Deck 10: Activity-Based Costing
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 10: Activity-Based Costing
1
Figure 10-4
Jamie Ltd. had the following information:
Refer to Figure 10-4. What is the mark up based on materials?
A) 400.0%
B) 185.7%
C) 42.9%
D) 71.4%
Jamie Ltd. had the following information:

Refer to Figure 10-4. What is the mark up based on materials?
A) 400.0%
B) 185.7%
C) 42.9%
D) 71.4%
A
2
Products might consume overhead in different proportions due to
A) differences in product size.
B) differences in setup times.
C) differences in product complexity.
D) all of the above.
A) differences in product size.
B) differences in setup times.
C) differences in product complexity.
D) all of the above.
D
3
Which of the following is a FALSE statement about target costing?
A) Target costing is a method of determining the cost of a product or service based on the price that customers are willing to pay.
B) The cost is calculated by subtracting the desired profit from the target price.
C) Target costing is an interactive process.
D) Target costing is cost driven.
A) Target costing is a method of determining the cost of a product or service based on the price that customers are willing to pay.
B) The cost is calculated by subtracting the desired profit from the target price.
C) Target costing is an interactive process.
D) Target costing is cost driven.
D
4
____ is where a higher price is charged at the beginning of a product's life cycle.
A) Penetration pricing
B) Predatory pricing
C) Price skimming
D) Target costing
A) Penetration pricing
B) Predatory pricing
C) Price skimming
D) Target costing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Figure 10-2
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Refer to Figure 10-2. What is the profit (loss) from Option One?
A) £1,050,000
B) £210,000
C) £950,000
D) £110,000
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Refer to Figure 10-2. What is the profit (loss) from Option One?
A) £1,050,000
B) £210,000
C) £950,000
D) £110,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Figure 10-3
Farr Company had the following information:
Refer to Figure 10-3. What is the mark up based on prime costs?
A) 300.0%
B) 133.3%
C) 50.0%
D) 166.7%
Farr Company had the following information:

Refer to Figure 10-3. What is the mark up based on prime costs?
A) 300.0%
B) 133.3%
C) 50.0%
D) 166.7%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following stages is characterized by rapid increases in sales and production?
A) Introduction
B) Growth
C) Maturity
D) Decline
A) Introduction
B) Growth
C) Maturity
D) Decline

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following stages has revenues for the entire industry decreasing?
A) Introduction
B) Growth
C) Maturity
D) Decline
A) Introduction
B) Growth
C) Maturity
D) Decline

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Figure 10-1
Wheat Manufacturing has four categories of overhead. The four categories and the expected overhead costs for each category for next year are as follows: Currently, overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate based upon budgeted direct labour hours. For next year, 20,000 direct labour hours are budgeted.
Currently, overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate based upon budgeted direct labour hours. For next year, 20,000 direct labour hours are budgeted.
The company has been asked to submit a bid for a proposed job. The plant manager feels that obtaining this job would result in new business in future years. Usually bids are based upon full manufacturing cost plus 15 per cent.
Estimates for the proposed job are as follows: In the past, full manufacturing cost has been calculated by allocating overhead using a volume-based cost driver--direct labour hours. The plant manager has heard of a new way of applying overhead that uses cost pools and cost drivers.
In the past, full manufacturing cost has been calculated by allocating overhead using a volume-based cost driver--direct labour hours. The plant manager has heard of a new way of applying overhead that uses cost pools and cost drivers.
Expected activity for the four activity-based cost drivers that would be used are as follows:
Refer to Figure 10-1. If Wheat Manufacturing used activity-based cost drivers to assign overhead and the company's bid is full cost plus 15 per cent, the company's bid would be
A) £12,696.00
B) £13,965.60
C) £10,120.00
D) £9,936.00
Wheat Manufacturing has four categories of overhead. The four categories and the expected overhead costs for each category for next year are as follows:
 Currently, overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate based upon budgeted direct labour hours. For next year, 20,000 direct labour hours are budgeted.
Currently, overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate based upon budgeted direct labour hours. For next year, 20,000 direct labour hours are budgeted.The company has been asked to submit a bid for a proposed job. The plant manager feels that obtaining this job would result in new business in future years. Usually bids are based upon full manufacturing cost plus 15 per cent.
Estimates for the proposed job are as follows:
 In the past, full manufacturing cost has been calculated by allocating overhead using a volume-based cost driver--direct labour hours. The plant manager has heard of a new way of applying overhead that uses cost pools and cost drivers.
In the past, full manufacturing cost has been calculated by allocating overhead using a volume-based cost driver--direct labour hours. The plant manager has heard of a new way of applying overhead that uses cost pools and cost drivers.Expected activity for the four activity-based cost drivers that would be used are as follows:

Refer to Figure 10-1. If Wheat Manufacturing used activity-based cost drivers to assign overhead and the company's bid is full cost plus 15 per cent, the company's bid would be
A) £12,696.00
B) £13,965.60
C) £10,120.00
D) £9,936.00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Figure 10-2
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Refer to Figure 10-2. Which option is preferred?
A) Option One
B) Option Two
C) Option Three
D) Options One and Three are equally preferred.
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Refer to Figure 10-2. Which option is preferred?
A) Option One
B) Option Two
C) Option Three
D) Options One and Three are equally preferred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Figure 10-4
Jamie Ltd. had the following information:
Refer to Figure 10-4. What would be the price for something that has a cost of £500, assuming that the mark up is based on cost of goods sold?
A) £833
B) £625
C) £708
D) £2,000
Jamie Ltd. had the following information:

Refer to Figure 10-4. What would be the price for something that has a cost of £500, assuming that the mark up is based on cost of goods sold?
A) £833
B) £625
C) £708
D) £2,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Figure 10-3
Farr Company had the following information:
Refer to Figure 10-3. What is the mark up based on cost of goods sold?
A) 50.0%
B) 100.0%
C) 37.5%
D) 62.5%
Farr Company had the following information:

Refer to Figure 10-3. What is the mark up based on cost of goods sold?
A) 50.0%
B) 100.0%
C) 37.5%
D) 62.5%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
____ is the pricing of a new product at a low initial price to build market share quickly.
A) Penetration pricing
B) Predatory pricing
C) Price skimming
D) Target costing
A) Penetration pricing
B) Predatory pricing
C) Price skimming
D) Target costing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Figure 10-2
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Refer to Figure 10-2. What is the profit (loss) from Option Two?
A) £600,000
B) £100,000
C) £40,000
D) (£100,000)
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Refer to Figure 10-2. What is the profit (loss) from Option Two?
A) £600,000
B) £100,000
C) £40,000
D) (£100,000)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Price skimming occurs in which of the following life-cycle stages?
A) Introduction
B) Growth
C) Maturity
D) Decline
A) Introduction
B) Growth
C) Maturity
D) Decline

