Deck 4: Introduction to Probability
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/94
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: Introduction to Probability
1
A method of assigning probabilities based upon judgment is referred to as the _____ method.
A) relative
B) probability
C) classical
D) subjective
A) relative
B) probability
C) classical
D) subjective
subjective
2
When the assumption of equally likely outcomes is used to assign probability values, the method used to assign probabilities is referred to as the _____ method.
A) relative frequency
B) subjective
C) probability
D) classical
A) relative frequency
B) subjective
C) probability
D) classical
classical
3
The collection of all possible sample points in an experiment is
A) the sample space.
B) an event.
C) a combination.
D) the population.
A) the sample space.
B) an event.
C) a combination.
D) the population.
the sample space.
4
The sample space refers to
A) any particular experimental outcome.
B) the sample size minus one.
C) the set of all possible experimental outcomes.
D) an event.
A) any particular experimental outcome.
B) the sample size minus one.
C) the set of all possible experimental outcomes.
D) an event.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
From a group of six people, two individuals are to be selected at random. How many selections are possible?
A) 12
B) 36
C) 15
D) 8
A) 12
B) 36
C) 15
D) 8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Each individual outcome of an experiment is called
A) the sample space.
B) a sample point.
C) a trial.
D) an event.
A) the sample space.
B) a sample point.
C) a trial.
D) an event.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The counting rule that is used for counting the number of experimental outcomes when n objects are selected from a set of N objects where order of selection is important is called the counting rule for
A) permutations.
B) combinations.
C) independent events.
D) multiple-step random experiments.
A) permutations.
B) combinations.
C) independent events.
D) multiple-step random experiments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Two events with nonzero probabilities
A) can be both mutually exclusive and independent.
B) can not be both mutually exclusive and independent.
C) are always mutually exclusive.
D) are always independent.
A) can be both mutually exclusive and independent.
B) can not be both mutually exclusive and independent.
C) are always mutually exclusive.
D) are always independent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
An experiment consists of selecting a student body president and vice president. All undergraduate students (freshmen through seniors) are eligible for these offices. How many sample points (possible outcomes as to the classifications) exist?
A) 4
B) 16
C) 8
D) 32
A) 4
B) 16
C) 8
D) 32

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The range of probability values is
A) 0 to infinity.
B) minus infinity to plus infinity.
C) 0 to 1.
D) -1 to 1.
A) 0 to infinity.
B) minus infinity to plus infinity.
C) 0 to 1.
D) -1 to 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
When the results of experimentation or historical data are used to assign probability values, the method used to assign probabilities is referred to as the _____ method.
A) relative frequency
B) subjective
C) classical
D) posterior
A) relative frequency
B) subjective
C) classical
D) posterior

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Two events are mutually exclusive
A) if their intersection is 1.
B) if they have no sample points in common.
C) if their intersection is 0.5.
D) if most of their sample points are in common.
A) if their intersection is 1.
B) if they have no sample points in common.
C) if their intersection is 0.5.
D) if most of their sample points are in common.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The counting rule that is used for counting the number of experimental outcomes when n objects are selected from a set of N objects where order of selection is not important is called the rule for
A) permutations.
B) combinations.
C) independent events.
D) multiple-step experiments.
A) permutations.
B) combinations.
C) independent events.
D) multiple-step experiments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Any process that generates well-defined outcomes is a(n)
A) event.
B) experiment.
C) sample point.
D) sample space.
A) event.
B) experiment.
C) sample point.
D) sample space.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is always true?
A) -1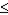 P(Ei)
P(Ei) 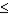 1
1
B) P(A) = 1 - P(Ac)
C) P(A) + P(B) = 1
D) ∑P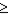 1
1
A) -1
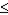 P(Ei)
P(Ei) 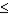 1
1B) P(A) = 1 - P(Ac)
C) P(A) + P(B) = 1
D) ∑P
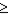 1
1
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The intersection of two mutually exclusive events
A) can be any value between 0 to1.
B) must always be equal to 1.
C) must always be equal to 0.
D) can be any positive value.
A) can be any value between 0 to1.
B) must always be equal to 1.
C) must always be equal to 0.
D) can be any positive value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Events that have no sample points in common are
A) independent events.
B) supplements.
C) mutually exclusive events.
D) complements.
A) independent events.
B) supplements.
C) mutually exclusive events.
D) complements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Initial estimates of the probabilities of events are known as _____ probabilities.
A) subjective
B) posterior
C) conditional
D) prior
A) subjective
B) posterior
C) conditional
D) prior

