Deck 11: Pricing Decisions and Profitability Analysis
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 11: Pricing Decisions and Profitability Analysis
1
All of the following are nonunit-based activity drivers EXCEPT
A) number of setups.
B) number of direct labour hours.
C) number of inspections.
D) number of material moves.
A) number of setups.
B) number of direct labour hours.
C) number of inspections.
D) number of material moves.
B
2
Figure 11-2
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers: Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Refer to Figure 11-2. What is the cost pool rate for the batch-level activities?
A) £80.00 per machine hour
B) £13,500.00 per setup
C) £17.20 per machine hour
D) £97.20 per machine hour
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Refer to Figure 11-2. What is the cost pool rate for the batch-level activities?
A) £80.00 per machine hour
B) £13,500.00 per setup
C) £17.20 per machine hour
D) £97.20 per machine hour
B
3
Figure 11-2
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers: Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Refer to Figure 11-2. What is the cost pool rate for the facility-level activities?
A) £80.00 per machine hour
B) £13,500.00 per setup
C) £17.20 per machine hour
D) £97.20 per machine hour
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Refer to Figure 11-2. What is the cost pool rate for the facility-level activities?
A) £80.00 per machine hour
B) £13,500.00 per setup
C) £17.20 per machine hour
D) £97.20 per machine hour
C
4
All of the following are unit-based activity drivers EXCEPT
A) machine hours.
B) number of setups.
C) number of units.
D) direct labour hours.
A) machine hours.
B) number of setups.
C) number of units.
D) direct labour hours.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Figure 12-3
The Lee Company must choose between two mutually exclusive alternatives. With alternative 1 an inferior product will be marketed that is best suited to low levels of demand whereas alternative 2 is a superior product that is best suited to high levels of demand. There are only two possible levels of demand - high and low and the probabilities of each event occurring is 0.5. The predicted profits for each alterative are: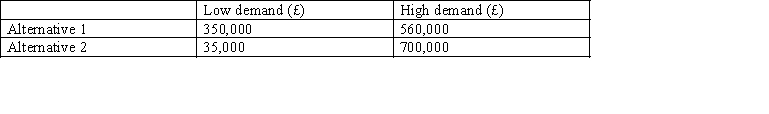
If activity-based costing is used, insurance on the plant would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
The Lee Company must choose between two mutually exclusive alternatives. With alternative 1 an inferior product will be marketed that is best suited to low levels of demand whereas alternative 2 is a superior product that is best suited to high levels of demand. There are only two possible levels of demand - high and low and the probabilities of each event occurring is 0.5. The predicted profits for each alterative are:

If activity-based costing is used, insurance on the plant would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Figure 11-1
Ubben Manufacturing uses an activity-based costing system. The company produces Model X and Model Y. Information relating to the two products is as follows: The following costs are reported:
The following costs are reported: 
Refer to Figure 11-1. Setups would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
Ubben Manufacturing uses an activity-based costing system. The company produces Model X and Model Y. Information relating to the two products is as follows:
 The following costs are reported:
The following costs are reported: 
Refer to Figure 11-1. Setups would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If activity-based costing is used, setups would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Figure 11-2
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers: Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Refer to Figure 11-2. What is(are) the product-level activity(ies)?
A) engineering
B) setups
C) inspecting
D) none of the above
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Refer to Figure 11-2. What is(are) the product-level activity(ies)?
A) engineering
B) setups
C) inspecting
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Figure 12-3
The Lee Company must choose between two mutually exclusive alternatives. With alternative 1 an inferior product will be marketed that is best suited to low levels of demand whereas alternative 2 is a superior product that is best suited to high levels of demand. There are only two possible levels of demand - high and low and the probabilities of each event occurring is 0.5. The predicted profits for each alterative are:
If activity-based costing is used, product inspections would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
The Lee Company must choose between two mutually exclusive alternatives. With alternative 1 an inferior product will be marketed that is best suited to low levels of demand whereas alternative 2 is a superior product that is best suited to high levels of demand. There are only two possible levels of demand - high and low and the probabilities of each event occurring is 0.5. The predicted profits for each alterative are:

If activity-based costing is used, product inspections would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Figure 11-2
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers: Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Refer to Figure 11-2. What is the cost pool overhead rate for the unit-level activities?