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Figure 10-2
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The mark up is a percentage applied to base cost.
B) The mark up is an absolute rule.
C) A major advantage of mark up pricing is that standard mark ups are easy to apply.
D) The mark up can be calculated using a variety of bases.
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The mark up is a percentage applied to base cost.
B) The mark up is an absolute rule.
C) A major advantage of mark up pricing is that standard mark ups are easy to apply.
D) The mark up can be calculated using a variety of bases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Figure 10-5
Ander Company produces precision equipment for major buyers. Of the six customers, one accounts for 40 per cent of the sales, with the remaining five accounting for the rest of the sales. The five smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Ander's customer activity follow: Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Refer to Figure 10-5, what amount of order-filling costs would be allocated to the large customer if these costs are allocated based on sales volume?
A) £144,000
B) £216,000
C) £150,000
D) £225,000
Ander Company produces precision equipment for major buyers. Of the six customers, one accounts for 40 per cent of the sales, with the remaining five accounting for the rest of the sales. The five smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Ander's customer activity follow:
 Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.Refer to Figure 10-5, what amount of order-filling costs would be allocated to the large customer if these costs are allocated based on sales volume?
A) £144,000
B) £216,000
C) £150,000
D) £225,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Figure 10-2
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Refer to Figure 10-2. What is the profit (loss) from Option Three?
A) £215,000
B) £1,200,000
C) £110,000
D) (£60,000)
Anderson Company manufactures a variety of toys and games. John Boone, president, is disappointed in the sales of a new board game. The game sold only 10,000 units in 2011 when 30,000 were projected. Sales for 2008 look no better. At £100 per game, it is not a hot seller. Direct costs of the board game are £56 variable cost and £100,000 fixed. John is considering several options. Option One: Cut the price to £70 and perhaps sell 15,000 units. Option Two: Cut the price to £60, reduce material costs by £10, and cut advertising by £60,000. Anticipated volume for this option is 10,000 units. Option Three: Cut the price to £80 and include a £10 mail-in rebate offer. It is anticipated that 15,000 units could be sold and only 30 per cent of the rebate coupons would be redeemed.
Refer to Figure 10-2. What is the profit (loss) from Option Three?
A) £215,000
B) £1,200,000
C) £110,000
D) (£60,000)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The activity-based resource usage model improves managerial control and decision making such as
A) the best way to use excess activity capacity in the system.
B) maximization of individual unit performance.
C) increasing the allocation of costs.
D) focusing on managing costs rather than activities.
A) the best way to use excess activity capacity in the system.
B) maximization of individual unit performance.
C) increasing the allocation of costs.
D) focusing on managing costs rather than activities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Figure 10-1
Wheat Manufacturing has four categories of overhead. The four categories and the expected overhead costs for each category for next year are as follows: Currently, overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate based upon budgeted direct labour hours. For next year, 20,000 direct labour hours are budgeted.
Currently, overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate based upon budgeted direct labour hours. For next year, 20,000 direct labour hours are budgeted.
The company has been asked to submit a bid for a proposed job. The plant manager feels that obtaining this job would result in new business in future years. Usually bids are based upon full manufacturing cost plus 15 per cent.
Estimates for the proposed job are as follows: In the past, full manufacturing cost has been calculated by allocating overhead using a volume-based cost driver--direct labour hours. The plant manager has heard of a new way of applying overhead that uses cost pools and cost drivers.
In the past, full manufacturing cost has been calculated by allocating overhead using a volume-based cost driver--direct labour hours. The plant manager has heard of a new way of applying overhead that uses cost pools and cost drivers.
Expected activity for the four activity-based cost drivers that would be used are as follows:
Refer to Figure 10-1. If Wheat Manufacturing used direct labour hours as the cost driver and the company's bid is full cost plus 15 per cent, the company's bid would be
Wheat Manufacturing has four categories of overhead. The four categories and the expected overhead costs for each category for next year are as follows:
 Currently, overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate based upon budgeted direct labour hours. For next year, 20,000 direct labour hours are budgeted.
Currently, overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate based upon budgeted direct labour hours. For next year, 20,000 direct labour hours are budgeted.The company has been asked to submit a bid for a proposed job. The plant manager feels that obtaining this job would result in new business in future years. Usually bids are based upon full manufacturing cost plus 15 per cent.
Estimates for the proposed job are as follows:
 In the past, full manufacturing cost has been calculated by allocating overhead using a volume-based cost driver--direct labour hours. The plant manager has heard of a new way of applying overhead that uses cost pools and cost drivers.
In the past, full manufacturing cost has been calculated by allocating overhead using a volume-based cost driver--direct labour hours. The plant manager has heard of a new way of applying overhead that uses cost pools and cost drivers.Expected activity for the four activity-based cost drivers that would be used are as follows:

Refer to Figure 10-1. If Wheat Manufacturing used direct labour hours as the cost driver and the company's bid is full cost plus 15 per cent, the company's bid would be