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A graphical method of representing the sample points of an experiment is a
A) stacked bar chart.
B) dot plot.
C) stem-and-leaf display.
D) tree diagram.
A) stacked bar chart.
B) dot plot.
C) stem-and-leaf display.
D) tree diagram.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In statistical experiments, each time the experiment is repeated
A) the same outcome must occur.
B) the same outcome can not occur again.
C) a different outcome might occur.
D) a different out come must occur.
A) the same outcome must occur.
B) the same outcome can not occur again.
C) a different outcome might occur.
D) a different out come must occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The symbol ∪ shows the
A) union of events.
B) intersection of two events.
C) sum of the probabilities of events.
D) sample space.
A) union of events.
B) intersection of two events.
C) sum of the probabilities of events.
D) sample space.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
If P(A) = 0.4, P(B | A) = 0.35, P(A ∪ B) = 0.69, then P(B) =
A) 0.14.
B) 0.43.
C) 0.75.
D) 0.59.
A) 0.14.
B) 0.43.
C) 0.75.
D) 0.59.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The symbol ∩ shows the
A) union of events.
B) intersection of two events.
C) sum of the probabilities of events.
D) sample space.
A) union of events.
B) intersection of two events.
C) sum of the probabilities of events.
D) sample space.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Bayes' theorem is used to compute
A) the prior probabilities.
B) the union of events.
C) intersection of events.
D) the posterior probabilities.
A) the prior probabilities.
B) the union of events.
C) intersection of events.
D) the posterior probabilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
If a six sided die is tossed two times and "3" shows up both times, the probability of "3" on the third trial is
A) much larger than any other outcome.
B) much smaller than any other outcome.
C) the same as any other outcome.
D) not able to be determined before the die is tossed.
A) much larger than any other outcome.
B) much smaller than any other outcome.
C) the same as any other outcome.
D) not able to be determined before the die is tossed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Each customer entering a department store will either buy or not buy some merchandise. An experiment consists of following 5 customers and determining whether or not they purchase any merchandise. The number of sample points in this experiment is
A) 5.
B) 10.
C) 25.
D) 64.
A) 5.
B) 10.
C) 25.
D) 64.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
An experiment consists of three steps. There are five possible results on the first step, two possible results on the second step, and three possible results on the third step. The total number of experimental outcomes is
A) 10.
B) 625.
C) 150.
D) 180.
A) 10.
B) 625.
C) 150.
D) 180.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Four applications for admission to a local university are checked, and it is determined whether each applicant is male or female. The number of sample points in this experiment is
A) 2.
B) 4.
C) 16.
D) 8.
A) 2.
B) 4.
C) 16.
D) 8.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
An experiment consists of tossing 4 coins successively. The number of sample points in this experiment is
A) 16.
B) 8.
C) 4.
D) 2.
A) 16.
B) 8.
C) 4.
D) 2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The addition law is potentially helpful when we are interested in computing the probability of
A) independent events
B) the intersection of two events
C) the union of two events
D) conditional events
A) independent events
B) the intersection of two events
C) the union of two events
D) conditional events

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Of six letters (A, B, C, D, E, and F), two letters are to be selected at random. How many outcomes are possible?
A) 30
B) 11
C) 6!
D) 15
A) 30
B) 11
C) 6!
D) 15

