Deck 8: Accounting for Income Taxes
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Accounting for Income Taxes
1
Which statement best describes the "deferral method"?
A)This method focuses on the balance sheet.
B)This method is an example of a "tax allocation" approach.
C)This is the same as the "accrual method" of tax accounting.
D)This method is used by companies reporting using IFRS.
A)This method focuses on the balance sheet.
B)This method is an example of a "tax allocation" approach.
C)This is the same as the "accrual method" of tax accounting.
D)This method is used by companies reporting using IFRS.
B
2
Which statement is correct?
A)The deferral and accrual methods produce the same tax expense when tax rates are constant.
B)The deferral method applies new tax rates to accumulated tax balances.
C)The accrual method applies new tax rates to only to current year's income.
D)The deferral and accrual methods produce the same tax expense when tax rates are falling.
A)The deferral and accrual methods produce the same tax expense when tax rates are constant.
B)The deferral method applies new tax rates to accumulated tax balances.
C)The accrual method applies new tax rates to only to current year's income.
D)The deferral and accrual methods produce the same tax expense when tax rates are falling.
A
3
Why is the taxes payable method not an accepted approach under IFRS? What difference explains why ASPE permits this approach in addition to the accrual approach?
IFRS does not allow the taxes payable method because it is neither consistent with accrual accounting generally nor with the IFRS Conceptual Framework. The taxes payable method is similar to cash basis accounting and does not reflect the effect of transactions when they occur. Not recording the effect of deferred taxes is inconsistent with the definition and recognition criteria for assets and liabilities. ASPE permits the taxes payable approach because of the different costs and benefits faced by private enterprises. This method is less costly, and the limited user base, being primarily owners and lenders, are more concerned about cash flows and can obtain information about deferred taxes should they need it.
4
GMS Corp. reported $680,000 in income tax expense for the year under the accrual method. Its balance sheet reported an overall increase in deferred income tax liability of $40,000 and a decrease in income tax payable of $50,000. How much would GMS report as income tax expense had it used the taxes payable method?
A)$680,000
B)$630,000
C)$720,000
D)$640,000
A)$680,000
B)$630,000
C)$720,000
D)$640,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which statement is not correct?
A)The accrual method focuses on the balance sheet.
B)The deferral method focuses on the income statement.
C)The deferral method matches tax expense to the balance sheet.
D)The accrual and deferral methods are both tax allocation methods.
A)The accrual method focuses on the balance sheet.
B)The deferral method focuses on the income statement.
C)The deferral method matches tax expense to the balance sheet.
D)The accrual and deferral methods are both tax allocation methods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A company facing a 45% tax rate has calculated its taxable income for the year to be $2,100,000. It made installment payments during the year totalling $955,000; this amount has been recorded in an asset account as "income tax installments"
Required:
Prepare the journal entry to record the adjusting entry for income taxes at the end of the year under the taxes payable method.
Required:
Prepare the journal entry to record the adjusting entry for income taxes at the end of the year under the taxes payable method.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which statement is correct?
A)Financial reporting rules are generally consistent with tax reporting rules.
B)Tax rules are generally consistent the principles used in accrual accounting.
C)Tax rules generally require a higher degree of reliability than financial reporting.
D)Accounting income is generally similar to taxable income.
A)Financial reporting rules are generally consistent with tax reporting rules.
B)Tax rules are generally consistent the principles used in accrual accounting.
C)Tax rules generally require a higher degree of reliability than financial reporting.
D)Accounting income is generally similar to taxable income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which statement is correct about the "taxes payable method"?
A)It is the accounting method used under both ASPE and IFRS.
B)It records an amount for income tax equal to the tax payments required.
C)It matches income with the associated income tax expense.
D)It records an amount for income tax equal to the net income before tax.
A)It is the accounting method used under both ASPE and IFRS.
B)It records an amount for income tax equal to the tax payments required.
C)It matches income with the associated income tax expense.
D)It records an amount for income tax equal to the net income before tax.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which method reflects the tax effect in the period that tax is payable?
A)Accrual method.
B)Taxes payable method.
C)Deferral method.
D)Tax allocation method.
A)Accrual method.
B)Taxes payable method.
C)Deferral method.
D)Tax allocation method.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Compare and contrast the two tax allocation methods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which statement is accurate?
A)The taxes payable method is also known as the "deferral method."
