Deck 6: Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/79
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 6: Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change
1
A system receives 575 J of heat and delivers 425 J of work. Calculate the change in the internal energy, E, of the system.
A) -150 J
B) 150 J
C) -1000 J
D) 1000 J
E) 575 J
A) -150 J
B) 150 J
C) -1000 J
D) 1000 J
E) 575 J
150 J
2
An ideal gas (the system) is contained in a flexible balloon at a pressure of 1 atm and is initially at a temperature of 20. C. The surrounding air is at the same pressure, but its temperature is 25 C. When the system has equilibrated with its surroundings, both systems and surroundings are at 25 C and 1 atm. In changing from the initial to the final state, which one of the following relationships regarding the system is correct?
A) ( E < 0)
B) ( E = 0)
C) ( H = 0)
D) w > 0
E) q > 0
A) ( E < 0)
B) ( E = 0)
C) ( H = 0)
D) w > 0
E) q > 0
q > 0
3
In which of the following processes is H = E ?
A) Two moles of ammonia gas are cooled from 325 C to 300 C at 1.2 atm.
B) One gram of water is vaporized at 100 C and 1 atm.
C) Two moles of hydrogen iodide gas react to form hydrogen gas and iodine gas in a 40-L container.
D) Calcium carbonate is heated to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide in a container with variable volume.
E) One mole of solid carbon dioxide sublimes to the gas phase.
A) Two moles of ammonia gas are cooled from 325 C to 300 C at 1.2 atm.
B) One gram of water is vaporized at 100 C and 1 atm.
C) Two moles of hydrogen iodide gas react to form hydrogen gas and iodine gas in a 40-L container.
D) Calcium carbonate is heated to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide in a container with variable volume.
E) One mole of solid carbon dioxide sublimes to the gas phase.
Two moles of hydrogen iodide gas react to form hydrogen gas and iodine gas in a 40-L container.
4
A system delivers 225 J of heat to the surroundings while delivering 645 J of work. Calculate the change in the internal energy, E, of the system.
A) -420 J
B) 420 J
C) -870 J
D) 870 J
E) -225 J
A) -420 J
B) 420 J
C) -870 J
D) 870 J
E) -225 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
For which one of the following reactions will H be approximately (or exactly) equal to E?
A) H2(g) + Br2(g) 2HBr(g)
B) H2O(l) H2O(g)
C) CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
D) 2H(g) + O(g) H2O(l)
E) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
A) H2(g) + Br2(g) 2HBr(g)
B) H2O(l) H2O(g)
C) CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
D) 2H(g) + O(g) H2O(l)
E) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A system delivers 1275 J of heat while the surroundings perform 855 J of work on it. Calculate E in J.
A) -2130 J
B) -420 J
C) 420 J
D) 2130 J
E) -1275 J
A) -2130 J
B) -420 J
C) 420 J
D) 2130 J
E) -1275 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The dissolution of barium hydroxide in water is an exothermic process. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The enthalpy of solid barium hydroxide plus pure water is less than that of the solution, at the same temperature.
B) The enthalpy of solid barium hydroxide plus pure water is greater than that of the solution, at the same temperature.
C) The enthalpy of solid barium hydroxide plus pure water is the same as that of the solution, at the same temperature.
D) The temperature of the solution is lower than of the barium hydroxide and water before mixing.
E) When barium hydroxide dissolves in water, the system does work on the surroundings.
A) The enthalpy of solid barium hydroxide plus pure water is less than that of the solution, at the same temperature.
B) The enthalpy of solid barium hydroxide plus pure water is greater than that of the solution, at the same temperature.
C) The enthalpy of solid barium hydroxide plus pure water is the same as that of the solution, at the same temperature.
D) The temperature of the solution is lower than of the barium hydroxide and water before mixing.
E) When barium hydroxide dissolves in water, the system does work on the surroundings.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A system expands from a volume of 1.00 L to 2.00 L against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm. The work (w) done by the system, in J, is:
A) 1.00 J
B) 2.00 J
C) 1.01 * 102 J
D) 1.01 * 105 J
E) None of these choices is correct.
A) 1.00 J
B) 2.00 J
C) 1.01 * 102 J
D) 1.01 * 105 J
E) None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In which one of the following reactions would you expect H to be substantially greater than E (i.e., H > E)?
