Deck 2: An Introduction to Linear Programming
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: An Introduction to Linear Programming
1
A redundant constraint is a binding constraint.
False
2
Because the dual price represents the improvement in the value of the optimal solution per unit increase in right-hand-side, a dual price cannot be negative.
False
3
The standard form of a linear programming problem will have the same solution as the original problem.
True
4
The point (3, 2) is feasible for the constraint 2x1 + 6x2 ≤ 30.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
No matter what value it has, each objective function line is parallel to every other objective function line in a problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A range of optimality is applicable only if the other coefficient remains at its original value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Alternative optimal solutions occur when there is no feasible solution to the problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Only binding constraints form the shape (boundaries) of the feasible region.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
An infeasible problem is one in which the objective function can be increased to infinity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Because surplus variables represent the amount by which the solution exceeds a minimum target, they are given positive coefficients in the objective function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In a feasible problem, an equal-to constraint cannot be nonbinding.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Increasing the right-hand side of a nonbinding constraint will not cause a change in the optimal solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A linear programming problem can be both unbounded and infeasible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Decision variables limit the degree to which the objective in a linear programming problem is satisfied.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
It is possible to have exactly two optimal solutions to a linear programming problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The constraint 2x1 − x2 = 0 passes through the point (200,100).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
An optimal solution to a linear programming problem can be found at an extreme point of the feasible region for the problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In a linear programming problem, the objective function and the constraints must be linear functions of the decision variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
An unbounded feasible region might not result in an unbounded solution for a minimization or maximization problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The constraint 5x1 − 2x2 ≤ 0 passes through the point (20, 50).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A redundant constraint results in
A) no change in the optimal solution(s)
B) an unbounded solution
C) no feasible solution
D) alternative optimal solutions
A) no change in the optimal solution(s)
B) an unbounded solution
C) no feasible solution
D) alternative optimal solutions

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following special cases does not require reformulation of the problem in order to obtain a solution?
A) alternate optimality
B) infeasibility
C) unboundedness
D) each case requires a reformulation.
A) alternate optimality
B) infeasibility
C) unboundedness
D) each case requires a reformulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Decision variables
A) tell how much or how many of something to produce, invest, purchase, hire, etc.
B) represent the values of the constraints.
C) measure the objective function.
D) must exist for each constraint.
A) tell how much or how many of something to produce, invest, purchase, hire, etc.
B) represent the values of the constraints.
C) measure the objective function.
D) must exist for each constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The improvement in the value of the objective function per unit increase in a right-hand side is the
A) sensitivity value.
B) dual price.
C) constraint coefficient.
D) slack value.
A) sensitivity value.
B) dual price.
C) constraint coefficient.
D) slack value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A solution that satisfies all the constraints of a linear programming problem except the nonnegativity constraints is called
A) optimal.
B) feasible.
C) infeasible.
D) semi-feasible.
A) optimal.
B) feasible.
C) infeasible.
D) semi-feasible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Whenever all the constraints in a linear program are expressed as equalities, the linear program is said to be written in
A) standard form.
B) bounded form.
C) feasible form.
D) alternative form.
A) standard form.
B) bounded form.
C) feasible form.
D) alternative form.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The three assumptions necessary for a linear programming model to be appropriate include all of the following except
A) proportionality
B) additivity
C) divisibility
D) normality
A) proportionality
B) additivity
C) divisibility
D) normality

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
All linear programming problems have all of the following properties EXCEPT
A) a linear objective function that is to be maximized or minimized.
B) a set of linear constraints.
C) alternative optimal solutions.
D) variables that are all restricted to nonnegative values.
A) a linear objective function that is to be maximized or minimized.
B) a set of linear constraints.
C) alternative optimal solutions.
D) variables that are all restricted to nonnegative values.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
As long as the slope of the objective function stays between the slopes of the binding constraints
A) the value of the objective function won't change.
B) there will be alternative optimal solutions.
C) the values of the dual variables won't change.
D) there will be no slack in the solution.
A) the value of the objective function won't change.
B) there will be alternative optimal solutions.
C) the values of the dual variables won't change.
D) there will be no slack in the solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a valid objective function for a linear programming problem?
A) Max 5xy
B) Min 4x + 3y + (2/3)z
C) Max 5x2 + 6y2
D) Min (x1 + x2)/x3
A) Max 5xy
B) Min 4x + 3y + (2/3)z
C) Max 5x2 + 6y2
D) Min (x1 + x2)/x3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Infeasibility means that the number of solutions to the linear programming models that satisfies all constraints is
A) at least 1.
B) 0.
C) an infinite number.
D) at least 2.
A) at least 1.
B) 0.
C) an infinite number.