B)The deferral method and the accrual method are "tax allocation" approaches.
C)The income statement approach is also known as the "accrual method."
D)The balance sheet approach is also known as the "deferral method."
A)The taxes payable method is also known as the "deferral method."
B)The deferral method and the accrual method are "tax allocation" approaches.
C)The income statement approach is also known as the "accrual method."
D)The balance sheet approach is also known as the "deferral method."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
A company earns $390,000 in pre-tax income, while its tax return shows taxable income of $280,000. At a tax rate of 35%, how much is the income tax expense under the taxes payable method permitted under ASPE?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which accurately describes the purpose of the taxes payable method?
A)It represents the amount of income recognized for accounting purposes.
B)It represents the amount of income recognized for tax purposes.
C)It calculates tax expense based on the accounting income before tax.
D)It calculates tax expense based on the amount payable to tax authorities.
A)It represents the amount of income recognized for accounting purposes.
B)It represents the amount of income recognized for tax purposes.
C)It calculates tax expense based on the accounting income before tax.
D)It calculates tax expense based on the amount payable to tax authorities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A company earns $490,000 in pre-tax income, while its tax return shows taxable income of $380,000. At a tax rate of 35%, how much is the income tax expense under the taxes payable method permitted under ASPE?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which method does not use "temporary differences" to account for income tax expense?
A)The taxes payable method.
B)The deferral method.
C)The accrual method.
D)The tax allocation method.
A)The taxes payable method.
B)The deferral method.
C)The accrual method.
D)The tax allocation method.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What is one reason to use the taxes payable method?
A)It is a complicated method, but results in the least tax expense.
B)A company only pays tax once a year under this method.
C)It results in the best matching for the balance sheet.
D)It is the least costly method for tax accounting.
A)It is a complicated method, but results in the least tax expense.
B)A company only pays tax once a year under this method.
C)It results in the best matching for the balance sheet.
D)It is the least costly method for tax accounting.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which statement is correct?
A)IFRS allows the taxes payable method because it is consistent with accrual accounting generally and with the IFRS Conceptual Framework.
B)The taxes payable method is similar to accrual basis accounting and reflects the effect of transactions when they occur.
C)ASPE permits the taxes payable approach because of the different costs and benefits faced by private enterprises.
D))Recording the effect of deferred taxes is inconsistent with the definition and recognition criteria for assets and liabilities.
A)IFRS allows the taxes payable method because it is consistent with accrual accounting generally and with the IFRS Conceptual Framework.
B)The taxes payable method is similar to accrual basis accounting and reflects the effect of transactions when they occur.
C)ASPE permits the taxes payable approach because of the different costs and benefits faced by private enterprises.
D))Recording the effect of deferred taxes is inconsistent with the definition and recognition criteria for assets and liabilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A company earned $860,000 in pre-tax income, while its tax return showed taxable income of $560,000. At a tax rate of 40%, how much is the income tax expense under the taxes payable method permitted under ASPE?
A)$224,000
B)$344,000
C)$120,000
D)$196,000
A)$224,000
B)$344,000
C)$120,000
D)$196,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which statement is accurate?
A)Accounting income is generally higher than taxable income.
B)Accounting income is determined by financial reporting.
C)The balance sheet is unaffected by the tax accounting method.
D)The taxes payable method is a "tax allocation" approach.
A)Accounting income is generally higher than taxable income.
B)Accounting income is determined by financial reporting.
C)The balance sheet is unaffected by the tax accounting method.
D)The taxes payable method is a "tax allocation" approach.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What is the accepted method of accounting for taxes under IFRS and ASPE? Accrual method or taxes payable method?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
When will there be a recapture of depreciation?
A)When proceeds of disposal are less than undepreciated capital cost.
B)When proceeds of disposal are between undepreciated capital cost and original cost.
C)When proceeds of disposal are more than undepreciated capital cost.
D)When proceeds of disposal are less than original cost.
A)When proceeds of disposal are less than undepreciated capital cost.
B)When proceeds of disposal are between undepreciated capital cost and original cost.
C)When proceeds of disposal are more than undepreciated capital cost.
D)When proceeds of disposal are less than original cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which statement is correct?
A)Undepreciated capital cost (UCC)is the net carrying amount of an asset or asset class for tax purposes.
B)A deductible temporary difference is a temporary difference that results in future taxable income being more than accounting income.