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Assume your favorite soccer team has 4 games left to finish the season. The outcome of each game can be win, lose or tie. The number of possible outcomes is
A) 4.
B) 12.
C) 64.
D) 81.
A) 4.
B) 12.
C) 64.
D) 81.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The multiplication law is potentially helpful when we are interested in computing the probability of
A) mutually exclusive events.
B) the intersection of two events.
C) the union of two events.
D) conditional events.
A) mutually exclusive events.
B) the intersection of two events.
C) the union of two events.
D) conditional events.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
If a penny is tossed three times and comes up heads all three times, the probability of heads on the fourth trial is
A) 0.
B) 1/16.
C) 1/2.
D) larger than the probability of tails.
A) 0.
B) 1/16.
C) 1/2.
D) larger than the probability of tails.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.5 and P(A ∩ B) = 0.12, then, P(B) =
A) 0.240.
B) 0.060.
C) 0.380.
D) 0.620.
A) 0.240.
B) 0.060.
C) 0.380.
D) 0.620.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
If two events are independent, then
A) they must be mutually exclusive.
B) the sum of their probabilities must be equal to one.
C) their intersection must be zero.
D) the product of their probabilities gives their intersection.
A) they must be mutually exclusive.
B) the sum of their probabilities must be equal to one.
C) their intersection must be zero.
D) the product of their probabilities gives their intersection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Assuming that each of the 52 cards in an ordinary deck has a probability of 1/52 of being drawn, what is the probability of drawing a black card?
A) 1/52
B) 4/52
C) 13/52
D) 26/52
A) 1/52
B) 4/52
C) 13/52
D) 26/52

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The union of events A and B is the event containing all the sample points belonging to
A) B or A.
B) A or B.
C) A or B or both.
D) A or B, but not both.
A) B or A.
B) A or B.
C) A or B or both.
D) A or B, but not both.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The sum of the probabilities of two complementary events is
A) 0.
B) 0.5.
C) 0.57.
D) 1.0.
A) 0.
B) 0.5.
C) 0.57.
D) 1.0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The set of all possible outcomes of an experiment is
A) a sample point.
B) an event.
C) the population.
D) the sample space.
A) a sample point.
B) an event.
C) the population.
D) the sample space.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Events A and B are mutually exclusive with P(C) = 0.35 and P(B) = 0.25. Then, P(Bc) =
A) 0.62.
B) 0.50.
C) 0.75.
D) 0.60.
A) 0.62.
B) 0.50.
C) 0.75.
D) 0.60.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A six-sided die is tossed 4times. The probability of observing four ones in a row is
A) 4/6.
B) 1/6.
C) 1/4096.
D) 1/1296.
A) 4/6.
B) 1/6.
C) 1/4096.
D) 1/1296.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
A method of assigning probabilities based on historical data is called the _____ method.
A) classical
B) subjective
C) relative frequency
D) progressive
A) classical
B) subjective
C) relative frequency
D) progressive

