Deck 8: Tests of Hypotheses Based on a Single Sample
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Tests of Hypotheses Based on a Single Sample
1
The rejection region is called __________ if it consists only of small values of the test statistic.
lower-tailed
2
A __________ error is usually more serious than a __________ error.
type I, type II
3
Suppose a test procedure about the population mean 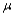 is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation
is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation 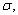 then if the alternative hypothesis is
then if the alternative hypothesis is 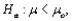 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 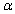 test is __________.
test is __________.
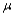 is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation
is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation 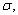 then if the alternative hypothesis is
then if the alternative hypothesis is 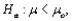 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 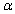 test is __________.
test is __________.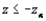
4
A __________ error involves not rejecting the null hypothesis 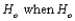 is false.
is false.
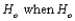 is false.
is false.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The rejection region is called __________ if it consists only of large values of the test statistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The null hypothesis will be rejected if and only if the observed or computed __________ value falls in the __________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Suppose a test procedure about the population mean 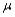 is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation
is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation 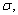 then if the alternative hypothesis is
then if the alternative hypothesis is 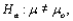 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 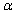 test is either __________ or __________.
test is either __________ or __________.
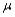 is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation
is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation 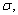 then if the alternative hypothesis is
then if the alternative hypothesis is 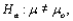 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 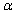 test is either __________ or __________.
test is either __________ or __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
If the null hypothesis is 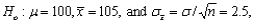 then the test statistic value is z = __________.
then the test statistic value is z = __________.
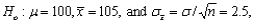 then the test statistic value is z = __________.
then the test statistic value is z = __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
An engineer has suggested a change in the production process in the belief that it will result in a reduced defective rate. Let p denote the true proportion of defective items resulting from the changed process, and that 5% of items produced by a manufacturer during a certain period were defective. Then the research hypothesis is the assertion that __________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The __________ hypothesis should be identified with the hypothesis of no change, no difference, no improvement, and son on.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A __________ error consists of rejecting the null hypothesis 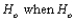 is true.
is true.
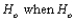 is true.
is true.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
For any significance level 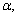 the two-tailed rejection region
the two-tailed rejection region 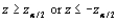 has type I error probability equal to __________.
has type I error probability equal to __________.
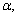 the two-tailed rejection region
the two-tailed rejection region 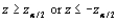 has type I error probability equal to __________.
has type I error probability equal to __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
If 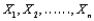 is a random sample from a normal distribution, and the sample size n is small, then the standardized variable
is a random sample from a normal distribution, and the sample size n is small, then the standardized variable 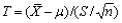 has a __________ distribution with __________ degrees of freedom.
has a __________ distribution with __________ degrees of freedom.
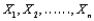 is a random sample from a normal distribution, and the sample size n is small, then the standardized variable
is a random sample from a normal distribution, and the sample size n is small, then the standardized variable 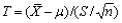 has a __________ distribution with __________ degrees of freedom.
has a __________ distribution with __________ degrees of freedom.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Suppose a test procedure about the population mean 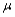 is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation
is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation 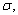 then if the alternative hypothesis is
then if the alternative hypothesis is 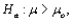 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 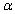 test is __________.
test is __________.
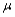 is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation
is performed, when the population is normal with known standard deviation 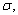 then if the alternative hypothesis is
then if the alternative hypothesis is 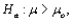 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 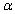 test is __________.
test is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The probabilities of type I and type II errors are traditionally denoted by the Greek letters __________ and __________, respectively.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Suppose a test procedure about the population mean 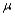 is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is
is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is 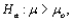 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 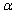 test is __________.
test is __________.
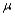 is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is
is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is 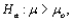 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 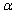 test is __________.
test is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Suppose a test procedure about the population mean 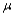 is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is
is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is 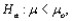 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 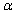 test is __________.
test is __________.
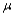 is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is
is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is 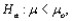 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 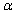 test is __________.
test is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In many situations, the alternative hypothesis is referred to as the __________ hypothesis, since it is the statement the researcher would really like to validate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The value 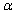 that represents the probability of type I error is often referred to as the __________ of the test.
that represents the probability of type I error is often referred to as the __________ of the test.
