Deck 17: Linear Programming: Simplex Method
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/51
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 17: Linear Programming: Simplex Method
1
The coefficient of an artificial variable in the objective function is zero.
False
2
If a variable is not in the basis, its value is 0.
True
3
When a set of simultaneous equations has more variables than constraints,
A) it is a basic set.
B) it is a feasible set.
C) there is a unique solution.
D) there are many solutions.
A) it is a basic set.
B) it is a feasible set.
C) there is a unique solution.
D) there are many solutions.
D
4
In a simplex tableau, there is a variable associated with each column and both a constraint and a basic variable associated with each row.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The purpose of row operations is to create a unit column for the entering variable while maintaining unit columns for the remaining basic variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The basic solution to a problem with three equations and four variables would assign a value of 0 to
A) 0 variables.
B) 1 variable.
C) 3 variables.
D) 7 variables.
A) 0 variables.
B) 1 variable.
C) 3 variables.
D) 7 variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Coefficients in a nonbasic column in a simplex tableau indicate the amount of decrease in the current basic variables when the value of the nonbasic variable is increased from 0 to 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A basic solution and a basic feasible solution
A) are the same thing.
B) differ in the number of variables allowed to be zero.
C) describe interior points and exterior points, respectively.
D) differ in their inclusion of nonnegativity restrictions.
A) are the same thing.
B) differ in the number of variables allowed to be zero.
C) describe interior points and exterior points, respectively.
D) differ in their inclusion of nonnegativity restrictions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Artificial variables are added for the purpose of obtaining an initial basic feasible solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
To determine a basic solution set of n−m, the variables equal to zero and solve the m linear constraint equations for the remaining m variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The variable to remove from the current basis is the variable with the smallest positive cj − zj value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
At each iteration of the simplex procedure, a new variable becomes basic and a currently basic variable becomes nonbasic, preserving the same number of basic variables and improving the value of the objective function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
When a system of simultaneous equations has more variables than equations, there is a unique solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A solution is optimal when all values in the cj − zj row of the simplex tableau are either zero or positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A basic feasible solution satisfies the nonnegativity restriction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The variable to enter into the basis is the variable with the largest positive cj − zj value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Every extreme point of the graph of a two variable linear programming problem is a basic feasible solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which is not required for a problem to be in tableau form?
A) Each constraint must be written as an equation.
B) Each of the original decision variables must have a coefficient of 1 in one equation and 0 in every other equation.
C) There is exactly one basic variable in each constraint.
D) The right-hand side of each constraint must be nonnegative.
A) Each constraint must be written as an equation.
B) Each of the original decision variables must have a coefficient of 1 in one equation and 0 in every other equation.
C) There is exactly one basic variable in each constraint.
D) The right-hand side of each constraint must be nonnegative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
We recognize infeasibility when one or more of the artificial variables do not remain in the solution at a positive value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Algebraic methods such as the simplex method are used to solve
A) nonlinear programming problems.
B) any size linear programming problem.
C) programming problems under uncertainty.
D) graphical models.
A) nonlinear programming problems.
B) any size linear programming problem.
C) programming problems under uncertainty.
D) graphical models.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Write the following problem in tableau form. Which variables would be in the initial basis?
Max
x1 + 2x2
s.t.
3x1 + 4x2 ≤ 100
2x1 + 3.5x2 ≥ 60
2x1 − 1x2 = 4
x1 , x2 ≥ 0
Max
x1 + 2x2
s.t.
3x1 + 4x2 ≤ 100
2x1 + 3.5x2 ≥ 60
2x1 − 1x2 = 4
x1 , x2 ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Infeasibility exists when one or more of the artificial variables
A) remain in the final solution as a negative value.
B) remain in the final solution as a positive value.
C) have been removed from the basis.
D) remain in the basis.
A) remain in the final solution as a negative value.
B) remain in the final solution as a positive value.
C) have been removed from the basis.
D) remain in the basis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A simplex tableau is shown below. 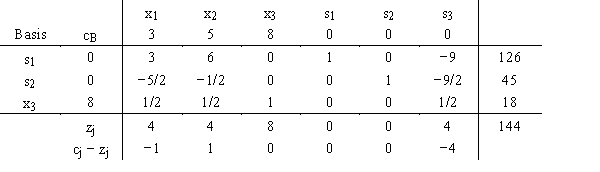
a.
Do one more iteration of the simplex procedure.
b.
What is the current complete solution?
c.
Is this solution optimal? Why or why not?