A) £80.00 per machine hour
B) £13,500.00 per setup
C) £17.20 per machine hour
D) £97.20 per machine hour
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Refer to Figure 11-2. What is the cost pool overhead rate for the unit-level activities?
A) £80.00 per machine hour
B) £13,500.00 per setup
C) £17.20 per machine hour
D) £97.20 per machine hour

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Maintenance of the production equipment would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) product-level activity.
C) cell-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) product-level activity.
C) cell-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Figure 11-2
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers: Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Refer to Figure 11-2. What is(are) the batch-level activity(ies)?
A) engineering
B) setups
C) inspecting
D) all of the above
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Refer to Figure 11-2. What is(are) the batch-level activity(ies)?
A) engineering
B) setups
C) inspecting
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Figure 11-2
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers: Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Refer to Figure 11-2. What is(are) the facility-level activity(ies)?
A) providing utilities
B) providing space
C) inspecting
D) both a and b
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Refer to Figure 11-2. What is(are) the facility-level activity(ies)?
A) providing utilities
B) providing space
C) inspecting
D) both a and b

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Figure 11-2
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers: Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Refer to Figure 11-2. What is(are) the unit-level activity(ies)?
A) engineering
B) setups
C) inspecting
D) machining
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Refer to Figure 11-2. What is(are) the unit-level activity(ies)?
A) engineering
B) setups
C) inspecting
D) machining

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Figure 11-1
Ubben Manufacturing uses an activity-based costing system. The company produces Model X and Model Y. Information relating to the two products is as follows: The following costs are reported:
The following costs are reported: 
Refer to Figure 11-1. Machine-related overhead would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
Ubben Manufacturing uses an activity-based costing system. The company produces Model X and Model Y. Information relating to the two products is as follows:
 The following costs are reported:
The following costs are reported: 
Refer to Figure 11-1. Machine-related overhead would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Figure 12-3
The Lee Company must choose between two mutually exclusive alternatives. With alternative 1 an inferior product will be marketed that is best suited to low levels of demand whereas alternative 2 is a superior product that is best suited to high levels of demand. There are only two possible levels of demand - high and low and the probabilities of each event occurring is 0.5. The predicted profits for each alterative are:
The use of unit-based activity drivers to assign costs tends to
A) overcost low-volume products.
B) overcost high-volume products.
C) undercost all products.
D) overcost all products.
The Lee Company must choose between two mutually exclusive alternatives. With alternative 1 an inferior product will be marketed that is best suited to low levels of demand whereas alternative 2 is a superior product that is best suited to high levels of demand. There are only two possible levels of demand - high and low and the probabilities of each event occurring is 0.5. The predicted profits for each alterative are:

The use of unit-based activity drivers to assign costs tends to
A) overcost low-volume products.
B) overcost high-volume products.
C) undercost all products.
D) overcost all products.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
If activity-based costing is used, electricity usage would be an example of a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Figure 11-2
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers: Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Refer to Figure 11-2. What is the cost pool rate for the product-level activities?
A) £80.00 per machine hour
B) £13,500.00 per setup
C) £17.20 per machine hour
D) none of the above
Owens Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Refer to Figure 11-2. What is the cost pool rate for the product-level activities?
A) £80.00 per machine hour
B) £13,500.00 per setup
C) £17.20 per machine hour
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following quantities is an example of an activity driver in activity-based costing?
A) number of setups
B) number of orders placed
C) number of machine hours
D) all of the above
A) number of setups
B) number of orders placed
C) number of machine hours
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Figure 12-3
The Lee Company must choose between two mutually exclusive alternatives. With alternative 1 an inferior product will be marketed that is best suited to low levels of demand whereas alternative 2 is a superior product that is best suited to high levels of demand. There are only two possible levels of demand - high and low and the probabilities of each event occurring is 0.5. The predicted profits for each alterative are:
Riley, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and activity drivers for next year: The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours. If the activity drivers are used to allocate overhead costs, the unit cost (rounded to two decimal places) for Job BB would be
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours. If the activity drivers are used to allocate overhead costs, the unit cost (rounded to two decimal places) for Job BB would be
A) £21.40.
B) £26.56.
C) £26.95.
D) £27.03.