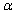 that represents the probability of type I error is often referred to as the __________ of the test.
that represents the probability of type I error is often referred to as the __________ of the test.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In our treatment of hypothesis testing, the __________ hypothesis will always be stated as an equality claim.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
For an upper-tailed z test, the level of significance 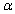 is just the area under the z curve to the __________ of the critical value __________.
is just the area under the z curve to the __________ of the critical value __________.
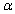 is just the area under the z curve to the __________ of the critical value __________.
is just the area under the z curve to the __________ of the critical value __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Suppose that a test procedure about the population proportion p is performed, and that the sample proportion 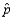 is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is
is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is 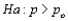 , then the rejection region for a level
, then the rejection region for a level 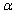 test is __________.
test is __________.
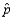 is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is
is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is 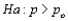 , then the rejection region for a level
, then the rejection region for a level 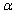 test is __________.
test is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The smallest level of significance 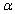 for which the null hypothesis
for which the null hypothesis 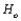 would be rejected is the tail area captured by the computed value of the test statistic. This smallest
would be rejected is the tail area captured by the computed value of the test statistic. This smallest 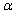 is referred to as the __________.
is referred to as the __________.
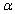 for which the null hypothesis
for which the null hypothesis 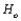 would be rejected is the tail area captured by the computed value of the test statistic. This smallest
would be rejected is the tail area captured by the computed value of the test statistic. This smallest 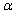 is referred to as the __________.
is referred to as the __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
If the calculated test statistic for an upper-tailed z test is 2.15, then the P-value is __________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Suppose that a test procedure about the population proportion p is performed, and that the sample proportion 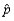 is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is
is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is 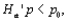 then the rejection region for a level
then the rejection region for a level 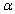 test is __________.
test is __________.
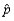 is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is
is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is 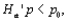 then the rejection region for a level
then the rejection region for a level 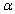 test is __________.
test is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
If the calculated test statistic for two-tailed z test is -1.84, then the P-value is __________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Suppose that a t test of 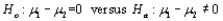 is based on 18 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is t = - 1.80, then the P-value for this test is __________.
is based on 18 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is t = - 1.80, then the P-value for this test is __________.
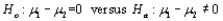 is based on 18 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is t = - 1.80, then the P-value for this test is __________.
is based on 18 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is t = - 1.80, then the P-value for this test is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
If the P-value is smaller than or equal to the level of significance 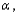 then the researcher should __________ at level
then the researcher should __________ at level 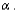
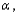 then the researcher should __________ at level
then the researcher should __________ at level 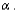

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Suppose that a test procedure about the population proportion p is performed, and that the sample proportion 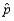 is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is
is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is 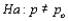 , then the rejection region for a level
, then the rejection region for a level 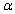 test is either __________ or __________.
test is either __________ or __________.
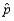 is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is
is approximately normally distributed. If the alternative hypothesis is 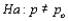 , then the rejection region for a level
, then the rejection region for a level 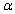 test is either __________ or __________.
test is either __________ or __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Suppose that a z test of 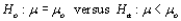 is conducted. The critical value
is conducted. The critical value 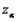 is determined by specifying __________ and using the fact that
is determined by specifying __________ and using the fact that 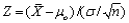 has a __________ distribution when
has a __________ distribution when 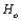 is true.
is true.
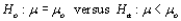 is conducted. The critical value
is conducted. The critical value 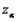 is determined by specifying __________ and using the fact that
is determined by specifying __________ and using the fact that 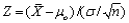 has a __________ distribution when
has a __________ distribution when 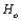 is true.
is true.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Let p denote the proportion of individuals in a population who possess a specified property, and X denote the number of individuals in the sample who possess the same property. Provided that the sample size n is small relative to the population size, then X has approximately a __________ distribution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Suppose that when data from an experiment was analyzed, the P-value for testing 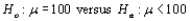 was calculated as .047. At the .01 level,
was calculated as .047. At the .01 level, 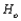 would __________.
would __________.
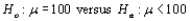 was calculated as .047. At the .01 level,
was calculated as .047. At the .01 level, 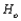 would __________.
would __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Suppose that a z test of 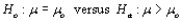 is conducted. Intuition then suggests rejecting
is conducted. Intuition then suggests rejecting 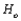 when the value of test statistic z is __________.
when the value of test statistic z is __________.