a.
Do one more iteration of the simplex procedure.
b.
What is the current complete solution?
c.
Is this solution optimal? Why or why not?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Comment on the solution shown in this simplex tableau. 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Unit columns are used to identify
A) the tableau.
B) the c row.
C) the b column.
D) the basic variables.
A) the tableau.
B) the c row.
C) the b column.
D) the basic variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In the simplex method, a tableau is optimal only if all the cj − zj values are
A) zero or negative.
B) zero.
C) negative and nonzero.
D) positive and nonzero.
A) zero or negative.
B) zero.
C) negative and nonzero.
D) positive and nonzero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The values in the cj − zj , or net evaluation, row indicate
A) the value of the objective function.
B) the decrease in value of the objective function that will result if one unit of the variable corresponding to the jth column of the A matrix is brought into the basis.
C) the net change in the value of the objective function that will result if one unit of the variable corresponding to the jth column of the A matrix is brought into the basis.
D) the values of the decision variables.
A) the value of the objective function.
B) the decrease in value of the objective function that will result if one unit of the variable corresponding to the jth column of the A matrix is brought into the basis.
C) the net change in the value of the objective function that will result if one unit of the variable corresponding to the jth column of the A matrix is brought into the basis.
D) the values of the decision variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Given the following initial simplex tableau 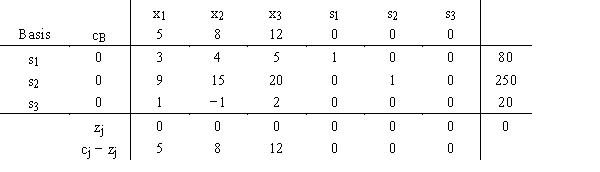
a.What variables form the basis?
b.What are the current values of the decision variables?
c.What is the current value of the objective function?
d.Which variable will be made positive next, and what will its value be?Which variable that is currently positive will become 0?
f.What value will the objective function have next?

a.What variables form the basis?
b.What are the current values of the decision variables?
c.What is the current value of the objective function?
d.Which variable will be made positive next, and what will its value be?Which variable that is currently positive will become 0?
f.What value will the objective function have next?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Determine from a review of the following tableau whether the linear programming problem has multiple optimal solutions. 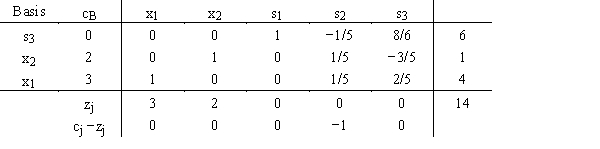


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A simplex table is shown below. 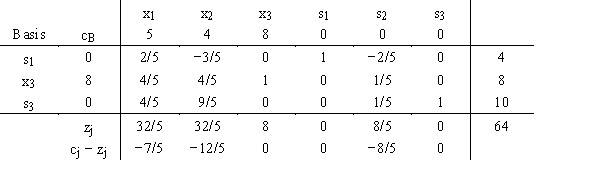
a.What is the current complete solution?
b.The 32/5 for z1 is composed of 0 + 8(4/5) + 0. Explain the meaning of this number.
c.Explain the meaning of the −12/5 value for c 2 − z2.