D) at least 2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
All of the following statements about a redundant constraint are correct EXCEPT
A) A redundant constraint does not affect the optimal solution.
B) A redundant constraint does not affect the feasible region.
C) Recognizing a redundant constraint is easy with the graphical solution method.
D) At the optimal solution, a redundant constraint will have zero slack.
A) A redundant constraint does not affect the optimal solution.
B) A redundant constraint does not affect the feasible region.
C) Recognizing a redundant constraint is easy with the graphical solution method.
D) At the optimal solution, a redundant constraint will have zero slack.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A) A feasible solution satisfies all constraints.
B) An optimal solution satisfies all constraints.
C) An infeasible solution violates all constraints.
D) A feasible solution point does not have to lie on the boundary of the feasible region.
A) A feasible solution satisfies all constraints.
B) An optimal solution satisfies all constraints.
C) An infeasible solution violates all constraints.
D) A feasible solution point does not have to lie on the boundary of the feasible region.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
In what part(s) of a linear programming formulation would the decision variables be stated?
A) objective function and the left-hand side of each constraint
B) objective function and the right-hand side of each constraint
C) the left-hand side of each constraint only
D) the objective function only
A) objective function and the left-hand side of each constraint
B) objective function and the right-hand side of each constraint
C) the left-hand side of each constraint only
D) the objective function only

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The maximization or minimization of a quantity is the
A) goal of management science.
B) decision for decision analysis.
C) constraint of operations research.
D) objective of linear programming.
A) goal of management science.
B) decision for decision analysis.
C) constraint of operations research.
D) objective of linear programming.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A variable added to the left-hand side of a less-than-or-equal-to constraint to convert the constraint into an equality is
A) a standard variable
B) a slack variable
C) a surplus variable
D) a non-negative variable
A) a standard variable
B) a slack variable
C) a surplus variable
D) a non-negative variable

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If there is a maximum of 4,000 hours of labor available per month and 300 ping-pong balls (x1) or 125 wiffle balls (x2) can be produced per hour of labor, which of the following constraints reflects this situation?
A) 300x1 + 125x2 > 4,000
B) 300x1 + 125x2 < 4,000
C) 425(x1 + x2) < 4,000
D) 300x1 + 125x2 = 4,000
A) 300x1 + 125x2 > 4,000
B) 300x1 + 125x2 < 4,000
C) 425(x1 + x2) < 4,000
D) 300x1 + 125x2 = 4,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A constraint that does not affect the feasible region is a
A) non-negativity constraint.
B) redundant constraint.
C) standard constraint.
D) slack constraint.
A) non-negativity constraint.
B) redundant constraint.
C) standard constraint.
D) slack constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Slack
A) is the difference between the left and right sides of a constraint.
B) is the amount by which the left side of a ≤ constraint is smaller than the right side.
C) is the amount by which the left side of a ≥ constraint is larger than the right side.
D) exists for each variable in a linear programming problem.
A) is the difference between the left and right sides of a constraint.
B) is the amount by which the left side of a ≤ constraint is smaller than the right side.
C) is the amount by which the left side of a ≥ constraint is larger than the right side.
D) exists for each variable in a linear programming problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
To find the optimal solution to a linear programming problem using the graphical method
A) find the feasible point that is the farthest away from the origin.
B) find the feasible point that is at the highest location.
C) find the feasible point that is closest to the origin.
D) None of the alternatives is correct.
A) find the feasible point that is the farthest away from the origin.
B) find the feasible point that is at the highest location.
C) find the feasible point that is closest to the origin.
D) None of the alternatives is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Does the following linear programming problem exhibit infeasibility, unboundedness, or alternate optimal solutions? Explain.
Min
3X + 3Y
s.t.
1X + 2Y ≤ 16
1X + 1Y ≤ 10
5X + 3Y ≤ 45
X , Y ≥ 0
Min
3X + 3Y
s.t.
1X + 2Y ≤ 16
1X + 1Y ≤ 10
5X + 3Y ≤ 45
X , Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Given the following linear program:
Min
150X + 210Y
s.t.
3.8X + 1.2Y ≥ 22.8
Y ≥ 6
Y ≤ 15
45X + 30Y = 630
X, Y ≥ 0
Solve the problem graphically. How many extreme points exist for this problem?
Min
150X + 210Y
s.t.
3.8X + 1.2Y ≥ 22.8
Y ≥ 6
Y ≤ 15
45X + 30Y = 630
X, Y ≥ 0
Solve the problem graphically. How many extreme points exist for this problem?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Does the following linear programming problem exhibit infeasibility, unboundedness, or alternate optimal solutions? Explain.
Min
1X + 1Y
s.t.
5X + 3Y ≤ 30
3X + 4Y ≥ 36
Y ≤ 7
X , Y ≥ 0
Min
1X + 1Y
s.t.
