Deck 8: Continuous Probability Distributions
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Continuous Probability Distributions
1
Given that Z is a standard normal variable, the value z for which P(Z z) = 0.2580 is:
A) 0.70 .
B) 0.758 .
C) - 0.65 .
D) & 0.242 .
A) 0.70 .
B) 0.758 .
C) - 0.65 .
D) & 0.242 .
- 0.65 .
2
Given that X is a normal variable, which of the following statements is (are) true? 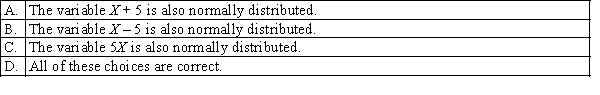 S
S
 S
SD
3
If the random variable X is normally distributed with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 8, then P(X ≤ 75) is: 

D
4
What proportion of the data from a normal distribution is within 2 standard deviations of the mean? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following is always true for all probability density functions of continuous random variables? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Like the normal distribution, the exponential density function f(x): 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Given that the random variable X is normally distributed with a mean of 20 and a standard deviation of 7, P(28 X 30) is:
A) 2
B) 0.0507 .
C) 0.8729
D 0.9236
A) 2
B) 0.0507 .
C) 0.8729
D 0.9236

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, what is the value of Z if the area to the left of Z is 0.1949? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
If the continuous random variable X is uniformly distributed over the interval [15, 25], then the mean of X is: ![If the continuous random variable X is uniformly distributed over the interval [15, 25], then the mean of X is:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5762/11eb0ead_0925_6a6e_9431_f79e57de4ca4_TB5762_00.jpg)
![If the continuous random variable X is uniformly distributed over the interval [15, 25], then the mean of X is:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5762/11eb0ead_0925_6a6e_9431_f79e57de4ca4_TB5762_00.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, P(-1.23 Z 1.89) is:
A) 0.1903 .
B) 0 . .9706 .
C) 0.8907 .
D) 0.7803 .
A) 0.1903 .
B) 0 . .9706 .
C) 0.8907 .
D) 0.7803 .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If the random variable X is exponentially distributed with parameter 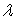 = 4, then the probability P(X
= 4, then the probability P(X 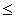 0.25), up to 4 decimal places, is:
0.25), up to 4 decimal places, is: 
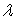 = 4, then the probability P(X
= 4, then the probability P(X 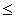 0.25), up to 4 decimal places, is:
0.25), up to 4 decimal places, is: 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, what is the value of Z if the area to the right of Z is 0.8212? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
If X is a normal random variable with a standard deviation of 10, then 3X has a standard deviation equal to: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
If Z is a standard normal random variable, then P(-2.28 Z -1.96 ) is:
A) 0.0250 .
B) 0.0146 .
C) - 0.0104 .
D) 0.0 .0104 .
A) 0.0250 .
B) 0.0146 .
C) - 0.0104 .
D) 0.0 .0104 .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
If the random variable X is exponentially distributed with parameter 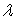 = 3, then P(X
= 3, then P(X 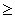 2), up to 4 decimal places, is:
2), up to 4 decimal places, is: 
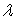 = 3, then P(X
= 3, then P(X 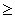 2), up to 4 decimal places, is:
2), up to 4 decimal places, is: 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What are the values of z that correspond to the P(-z Z z) equal to 0.4778?
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) None of these choices are correct.
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following distributions is suitable to model the length of time that elapses before the first telephone call is received by a switchboard? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
If the random variable X is exponentially distributed with parameter = 1.75, then P(1.5 X 3.8), up to 4 decimal places, is:
A)
B) .
C)
D) .
A)
B) .
C)
D) .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, P(Z > − 2.68) is: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A standard normal distribution is a normal distribution with: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Find the value of σ if it is know that X is normally distributed with mean 5 and 14.92% of the values are above 8? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The probability density function f(x) for a uniform random variable X defined over the interval [1, 11] is: ![The probability density function f(x) for a uniform random variable X defined over the interval [1, 11] is:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5762/11eb0ead_0927_3f48_9431_31d70fe4b71d_TB5762_00.jpg)
![The probability density function f(x) for a uniform random variable X defined over the interval [1, 11] is:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5762/11eb0ead_0927_3f48_9431_31d70fe4b71d_TB5762_00.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which of the following distributions is considered the cornerstone distribution of statistical inference? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following distributions is not symmetrical? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following is true for a normal distribution? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
If the random variable X is exponentially distributed, then which of the following statements best describes the mean of X? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
If Z is a standard normal random variable, the area between z = 0.0 and z =1.30 is 0.4032, while the area between z = 0.0 and z = 1.50 is 0.4332. What is the area between z = -1.30 and z = 1.50? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The height of the function for a uniform probability density function f(x): 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The mean of the exponential distribution equals the mean of the Poisson distribution only when the former distribution has a mean equal to: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The probability density function f(x) of a random variable X that is normally distributed is completely determined once the: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The probability density function, f(x), for any continuous random variable X, represents: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The expected value, E(X), of a uniform random variable X defined over the interval 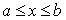 , is:
, is: 
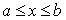 , is:
, is: 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Find the value of µ, if X is a normal random variable, with standard deviation 2, and 2.5% of the values are below 1? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The probability density function f(x) of a random variable X that is uniformly distributed between a and b is: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not true for a random variable X that is uniformly distributed over the interval ?
A) E ( X ) = ( a + b ) / 2
B) =
C)
D) f ( x ) =
A) E ( X ) = ( a + b ) / 2
B) =
C)
D) f ( x ) =

