gain land.
B) All were conservative monarchies and wanted to keep France in check.
C) They were more concerned with their colonial reforms than European stability.
D) They had been allies of Napoleon until they changed sides.
All were conservative monarchies and wanted to keep France in check.
4
In what way is the so-called scientific racism of the late nineteenth century depicted in this postcard entitled "The Expulsion of the Jews from Russia"? 
A) The Germans, whom the Russians perceived as an inferior people, are welcoming the Jews.
B) The Jews are depicted in an exaggerated caricature-style intended to portray them as an
Inferior race.
C) The clothing styles worn by the Jews were those typically associated with the lower classes.
D) All of the cities listed on the signposts were typically perceived as safe havens for those
Deemed intellectually and culturally inferior.

A) The Germans, whom the Russians perceived as an inferior people, are welcoming the Jews.
B) The Jews are depicted in an exaggerated caricature-style intended to portray them as an
Inferior race.
C) The clothing styles worn by the Jews were those typically associated with the lower classes.
D) All of the cities listed on the signposts were typically perceived as safe havens for those
Deemed intellectually and culturally inferior.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The Ten Hours Act limited the factory workday for which of the following groups?
A) Women and young people
B) Men older than thirty
C) All workers
D) Weavers
A) Women and young people
B) Men older than thirty
C) All workers
D) Weavers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What ideas united the victorious allies at the Congress of Vienna?
A) They were all motivated by traditional ideas about the balance of power.
B) They all wanted to resurrect the Holy Roman Empire under Habsburg rule.
C) They were all motivated by a desire to punish France harshly and reduced it in size.
D) They sought to establish constitutional monarchies in the areas conquered by Napoleon.
A) They were all motivated by traditional ideas about the balance of power.
B) They all wanted to resurrect the Holy Roman Empire under Habsburg rule.
C) They were all motivated by a desire to punish France harshly and reduced it in size.
D) They sought to establish constitutional monarchies in the areas conquered by Napoleon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following was true of the Karlsbad Decrees?
A) They sparked the revolutions of 1848.
B) They instituted repressive measures in the German Confederation.
C) They established a constitutional monarchy in France.
D) They created a military alliance out of the Congress of Vienna.
A) They sparked the revolutions of 1848.
B) They instituted repressive measures in the German Confederation.
C) They established a constitutional monarchy in France.
D) They created a military alliance out of the Congress of Vienna.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
To help Austria subdue Hungary, what country's leader sent troops to occupy the territory in 1849?
A) Bohemia
B) France
C) Russia
D) Prussia
A) Bohemia
B) France
C) Russia
D) Prussia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
What kind of government emerged in France in the aftermath of the revolution of 1848?
A) An enduring socialist government
B) A conservative government led by an emperor
C) A moderate democratic republic with universal manhood suffrage
D) A military dictatorship led by the army's top general
A) An enduring socialist government
B) A conservative government led by an emperor
C) A moderate democratic republic with universal manhood suffrage
D) A military dictatorship led by the army's top general

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
What class did Marx believe would rise up in revolution?
A) The landed aristocracy
B) Intellectuals
C) The middle class
D) Industrial factory workers
A) The landed aristocracy
B) Intellectuals
C) The middle class
D) Industrial factory workers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Between 1815 and 1850, most people who believed in nationalism
A) opposed liberalism.
B) also favored democratic republicanism.
C) were concerned about growing industrialization.
D) distrusted the common masses.
A) opposed liberalism.
B) also favored democratic republicanism.
C) were concerned about growing industrialization.
D) distrusted the common masses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Early French socialists focused on which of the following?
A) Workers' revolutions
B) Land use reform
C) Overthrowing monarchies
D) Economic planning
A) Workers' revolutions
B) Land use reform
C) Overthrowing monarchies
D) Economic planning

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Austria's foreign minister, Klemens von Metternich, dominated the politics and policies of what?
A) Russia
B) The Austro-Hungarian Empire
C) The German Confederation
D) Great Britain
A) Russia
B) The Austro-Hungarian Empire
C) The German Confederation
D) Great Britain