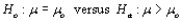 is conducted. Intuition then suggests rejecting
is conducted. Intuition then suggests rejecting 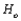 when the value of test statistic z is __________.
when the value of test statistic z is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Suppose a test procedure about the population mean 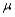 is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is
is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is 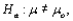 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 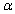 test is either __________ or __________.
test is either __________ or __________.
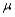 is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is
is performed, when the population is normal and the sample size n is small, then if the alternative hypothesis is 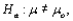 the rejection region for a level
the rejection region for a level 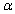 test is either __________ or __________.
test is either __________ or __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
It is customary to call the data significant when the null hypothesis is __________, and not significant otherwise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Let p denote the proportion of individuals in a population who possess a specified property, and X denote the number of individuals in the sample who possess the same property. Provided that the sample size n is large, then both X and the estimator 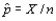 are approximately __________ distributed.
are approximately __________ distributed.
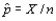 are approximately __________ distributed.
are approximately __________ distributed.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Let p denote the proportion of individuals in a population who possess a specified property, and X denote the number of individuals in the sample who possess the same property. The estimator 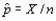 is __________ if
is __________ if 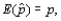 and its standard deviation
and its standard deviation 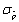 = __________.
= __________.
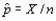 is __________ if
is __________ if 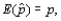 and its standard deviation
and its standard deviation 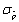 = __________.
= __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
As the level of significance 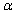 decreases, the critical value __________.
decreases, the critical value __________.
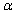 decreases, the critical value __________.
decreases, the critical value __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If the P-value is larger than the level of significance 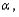 then the researcher should __________ at level
then the researcher should __________ at level 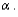
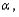 then the researcher should __________ at level
then the researcher should __________ at level 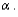

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Suppose that a t test of 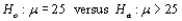 is based on 10 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is t = 2.4, then the P-value for this test is __________.
is based on 10 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is t = 2.4, then the P-value for this test is __________.
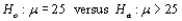 is based on 10 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is t = 2.4, then the P-value for this test is __________.
is based on 10 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is t = 2.4, then the P-value for this test is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements are not true?
A) A test statistic is a function of the sample data on which the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis is to be based.
B) A rejection region consists of the set of all test statistic values for which the null hypothesis will be rejected.
C) A rejection region consists of the set of all test statistic values for which the alternative hypothesis will be rejected.
D) A good hypothesis-testing procedure is one for which the probability of making either type I or type II error is small.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) A test statistic is a function of the sample data on which the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis is to be based.
B) A rejection region consists of the set of all test statistic values for which the null hypothesis will be rejected.
C) A rejection region consists of the set of all test statistic values for which the alternative hypothesis will be rejected.
D) A good hypothesis-testing procedure is one for which the probability of making either type I or type II error is small.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements are true?
A) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to the left of
)
B) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to the right of
)
C) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to either side of
)
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to the left of
)
B) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to the right of
)
C) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to either side of
)
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In hypothesis-testing analysis, a type II error occurs only if
A) the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true.
B) the null hypothesis is rejected when it is false.
C) the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false.
D) the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is true.
A) the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true.
B) the null hypothesis is rejected when it is false.
C) the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false.
D) the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements are true in testing based on a sample of size 15 from a normal population with unknown standard deviation ?
A) The test procedure requires the use of standard normal distribution.
B) The test procedure requires the use of binomial distribution.
C) The test procedure requires the use of exponential distribution.
D) The test procedure requires the use of t-distribution with 15 degrees of freedom.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) The test procedure requires the use of standard normal distribution.
B) The test procedure requires the use of binomial distribution.
C) The test procedure requires the use of exponential distribution.
D) The test procedure requires the use of t-distribution with 15 degrees of freedom.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If denotes the parameter of interest, and the simplified null hypothesis has the form is a specified number called the "null value" of the parameter, then the alternative hypothesis will be
A)
(so the implicit null hypothesis is
B)
(so the implicit null hypothesis is
C)
D) The alternative hypothesis will look like any of the above three assertions.