5X + 3Y ≤ 30
3X + 4Y ≥ 36
Y ≤ 7
X , Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Muir Manufacturing produces two popular grades of commercial carpeting among its many other products. In the coming production period, Muir needs to decide how many rolls of each grade should be produced in order to maximize profit. Each roll of Grade X carpet uses 50 units of synthetic fiber, requires 25 hours of production time, and needs 20 units of foam backing. Each roll of Grade Y carpet uses 40 units of synthetic fiber, requires 28 hours of production time, and needs 15 units of foam backing.
The profit per roll of Grade X carpet is $200 and the profit per roll of Grade Y carpet is $160. In the coming production period, Muir has 3000 units of synthetic fiber available for use. Workers have been scheduled to provide at least 1800 hours of production time (overtime is a possibility). The company has 1500 units of foam backing available for use.
Develop and solve a linear programming model for this problem.
The profit per roll of Grade X carpet is $200 and the profit per roll of Grade Y carpet is $160. In the coming production period, Muir has 3000 units of synthetic fiber available for use. Workers have been scheduled to provide at least 1800 hours of production time (overtime is a possibility). The company has 1500 units of foam backing available for use.
Develop and solve a linear programming model for this problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Solve the following linear program graphically.
Max
5X + 7Y
s.t.
X ≤ 6
2X + 3Y ≤ 19
X + Y ≤ 8
X, Y ≥ 0
Max
5X + 7Y
s.t.
X ≤ 6
2X + 3Y ≤ 19
X + Y ≤ 8
X, Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Solve the following system of simultaneous equations.
6X + 2Y = 50
2X + 4Y = 20
6X + 2Y = 50
2X + 4Y = 20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Find the complete optimal solution to this linear programming problem.
Max
5X + 3Y
s.t.
2X + 3Y ≤ 30
2X + 5Y ≤ 40
6X − 5Y ≤ 0
X , Y ≥ 0
Max
5X + 3Y
s.t.
2X + 3Y ≤ 30
2X + 5Y ≤ 40
6X − 5Y ≤ 0
X , Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Explain how to graph the line x1 − 2x2 ≥ 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Explain the difference between profit and contribution in an objective function. Why is it important for the decision
maker to know which of these the objective function coefficients represent?
maker to know which of these the objective function coefficients represent?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
For the following linear programming problem, determine the optimal solution by the graphical solution method
Max
−X + 2Y
s.t.
6X − 2Y ≤ 3
−2X + 3Y ≤ 6
X + Y ≤ 3
X, Y ≥ 0
Max
−X + 2Y
s.t.
6X − 2Y ≤ 3
−2X + 3Y ≤ 6
X + Y ≤ 3
X, Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
For the following linear programming problem, determine the optimal solution by the graphical solution method. Are any of the constraints redundant? If yes, then identify the constraint that is redundant.
Max
X + 2Y
s.t.
X + Y ≤ 3
X − 2Y ≥ 0
Y ≤ 1
X, Y ≥ 0
Max
X + 2Y
s.t.
X + Y ≤ 3
X − 2Y ≥ 0
Y ≤ 1
X, Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Solve the following system of simultaneous equations.
6X + 4Y = 40
2X + 3Y = 20
6X + 4Y = 40
2X + 3Y = 20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Consider the following linear programming problem
Max
8X + 7Y
s.t.
15X + 5Y ≤ 75
10X + 6Y ≤ 60
X + Y ≤ 8
X, Y ≥ 0
a.Use a graph to show each constraint and the feasible region.
b.Identify the optimal solution point on your graph. What are the values of X and Y at the optimal solution?
c.What is the optimal value of the objective function?
Max
8X + 7Y
s.t.
15X + 5Y ≤ 75
10X + 6Y ≤ 60
X + Y ≤ 8
X, Y ≥ 0
a.Use a graph to show each constraint and the feasible region.
b.Identify the optimal solution point on your graph. What are the values of X and Y at the optimal solution?
c.What is the optimal value of the objective function?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Find the complete optimal solution to this linear programming problem.
Min
3X + 3Y
s.t.
12X + 4Y ≥ 48
10X + 5Y ≥ 50
4X + 8Y ≥ 32
X , Y ≥ 0
Min
3X + 3Y
s.t.
12X + 4Y ≥ 48
10X + 5Y ≥ 50
4X + 8Y ≥ 32
X , Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Consider the following linear program:
Max
60X + 43Y
s.t.
X + 3Y ≥ 9
6X − 2Y = 12
X + 2Y ≤ 10
X, Y ≥ 0
a.
Write the problem in standard form.
b.
What is the feasible region for the problem?
c.