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What did liberals and democrats see as the ultimate source for good government?
A) The monarchy
B) God
C) The people
D) Scientific rationalism
A) The monarchy
B) God
C) The people
D) Scientific rationalism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Camillo Benso di Cavour sought to unite Italy under the authority of what state(s)?
A) The Papal States
B) Naples
C) Sardinia
D) Sicily
A) The Papal States
B) Naples
C) Sardinia
D) Sicily

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Where did the doctrine of socialism begin?
A) Russia
B) Great Britain
C) Germany
D) France
A) Russia
B) Great Britain
C) Germany
D) France

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The Great Famine of 1845-1851 devastated the population of what country?
A) England
B) Ireland
C) France
D) Russia
A) England
B) Ireland
C) France
D) Russia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a doctrine of economic liberalism that emphasizes unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference?
A) Laissez faire
B) Mercantilism
C) Trickle-down economics
D) Value theory
A) Laissez faire
B) Mercantilism
C) Trickle-down economics
D) Value theory

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
This political cartoon is of the Congress of Vienna, during which European leaders divided Europe amongst themselves. Why is Napoleon, who is seen severing France from the rest of Europe, included in this cartoon? 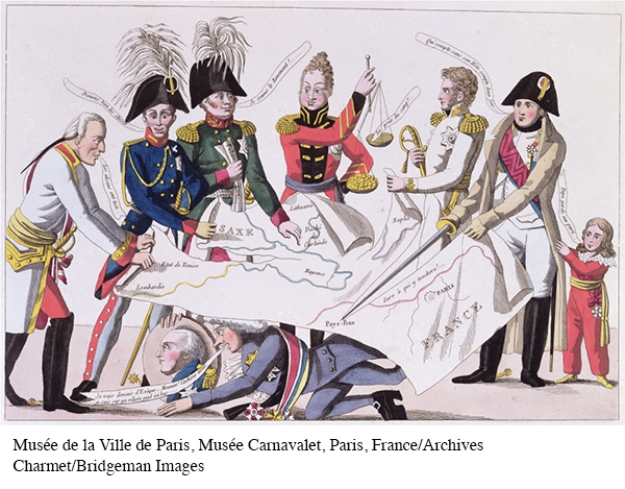
A) Napoleon temporarily escaped his exile on the island of Elbe.
B) It was believed that even while in exile Napoleon wielded influence over the Congress.
C) Congress attendees cared only for satisfying their own territorial ambitions.
D) The artist believed that Napoleon's reign had forever destroyed any hope of a future unified Europe.

A) Napoleon temporarily escaped his exile on the island of Elbe.
B) It was believed that even while in exile Napoleon wielded influence over the Congress.
C) Congress attendees cared only for satisfying their own territorial ambitions.
D) The artist believed that Napoleon's reign had forever destroyed any hope of a future unified Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The fatal obstacle to German unification under Prussian leadership in 1850 was the
A) middle class's lack of enthusiasm.
B) opposition of Austria and Russia.
C) war with Hungary.
D) opposition of Britain and France.
A) middle class's lack of enthusiasm.
B) opposition of Austria and Russia.
C) war with Hungary.
D) opposition of Britain and France.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
What was the most significant difference between Austria and the rest of the German states in 1853?
A) Language
B) Membership in the Zollverein
C) Political systems
D) Ethnic makeups
A) Language
B) Membership in the Zollverein
C) Political systems
D) Ethnic makeups

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What was one important German response to the Austro-Prussian War of 1866?
A) Industrial workers rebelled and captured Wilhelm I.
B) Critics of the government were imprisoned and/or deported by Bismarck.
C) Middle-class liberals adopted Bismarck's brand of nationalism.
D) Catholics formed a political party to protect their interests.
A) Industrial workers rebelled and captured Wilhelm I.
B) Critics of the government were imprisoned and/or deported by Bismarck.
C) Middle-class liberals adopted Bismarck's brand of nationalism.
D) Catholics formed a political party to protect their interests.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
An English law passed in 1882 granted which of the following to married women?
A) Voting rights
B) Equal wages
C) Full property rights
D) The right to attend universities
A) Voting rights
B) Equal wages
C) Full property rights
D) The right to attend universities