E) The alternative hypothesis must be the assertion specified in (C).
A)
(so the implicit null hypothesis is
B)
(so the implicit null hypothesis is
C)
D) The alternative hypothesis will look like any of the above three assertions.
E) The alternative hypothesis must be the assertion specified in (C).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements are not true if a test procedure about the population mean is performed when the population is normal with known standard deviation ?
A) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is an upper-tailed test.
B) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is an upper-tailed test.
C) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is a lower-tailed test.
D) The rejection region for level
Test is either
Or
If the test is a two-tailed test.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is an upper-tailed test.
B) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is an upper-tailed test.
C) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is a lower-tailed test.
D) The rejection region for level
Test is either
Or
If the test is a two-tailed test.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Knowledge of the test statistic's distribution when the null hypothesis is true allows us to construct a rejection region for which the type I error probability is controlled at the desired level.
B) The rejection region for the t test differs from that for the z test only in that a t critical value replaces the z critical value.
C) If
(n is small) is a random sample from a normal distribution, the standardized variable
Has a t distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom.
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) Knowledge of the test statistic's distribution when the null hypothesis is true allows us to construct a rejection region for which the type I error probability is controlled at the desired level.
B) The rejection region for the t test differs from that for the z test only in that a t critical value replaces the z critical value.
C) If
(n is small) is a random sample from a normal distribution, the standardized variable
Has a t distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom.
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
One must be especially careful in interpreting evidence when the sample size is __________, since any small departure from 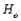 will almost surely be detected by a test, yet such a departure may have little practical significance.
will almost surely be detected by a test, yet such a departure may have little practical significance.
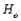 will almost surely be detected by a test, yet such a departure may have little practical significance.
will almost surely be detected by a test, yet such a departure may have little practical significance.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The likelihood ratio test procedure consists of rejecting the null hypothesis 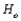 when the likelihood ratio statistic value
when the likelihood ratio statistic value  is __________.
is __________.
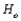 when the likelihood ratio statistic value
when the likelihood ratio statistic value  is __________.
is __________.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements are true?
A) The probability of type I error,
Is computed using the probability distribution of the test statistic when the null hypothesis is true.
B) The probability of type II error,
Requires knowing the distribution of the test statistic when the null hypothesis is false.
C) The probability of type I error,
Is computed by summing over probabilities of test statistic values in the rejection region.
D) The probability of type II error,
Is computed by summing over probabilities of test statistic values in the complement of the rejection region.
E) All of the above statements are true.
A) The probability of type I error,
Is computed using the probability distribution of the test statistic when the null hypothesis is true.
B) The probability of type II error,
Requires knowing the distribution of the test statistic when the null hypothesis is false.
C) The probability of type I error,
Is computed by summing over probabilities of test statistic values in the rejection region.
D) The probability of type II error,
Is computed by summing over probabilities of test statistic values in the complement of the rejection region.
E) All of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements are not true?
A) A rejection region is called upper-tailed if it consists only of large values of the test statistic.
B) A rejection region is called upper-tailed if it consists only of small values of the test statistic.
C) A rejection region is called lower-tailed if it consists only of small values of the test statistic.
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) A rejection region is called upper-tailed if it consists only of large values of the test statistic.
B) A rejection region is called upper-tailed if it consists only of small values of the test statistic.
C) A rejection region is called lower-tailed if it consists only of small values of the test statistic.
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which of the following statements are not correctly stated?
A) The two possible conclusions from a hypothesis-testing analysis are rejecting the null hypothesis
Or accepting
)
B) In many situations, the alternative hypothesis
Is referred to as the "research hypothesis" since it is the claim that the researcher would really like to validate.
C) In our treatment of hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis will always be stated as an equality claim.
D) A test statistic is a rule, based on sample data, for deciding whether to reject the null hypothesis.
E) All of the above statements are correctly stated.
A) The two possible conclusions from a hypothesis-testing analysis are rejecting the null hypothesis
Or accepting
)
B) In many situations, the alternative hypothesis
Is referred to as the "research hypothesis" since it is the claim that the researcher would really like to validate.