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
If A and B are mutually exclusive events with P(A) = 0.3 and P(B) = 0.5, then P(A ∩ B) =
A) 0.30.
B) 0.15.
C) 0.00.
D) 0.20.
A) 0.30.
B) 0.15.
C) 0.00.
D) 0.20.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If a coin is tossed three times, the likelihood of obtaining three heads in a row is
A) 0.0.
B) 0.500.
C) 0.875.
D) 0.125.
A) 0.0.
B) 0.500.
C) 0.875.
D) 0.125.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A perfectly balanced coin is tossed 6 times, and tails appears on all six tosses. Then, on the seventh trial
A) tail can not appear.
B) head has a larger chance of appearing than tail.
C) tail has a better chance of appearing than head.
D) tail has same chance of appearing as the head.
A) tail can not appear.
B) head has a larger chance of appearing than tail.
C) tail has a better chance of appearing than head.
D) tail has same chance of appearing as the head.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.05 and P(B) = 0.65, then P(A ∩ B) =
A) 0.05.
B) 0.0325.
C) 0.65.
D) 0.8.
A) 0.05.
B) 0.0325.
C) 0.65.
D) 0.8.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If P(A) = 0.62, P(B) = 0.47, and P(A ∪ B) = 0.88, then P(A ∩ B) =
A) 0.2914.
B) 1.9700.
C) 0.6700.
D) 0.2100.
A) 0.2914.
B) 1.9700.
C) 0.6700.
D) 0.2100.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A lottery is conducted using four urns. Each urn contains chips numbered from 0 to 9. One chip is selected at random from each urn. The total number of sample points in the sample space is
A) 40.
B) 6,561.
C) 1,048,576.
D) 10,000.
A) 40.
B) 6,561.
C) 1,048,576.
D) 10,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Of the last 100 customers entering a computer shop, 40have purchased a computer. If the classical method for computing probability is used, the probability that the next customer will purchase a computer is
A) 0.40.
B) 0.50.
C) 1.00.
D) 0.60.
A) 0.40.
B) 0.50.
C) 1.00.
D) 0.60.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If P(A) = 0.58, P(B) = 0.44, and P(A ∩ B) = 0.25, then P(A ∪ B) =
A) 1.02.
B) 0.77.
C) 0.11.
D) 0.39.
A) 1.02.
B) 0.77.
C) 0.11.
D) 0.39.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The probability of the occurrence of event A in an experiment is 1/3. If the experiment is performed 2 times and event A did not occur, then on the third trial event A
A) must occur.
B) may occur.
C) could not occur.
D) has a 2/3 probability of occurring.
A) must occur.
B) may occur.
C) could not occur.
D) has a 2/3 probability of occurring.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Events A and B are mutually exclusive. Which of the following statements is also true?
A) A and B are also independent.
B) P(A ∪ B) = P(A)P(B)
C) P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B)
D) P(A ∩ B) = P(A) + P(B)
A) A and B are also independent.
B) P(A ∪ B) = P(A)P(B)
C) P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B)
D) P(A ∩ B) = P(A) + P(B)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
An experiment consists of four outcomes with P(E1) = 0.2, P(E2) = 0.25, and P(E3) = 0.05. The probability of outcome E4 is
A) 0.500.
B) 0.0025.
C) 0.100.
D) 0.
A) 0.500.
B) 0.0025.
C) 0.100.
D) 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
If A and B are mutually exclusive events with P(A) = 0.25 and P(B) = 0.4, then P(A ∪ B) =
A) 0.
B) 0.15.
C) 0.1.
D) 0.65.
A) 0.
B) 0.15.
C) 0.1.
D) 0.65.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
In an experiment, events A and B are mutually exclusive. If P(A) = 0.6, then the probability of B
A) cannot be larger than 0.4.
B) can be any value greater than 0.6.
C) can be any value between 0 to 1.
D) cannot be determined with the information given.
A) cannot be larger than 0.4.
B) can be any value greater than 0.6.
C) can be any value between 0 to 1.
D) cannot be determined with the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.4 and P(B) = 0.25, then P(A ∩ B) =
A) 0.65.
B) 0.1.
C) 0.625.
D) 0.15.
A) 0.65.
B) 0.1.
C) 0.625.
D) 0.15.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.5 and P(B) = 0.5, then P(A ∩ B) is
A) 0.00.
B) 1.00.
C) 0.5.
D) 0.25.
A) 0.00.
B) 1.00.
C) 0.5.
D) 0.25.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A method of assigning probabilities which assumes that the experimental outcomes are equally likely is referred to as the _____ method.
A) objective
B) classical
C) subjective
D) experimental
A) objective
B) classical
C) subjective
D) experimental

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.2 and P(B) = 0.6, then P(A ∪ B) =
A) 0.62.
B) 0.12.
C) 0.60.
D) 0.68.
A) 0.62.
B) 0.12.
C) 0.60.
D) 0.68.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Assume your favorite soccer team has 3 games left to finish the season. The outcome of each game can be win, lose, or tie. How many possible outcomes exist?
A) 7
B) 27
C) 36
D) 64
A) 7
B) 27
C) 36
D) 64

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
If P(A) = 0.45, P(B) = 0.55, and P(A ∪ B) = 0.78, then P(A | B) =
A) 0.00
B) 0.45
C) 0.22
D) 0.40
A) 0.00
B) 0.45
C) 0.22
D) 0.40