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
How did the invention of the steam engine affect urbanization?
A) It mechanized agriculture and drew people away from urban areas.
B) It allowed for the building of factories away from water, thus contributing to urbanization.
C) It encouraged the development of commuter rail systems based on the steam locomotive.
D) It generated so much pollution that factories were moved to the outskirts of towns.
A) It mechanized agriculture and drew people away from urban areas.
B) It allowed for the building of factories away from water, thus contributing to urbanization.
C) It encouraged the development of commuter rail systems based on the steam locomotive.
D) It generated so much pollution that factories were moved to the outskirts of towns.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
For what is Georges Haussmann best remembered?
A) Leading massive rebuilding projects in Paris
B) Developing the antiseptic method
C) Writing realistic novels of lower-class life
D) Promoting positivist philosophy
A) Leading massive rebuilding projects in Paris
B) Developing the antiseptic method
C) Writing realistic novels of lower-class life
D) Promoting positivist philosophy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
According to Map 24.1, "Europe in 1815," Austria became the largest kingdom within the German Confederation after the Congress of Vienna awarded it territory. This territory later became part of which country? 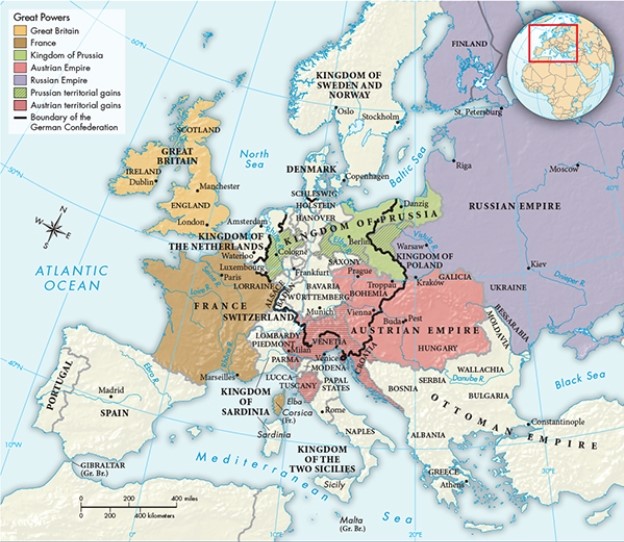
A) Hungary
B) Bohemia
C) Bosnia
D) Italy

A) Hungary
B) Bohemia
C) Bosnia
D) Italy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
At the end of the nineteenth century, white-collar employees were identified with what group?
A) The working class
B) Labor aristocracy
C) The middle class
D) The propertied class
A) The working class
B) Labor aristocracy
C) The middle class
D) The propertied class

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What transportation innovation was introduced to European cities in the 1890s?
A) Trains
B) Steam cars
C) Bicycles
D) Electric streetcars
A) Trains
B) Steam cars
C) Bicycles
D) Electric streetcars

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
What evidence of the impact of technology on everyday life can be found in this painting of Madrid? 
A) Telegraph wires
B) Horse-drawn carriages
C) Electric streetcars
D) A large public square

A) Telegraph wires
B) Horse-drawn carriages
C) Electric streetcars
D) A large public square

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
In the nineteenth century, same-sex attraction was identified as which of the following?
A) A perversion
B) Acceptable only among the upper classes
C) A generally accepted sexual practice
D) Legally protected for single men only
A) A perversion
B) Acceptable only among the upper classes
C) A generally accepted sexual practice
D) Legally protected for single men only