A) H2(g) + Br2(g) 2HBr(g)
B) CO2(s) CO2(g)
C) C2H2(g) + H2(g) C2H4(g)
D) H2O(s) H2O(l)
E) HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
A) H2(g) + Br2(g) 2HBr(g)
B) CO2(s) CO2(g)
C) C2H2(g) + H2(g) C2H4(g)
D) H2O(s) H2O(l)
E) HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A system that does no work but which transfers heat to the surroundings has:
A) q < 0, E > 0
B) q < 0, E < 0
C) q > 0, E > 0
D) q > 0, E < 0
E) q < 0, E = 0
A) q < 0, E > 0
B) q < 0, E < 0
C) q > 0, E > 0
D) q > 0, E < 0
E) q < 0, E = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
and does work on the surroundings has:
A) w < 0, E = 0
B) w > 0, E > 0
C) w > 0, E < 0
D) w < 0, E > 0
E) w < 0, E < 0
A) w < 0, E = 0
B) w > 0, E > 0
C) w > 0, E < 0
D) w < 0, E > 0
E) w < 0, E < 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction?
A) ( H < 0, process is exothermic)
B) ( H > 0, process is exothermic)
C) ( H < 0, process is endothermic)
D) ( H > 0, process is endothermic)
E) ( H = 0, since cold packs are sealed)
A) ( H < 0, process is exothermic)
B) ( H > 0, process is exothermic)
C) ( H < 0, process is endothermic)
D) ( H > 0, process is endothermic)
E) ( H = 0, since cold packs are sealed)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A system contracts from an initial volume of 15.0 L to a final volume of 10.0 L under a constant external pressure of 0.800 atm. The value of w, in J, is:
A) -4.0 J
B) 4.0 J
C) -405 J
D) 405 J
E) 4.05 *103 J
A) -4.0 J
B) 4.0 J
C) -405 J
D) 405 J
E) 4.05 *103 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which one of the following relationships is always correct?
A) potential energy + kinetic energy = constant
B) E = q + w
C) ( E = H - P V)
D) H = E + PV
E) ( H = qv)
A) potential energy + kinetic energy = constant
B) E = q + w
C) ( E = H - P V)
D) H = E + PV
E) ( H = qv)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A system that does no work but which receives heat from the surroundings has:
A) q < 0, E > 0
B) q > 0, E < 0
C) q = E
D) q = - E
E) w = E
A) q < 0, E > 0
B) q > 0, E < 0
C) q = E
D) q = - E
E) w = E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
and has work done on it by the surroundings has:
A) w = E
B) w = - E
C) w > 0, E < 0
D) w < 0, E > 0
E) w > E
A) w = E
B) w = - E
C) w > 0, E < 0
D) w < 0, E > 0
E) w > E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Two solutions (the system), each of 25.0 mL volume and at 25.0 C, are mixed in a beaker. A reaction occurs between them, and the temperature rises to 35.0 C. After the products have equilibrated with the surroundings, the temperature is again 25.0 C and the total volume is 50.0 mL. No gases are involved in the reaction. Which one of the following relationships concerning the change from initial to final states (both at 25.0 C) is correct?
A) ( E = 0)
B) ( H = 0)
C) ( E > 0)
D) q = 0
E) w = 0
A) ( E = 0)
B) ( H = 0)
C) ( E > 0)
D) q = 0
E) w = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A system absorbs 21.6 kJ of heat while performing 6.9 kJ of work on the surroundings. If the initial internal energy, E, is 61.2 kJ, what is the final value of E?
A) 32.7 kJ
B) 46.5 kJ
C) 75.9 kJ
D) 82.8 kJ
E) 89.7 kJ
A) 32.7 kJ
B) 46.5 kJ
C) 75.9 kJ
D) 82.8 kJ
E) 89.7 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A system initially has an internal energy E of 501 J. It undergoes a process during which it releases 111 J of heat energy to the surroundings, and does work of 222 J. What is the final energy of the system, in J?
A) 168 J
B) 390 J
C) 612 J
D) 834 J
E) cannot be calculated without more information
A) 168 J
B) 390 J
C) 612 J
D) 834 J
E) cannot be calculated without more information

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In a phase change of water between the liquid and the gas phases, 770.1 kJ of energy was released by the system. What was the product, and how much of it was formed in the phase change? (Data: H2O(l) H2O(g) H = 44.01 kJ/mol.)
A) 315 g water vapor was produced.
B) 17.5 g of water vapor was produced.
C) 17.5 mol of water vapor was produced.
D) 17.5 mol of liquid water was produced.
E) 17.5 g of liquid water was produced.
A) 315 g water vapor was produced.
B) 17.5 g of water vapor was produced.
C) 17.5 mol of water vapor was produced.
D) 17.5 mol of liquid water was produced.
E) 17.5 g of liquid water was produced.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The Starship Enterprise is caught in a time warp and Spock is forced to use the primitive techniques of the 20th century to determine the specific heat capacity of an unknown mineral. The 307-g sample was heated to 98.7 C and placed into a calorimeter containing 72.4 g of water at 23.6 C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter was 15.7 J/K. The final temperature in the calorimeter was 32.4 C. What is the specific heat capacity of the mineral?