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Posterior probabilities are computed using
A) the Multiplication Law.
B) Chebyshev's theorem.
C) the empirical rule.
D) Bayes' theorem.
A) the Multiplication Law.
B) Chebyshev's theorem.
C) the empirical rule.
D) Bayes' theorem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
If P(A) = 0.50, P(B) = 0.40 and P(A ∪ B) = 0.88, then P(B | A) =
A) 0.02.
B) 0.03.
C) 0.04.
D) 0.05.
A) 0.02.
B) 0.03.
C) 0.04.
D) 0.05.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
An element of the sample space is
A) an event.
B) an experiment.
C) a sample point.
D) probability.
A) an event.
B) an experiment.
C) a sample point.
D) probability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The complement of P(A | B) is
A) P(AC | B).
B) P(A | BC).
C) P(B | A).
D) P(A B).
A) P(AC | B).
B) P(A | BC).
C) P(B | A).
D) P(A B).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.4 and P(B) = 0.25, then P(A ∪ B) =
A) 0.65.
B) 0.55.
C) 0.10.
D) 0.75.
A) 0.65.
B) 0.55.
C) 0.10.
D) 0.75.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If P(A) = 0.48, P(A ∪ B) = 0.82, and P(B) = 0.54, then P(A ∩ B) =
A) 0.3936.
B) 0.3400.
C) 0.2000.
D) 1.0200.
A) 0.3936.
B) 0.3400.
C) 0.2000.
D) 1.0200.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Each customer entering a department store will either buy or not buy some merchandise. An experiment consists of following 3 customers and determining whether or not they purchase any merchandise. How many sample points exist in the above experiment? (Note that each customer is either a purchaser or non-purchaser.)
A) 3
B) 6
C) 8
D) 9
A) 3
B) 6
C) 8
D) 9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.35 and P(B) = 0.20, then, P(A ∪ B) =
A) 0.07.
B) 0.62.
C) 0.55.
D) 0.48.
A) 0.07.
B) 0.62.
C) 0.55.
D) 0.48.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
If P(A) = 0.7, P(B) = 0.6, P(A ∩ B) = 0, then events A and B are
A) supplementary events.
B) mutually exclusive.
C) independent events.
D) complements of each other.
A) supplementary events.
B) mutually exclusive.
C) independent events.
D) complements of each other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Six puppies were born in a litter, and it is determined whether each puppy is male or female. How many sample points exist in the above experiment?
A) 64
B) 32
C) 16
D) 4
A) 64
B) 32
C) 16
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Revised probabilities of events based on additional information are _____ probabilities.
A) joint
B) posterior
C) independent
D) complementary
A) joint
B) posterior
C) independent
D) complementary

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Some of the CDs produced by a manufacturer are defective. From the production line, 4 CDs are selected and inspected. How many sample points exist in this experiment?
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 256
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 256

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The probability of at least one head in two flips of a coin is
A) 0.25.
B) 0.33.
C) 0.50.
D) 0.75.
A) 0.25.
B) 0.33.
C) 0.50.
D) 0.75.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
If A and B are mutually exclusive, then
A) P(A) + P(B) = 0.
B) P(A) + P(B) = 1.
C) P(A ∩ B) = 0.
D) P(A ∩ B) = 1.
A) P(A) + P(B) = 0.
B) P(A) + P(B) = 1.
C) P(A ∩ B) = 0.
D) P(A ∩ B) = 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The probability of an intersection of two events is computed using the _____ law.
A) addition
B) subtraction
C) multiplication
D) division
A) addition
B) subtraction
C) multiplication
D) division

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
If X and Y are mutually exclusive events with P(A) = 0.295, P(B) = 0.32, then P(A | B) =
A) 0.0944.
B) 0.6150.
C) 1.0000.
D) 0.0000.
A) 0.0944.
B) 0.6150.
C) 1.0000.
D) 0.0000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
If A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.38 and P(B) = 0.55, then P(A | B) =
A) 0.209.
B) 0.000.
C) 0.550.
D) 0.380.
A) 0.209.
B) 0.000.
C) 0.550.
D) 0.380.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
From nine cards numbered 1 through 9, two cards are drawn. Consider the selection and classification of the cards as odd or even as an experiment. How many sample points are there for this experiment?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 9
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 94 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