The Lee Company must choose between two mutually exclusive alternatives. With alternative 1 an inferior product will be marketed that is best suited to low levels of demand whereas alternative 2 is a superior product that is best suited to high levels of demand. There are only two possible levels of demand - high and low and the probabilities of each event occurring is 0.5. The predicted profits for each alterative are:

Riley, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and activity drivers for next year:
 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours. If the activity drivers are used to allocate overhead costs, the unit cost (rounded to two decimal places) for Job BB would be
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours. If the activity drivers are used to allocate overhead costs, the unit cost (rounded to two decimal places) for Job BB would beA) £21.40.
B) £26.56.
C) £26.95.
D) £27.03.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
An example of a production or unit-level driver is
A) pounds of direct materials.
B) number of setups.
C) number of batches.
D) number of product lines.
A) pounds of direct materials.
B) number of setups.
C) number of batches.
D) number of product lines.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Figure 11-5
Granite, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year: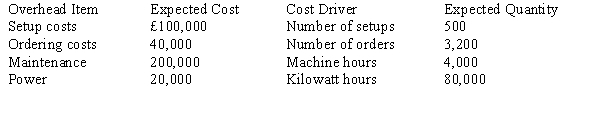 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year: 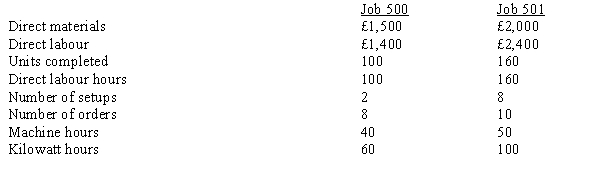 The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
Refer to Figure 11-5. If Granite, SA., used activity-based cost drivers to allocate overhead costs, the unit cost for Job 500 would be
A) £53.15.
B) £54.15.
C) £56.67.
D) £57.15.
Granite, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year:
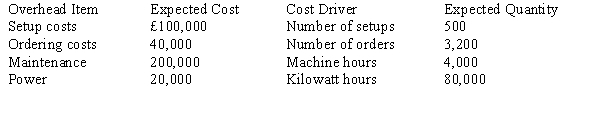 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.Refer to Figure 11-5. If Granite, SA., used activity-based cost drivers to allocate overhead costs, the unit cost for Job 500 would be
A) £53.15.
B) £54.15.
C) £56.67.
D) £57.15.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Figure 11-4
The Overdale plant has two categories of overhead: maintenance and inspection. Costs expected for these categories for the coming year are as follows: The plant currently applies overhead using direct labour hours and expected capacity of 80,000 direct labour hours. The following data has been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job:
The plant currently applies overhead using direct labour hours and expected capacity of 80,000 direct labour hours. The following data has been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job:  Total expected machine hours for all jobs during the year are 40,000, and the total expected number of inspections is 2,500.
Total expected machine hours for all jobs during the year are 40,000, and the total expected number of inspections is 2,500.
Refer to Figure 11-4 above. Using activity-based costing and the appropriate cost drivers, the total cost of the potential job would be
A) £9,230.
B) £8,180.
C) £2,250.
D) £1,680.
The Overdale plant has two categories of overhead: maintenance and inspection. Costs expected for these categories for the coming year are as follows:
 The plant currently applies overhead using direct labour hours and expected capacity of 80,000 direct labour hours. The following data has been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job:
The plant currently applies overhead using direct labour hours and expected capacity of 80,000 direct labour hours. The following data has been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job:  Total expected machine hours for all jobs during the year are 40,000, and the total expected number of inspections is 2,500.
Total expected machine hours for all jobs during the year are 40,000, and the total expected number of inspections is 2,500.Refer to Figure 11-4 above. Using activity-based costing and the appropriate cost drivers, the total cost of the potential job would be
A) £9,230.
B) £8,180.
C) £2,250.
D) £1,680.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Figure 11-5
Granite, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year: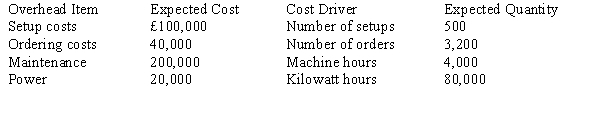 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
Refer to Figure 11-5. If Granite, SA., used activity-based cost drivers to allocate overhead costs, the total cost of Job 500 would be
A) £5,715.