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Figure 10-5
Ander Company produces precision equipment for major buyers. Of the six customers, one accounts for 40 per cent of the sales, with the remaining five accounting for the rest of the sales. The five smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Ander's customer activity follow: Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Refer to Figure 10-5 above, what amount of sales-force costs would be allocated to the five smaller customers if these costs are allocated based on sales volume?
A) £144,000
B) £216,000
C) £150,000
D) £225,000
Ander Company produces precision equipment for major buyers. Of the six customers, one accounts for 40 per cent of the sales, with the remaining five accounting for the rest of the sales. The five smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Ander's customer activity follow:
 Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.Refer to Figure 10-5 above, what amount of sales-force costs would be allocated to the five smaller customers if these costs are allocated based on sales volume?
A) £144,000
B) £216,000
C) £150,000
D) £225,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Setting prices below cost for the purpose of injuring competitors and eliminating competition is
A) predatory pricing.
B) target pricing.
C) price discrimination.
D) price gouging.
A) predatory pricing.
B) target pricing.
C) price discrimination.
D) price gouging.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
If activity-based costing is used, modifications made by engineering to the product design of several products would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Many products have a predictable profit or product life cycle. Describe the product life cycle from the marketing perspective. In addition, graph profit versus the different phases. Finally, discuss the impact of the product life cycle on products, learning effects, setups, purchasing, and marketing expenses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Nordholm Construction Company builds houses. Each job requires a bid. Nordholm's bidding policy is to estimate the costs of materials, direct labour, and subcontractor's costs. These are totaled and a mark up is applied to cover overhead and profit. In the coming year, Nordholm believes it will be the successful bidder on ten jobs with the following total revenues and costs:  The residual will cover overhead and profits.
The residual will cover overhead and profits.
Required:
a.
What is the mark up percentage on total direct costs?
b.
Suppose Nordholm is asked to bid on a job with estimated direct costs of £55,000. What is the bid? If the customer complains that the profit seems pretty high, how might Nordholm counter that?
 The residual will cover overhead and profits.
The residual will cover overhead and profits.Required:
a.
What is the mark up percentage on total direct costs?
b.
Suppose Nordholm is asked to bid on a job with estimated direct costs of £55,000. What is the bid? If the customer complains that the profit seems pretty high, how might Nordholm counter that?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements concerning target costing is NOT true?
A) Implementing target costing requires detailed information on the cost of alternative activities.
B) Target costing can be applied to components of products as well as the new products as a whole.
C) A primary advantage of target costing is that it requires little or no coordination among processes.
D) Short product life cycles increase the importance of target costing.
A) Implementing target costing requires detailed information on the cost of alternative activities.
B) Target costing can be applied to components of products as well as the new products as a whole.
C) A primary advantage of target costing is that it requires little or no coordination among processes.
D) Short product life cycles increase the importance of target costing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Johnson Company produces office equipment for 16 major buyers. Of the 16 customers, one accounts for 50 per cent of the sales, with the remaining 15 accounting for the rest of the sales. The 15 smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Johnson's customer activity follow:  Order-filling costs for Johnson Company total £270,000, and sales-force costs are £300,000.
Order-filling costs for Johnson Company total £270,000, and sales-force costs are £300,000.
Required:
a.
Determine the amount of selling costs (order-filling and sales-force costs) allocated to (1) the large customer and (2) the 15 smaller customers if these costs are allocated based on sales volume.
b.
b.
Determine the amount of selling costs (order-filling and sales-force costs) allocated to (1) the large customer and (2) the 15 smaller customers if these costs are assigned using activity-based costing.
c.
Comment on the differences in amounts attributed to the smaller customers in requirements a and
 Order-filling costs for Johnson Company total £270,000, and sales-force costs are £300,000.
Order-filling costs for Johnson Company total £270,000, and sales-force costs are £300,000.Required:
a.
Determine the amount of selling costs (order-filling and sales-force costs) allocated to (1) the large customer and (2) the 15 smaller customers if these costs are allocated based on sales volume.
b.
b.
Determine the amount of selling costs (order-filling and sales-force costs) allocated to (1) the large customer and (2) the 15 smaller customers if these costs are assigned using activity-based costing.
c.
Comment on the differences in amounts attributed to the smaller customers in requirements a and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Cost-based pricing has traditionally been important because:
A) cost data are available.
B) cost-based prices are defensible.
C) revenues must exceed costs if the firm is to remain in business.
D) of all of the above.
A) cost data are available.
B) cost-based prices are defensible.
C) revenues must exceed costs if the firm is to remain in business.
D) of all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Figure 10-6
Multiple Products Co. has predicted the following costs for this year for 100,000 units: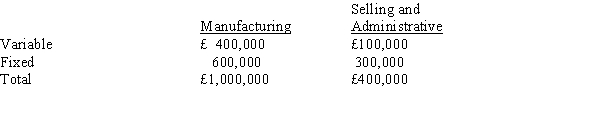
Refer to Figure 10-6. What is the mark up on variable costs needed to achieve a target profit of £100,000?
A) 375 per cent
B) 275 per cent
C) 250 per cent
D) 200 per cent
Multiple Products Co. has predicted the following costs for this year for 100,000 units:

Refer to Figure 10-6. What is the mark up on variable costs needed to achieve a target profit of £100,000?
A) 375 per cent
B) 275 per cent
C) 250 per cent
D) 200 per cent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following accurately describes the effect target costing has on the manufacturing design function?
A) Target costing allows the design engineer's job to end once the product is designed.
B) Target costing forces design engineers to explicitly consider the costs of manufacturing and other aspects of business that traditionally fall outside the engineering department.
C) Target costing defines clear lines of responsibility among departments allowing for design engineers to be evaluated purely on meeting the customer's functional requirements.
D) Target costing has no implications for design engineering.
A) Target costing allows the design engineer's job to end once the product is designed.
B) Target costing forces design engineers to explicitly consider the costs of manufacturing and other aspects of business that traditionally fall outside the engineering department.
C) Target costing defines clear lines of responsibility among departments allowing for design engineers to be evaluated purely on meeting the customer's functional requirements.
D) Target costing has no implications for design engineering.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A target cost is computed as
A) the cost to manufacture plus a desired mark up.
B) the cost to manufacture plus the designated selling expenses.
C) the market willingness to pay less the cost to manufacture.
D) the market willingness to pay less the desired profit.
A) the cost to manufacture plus a desired mark up.
B) the cost to manufacture plus the designated selling expenses.
C) the market willingness to pay less the cost to manufacture.
D) the market willingness to pay less the desired profit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
World-class organizations operating in competitive markets are more likely to take which one of the following approaches toward pricing?
A) Begin with cost data as given and determine price by adding a reasonable mark-up.
B) Determine price based on the amount management believes customers are willing to pay.
C) Employ a cost-based approach to pricing.
D) Determine the price that keeps the facilities fully utilized.
A) Begin with cost data as given and determine price by adding a reasonable mark-up.
B) Determine price based on the amount management believes customers are willing to pay.
C) Employ a cost-based approach to pricing.
D) Determine the price that keeps the facilities fully utilized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Bay Company produces boats for 11 major buyers. Of the 11 customers, one accounts for 45 per cent of the sales, with the remaining ten accounting for the rest of the sales. The ten smaller customers purchase boats in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Bay's customer activity follow:  Order-filling costs for Bay Company total £401,500, and sales-force costs are £260,000.
Order-filling costs for Bay Company total £401,500, and sales-force costs are £260,000.
Required:
a.
Determine the amount of selling costs (order-filling and sales-force costs) allocated to (1) the large customer and (2) the ten smaller customers if these costs are allocated based on sales volume.
b.
b.
Determine the amount of selling costs (order-filling and sales-force costs) allocated to (1) the large customer and (2) the ten smaller customers if these costs are assigned using activity-based costing.
c.
Comment on the differences in amounts attributed to the smaller customers in requirements a and
 Order-filling costs for Bay Company total £401,500, and sales-force costs are £260,000.
Order-filling costs for Bay Company total £401,500, and sales-force costs are £260,000.Required:
a.
Determine the amount of selling costs (order-filling and sales-force costs) allocated to (1) the large customer and (2) the ten smaller customers if these costs are allocated based on sales volume.
b.
b.
Determine the amount of selling costs (order-filling and sales-force costs) allocated to (1) the large customer and (2) the ten smaller customers if these costs are assigned using activity-based costing.
c.
Comment on the differences in amounts attributed to the smaller customers in requirements a and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
If activity-based costing is used, materials handling would be classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
When cost-based pricing is employed and mark up is based on manufacturing costs, the mark up must be sufficiently large enough to:
A) cover selling expenses.
B) cover administrative expenses.
C) provide for the desired profit.
D) accomplish all of the above.
A) cover selling expenses.
B) cover administrative expenses.
C) provide for the desired profit.
D) accomplish all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements describes a legitimate disadvantage of cost-based pricing?
A) Marginal costs and revenues are difficult to measure.
B) Determining the amount a customer is willing to pay may require sufficient estimation.
C) Customers may not be willing to pay the price determined by the procedure.
D) all of the above
A) Marginal costs and revenues are difficult to measure.
B) Determining the amount a customer is willing to pay may require sufficient estimation.
C) Customers may not be willing to pay the price determined by the procedure.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Figure 10-5
Ander Company produces precision equipment for major buyers. Of the six customers, one accounts for 40 per cent of the sales, with the remaining five accounting for the rest of the sales. The five smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Ander's customer activity follow: Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Refer to Figure 10-5 above, what amount of order-filling costs would be allocated to the large customer if these costs are allocated using an activity-based costing approach?
A) £10,000
B) £350,000
C) £28,800
D) £331,200
Ander Company produces precision equipment for major buyers. Of the six customers, one accounts for 40 per cent of the sales, with the remaining five accounting for the rest of the sales. The five smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Ander's customer activity follow:
 Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.Refer to Figure 10-5 above, what amount of order-filling costs would be allocated to the large customer if these costs are allocated using an activity-based costing approach?
A) £10,000
B) £350,000
C) £28,800
D) £331,200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Figure 10-6
Multiple Products Co. has predicted the following costs for this year for 100,000 units:
Refer to Figure 10-6. What is the mark up on variable costs needed to break even?
A) 100 per cent
B) 40 per cent
C) 140 per cent
D) 180 per cent
Multiple Products Co. has predicted the following costs for this year for 100,000 units:

Refer to Figure 10-6. What is the mark up on variable costs needed to break even?
A) 100 per cent
B) 40 per cent
C) 140 per cent
D) 180 per cent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Figure 10-5
Ander Company produces precision equipment for major buyers. Of the six customers, one accounts for 40 per cent of the sales, with the remaining five accounting for the rest of the sales. The five smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Ander's customer activity follow: Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Refer to Figure 10-5 above, what amount of order-filling costs would be allocated to the five smaller customers if these costs are allocated using an activity-based costing approach?
A) £10,000
B) £350,000
C) £28,800
D) £331,200
Ander Company produces precision equipment for major buyers. Of the six customers, one accounts for 40 per cent of the sales, with the remaining five accounting for the rest of the sales. The five smaller customers purchase equipment in roughly equal quantities. Orders placed by the smaller customers are about the same size. Data concerning Ander's customer activity follow:
 Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.
Order-filling costs for Ander Company total £360,000, and sales-force costs are £375,000.Refer to Figure 10-5 above, what amount of order-filling costs would be allocated to the five smaller customers if these costs are allocated using an activity-based costing approach?
A) £10,000
B) £350,000
C) £28,800
D) £331,200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Figure 10-6
Multiple Products Co. has predicted the following costs for this year for 100,000 units:
Refer to Figure 10-6. What is the manufacturing cost mark up needed to obtain a target profit of £100,000?
A) 100 per cent
B) 67 per cent
C) 50 per cent
D) 25 per cent
Multiple Products Co. has predicted the following costs for this year for 100,000 units:

Refer to Figure 10-6. What is the manufacturing cost mark up needed to obtain a target profit of £100,000?
A) 100 per cent
B) 67 per cent
C) 50 per cent
D) 25 per cent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