A) 0.124 J/(g ? K)
B) 0.131 J/(g ? K)
C) 0.138 J/(g ? K)
D) 0.145 J/(g ? K)
E) None of these choices is correct.
A) 0.124 J/(g ? K)
B) 0.131 J/(g ? K)
C) 0.138 J/(g ? K)
D) 0.145 J/(g ? K)
E) None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A 275-g sample of nickel at 100.0 C is placed in 100.0 mL of water at 22.0 C. What is the final temperature of the water? Assume that no heat is lost to or gained from the surroundings. Specific heat capacity of nickel = 0.444 J/(g ? K)
A) 39.6 C
B) 40.8 C
C) 61.0 C
D) 79.2 C
E) 82.4 C
A) 39.6 C
B) 40.8 C
C) 61.0 C
D) 79.2 C
E) 82.4 C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not a state function?
A) internal energy
B) volume
C) work
D) pressure
E) enthalpy
A) internal energy
B) volume
C) work
D) pressure
E) enthalpy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Benzene is a starting material in the synthesis of nylon fibers and polystyrene (styrofoam). Its specific heat capacity is 1.74 J/(g ? K). If 16.7 kJ of energy is absorbed by a 225-g sample of benzene at 20.0 C, what is its final temperature?
A) -22.7 C
B) 36.7 C
C) 42.7 C
D) 62.7 C
E) None of these choices is correct.
A) -22.7 C
B) 36.7 C
C) 42.7 C
D) 62.7 C
E) None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A piece of copper metal is initially at 100.0 C. It is dropped into a coffee cup calorimeter containing 50.0 g of water at a temperature of 20.0 C. After stirring, the final temperature of both copper and water is 25.0 C. Assuming no heat losses, and that the specific heat (capacity) of water is 4.18 J/(g ? K), what is the heat capacity of the copper in J/K?
A) 2.79 J/K
B) 3.33 J/K
C) 13.9 J/K
D) 209 J/K
E) None of these choices is correct.
A) 2.79 J/K
B) 3.33 J/K
C) 13.9 J/K
D) 209 J/K
E) None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Natural gas, or methane, is an important fuel. Combustion of one mole of methane releases 802.3 kilojoules of energy. How much energy does that represent in kilocalories?
A) 1.92 *10¯1 kcal
B) 1.92 * 102 kcal
C) 3.36 * 103 kcal
D) 1.92 *105 kcal
E) 3.36 * 106 kcal
A) 1.92 *10¯1 kcal
B) 1.92 * 102 kcal
C) 3.36 * 103 kcal
D) 1.92 *105 kcal
E) 3.36 * 106 kcal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A Snickers candy bar contains 280 Calories, of which the fat content accounts for 120 Calories. What is the energy of the fat content, in kJ?
A) 5.0 *10¯1 kJ
B) 29 kJ
C) 5.0 *102 kJ
D) 1.2 * 103 kJ
E) 5.0 * 105 kJ
A) 5.0 *10¯1 kJ
B) 29 kJ
C) 5.0 *102 kJ
D) 1.2 * 103 kJ
E) 5.0 * 105 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Sand is converted to pure silicon in a three step process. The third step is SiCl4(g) + 2Mg(s) 2MgCl2(s) + Si(s), H = -625.6 kJ
What is the enthalpy change when 25.0 mol of silicon tetrachloride is converted to elemental silicon?
A) -25.0 kJ
B) -7820 kJ
C) -1.56 * 104 kJ
D) -3.13 * 104 kJ
E) None of these choices is correct.
What is the enthalpy change when 25.0 mol of silicon tetrachloride is converted to elemental silicon?
A) -25.0 kJ
B) -7820 kJ
C) -1.56 * 104 kJ
D) -3.13 * 104 kJ
E) None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A backpacker collects snow at 0 C, and places it in a cooking pot on a camp stove. It takes 643 kJ of heat energy to melt the snow and bring the water to boiling. Assuming no heat loss, and neglecting the specific heat capacity of the pot, calculate the mass of snow that the backpacker collected. (Data: specific heat capacity of liquid water, c = 4.18 J/g ? K; and H2O(s) H2O(l) H = Hfusion = 6.02 kJ/mol)
A) 1.92 kg
B) 1.90 kg
C) 1.52 kg
D) 855 g
E) < 800 g
A) 1.92 kg
B) 1.90 kg
C) 1.52 kg
D) 855 g
E) < 800 g

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Your favorite candy bar, Gummy Beakers, contains 1.2 *106 J of energy while your favorite soft drink, Bolt, contains 6.7 *105 J. If you eat two packs of Gummy Beakers a day and drink 3 cans of Bolt, what percent of your 2000 Calorie daily food intake is left for broccoli, beans, beef, etc.?