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The long-established customs union among the German states was known as the
A) Red Shirts.
B) Zollverein.
C) Werke.
D) North German Confederation.
A) Red Shirts.
B) Zollverein.
C) Werke.
D) North German Confederation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
What ended the era of Alexander II's reforms?
A) A massive peasant revolt
B) His assassination
C) His army's failed invasion of Manchuria
D) An outbreak of cholera
A) A massive peasant revolt
B) His assassination
C) His army's failed invasion of Manchuria
D) An outbreak of cholera

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
How did the upper middle class change as the nineteenth century progressed?
A) It tended to merge with the old aristocracy.
B) It began to form tighter bonds with the rest of the middle class.
C) It expressed a high degree of social conscience.
D) It retained a frugal attitude and modest display of wealth.
A) It tended to merge with the old aristocracy.
B) It began to form tighter bonds with the rest of the middle class.
C) It expressed a high degree of social conscience.
D) It retained a frugal attitude and modest display of wealth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Who was the leader of the final campaign to unite north and south Italy?
A) Giuseppe Garibaldi
B) Camillo Benso di Cavour
C) Father Gioberti
D) Victor Emmanuel
A) Giuseppe Garibaldi
B) Camillo Benso di Cavour
C) Father Gioberti
D) Victor Emmanuel

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Why did Prussia's King Wilhelm I try to raise taxes in 1862?
A) He wanted to double the size of the army.
B) He planned to invade Austria.
C) He wanted to build new industries.
D) He was hoping to acquire more colonies.
A) He wanted to double the size of the army.
B) He planned to invade Austria.
C) He wanted to build new industries.
D) He was hoping to acquire more colonies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The October Manifesto of Nicholas II created the Duma, which was what?
A) A reform movement with the army
B) The new liberal constitution of Russia
C) A modern railroad to Siberia
D) Russia's popularly elected parliament
A) A reform movement with the army
B) The new liberal constitution of Russia
C) A modern railroad to Siberia
D) Russia's popularly elected parliament

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
In a plan to force Austria to give up its territory in Italy, Cavour secured a secret alliance with what country?
A) Great Britain
B) Prussia
C) Russia
D) France
A) Great Britain
B) Prussia
C) Russia
D) France

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
What was the "labor aristocracy" of the nineteenth century?
A) Traditional farm workers
B) Highly skilled workers
C) Factory owners
D) Literate workers
A) Traditional farm workers
B) Highly skilled workers
C) Factory owners
D) Literate workers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
What did Edwin Chadwick's work lead to?
A) Great Britain's first public health law
B) Great Britain's first social welfare law
C) Great Britain's first antidiscrimination law
D) Great Britain's first minimum wage law
A) Great Britain's first public health law
B) Great Britain's first social welfare law
C) Great Britain's first antidiscrimination law
D) Great Britain's first minimum wage law

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following pushed Russia toward modernization?
A) The loss of Silesia to Austria
B) An unsuccessful war with Poland
C) A rebellion of serfs
D) The Crimean War
A) The loss of Silesia to Austria
B) An unsuccessful war with Poland
C) A rebellion of serfs
D) The Crimean War

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
In central and eastern Europe, what did romantic writers focus on?
A) Subjects from the ancient world
B) Emulating French culture
C) Local languages and peasant folktales, songs, and proverbs
D) The glorification of their national heroes
A) Subjects from the ancient world
B) Emulating French culture
C) Local languages and peasant folktales, songs, and proverbs
D) The glorification of their national heroes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following was a consequence of the Dreyfus affair?
A) It revived the prestige of the French army.
B) It drove a wedge between Catholics and anti-Semites.
C) It revived republican distrust of Catholicism.
D) It fanned the flames of French imperialism.
A) It revived the prestige of the French army.
B) It drove a wedge between Catholics and anti-Semites.
C) It revived republican distrust of Catholicism.
D) It fanned the flames of French imperialism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
What was an important argument of the philosopher Herbert Spencer?
A) The new science of sociology could uncover the basic laws of human society.
B) There was a divine creation for each species of animal.
C) The concept of "race" had no scientific basis.
D) The human race was driven by "the survival of the fittest."
A) The new science of sociology could uncover the basic laws of human society.
B) There was a divine creation for each species of animal.
C) The concept of "race" had no scientific basis.
D) The human race was driven by "the survival of the fittest."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
How did the working class become subdivided into specialized classes?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Was the new German Empire of 1871 a nationalist or a liberal state? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What were the guiding principles behind the Quadruple Alliance and the Congress of Vienna?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What were the major problems facing nineteenth-century European cities? How and with what degree of success were these problems addressed?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In terms of Italian unification, what did Victor Emmanuel, Cavour, and Garibaldi have in common, and how did they differ?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
What was the most troublesome political problem for Great Britain immediately prior to World War I?
A) Suffrage for women
B) National health insurance
C) Independence for India
D) Irish home rule
A) Suffrage for women
B) National health insurance
C) Independence for India
D) Irish home rule