B) £5,667.
C) £5,415.
D) £5,315.
Granite, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year:
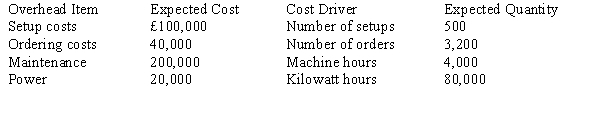 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.Refer to Figure 11-5. If Granite, SA., used activity-based cost drivers to allocate overhead costs, the total cost of Job 500 would be
A) £5,715.
B) £5,667.
C) £5,415.
D) £5,315.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Figure 11-4
The Overdale plant has two categories of overhead: maintenance and inspection. Costs expected for these categories for the coming year are as follows: The plant currently applies overhead using direct labour hours and expected capacity of 80,000 direct labour hours. The following data has been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job:
The plant currently applies overhead using direct labour hours and expected capacity of 80,000 direct labour hours. The following data has been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job:  Total expected machine hours for all jobs during the year are 40,000, and the total expected number of inspections is 2,500.
Total expected machine hours for all jobs during the year are 40,000, and the total expected number of inspections is 2,500.
Refer to Figure 11-4. Using direct labour hours to assign overhead, the total cost of the potential job would be
A) £9,500.
B) £6,000.
C) £3,000.
D) £1,600.
The Overdale plant has two categories of overhead: maintenance and inspection. Costs expected for these categories for the coming year are as follows:
 The plant currently applies overhead using direct labour hours and expected capacity of 80,000 direct labour hours. The following data has been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job:
The plant currently applies overhead using direct labour hours and expected capacity of 80,000 direct labour hours. The following data has been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job:  Total expected machine hours for all jobs during the year are 40,000, and the total expected number of inspections is 2,500.
Total expected machine hours for all jobs during the year are 40,000, and the total expected number of inspections is 2,500.Refer to Figure 11-4. Using direct labour hours to assign overhead, the total cost of the potential job would be
A) £9,500.
B) £6,000.
C) £3,000.
D) £1,600.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Basing overhead allocation solely on volume
A) will undercost high-volume products and overcost low-volume products.
B) will overcost high-volume products and undercost low-volume products.
C) is the sole basis of the activity-based costing model.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) will undercost high-volume products and overcost low-volume products.
B) will overcost high-volume products and undercost low-volume products.
C) is the sole basis of the activity-based costing model.
D) All of the above are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Figure 11-6
Peach, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year: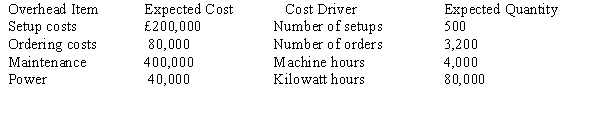 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
Refer to Figure 11-6. If Peach, SA., used direct labour hours to assign overhead, the unit cost for Job 401 would be
A) £117.50.
B) £111.88.
C) £105.00.
D) £102.50.
Peach, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year:
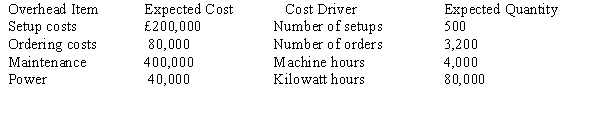 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.Refer to Figure 11-6. If Peach, SA., used direct labour hours to assign overhead, the unit cost for Job 401 would be
A) £117.50.
B) £111.88.
C) £105.00.
D) £102.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following items would be classified as committed resources (short-term)?
A) salaried employees
B) depreciation on building
C) fuel to generate electricity internally
D) lease on machinery
A) salaried employees
B) depreciation on building
C) fuel to generate electricity internally
D) lease on machinery

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
An activity-based costing system uses which of the following procedures?
A) Overhead costs are traced to departments, then costs are traced to products.
B) Overhead costs are traced to activities, then costs are traced to products.
C) Overhead costs are traced directly to products.
D) All overhead costs are expensed as incurred.
A) Overhead costs are traced to departments, then costs are traced to products.
B) Overhead costs are traced to activities, then costs are traced to products.
C) Overhead costs are traced directly to products.
D) All overhead costs are expensed as incurred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following items would be classified as flexible resources?