A) 53%
B) 47%
C) 27%
D) 11%
E) 0%
A) 53%
B) 47%
C) 27%
D) 11%
E) 0%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Ethylene glycol, used as a coolant in automotive engines, has a specific heat capacity of 2.42 J/(g-K). Calculate q when 3.65 kg of ethylene glycol is cooled from 132 C to 85 C.
A) -1900 kJ
B) -420 kJ
C) -99 kJ
D) -0.42 kJ
E) -4.2 *10¯6 kJ
A) -1900 kJ
B) -420 kJ
C) -99 kJ
D) -0.42 kJ
E) -4.2 *10¯6 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
15.0 g of ice cubes at 0.0 C are combined with 150. g of liquid water at 70.0 C in a coffee cup calorimeter. Calculate the final temperature reached, assuming no heat loss or gain from the surroundings. (Data: specific heat capacity of H2O(l), c = 4.18 J/g* C; H2O(s) H2O(l) H = 6.02 kJ/mol)
A) 0.0
B) 10.6
C) 30.7
D) 43.2
E) 56.4
A) 0.0
B) 10.6
C) 30.7
D) 43.2
E) 56.4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Calculate q when 28.6 g of water is heated from 22.0 C to 78.3 C.
A) 0.385 kJ
B) 1.61 kJ
C) 6.74 kJ
D) 9.37 kJ
E) 1.61 * 103 kJ
A) 0.385 kJ
B) 1.61 kJ
C) 6.74 kJ
D) 9.37 kJ
E) 1.61 * 103 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What is the final temperature when 20.0 g of water at 25 C is mixed with 30.0 g of water at 80 C?
A) 35 C
B) 42 C
C) 53 C
D) 58 C
E) 70 C
A) 35 C
B) 42 C
C) 53 C
D) 58 C
E) 70 C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
40.0 g of ice cubes at 0.0 C are combined with 150. g of liquid water at 20.0 C in a coffee cup calorimeter. Calculate the final temperature reached, assuming no heat loss or gain from the surroundings. (Data: specific heat capacity of H2O(l), c = 4.18 J/g- C; H2O(s) H2O(l) H = 6.02 kJ/mol)
A) 0.0
B) 10.6
C) 30.7
D) 43.2
E) 56.4
A) 0.0
B) 10.6
C) 30.7
D) 43.2
E) 56.4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
.
A) iron
B) copper
C) granite
D) gold
E) water
A) iron
B) copper
C) granite
D) gold
E) water

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A common laboratory reaction is the neutralization of an acid with a base. When 50.0 mL of 0.500 M HCl at 25.0 C is added to 50.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH at 25.0 C in a coffee cup calorimeter, the temperature of the mixture rises to 28.2 C. What is the heat of reaction per mole of acid? Assume the mixture has a specific heat capacity of 4.18 J/(g ? K) and that the densities of the reactant solutions are both 1.00 g/mL.
A) 670 J
B) 1300 J
C) 27 kJ
D) 54 kJ
E) > 100 kJ
A) 670 J
B) 1300 J
C) 27 kJ
D) 54 kJ
E) > 100 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The combustion of glucose (C6H12O6) with oxygen gas produces carbon dioxide and water. This process releases 2803 kJ per mole of glucose. When 3.00 mol of oxygen react in this way with glucose, what is the energy release in kcal? (Hint: Write a balanced equation for the combustion process.)
A) 223.5 kcal
B) 335.3 kcal
C) 1402 kcal
D) 2012 kcal
E) 5858 kcal
A) 223.5 kcal
B) 335.3 kcal
C) 1402 kcal
D) 2012 kcal
E) 5858 kcal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The specific heat capacity c of a metal is approximately related to its molar mass ? as follows: c * ? = 3R, where R is the universal gas constant, 8.314 J/mol-K. Use this relationship to identify the metal which has a specific heat capacity of 0.900 J/g ? K.
A) Li
B) Sn
C) Ca
D) Al
E) U
A) Li
B) Sn
C) Ca
D) Al
E) U

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
When Karl Kaveman adds chilled grog to his new granite mug, he removes 10.9 kJ of energy from the mug. If it has a mass of 625 g and was at 25 C, what is its new temperature? Specific heat capacity of granite = 0.79 J/(g ? K)
A) 3 C
B) 14 C
C) 22 C
D) 47 C
E) None of these choices is correct.