C) In our treatment of hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis will always be stated as an equality claim.
D) A test statistic is a rule, based on sample data, for deciding whether to reject the null hypothesis.
E) All of the above statements are correctly stated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements are not correct?
A) It is possible that the null hypothesis may be rejected when it is true.
B) It is impossible that the null hypothesis may be rejected when it is true.
C) It is possible that the null hypothesis may not be rejected when it is false.
D) All of the above statements are correct.
E) None of the above statements are correct.
A) It is possible that the null hypothesis may be rejected when it is true.
B) It is impossible that the null hypothesis may be rejected when it is true.
C) It is possible that the null hypothesis may not be rejected when it is false.
D) All of the above statements are correct.
E) None of the above statements are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements are not generally true?
A) A type I error is usually more serious than a type II error.
B) A type II error is usually more serious than a type I error.
C) A test with significance level
Is one for which the type I error probability is controlled at the specified level.
D) When an experiment and a sample size are fixed, then decreasing the size of the rejection region to obtain a smaller value of
(probability of type I error) results in a larger value of
(probability of type II error) for any particular parameter value consistent with the alternative hypothesis
)
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) A type I error is usually more serious than a type II error.
B) A type II error is usually more serious than a type I error.
C) A test with significance level
Is one for which the type I error probability is controlled at the specified level.
D) When an experiment and a sample size are fixed, then decreasing the size of the rejection region to obtain a smaller value of
(probability of type I error) results in a larger value of
(probability of type II error) for any particular parameter value consistent with the alternative hypothesis
)
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements are not true?
A) A statistical hypothesis is a claim or assertion either about the value of a single parameter, about the values of several parameters, or about the form of an entire probability distribution.
B) In any hypothesis-testing problem, there are two contradictory hypotheses under consideration.
C) A test of hypothesis is a method for using sample data to decide whether the null hypothesis should be rejected.
D) A type I error consists of not rejecting the null hypothesis
Is false.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) A statistical hypothesis is a claim or assertion either about the value of a single parameter, about the values of several parameters, or about the form of an entire probability distribution.
B) In any hypothesis-testing problem, there are two contradictory hypotheses under consideration.
C) A test of hypothesis is a method for using sample data to decide whether the null hypothesis should be rejected.
D) A type I error consists of not rejecting the null hypothesis
Is false.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements are true?
A) The null hypothesis, denoted by
, is the claim that is initially assumed to be true (the "prior belief" claim).
B) The alternative hypothesis, denoted by
, is the assertion that is contradictory to the null hypothesis
)
C) The null hypothesis
Will be rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis only if sample evidence suggests that
Is false.
D) If sample evidence does not strongly contradict the null hypothesis
, we will continue to believe in the truth of
)
E) All of the above statements are true.
A) The null hypothesis, denoted by
, is the claim that is initially assumed to be true (the "prior belief" claim).
B) The alternative hypothesis, denoted by
, is the assertion that is contradictory to the null hypothesis
)
C) The null hypothesis
Will be rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis only if sample evidence suggests that
Is false.
D) If sample evidence does not strongly contradict the null hypothesis
, we will continue to believe in the truth of
)
E) All of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements are not true for any significance level?
A) The one-tailed rejection region
Has type I error probability
B) The one-tailed rejection region
Has type I error probability
C) The two-tailed rejection region
Has type I error probability
, since area
Is captured under each of the tow tails of the z curve.
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) The one-tailed rejection region
Has type I error probability
B) The one-tailed rejection region
Has type I error probability
C) The two-tailed rejection region
Has type I error probability
, since area
Is captured under each of the tow tails of the z curve.
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
In hypothesis-testing analysis, a type I error occurs only if
A) the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true
B) the null hypothesis is rejected when it is false
C) the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false
D) the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is true
A) the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true
B) the null hypothesis is rejected when it is false
C) the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false
D) the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is true

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Suppose that a two-tailed test procedure about the population mean is performed when the population is normal, but the sample size n is small. The null hypothesis will be rejected at significance level if the value of the standardized test statistic t is such that
A)
B)
C) either
D)
E) None of the above inequalities are correct.