A) salaried employees
B) depreciation on building
C) fuel to generate electricity internally
D) lease on machinery
A) salaried employees
B) depreciation on building
C) fuel to generate electricity internally
D) lease on machinery

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Committed resources are
A) hard to purchase.
B) purchased precisely at the time the resource is needed and have no unused capacity.
C) supplied in advance of usage and may have unused capacity.
D) none of the above.
A) hard to purchase.
B) purchased precisely at the time the resource is needed and have no unused capacity.
C) supplied in advance of usage and may have unused capacity.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
More accurate product costing information is produced by assigning costs using
A) volume-based, plantwide rates.
B) volume-based, departmental rates.
C) activity-based pool rates.
D) All of the above produce accurate product costing information.
A) volume-based, plantwide rates.
B) volume-based, departmental rates.
C) activity-based pool rates.
D) All of the above produce accurate product costing information.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The overhead rates of the traditional-based approach to product costing use
A) nonunit-based cost drivers.
B) unit-based cost drivers.
C) process costing.
D) job-order costing.
A) nonunit-based cost drivers.
B) unit-based cost drivers.
C) process costing.
D) job-order costing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
In an activity-based cost system, what types of drivers are used to describe cost behaviour?
A) activity drivers
B) production or unit-level drivers
C) nonunit-level drivers
D) both production (or unit-level) and nonunit-level drivers
A) activity drivers
B) production or unit-level drivers
C) nonunit-level drivers
D) both production (or unit-level) and nonunit-level drivers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following items would be classified as committed resources (long-term)?
A) salaried employees
B) depreciation on building
C) lease on machinery
D) both b and c
A) salaried employees
B) depreciation on building
C) lease on machinery
D) both b and c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
An example of a nonunit-level driver is
A) pounds of direct materials.
B) number of setups.
C) number of machine hours where each product manufactured requires one machine hour.
D) number of labour hours.
A) pounds of direct materials.
B) number of setups.
C) number of machine hours where each product manufactured requires one machine hour.
D) number of labour hours.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
What is the initial step in implementing an activity-based costing system?
A) assigning costs to activities
B) assigning costs to products
C) identifying activities and attributes
D) dividing activity costs by activity drivers
A) assigning costs to activities
B) assigning costs to products
C) identifying activities and attributes
D) dividing activity costs by activity drivers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Resources that are only purchased precisely at the time the resource is needed are called
A) committed resources.
B) flexible resources.
C) scarce resources.
D) none of the above.
A) committed resources.
B) flexible resources.
C) scarce resources.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An activity cost driver is
A) a factor that causes variations in a cost.
B) another term for input measure.
C) the largest single category of cost in a company.
D) a variable cost.
A) a factor that causes variations in a cost.
B) another term for input measure.
C) the largest single category of cost in a company.
D) a variable cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
An activity-based cost system
A) differs from a traditional-based cost system in the nature and number of the cost drivers used.
B) uses both unit-based and nonunit-based cost drivers that reflect a cause-and-effect relationship.
C) can trace cost accurately to cost objects other than products.
D) does all of the above.
A) differs from a traditional-based cost system in the nature and number of the cost drivers used.
B) uses both unit-based and nonunit-based cost drivers that reflect a cause-and-effect relationship.
C) can trace cost accurately to cost objects other than products.
D) does all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Flanigan Manufacturing uses an activity-based cost system. The company produces Product R and Product X. Information concerning the two products is as follows:  The following costs are reported:
The following costs are reported:  Required:
Required: 
 The following costs are reported:
The following costs are reported:  Required:
Required: 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Explain how the activity resource usage model is used in assessing relevancy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Figure 11-6
Peach, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year: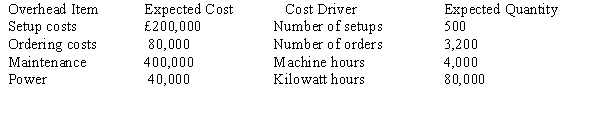 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
Refer to Figure 11-6. If Peach, SA., used activity-based cost drivers to allocate overhead costs, the unit cost for Job 401 would be (round to two decimal places)
A) £42.81.
B) £53.13.
C) £53.91.
D) £54.06.