A) 3 C
B) 14 C
C) 22 C
D) 47 C
E) None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which one of the following is not a correct formation reaction? (products are correct)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)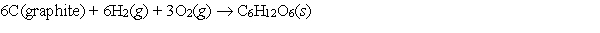
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
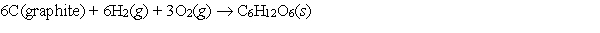

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Consider the equation E = q + w. Explain fully the meaning of all three terms in the equation, and also the implied sign convention for q and w.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Ethanol, C2H5OH, is being promoted as a clean fuel and is used as an additive in many gasoline mixtures. Calculate the H rxn for the combustion of ethanol. ( H f [C2H5OH(l)] = -277.7 kJ/mol; H f [CO2(g)] = -393.5 kJ/mol; H f [H2O(g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol)
A) -1234.7 kJ
B) -751.1 kJ
C) -357.6 kJ
D) 357.6 kJ
E) 1234.7 kJ
A) -1234.7 kJ
B) -751.1 kJ
C) -357.6 kJ
D) 357.6 kJ
E) 1234.7 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Use Hess's Law to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction 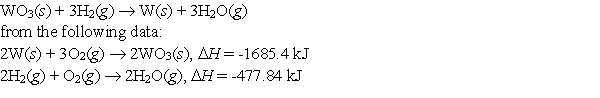
A) 125.9 kJ
B) 252.9 kJ
C) 364.9 kJ
D) 1207.6 kJ
E) None of these choices is correct.

A) 125.9 kJ
B) 252.9 kJ
C) 364.9 kJ
D) 1207.6 kJ
E) None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The highly exothermic thermite reaction, in which aluminum reduces iron(III) oxide to elemental iron, has been used by railroad repair crews to weld rails together.  What mass of iron is formed when 725 kJ of heat are released?
What mass of iron is formed when 725 kJ of heat are released?
A) 47 g
B) 65 g
C) 95 g
D) 112 g
E) 130 g
 What mass of iron is formed when 725 kJ of heat are released?
What mass of iron is formed when 725 kJ of heat are released?A) 47 g
B) 65 g
C) 95 g
D) 112 g
E) 130 g

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Calcium hydroxide, which reacts with carbon dioxide to form calcium carbonate, was used by the ancient Romans as mortar in stone structures. The reaction for this process is: 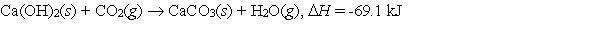 What is the enthalpy change if 3.8 mol of calcium carbonate is formed?
What is the enthalpy change if 3.8 mol of calcium carbonate is formed?
A) -18 kJ
B) -69 kJ
C) -73 kJ
D) -260 kJ
E) None of these choices is correct.
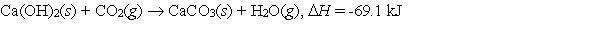 What is the enthalpy change if 3.8 mol of calcium carbonate is formed?
What is the enthalpy change if 3.8 mol of calcium carbonate is formed?A) -18 kJ
B) -69 kJ
C) -73 kJ
D) -260 kJ
E) None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Which one of the following equations represents the formation reaction of CH3OH(l)?
A) C(g) + 2H2(g) + ½O2(g) CH3OH(l)
B) C(g) + 4H(g) + O(g) CH3OH(l)
C) C(graphite) + 4H(g) + O(g) CH3OH(l)
D) C(diamond) + 4H(g) + O(g) CH3OH(l)
E) C(graphite) + 2H2(g) + ½O2(g) CH3OH(l)
A) C(g) + 2H2(g) + ½O2(g) CH3OH(l)
B) C(g) + 4H(g) + O(g) CH3OH(l)
C) C(graphite) + 4H(g) + O(g) CH3OH(l)
D) C(diamond) + 4H(g) + O(g) CH3OH(l)
E) C(graphite) + 2H2(g) + ½O2(g) CH3OH(l)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Use the following data to calculate the standard heat (enthalpy) of formation, Hf, of manganese(IV) oxide, MnO2 (s). 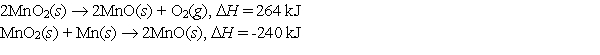
A) -504 kJ
B) -372 kJ
C) -24 kJ
D) 24 kJ
E) 504 kJ
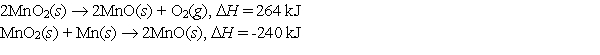
A) -504 kJ
B) -372 kJ
C) -24 kJ
D) 24 kJ
E) 504 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Calculate the H rxn for the following reaction. ( H f [AsH3(g)] = 66.4 kJ/mol; H f [H3AsO4(aq)] = -904.6 kJ/mol; H f [H2O(l)] = -285.8 kJ/mol) ![<strong>Calculate the \Delta H \degree <sub>rxn</sub> for the following reaction. ( \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [AsH<sub>3</sub>(g)] = 66.4 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [H<sub>3</sub>AsO<sub>4</sub>(aq)] = -904.6 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [H<sub>2</sub>O(l)] = -285.8 kJ/mol) </strong> A) -1981.4 kJ B) -685.2 kJ C) -172.2 kJ D) 172.2 kJ E) 685.2 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7799/11eb16b2_ff93_fb2b_984d_e9dcd13fc47f_TB7799_00.jpg)