a.What is the current complete solution?
b.The 32/5 for z1 is composed of 0 + 8(4/5) + 0. Explain the meaning of this number.
c.Explain the meaning of the −12/5 value for c 2 − z2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
What coefficient is assigned to an artificial variable in the objective function?
A) zero.
B) one.
C) a very large negative number.
D) a very large positive number.
A) zero.
B) one.
C) a very large negative number.
D) a very large positive number.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
A minimization problem with four decision variables, two greater-than-or-equal-to constraints, and one equality constraint will have
A) 2 surplus variables, 3 artificial variables, and 3 variables in the basis.
B) 4 surplus variables, 2 artificial variables, and 4 variables in the basis.
C) 3 surplus variables, 3 artificial variables, and 4 variables in the basis.
D) 2 surplus variables, 2 artificial variables, and 3 variables in the basis.
A) 2 surplus variables, 3 artificial variables, and 3 variables in the basis.
B) 4 surplus variables, 2 artificial variables, and 4 variables in the basis.
C) 3 surplus variables, 3 artificial variables, and 4 variables in the basis.
D) 2 surplus variables, 2 artificial variables, and 3 variables in the basis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Write the following problem in tableau form. Which variables would be in the initial basic solution?
Min Z
= −3x1 + x2 + x3
s.t.
x1 − 2x2 + x3 ≤ 11
−4 x1 + x2 + 2x3 ≥ 3
2x1 − x3 ≥ −1
Min Z
= −3x1 + x2 + x3
s.t.
x1 − 2x2 + x3 ≤ 11
−4 x1 + x2 + 2x3 ≥ 3
2x1 − x3 ≥ −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The purpose of the tableau form is to provide
A) infeasible solution.
B) optimal infeasible solution.
C) initial basic feasible solution.
D) degenerate solution.
A) infeasible solution.
B) optimal infeasible solution.
C) initial basic feasible solution.
D) degenerate solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
An alternative optimal solution is indicated when in the simplex tableau
A) a non-basic variable has a value of zero in the cj − zj row.
B) a basic variable has a positive value in the cj − zj row.
C) a basic variable has a value of zero in the cj − zj row.
D) a non-basic variable has a positive value in the cj − zj row.
A) a non-basic variable has a value of zero in the cj − zj row.
B) a basic variable has a positive value in the cj − zj row.
C) a basic variable has a value of zero in the cj − zj row.
D) a non-basic variable has a positive value in the cj − zj row.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Write the following problem in tableau form. Which variables would be in the initial basic solution?
Min Z =
3x1 + 8x2
s.t.
x1 + x2 ≤ 200
x1 ≤ 80
x2 ≤ 60
Min Z =
3x1 + 8x2
s.t.
x1 + x2 ≤ 200
x1 ≤ 80
x2 ≤ 60

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
When there is a tie between two or more variables for removal from the simplex tableau,
A) post-optimality analysis is required.
B) their dual prices will be equal.
C) converting the pivot element will break the tie.
D) a condition of degeneracy is present.
A) post-optimality analysis is required.
B) their dual prices will be equal.
C) converting the pivot element will break the tie.
D) a condition of degeneracy is present.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Solve the following problem by the simplex method.
Max
14x1 + 14.5x2 + 18x3
s.t.
x1 + 2x2 + 2.5x3 ≤ 50
x1 + x2 + 1.5x3 ≤ 30
x1 , x2 , x3 ≥ 0
Max
14x1 + 14.5x2 + 18x3
s.t.
x1 + 2x2 + 2.5x3 ≤ 50
x1 + x2 + 1.5x3 ≤ 30
x1 , x2 , x3 ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Solve the following problem by the simplex method.
Max
100x1 + 120x2 + 85x3
s.t.
3x1 + 1x2 + 6x3 ≤ 120
5x1 + 8x2 + 2x3 ≤ 160
x1 , x2 , x3 ≥ 0
Max
100x1 + 120x2 + 85x3
s.t.
3x1 + 1x2 + 6x3 ≤ 120
5x1 + 8x2 + 2x3 ≤ 160
x1 , x2 , x3 ≥ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not a step that is necessary to prepare a linear programming problem for solution using the simplex method?
A) formulate the problem.
B) set up the standard form by adding slack and/or subtracting surplus variables.
C) perform elementary row and column operations.
D) set up the tableau form.
A) formulate the problem.
B) set up the standard form by adding slack and/or subtracting surplus variables.
C) perform elementary row and column operations.
D) set up the tableau form.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
What is the criterion for entering a new variable into the basis?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A manager for a food company is putting together a buffet and she is trying to determine the best mix of
crab and steak to be served. Below are variable definitions she developed including vitamin, mineral and protein requirements. Also included below is an optimal simplex tableau she obtained from her
computations. She is interested in interpreting what it means.
Variable definitions:
xl = amount of crab (oz) to be served per buffet batch
x2 = amount of steak (oz) to be served per buffet batch
s1 = vitamin A units provided in excess of requirements
s2 = mineral units provided in excess of requirements
s3 = protein units provided in excess of requirements
Optimal tableau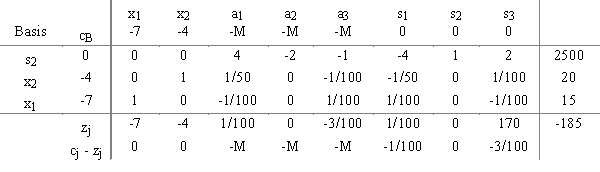
crab and steak to be served. Below are variable definitions she developed including vitamin, mineral and protein requirements. Also included below is an optimal simplex tableau she obtained from her
computations. She is interested in interpreting what it means.
Variable definitions:
xl = amount of crab (oz) to be served per buffet batch
x2 = amount of steak (oz) to be served per buffet batch
s1 = vitamin A units provided in excess of requirements
s2 = mineral units provided in excess of requirements
s3 = protein units provided in excess of requirements
Optimal tableau