Peach, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year:
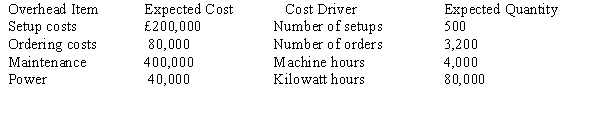 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 4,000 direct labour hours.Refer to Figure 11-6. If Peach, SA., used activity-based cost drivers to allocate overhead costs, the unit cost for Job 401 would be (round to two decimal places)
A) £42.81.
B) £53.13.
C) £53.91.
D) £54.06.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Holbrook, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year:  The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 40,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 40,000 direct labour hours.
Required:
a.
Determine the unit cost for each job using direct labour hours to apply overhead.
b.
Determine the unit cost for each job using the four cost drivers. (Round amounts to two decimal places.)
c.
Which method produces the more accurate cost assignment? Why?
 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 40,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 40,000 direct labour hours.Required:
a.
Determine the unit cost for each job using direct labour hours to apply overhead.
b.
Determine the unit cost for each job using the four cost drivers. (Round amounts to two decimal places.)
c.
Which method produces the more accurate cost assignment? Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Identify Cooper and Kaplan's four categories of activities and provide a brief description of each category.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The most critical step in activity-based costing is identifying cost drivers. Explain this statement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Books Company manufactures and sells two products: Soft Cover (S) and Hard Cover (H). The firm's activities have been analyzed and placed into a hierarchy of activity costs. Presented is information on activity cost drivers and costs per unit of cost driver at each activity level.  During January 2012, Books Company produced 10,000 units of Soft Covers and 5,000 units of Hard Covers. Each batch of products includes 1,000 units of Soft Covers or 1,000 units of Hard Covers.
During January 2012, Books Company produced 10,000 units of Soft Covers and 5,000 units of Hard Covers. Each batch of products includes 1,000 units of Soft Covers or 1,000 units of Hard Covers.
Required:
Determine the total costs for each activity level and the total predicted costs for January.
 During January 2012, Books Company produced 10,000 units of Soft Covers and 5,000 units of Hard Covers. Each batch of products includes 1,000 units of Soft Covers or 1,000 units of Hard Covers.
During January 2012, Books Company produced 10,000 units of Soft Covers and 5,000 units of Hard Covers. Each batch of products includes 1,000 units of Soft Covers or 1,000 units of Hard Covers.Required:
Determine the total costs for each activity level and the total predicted costs for January.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Ernest, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for next year:  The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 32,000 direct labour hours. (Round amounts to two decimal places.)
The company's normal activity is 32,000 direct labour hours. (Round amounts to two decimal places.)
Required:
a.
Determine the unit cost for each job using direct labour hours to apply overhead.
b.
Determine the unit cost for each job using the four cost drivers.
c.
Which method produces the more accurate cost assignment? Why?
 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 32,000 direct labour hours. (Round amounts to two decimal places.)
The company's normal activity is 32,000 direct labour hours. (Round amounts to two decimal places.)Required:
a.
Determine the unit cost for each job using direct labour hours to apply overhead.
b.
Determine the unit cost for each job using the four cost drivers.
c.
Which method produces the more accurate cost assignment? Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Discuss how volume-based unit-level analysis underestimates and/or overestimates the cost of products.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Batch-related costs are added to which of the following costs in break-even analysis?
A) variable
B) fixed
C) mixed
D) none of the above
A) variable
B) fixed
C) mixed
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Briefly discuss the problem with the unit-level approach to cost estimation and discuss some of the errors that may occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Lyons, SA., has identified the following overhead costs and activity drivers for next year:  The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 20,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 20,000 direct labour hours.
Required:
a.
Determine the unit cost for each job using direct labour hours to apply overhead.
b.
Determine the unit cost for each job using the four activity drivers. (Round amounts to 2 decimal places.)
c.
Which method produces the more accurate cost assignment? Why?
 The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:
The following are two of the jobs completed during the year:  The company's normal activity is 20,000 direct labour hours.
The company's normal activity is 20,000 direct labour hours.Required:
a.
Determine the unit cost for each job using direct labour hours to apply overhead.
b.
Determine the unit cost for each job using the four activity drivers. (Round amounts to 2 decimal places.)
c.
Which method produces the more accurate cost assignment? Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Activity-based costing assigns costs to cost object by first
A) tracing costs to products and then tracing costs to cost objects.