A) -1981.4 kJ
B) -685.2 kJ
C) -172.2 kJ
D) 172.2 kJ
E) 685.2 kJ
![<strong>Calculate the \Delta H \degree <sub>rxn</sub> for the following reaction. ( \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [AsH<sub>3</sub>(g)] = 66.4 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [H<sub>3</sub>AsO<sub>4</sub>(aq)] = -904.6 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [H<sub>2</sub>O(l)] = -285.8 kJ/mol) </strong> A) -1981.4 kJ B) -685.2 kJ C) -172.2 kJ D) 172.2 kJ E) 685.2 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7799/11eb16b2_ff93_fb2b_984d_e9dcd13fc47f_TB7799_00.jpg)
A) -1981.4 kJ
B) -685.2 kJ
C) -172.2 kJ
D) 172.2 kJ
E) 685.2 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Nitric acid, which is among the top 15 chemicals produced in the United States, was first prepared over 1200 years ago by heating naturally occurring sodium nitrate (called saltpeter) with sulfuric acid and collecting the vapors produced. Calculate H ffor this reaction.
H f [NaNO3(s)] = -467.8 kJ/mol; H f[NaHSO4(s)] = -1125.5 kJ/mol; H f[H2SO4(l) = -814.0 kJ/mol; H f[HNO3(g)] = -135.1 kJ/mol. NaNO3(s) + H2SO4(l) NaHSO4(s) + HNO3(g)
A) -644.2 kJ
B) -291.4 kJ
C) -21.2 kJ
D) 21.2 kJ
E) 644.2 kJ
H f [NaNO3(s)] = -467.8 kJ/mol; H f[NaHSO4(s)] = -1125.5 kJ/mol; H f[H2SO4(l) = -814.0 kJ/mol; H f[HNO3(g)] = -135.1 kJ/mol. NaNO3(s) + H2SO4(l) NaHSO4(s) + HNO3(g)
A) -644.2 kJ
B) -291.4 kJ
C) -21.2 kJ
D) 21.2 kJ
E) 644.2 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Which one of the following statements about standard states is incorrect?
A) The standard state of a solid compound is the pure solid.
B) The standard state of a liquid compound is the pure liquid.
C) The standard state of a gaseous compound is the gas at a pressure of 1 atmosphere.
D) The standard state of an aqueous solute is a saturated solution in water.
E) The standard state of an element is the form in which it is stable at 1 atm and a specified temperature, usually 25 C.
A) The standard state of a solid compound is the pure solid.
B) The standard state of a liquid compound is the pure liquid.
C) The standard state of a gaseous compound is the gas at a pressure of 1 atmosphere.
D) The standard state of an aqueous solute is a saturated solution in water.
E) The standard state of an element is the form in which it is stable at 1 atm and a specified temperature, usually 25 C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Starting from equations relating pressure to force and force to work, derive the relationship w = -P V, explaining the steps in your argument.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
An important step in the synthesis of nitric acid is the conversion of ammonia to nitric oxide. ![<strong>An important step in the synthesis of nitric acid is the conversion of ammonia to nitric oxide. Calculate \Delta H \degree <sub>rxn</sub> for this reaction. \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [NH<sub>3</sub>(g)] = -45.9 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [NO(g)] = 90.3 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [H<sub>2</sub>O(g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol.</strong> A) -906.0 kJ B) -197.4 kJ C) -105.6 kJ D) 197.4 kJ E) 906.0 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7799/11eb16b2_ff93_d419_984d_f586d8137a8f_TB7799_00.jpg) Calculate H rxn for this reaction. H f [NH3(g)] = -45.9 kJ/mol; H f [NO(g)] = 90.3 kJ/mol; H f [H2O(g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol.
Calculate H rxn for this reaction. H f [NH3(g)] = -45.9 kJ/mol; H f [NO(g)] = 90.3 kJ/mol; H f [H2O(g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol.