A)
B)
C) either
D)
E) None of the above inequalities are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements are not true?
A) If the null hypothesis is
, then the test statistic value is t = -2.5.
B) If the alternative hypothesis has the form
, then an
Value less than
Certainly does not provide support for
)
C) If the alternative hypothesis has the form
, then an
Value that exceeds
By only a small amount (corresponding to z which is positive but small) does not suggest that
Should be rejected in favor of
)
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) If the null hypothesis is
, then the test statistic value is t = -2.5.
B) If the alternative hypothesis has the form
, then an
Value less than
Certainly does not provide support for
)
C) If the alternative hypothesis has the form
, then an
Value that exceeds
By only a small amount (corresponding to z which is positive but small) does not suggest that
Should be rejected in favor of
)
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements are needed in constructing the likelihood ratio test?
A) Finding the largest value of the likelihood for any
(by finding the maximum
Likelihood estimate within
And substituting back into the likelihood function).
B) Find the largest value of the likelihood for any
C) Forming the ratio
= maximum likelihood for
Maximum likelihood for
D) All of the above statements are needed.
E) Only statements A and B are needed.
A) Finding the largest value of the likelihood for any
(by finding the maximum
Likelihood estimate within
And substituting back into the likelihood function).
B) Find the largest value of the likelihood for any
C) Forming the ratio
= maximum likelihood for
Maximum likelihood for
D) All of the above statements are needed.
E) Only statements A and B are needed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements are not true if a test procedure about the population proportion p is performed provided that
A) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is an upper-tailed test.
B) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is a lower-tailed test.
C) The rejection region for level
Test is either
If the test is a two-tailed test.
D) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test statistic is an upper-tailed test.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is an upper-tailed test.
B) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test is a lower-tailed test.
C) The rejection region for level
Test is either
If the test is a two-tailed test.
D) The rejection region for level
Test is
If the test statistic is an upper-tailed test.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Let p denote the proportion of individuals in a population who possess a specified property, and let X denote the number of individuals in the sample who possess the same property. Provided that the sample size n is large, the estimator has approximately
A) a normal distribution
B) a binomial distribution
C) an exponential distribution
D) a Poisson distribution
A) a normal distribution
B) a binomial distribution
C) an exponential distribution
D) a Poisson distribution

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements are not true?
A) If the alternative hypothesis has the form
, then a
Certainly does not provide support for
)
B) If the alternative hypothesis has the form
, then a
By only a small amount (corresponding to z value which is positive but small) does not suggest that
Should be rejected in favor of
)
C) If the null hypothesis is
And n = 100, then the test statistic value is z = 4
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) If the alternative hypothesis has the form
, then a
Certainly does not provide support for
)
B) If the alternative hypothesis has the form
, then a
By only a small amount (corresponding to z value which is positive but small) does not suggest that
Should be rejected in favor of
)
C) If the null hypothesis is
And n = 100, then the test statistic value is z = 4
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Let 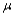 denote the true average radioactivity level (picocuries per liter). The value 5 pCi/L is considered the dividing line between safe and unsafe water. Would you recommend testing
denote the true average radioactivity level (picocuries per liter). The value 5 pCi/L is considered the dividing line between safe and unsafe water. Would you recommend testing 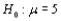 versus
versus 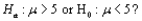 Explain your reasoning. (Hint: Think about the consequences of a type I and type II error for each possibility.)
Explain your reasoning. (Hint: Think about the consequences of a type I and type II error for each possibility.)
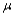 denote the true average radioactivity level (picocuries per liter). The value 5 pCi/L is considered the dividing line between safe and unsafe water. Would you recommend testing
denote the true average radioactivity level (picocuries per liter). The value 5 pCi/L is considered the dividing line between safe and unsafe water. Would you recommend testing 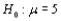 versus
versus 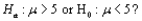 Explain your reasoning. (Hint: Think about the consequences of a type I and type II error for each possibility.)
Explain your reasoning. (Hint: Think about the consequences of a type I and type II error for each possibility.)