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
What is an artificial variable? Why is it necessary?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Describe and illustrate graphically the special cases that can occur in a linear programming solution. What clues for these cases does the simplex procedure supply?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
A student in a Management Science class developed this initial tableau for a maximization problem and
now wants to perform row operations to obtain the next tableau and check for an optimal solution.
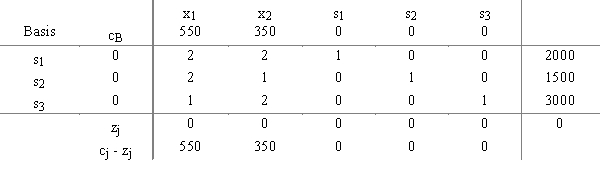
now wants to perform row operations to obtain the next tableau and check for an optimal solution.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
For each of the special cases of infeasibility, unboundedness, and alternate optimal solutions, tell what you would do next with your linear programming model if the case occurred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
List the steps to get a problem formulation to tableau form.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Comment on the solution shown in this simplex tableau. 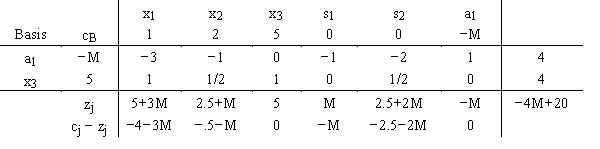


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Comment on the solution shown in this simplex tableau. 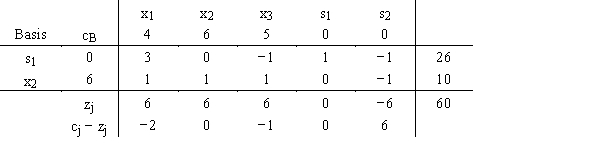


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The operations research analyst for a big manufacturing firm in Oregon developed the following variable definitions for a LP maximization problem she was working on. The company was trying to determine how many consoles of each model to produce next week given each console had to go through three production departments. She obtained the following optimal simplex tableau for the problem and wanted to interpret its meaning.
Variable definitions:
xl = number of model 1 consoles produced
x2 = number of model 2 consoles produced
s1 = unused personnel hours in department 1
s2 = unused personnel hours in department 2
s3 = unused personnel hours in department 3
objective function = total profit on model 1 and model 2 consoles produced in the coming week
Optimal tableau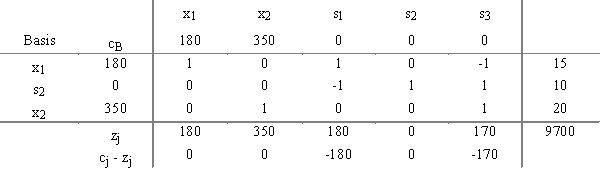
Variable definitions:
xl = number of model 1 consoles produced
x2 = number of model 2 consoles produced
s1 = unused personnel hours in department 1
s2 = unused personnel hours in department 2
s3 = unused personnel hours in department 3
objective function = total profit on model 1 and model 2 consoles produced in the coming week
Optimal tableau


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What is degeneracy and what can be done in the simplex procedure to overcome the problem?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 51 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