Show that regardless of the values of the actual objective function coefficients, the optimal solution will occur at one of two points. Solve for these points and then determine which one maximizes the current objective function.
Max
60X + 43Y
s.t.
X + 3Y ≥ 9
6X − 2Y = 12
X + 2Y ≤ 10
X, Y ≥ 0
a.
Write the problem in standard form.
b.
What is the feasible region for the problem?
c.
Show that regardless of the values of the actual objective function coefficients, the optimal solution will occur at one of two points. Solve for these points and then determine which one maximizes the current objective function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A businessman is considering opening a small specialized trucking firm. To make the firm profitable, it is estimated that it must have a daily trucking capacity of at least 84,000 cu. ft. Two types of trucks are appropriate for the specialized operation. Their characteristics and costs are summarized in the table below. Note that truck 2 requires 3 drivers for long haul trips. There are 41 potential drivers available and there are facilities for at most 40 trucks. The businessman's objective is to minimize the total cost outlay for trucks. 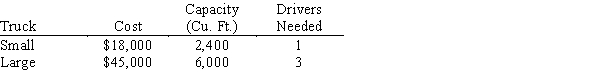
Solve the problem graphically and note there are alternate optimal solutions. Which optimal solution:
a.
uses only one type of truck?
b.
utilizes the minimum total number of trucks?
c.
uses the same number of small and large trucks?
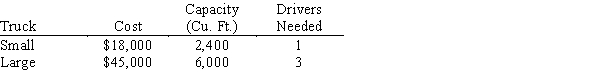
Solve the problem graphically and note there are alternate optimal solutions. Which optimal solution:
a.
uses only one type of truck?
b.
utilizes the minimum total number of trucks?
c.
uses the same number of small and large trucks?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Find the complete optimal solution to this linear programming problem.
Min
5X + 6Y
s.t.
3X + Y ≥ 15
X + 2Y ≥ 12
3X + 2Y ≥ 24
X , Y ≥ 0
Min
5X + 6Y
s.t.
3X + Y ≥ 15
X + 2Y ≥ 12
3X + 2Y ≥ 24
X , Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Find the complete optimal solution to this linear programming problem.
Max
2X + 3Y
s.t.
4X + 9Y ≤ 72
10X + 11Y ≤ 110
17X + 9Y ≤ 153
X , Y ≥ 0
Max
2X + 3Y
s.t.
4X + 9Y ≤ 72
10X + 11Y ≤ 110
17X + 9Y ≤ 153
X , Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Use this graph to answer the questions. 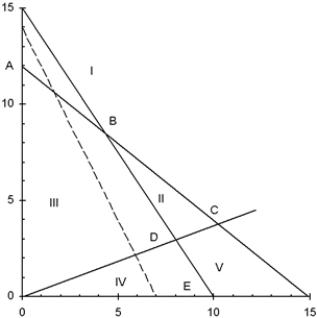 Max
Max
20X + 10Y
s.t.
12X + 15Y ≤ 180
15X + 10Y ≤ 150
3X − 8Y ≤ 0
X , Y ≥ 0
a.Which area (I, II, III, IV, or V) forms the feasible region?
b.Which point (A, B, C, D, or E) is optimal?
c.Which constraints are binding?
d.Which slack variables are zero?
 Max
Max20X + 10Y
s.t.
12X + 15Y ≤ 180
15X + 10Y ≤ 150
3X − 8Y ≤ 0
X , Y ≥ 0
a.Which area (I, II, III, IV, or V) forms the feasible region?
b.Which point (A, B, C, D, or E) is optimal?
c.Which constraints are binding?
d.Which slack variables are zero?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Solve the following linear program by the graphical method.
Max
4X + 5Y
s.t.
X + 3Y ≤ 22
−X + Y ≤ 4
Y ≤ 6
2X − 5Y ≤ 0
X, Y ≥ 0
Max
4X + 5Y
s.t.
X + 3Y ≤ 22
−X + Y ≤ 4
Y ≤ 6
2X − 5Y ≤ 0
X, Y ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Explain the concepts of proportionality, additivity, and divisibility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Explain the steps of the graphical solution procedure for a minimization problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Use a graph to illustrate why a change in an objective function coefficient does not necessarily lead to a change in
the optimal values of the decision variables, but a change in the right-hand sides of a binding constraint does lead to
new values.
the optimal values of the decision variables, but a change in the right-hand sides of a binding constraint does lead to
new values.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Explain the steps necessary to put a linear program in standard form.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Explain what to look for in problems that are infeasible or unbounded.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Create a linear programming problem with two decision variables and three constraints that will include both a slack
and a surplus variable in standard form. Write your problem in standard form.
and a surplus variable in standard form. Write your problem in standard form.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 66 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