B) tracing costs to departments and then tracing costs to products.
C) tracing costs to activities and then tracing costs to cost objects.
D) tracing costs to customers and then tracing costs to products.
A) tracing costs to products and then tracing costs to cost objects.
B) tracing costs to departments and then tracing costs to products.
C) tracing costs to activities and then tracing costs to cost objects.
D) tracing costs to customers and then tracing costs to products.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Funk Manufacturing Company produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:  Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Required:
a.
Identify the activities within each process as unit-level, batch-level, product-level, or facility-level.
b.
Create homogeneous cost pools. Identify the activities that belong to each pool and the activity driver that will be used for computing pool rates.
c.
Build an activity relational (i.e. cost) table.
d.
Compute the cost pool rates.
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Required:
a.
Identify the activities within each process as unit-level, batch-level, product-level, or facility-level.
b.
Create homogeneous cost pools. Identify the activities that belong to each pool and the activity driver that will be used for computing pool rates.
c.
Build an activity relational (i.e. cost) table.
d.
Compute the cost pool rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Compare and contrast traditional organization-based costing with activity-based costing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Hill Manufacturing uses an activity-based costing system. The company produces Model A and Model B. Information concerning the two products is as follows:  Required:
Required:
a.
Classify the following overhead activities as unit-level activities, batch-level activities, or product-level activities:
Power
Engineering
Setups
b.
Calculate the following:
A cost pool rate for power
A cost pool rate for setups
A cost pool rate for engineering
c.
Calculate the following:
Power costs assigned to Model B
Setups costs assigned to Model A
Engineering costs assigned to Model A
 Required:
Required: a.
Classify the following overhead activities as unit-level activities, batch-level activities, or product-level activities:
Power
Engineering
Setups
b.
Calculate the following:
A cost pool rate for power
A cost pool rate for setups
A cost pool rate for engineering
c.
Calculate the following:
Power costs assigned to Model B
Setups costs assigned to Model A
Engineering costs assigned to Model A

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Godwin Ltd. produces specially machined parts. The parts are produced in batches in one continuous manufacturing process. Each part is custom produced and requires special engineering design activity (based on customer specifications). Once the design is completed, the equipment can be set up for batch production. Once the batch is completed, a sample is taken and inspected to see if the parts are within the tolerances allowed. Thus, the manufacturing process has four activities: engineering, setups, machining, and inspecting. In addition, there is a sustaining process with two activities: providing utilities (plantwide) and providing space. Costs have been assigned to each activity using direct tracing and resource drivers:  Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
Required:
a.
Identify the activities within each process as unit-level, batch-level, product-level, or facility-level.
b.
Create homogeneous cost pools. Identify the activities that belong to each pool and the activity driver that will be used for computing pool rates.
c.
Build an activity relational (i.e. cost) table.
d.
Compute the cost pool rates.
 Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:
Activity drivers for each activity have been identified and their practical capacities listed:  The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.
The costs of facility-level activities are assigned using machine hours.Required:
a.
Identify the activities within each process as unit-level, batch-level, product-level, or facility-level.
b.
Create homogeneous cost pools. Identify the activities that belong to each pool and the activity driver that will be used for computing pool rates.
c.
Build an activity relational (i.e. cost) table.
d.
Compute the cost pool rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Describe the unit level approach to cost behaviour analysis. Discuss the appropriateness of this approach.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Hunter Company manufactures two products (XX and YY). The overhead costs have been divided into four cost pools that use the following activity drivers:  Required:
Required:
a.
Compute the allocation rates for each of the activity drivers listed.
b.
Allocate the overhead costs to Products XX and YY using activity-based costing.
c.
Compute the overhead rate using labour hours under the traditional functional-based costing system.
d.
Allocate the overhead costs to Products XX and YY using the traditional functional-based costing system overhead rate calculated in part (c).
 Required:
Required: a.
Compute the allocation rates for each of the activity drivers listed.
b.
Allocate the overhead costs to Products XX and YY using activity-based costing.
c.
Compute the overhead rate using labour hours under the traditional functional-based costing system.
d.
Allocate the overhead costs to Products XX and YY using the traditional functional-based costing system overhead rate calculated in part (c).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 59 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