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following distributions is appropriate to measure the length of time between arrivals at a grocery checkout counter? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If the random variable X is uniformly distributed between 40 and 60, then P(35 X 45) is:
A) 1.0 .
B) 0.5 .
C) 0.25 .
D) 0.0 .
A) 1.0 .
B) 0.5 .
C) 0.25 .
D) 0.0 .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
If the z-value for a given value x of the random variable X is z = 2.326, and the distribution of X is normal with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 5, to what x-value does this z-value correspond? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, the area to the left of a value z is expressed as: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The function f(x) that defines the probability distribution of a continuous random variable X is a: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Suppose that the probability p of a success on any trial of a binomial distribution equals 0.80. For which value of the number of trials, n, would the normal distribution provide a good approximation to the binomial distribution? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
If the mean of an exponential distribution is 4, then the value of the parameter 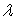 is:
is: 
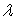 is:
is: 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In the normal distribution, the total area under the curve is equal to one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
In the exponential distribution, the value of x can be any of an infinite number of values in the given range.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
A continuous probability distribution represents a random variable having an infinite number of outcomes that may assume any number of values within an interval.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Given that X is a binomial random variable, the binomial probability P(X x) is approximated by the area under a normal curve to the left of:
A) x .
B) - x
C) x + 0.5 .
D) x - 0.5 .
A) x .
B) - x
C) x + 0.5 .
D) x - 0.5 .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
In the normal distribution, the curve is asymptotic but never intercepts the horizontal axis either to the left or right.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In the normal distribution, the curve is skewed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
If we standardise the normal curve, we express the original x values in terms of their number of standard deviations away from the mean.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following is not true for an exponential distribution with parameter 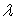 ?
? 
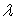 ?
? 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Given a binomial distribution with n trials and probability p of a success on any trial, a conventional rule of thumb is that the normal distribution will provide an adequate approximation of the binomial distribution if: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A smaller standard deviation of a normal distribution indicates that the distribution becomes: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which of the following is a characteristic of a normal distribution? 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, the mean of Z is: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Given that X is a binomial random variable, the binomial probability P(X 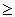 x) is approximated by the area under a normal curve to the right of:
x) is approximated by the area under a normal curve to the right of: 
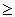 x) is approximated by the area under a normal curve to the right of:
x) is approximated by the area under a normal curve to the right of: 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
In the normal distribution, the mean, median and mode are all at the same position on the horizontal axis since the distribution is symmetric.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, a positive z value means that: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Given that Z is a standard normal variable, the variance of Z: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
In the normal distribution, the flatter the curve, the larger the standard deviation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Given that Z is a standard normal variable, the value z for which P(Z 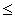 z) = 0.6736 is:
z) = 0.6736 is: 
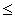 z) = 0.6736 is:
z) = 0.6736 is: 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Continuous probability distributions describe probabilities associated with random variables that are able to assume any of an infinite number of values.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
If the random variable X is exponentially distributed and the parameter of the distribution = 4, then P(X 0.25) = 0.3679.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Using the standard normal curve, the z-score representing the 75th percentile is 0.75.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Let z1 be a z-score that is unknown but identifiable by position and area. If the area to the right of z1 is 0.7291, the value of z1 is -0.61.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
For a normal curve, if the mean is 20 minutes and the standard deviation is 5 minutes, the area to the right of 13 minutes is 0.9192.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
If the random variable X is exponentially distributed with = 2 parameter, then the variance of the distribution is 0.5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
For a normal curve, if the mean is 25 minutes and the standard deviation is 5 minutes, the area to the right of 25 minutes is 0.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
A random variable X is standardised when each value of X has the mean of X subtracted from it, and the difference is divided by the standard deviation of X.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
A random variable X is normally distributed with a mean of 250 and a standard deviation of 50. Given that X = 175, its corresponding z-score is -1.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Using the standard normal curve, the z-score representing the 90th percentile is 1.28.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Using the standard normal curve, the probability or area between z = -1.28 and z = 1.28 is 0.1003

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Given that z is a standard normal random variable, a negative value of z indicates that the standard deviation of z is negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
The mean of any normal distribution is always zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Using the standard normal curve, the z-score representing the 10th percentile is 1.28.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The mean and standard deviation of a normally distributed random variable that has been standardised are one and zero, respectively.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The mean and the standard deviation of an exponential distribution are equal to each other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Let z1 be a z-score that is unknown but identifiable by position and area. If the symmetrical area between -z1 and + z1 is 0.9544, the value of z1 is 2.0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
A random variable X is normally distributed with a mean of 150 and a variance of 25. Given that
X = 120, its corresponding z-score is 6.0.
X = 120, its corresponding z-score is 6.0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Using the standard normal curve, the area between z = 0 and z = 3.50 is about 0.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
The mean and standard deviation of an exponential random variable cannot equal to each other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