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements are necessary to construct an appropriate test procedure?
A) Specify a test statistic.
B) Decide on the general form of the rejection region.
C) Select the specified numerical critical value or values that will separate the rejection region from the acceptance region.
D) All of the above statements are necessary.
E) Only A and B are necessary statements.
A) Specify a test statistic.
B) Decide on the general form of the rejection region.
C) Select the specified numerical critical value or values that will separate the rejection region from the acceptance region.
D) All of the above statements are necessary.
E) Only A and B are necessary statements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Before agreeing to purchase a large order of polyethylene sheaths for a particular type of high pressure oil-filled submarine power cable, a company wants to see conclusive evidence that the true standard deviation of sheath thickness is less than .05mm. What hypotheses should be tested, and why? In this context, what are the type I and type II errors?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Which of the following statements are true about the P-value, where z is the calculated value of the test statistic and is the corresponding cumulative area under the standard normal curve?
A) P-value =
For an upper-tailed test.
B) P-value =
For a lower-tailed test.
C) P-value =
For a lower-tailed test
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) P-value =
For an upper-tailed test.
B) P-value =
For a lower-tailed test.
C) P-value =
For a lower-tailed test
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Let the test statistic Z have a standard normal distribution when 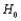 is true. Give the significance level for each of the following situations.
is true. Give the significance level for each of the following situations.
a. b.
b. 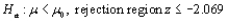 c.
c. 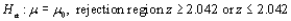
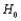 is true. Give the significance level for each of the following situations.
is true. Give the significance level for each of the following situations.a.
 b.
b. 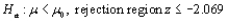 c.
c. 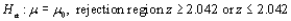

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements are true?
A) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to the left of
)
B) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to the right of
)
C) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to either side of
)
D) All of the above statements are true
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to the left of
)
B) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to the right of
)
C) When the alternative hypothesis is
, the null hypothesis
Should be rejected if
Is too far to either side of
)
D) All of the above statements are true
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Let p denote the proportion of individuals in a population who possess a specified property, and let X denote the number of individuals in the sample who possess the same property. Provided that the sample size n is small relative to the population size, X has approximately
A) a normal distribution
B) a binomial distribution
C) an exponential distribution
D) a Poisson distribution
A) a normal distribution
B) a binomial distribution
C) an exponential distribution
D) a Poisson distribution

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements are true?
A) When the results of an experiment are to be communicated to a large audience, rejection of
At level
Will be much more convincing if the observed value of the test statistic greatly exceeds the
Critical value than if it barely exceeds that value.
B) A large P-value would indicate statistical significance in that it would strongly suggest rejection of
C) In many experimental situations, only departures from
Of small magnitude would be worthy of detection, whereas a large departure from
Would have little practical significance.
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) When the results of an experiment are to be communicated to a large audience, rejection of
At level
Will be much more convincing if the observed value of the test statistic greatly exceeds the
Critical value than if it barely exceeds that value.
B) A large P-value would indicate statistical significance in that it would strongly suggest rejection of
C) In many experimental situations, only departures from
Of small magnitude would be worthy of detection, whereas a large departure from
Would have little practical significance.
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements are not true?
A) A P-value conveys much information about the strength of evidence against the null hypothesis
And allows an individual decision maker to draw a conclusion at any specified significance level
B) The P-value (or observed significance level) is the largest level of significance at which the null hypothesis
Would be rejected when a specified test procedure is used on a given data set.
C) If P-value
D) If P-value
E) All of the above statements are true.
A) A P-value conveys much information about the strength of evidence against the null hypothesis
And allows an individual decision maker to draw a conclusion at any specified significance level

B) The P-value (or observed significance level) is the largest level of significance at which the null hypothesis
Would be rejected when a specified test procedure is used on a given data set.
C) If P-value
D) If P-value
E) All of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Suppose that when data from an experiment was analyzed, the P-value for testing was calculated as .0244. Which of the following statements are true?
A)
Is rejected at .10 level.
B)
Is not rejected at .05 level.
C)
Is not rejected at .025 level.