A) -906.0 kJ
B) -197.4 kJ
C) -105.6 kJ
D) 197.4 kJ
E) 906.0 kJ
![<strong>An important step in the synthesis of nitric acid is the conversion of ammonia to nitric oxide. Calculate \Delta H \degree <sub>rxn</sub> for this reaction. \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [NH<sub>3</sub>(g)] = -45.9 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [NO(g)] = 90.3 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [H<sub>2</sub>O(g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol.</strong> A) -906.0 kJ B) -197.4 kJ C) -105.6 kJ D) 197.4 kJ E) 906.0 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7799/11eb16b2_ff93_d419_984d_f586d8137a8f_TB7799_00.jpg) Calculate H rxn for this reaction. H f [NH3(g)] = -45.9 kJ/mol; H f [NO(g)] = 90.3 kJ/mol; H f [H2O(g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol.
Calculate H rxn for this reaction. H f [NH3(g)] = -45.9 kJ/mol; H f [NO(g)] = 90.3 kJ/mol; H f [H2O(g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol.A) -906.0 kJ
B) -197.4 kJ
C) -105.6 kJ
D) 197.4 kJ
E) 906.0 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Stoichiometric amounts of nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas react in a calorimeter to produce 5.00 g of ammonia gas. The calorimeter temperature rises 0.42 C. The calorimeter and water have a combined heat capacity of 32.16 kJ/K. Calculate the heat of formation of ammonia, Hf , in kJ/mol. The formation reaction for ammonia is: 
A) -46 kJ/mol
B) -13.5 kJ/mol
C) -3.97 kJ/mol
D) 3.97 kJ/mol
E) 13.5 kJ/mol

A) -46 kJ/mol
B) -13.5 kJ/mol
C) -3.97 kJ/mol
D) 3.97 kJ/mol
E) 13.5 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which one of the following is a correct formation reaction?
A) C(diamond) C(graphite)
B) H2(g) + O(g) H2O(l)
C) C(graphite) + 4H(g) CH4(g)
D) 6C(graphite) + 6H2O(s) C6H12O6(s)
E) 2C(graphite) + 3H2(g) + ½O2(g) C2H5OH(l)
A) C(diamond) C(graphite)
B) H2(g) + O(g) H2O(l)
C) C(graphite) + 4H(g) CH4(g)
D) 6C(graphite) + 6H2O(s) C6H12O6(s)
E) 2C(graphite) + 3H2(g) + ½O2(g) C2H5OH(l)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Galena is the ore from which elemental lead is extracted. In the first step of the extraction process, galena is heated in air to form lead(II) oxide. 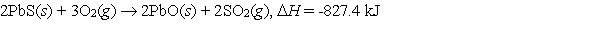 What mass of galena is converted to lead oxide if 975 kJ of heat are liberated?
What mass of galena is converted to lead oxide if 975 kJ of heat are liberated?
A) 203 g
B) 282 g
C) 406 g
D) 478 g
E) 564 g
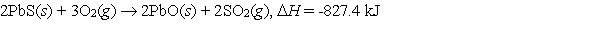 What mass of galena is converted to lead oxide if 975 kJ of heat are liberated?
What mass of galena is converted to lead oxide if 975 kJ of heat are liberated?A) 203 g
B) 282 g
C) 406 g
D) 478 g
E) 564 g

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Calculate the H rxn for the following reaction. ( H f [SiO2(s)] = -910.9 kJ/mol; H f [SiCl4(g)] = -657.0 kJ/mol; H f [HCl(g)] = -92.3 kJ/mol; H f [H2O (g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol) ![<strong>Calculate the \Delta H \degree <sub>rxn</sub> for the following reaction. ( \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [SiO<sub>2</sub>(s)] = -910.9 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [SiCl<sub>4</sub>(g)] = -657.0 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [HCl(g)] = -92.3 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [H<sub>2</sub>O (g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol) </strong> A) -139.5 kJ B) -137.4 kJ C) -104.4 kJ D) 104.4 kJ E) 139.5 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7799/11eb16b2_ff93_d41a_984d_cff61a2781f8_TB7799_00.jpg)
A) -139.5 kJ
B) -137.4 kJ
C) -104.4 kJ
D) 104.4 kJ
E) 139.5 kJ
![<strong>Calculate the \Delta H \degree <sub>rxn</sub> for the following reaction. ( \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [SiO<sub>2</sub>(s)] = -910.9 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [SiCl<sub>4</sub>(g)] = -657.0 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [HCl(g)] = -92.3 kJ/mol; \Delta H \degree <sub>f</sub> [H<sub>2</sub>O (g)] = -241.8 kJ/mol) </strong> A) -139.5 kJ B) -137.4 kJ C) -104.4 kJ D) 104.4 kJ E) 139.5 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7799/11eb16b2_ff93_d41a_984d_cff61a2781f8_TB7799_00.jpg)
A) -139.5 kJ
B) -137.4 kJ
C) -104.4 kJ
D) 104.4 kJ
E) 139.5 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Calculate the Hf rxn for the decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Hf [CaCO3(s)] = -1206.9 kJ/mol; Hf [CaO(s)] = -635.1 kJ/mol; HfB0 [CO2(g)] = -393.5 kJ/mol. CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