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Describe the different ethnic groups that made up the Austrian Empire. What impact did those groups have on the revolutions of 1848?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What changed politically in France as a result of the brutal destruction of the Paris Commune?
A) Radicals made strong gains in the 1871 national elections.
B) The National Assembly was closed.
C) The 1871 national elections were called off.
D) France formed a new national unity.
A) Radicals made strong gains in the 1871 national elections.
B) The National Assembly was closed.
C) The 1871 national elections were called off.
D) France formed a new national unity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
How did transportation change in nineteenth-century Europe, and how did this change the lives of urban citizens?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
How did scientific theory and concepts of race intersect in the late nineteenth century?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
What was the bacterial revolution?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
What did the journalist Theodor Herzl advocate?
A) The full emancipation of Jews in Prussia
B) Economic equality for German women
C) The creation of a Jewish state
D) The unification of Austria and Prussia
A) The full emancipation of Jews in Prussia
B) Economic equality for German women
C) The creation of a Jewish state
D) The unification of Austria and Prussia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
By 1913-1914, where had women gained the right to vote?
A) Great Britain and Sweden
B) France and the Netherlands
C) Germany
D) Norway and parts of the western United States
A) Great Britain and Sweden
B) France and the Netherlands
C) Germany
D) Norway and parts of the western United States

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
In the dual monarchy, what group gained independence in Hungary?
A) Serbs
B) Magyars
C) Czechs
D) Lutherans
A) Serbs
B) Magyars
C) Czechs
D) Lutherans

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What did Charles Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection tend to reinforce?
A) Views of secularists such as Spencer and Marx
B) The bacterial theory of disease tested by Pasteur
C) The Catholic Church's opposition to expansion of political participation
D) The drive for universal public education in Europe
A) Views of secularists such as Spencer and Marx
B) The bacterial theory of disease tested by Pasteur
C) The Catholic Church's opposition to expansion of political participation
D) The drive for universal public education in Europe

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
What developments inspired the work of early French socialists?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The exchange of which territories in this map reflect the dismantling of territorial concessions made during the Congress of Vienna? 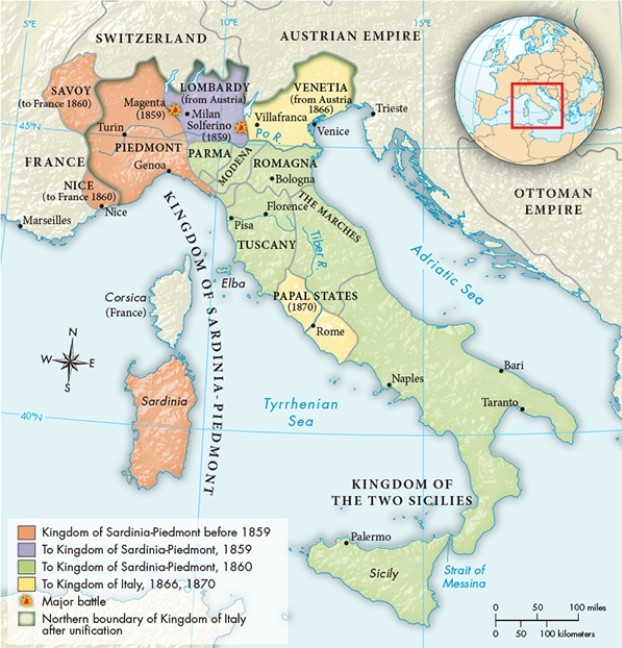
A) Lombardy and Venetia
B) Piedmont and Savoy
C) The Papal States and Nice
D) Romagna and Tuscany