D)
Is rejected at any level
E) All of the above statements are true.
A)
Is rejected at .10 level.
B)
Is not rejected at .05 level.
C)
Is not rejected at .025 level.
D)
Is rejected at any level
E) All of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements are true if the value of the test statistic for a two-tailed z test is z = -1.56?
A) P-value = .4406
B) P-value = .0594
C) P-value = .1188
D) .0594 < P-value < .1188
E) P-value = .0406
A) P-value = .4406
B) P-value = .0594
C) P-value = .1188
D) .0594 < P-value < .1188
E) P-value = .0406

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements are not true?
A) The test statistic
Has a standard normal distribution when
Is true.
B) The reliability of hypothesis testing procedure in reaching a correct decision can be assessed by studying type I error probability.
C) The process of reaching a decision by using the methodology of classical hypothesis testing involves selecting a level of significance
And then rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis
At that level
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.
A) The test statistic
Has a standard normal distribution when
Is true.
B) The reliability of hypothesis testing procedure in reaching a correct decision can be assessed by studying type I error probability.
C) The process of reaching a decision by using the methodology of classical hypothesis testing involves selecting a level of significance
And then rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis
At that level
D) All of the above statements are true.
E) None of the above statements are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Which of the following P-values will lead us to reject the null hypothesis at the .05 level?
A) .10
B) .025
C) .075
D) .15
E) Any P-value greater than .05
A) .10
B) .025
C) .075
D) .15
E) Any P-value greater than .05

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Suppose that a t test of is based on 12 degrees of freedom. If the calculated value of the test statistic is 2.8, then the P-value is
A) .008
B) .992
C) .016
D) .492
E) .496
A) .008
B) .992
C) .016
D) .492
E) .496

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Which of the following statements are true?
A) It is customary to call the data significant when
Is rejected.
B) It is customary to call the data not significant when
Is not rejected.
C) The calculation of the P-value depends on whether the test is upper-tailed, lower-tailed, or two-tailed.
D) The P-value for a z test (one based on a test statistic whose distribution when
Is true is at least approximately standard normal) is easily determined from the information in the standard normal probability table.
E) All of the above are true statements.
A) It is customary to call the data significant when
Is rejected.
B) It is customary to call the data not significant when
Is not rejected.
C) The calculation of the P-value depends on whether the test is upper-tailed, lower-tailed, or two-tailed.
D) The P-value for a z test (one based on a test statistic whose distribution when
Is true is at least approximately standard normal) is easily determined from the information in the standard normal probability table.
E) All of the above are true statements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Two different companies have applied to provide cable television service in a certain region. Let p denote the proportion of all potential subscribers who favor the first company over the second. Consider testing 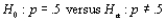 based on a random sample of 25 individuals. Let X denote the number in the sample who favor the first company and x represent the observed value of X.
based on a random sample of 25 individuals. Let X denote the number in the sample who favor the first company and x represent the observed value of X.
a. Which of the following rejection regions is most appropriate and why?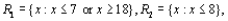
or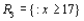
b. In the context of this problem situation, describe what type I and type II errors are.
c. What is the probability distribution of the test statistic X when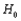
is true? Use it to compute
the probability of a type I error..
d. Compute the probability of a type II error for the selected region when p = .6 and p = .7.
e. Using the selected region, what would you conclude if 6 of the 25 queried favored company 1?
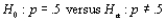 based on a random sample of 25 individuals. Let X denote the number in the sample who favor the first company and x represent the observed value of X.
based on a random sample of 25 individuals. Let X denote the number in the sample who favor the first company and x represent the observed value of X. a. Which of the following rejection regions is most appropriate and why?
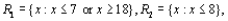
or
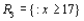
b. In the context of this problem situation, describe what type I and type II errors are.
c. What is the probability distribution of the test statistic X when
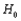
is true? Use it to compute
the probability of a type I error..
d. Compute the probability of a type II error for the selected region when p = .6 and p = .7.
e. Using the selected region, what would you conclude if 6 of the 25 queried favored company 1?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 92 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