A) -2235.5 kJ
B) -1448.5 kJ
C) -178.3 kJ
D) 178.3 kJ
E) 2235.5 kJ
Hf [CaCO3(s)] = -1206.9 kJ/mol; Hf [CaO(s)] = -635.1 kJ/mol; HfB0 [CO2(g)] = -393.5 kJ/mol. CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
A) -2235.5 kJ
B) -1448.5 kJ
C) -178.3 kJ
D) 178.3 kJ
E) 2235.5 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The compound carbon suboxide, C3O2, is a gas at room temperature. Use the data supplied to calculate the heat of formation of carbon suboxide. (Data:  H = 127.3 kJ/mol and H f of CO(g) = -110.5 kJ/mol)
H = 127.3 kJ/mol and H f of CO(g) = -110.5 kJ/mol)
A) 116.8
B) -93.7
C) 227.8
D) -348.3
E) 93.7
 H = 127.3 kJ/mol and H f of CO(g) = -110.5 kJ/mol)
H = 127.3 kJ/mol and H f of CO(g) = -110.5 kJ/mol)A) 116.8
B) -93.7
C) 227.8
D) -348.3
E) 93.7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction  from the following data:
from the following data: 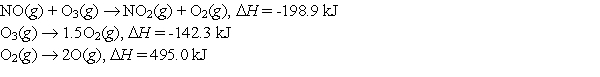
A) -551.6 kJ
B) -304.1 kJ
C) 190.9 kJ
D) 153.8 kJ
E) 438.4 kJ
 from the following data:
from the following data: 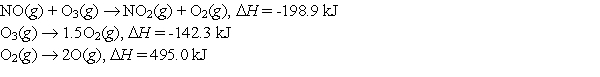
A) -551.6 kJ
B) -304.1 kJ
C) 190.9 kJ
D) 153.8 kJ
E) 438.4 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A mass of 1.250 g of benzoic acid (C7H6O2) was completely combusted in a bomb calorimeter. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter was 10.134 kJ/K and the heat of combustion of benzoic acid is -3226 kJ/mol, calculate (to three decimal places) the temperature increase that should have occurred in the apparatus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The enthalpy (H) of liquid water is greater than that of the same quantity of ice at the same temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The standard heat (enthalpy) of formation of graphite is zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
For all processes, both q and E will have the same sign.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
A) Starting from the equation H = E + PV, show how the relationship H = qp is derived. Clearly indicate any necessary assumptions or conditions.
B) In one sentence, state in full what is meant by the equation: H = qp.
B) In one sentence, state in full what is meant by the equation: H = qp.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Calculate, in J, the work done by 10.0 g of CO2 when it sublimes against a pressure of 1.00 atm to form gaseous CO2 at 0.0 C. The volume of CO2(s) can be neglected; CO2(g) can be assumed to behave ideally. The process occurring is CO2(s) CO2(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
For a reaction in a sealed, rigid container, H is always greater than E.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The only way in which a system can do work on the surroundings is by expansion against the external pressure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
For all processes, both q and w will have the same sign.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
A) State Hess's Law.
B) Use the H
data given below to calculate H
or the reaction:
C2H4(g) + H2(g) C2H6(g)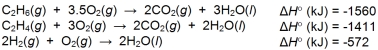
B) Use the H
data given below to calculate H
or the reaction:
C2H4(g) + H2(g) C2H6(g)
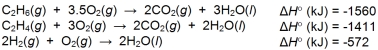

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Different chemical bonds have different potential energies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Standard heats (enthalpies) of formation of compounds, H f, may be positive or negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Although internal energy (E) is more fundamental and conceptually easier than enthalpy (H), in most chemical applications H is more relevant and useful than E. Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
The standard state of a substance in aqueous solution is a 1 M solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
H does not depend on the path of a reaction, but E does.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
E values obtained by bomb calorimetry can be converted to give accurate H values.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
In a reaction with high energy reactants and low energy products, q is negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
In an endothermic reaction, in going from the reactants to the products at the same temperature, the value of q is negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Clearly state the thermodynamic standard state of
A) an element or compound.
B) a solute.
A) an element or compound.
B) a solute.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