A) Lombardy and Venetia
B) Piedmont and Savoy
C) The Papal States and Nice
D) Romagna and Tuscany

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The 1860s saw the success of the nation-building efforts of Cavour in Italy and Bismarck in Germany. Choose either location and describe the process by which unification was achieved, assess the reasons for success, and indicate the consequences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions :
Zionism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
Zionism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions :
modernization
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
modernization
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The years 1815 to 1848 saw the emergence and evolution of socialism in France. Describe this evolution, being sure to emphasize the ideology's principal components. How did socialism reflect the attitudes and aspirations of working people of the time? How did the revolution of 1848 reflect the impact of socialist ideals?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions :
conservatism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
conservatism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer questions :
germ theory
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
germ theory
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
How do we account for the early success and later collapse of the revolutionary movements of 1848?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions :
socialism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
socialism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer questions :
Romanticism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
Romanticism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions :
bourgeoisie
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
bourgeoisie
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions :
Social Darwinism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
Social Darwinism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
How did the lives of European women change during the second half of the nineteenth century?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Use the following to answer questions :
nationalism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
nationalism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
What were the forces driving political reform in England after 1815, which involved the expansion of suffrage and the passage of laws regulating factory labor?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer questions :
liberalism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
liberalism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Use the following to answer questions :
proletariat
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
proletariat
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Use the following to answer questions :
Congress of Vienna
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
Congress of Vienna
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Use the following to answer questions :
revisionism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
revisionism
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Use the following to answer questions :
Dreyfus affair
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
Dreyfus affair
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Use the following to answer questions :
laissez faire
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.
laissez faire
A)A meeting of the Quadruple Alliance (Russia, Prussia, Austria, Great Britain) and France held in 1814-1815 to fashion a general peace settlement after the defeat of Napoleonic France.
B)A political philosophy that stressed retaining traditional values and institutions, including hereditary monarchy and a strong landowning aristocracy.
C)A philosophy whose principal ideas were equality and liberty; proponents demanded representative government and equality before the law as well as such individual freedoms as freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom from arbitrary arrest.
D)A doctrine of economic liberalism advocating unrestricted private enterprise and no government interference in the economy.
E)The idea that each people had its own spirit and its own cultural unity, which manifested itself especially in a common language and history and could serve as the basis for an independent political state.
F)A radical political doctrine that opposed individualism and that advocated international cooperation and a sense of community; key ideas were economic planning, greater economic equality, and state regulation of property.
G)The well-educated, prosperous, middle-class groups.
H)The Marxist term for the working class of modern industrialized society.
I)The changes that enable a country to compete effectively with the leading countries at a given time.
J)The result of a great general strike in Russia in 1905, it granted full civil rights and promised a popularly elected Duma (parliament) with real legislative power.
K)The idea that disease is caused by the spread of living organisms that can be controlled.
L)The idea, developed by Charles Darwin, that all life had gradually evolved from a common origin through a process of natural selection.
M)The application of the theory of biological evolution to human affairs, it sees the human race as driven to ever-greater specialization and progress by an unending economic struggle that determines the survival of the fittest.
N)A movement in art, literature, and music characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life
O)A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army was falsely accused and convicted of treason.
P)The movement toward Jewish political nationhood started by Theodor Herzl.
Q)An effort by various socialists to update Marxist doctrines to reflect the realities of the time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 82 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