C)A terminal loss is the tax loss arising from the sale of an asset for proceeds above its undepreciated capital cost.
D)Recaptured depreciation is the taxable income recorded for the reversal of previous capital cost allowance when the sale proceeds of an asset are less than its undepreciated capital cost.
A)Undepreciated capital cost (UCC)is the net carrying amount of an asset or asset class for tax purposes.
B)A deductible temporary difference is a temporary difference that results in future taxable income being more than accounting income.
C)A terminal loss is the tax loss arising from the sale of an asset for proceeds above its undepreciated capital cost.
D)Recaptured depreciation is the taxable income recorded for the reversal of previous capital cost allowance when the sale proceeds of an asset are less than its undepreciated capital cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
When will a terminal loss occur?
A)When proceeds of disposal are less than undepreciated capital cost.
B)When proceeds of disposal are between undepreciated capital cost and original cost.
C)When proceeds of disposal are more than undepreciated capital cost.
D)When proceeds of disposal are less than original cost.
A)When proceeds of disposal are less than undepreciated capital cost.
B)When proceeds of disposal are between undepreciated capital cost and original cost.
C)When proceeds of disposal are more than undepreciated capital cost.
D)When proceeds of disposal are less than original cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Why does Capital Cost Allowance (CCA)usually exceed the amount of depreciation for tax purposes?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Describe what is meant by a timing difference.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
What is a "taxable" temporary difference?
A)Results in future taxable income being higher than accounting income.
B)Results in future taxable income being less than accounting income.
C)The amount of income tax payable in the current and future periods.
D)Result of an event affecting accounting and taxable income in different periods.
A)Results in future taxable income being higher than accounting income.
B)Results in future taxable income being less than accounting income.
C)The amount of income tax payable in the current and future periods.
D)Result of an event affecting accounting and taxable income in different periods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Why does the tax system appear to treat profits and losses asymmetrically?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A company has income before tax of $200,000. The company also has a temporary difference of $80,000 relating to capital cost allowance (CCA)in excess of depreciation expense recorded for the year. There are no other permanent or temporary differences. The income tax rate is 40%. The taxes payable are:
A)$48,000
B)$80,000
C)$112,000
D)$32,000
A)$48,000
B)$80,000
C)$112,000
D)$32,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Why is it necessary to distinguish permanent differences from temporary differences?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following is an example of a "permanent difference"?
A)Warranty provisions.
B)Dividends received by corporations.
C)Depreciation on capital assets.
D)Completed contract method.
A)Warranty provisions.
B)Dividends received by corporations.
C)Depreciation on capital assets.
D)Completed contract method.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Explain the large and growing amount of deferred tax liabilities on corporations' balance sheets mentioned in the opening vignette of this chapter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Describe what is meant by a permanent difference.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A company has income before tax of $350,000, which includes a permanent difference of $65,000 relating to non-taxable dividend income. There are no other permanent or temporary differences. The income tax rate is 45%. The taxes payable are:
A)$186,750
B)$128,250
C)$157,500
D)$285,000
A)$186,750
B)$128,250
C)$157,500
D)$285,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
When will there be recapture and a capital gain?
A)When proceeds of disposal are less than undepreciated capital cost.
B)When proceeds of disposal are between undepreciated capital cost and original cost.
C)When proceeds of disposal are more than undepreciated capital cost.
D)When proceeds of disposal are more than original cost.
A)When proceeds of disposal are less than undepreciated capital cost.
B)When proceeds of disposal are between undepreciated capital cost and original cost.
C)When proceeds of disposal are more than undepreciated capital cost.
D)When proceeds of disposal are more than original cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following is true?
A)A deductible temporary difference is a temporary difference that results in future taxable income being more than accounting income.
B)A Deferred Tax Liability is the amount of income tax payable in future deferred tax liability periods as a result of taxable permanent differences.
C)A Taxable Temporary Difference is a temporary difference that results in future taxable income being less than accounting income.
D)A deferred tax asset is the amount of income tax recoverable in future periods as a result of deductible temporary differences, losses carried forward, or tax credits carried forward.
A)A deductible temporary difference is a temporary difference that results in future taxable income being more than accounting income.
B)A Deferred Tax Liability is the amount of income tax payable in future deferred tax liability periods as a result of taxable permanent differences.
C)A Taxable Temporary Difference is a temporary difference that results in future taxable income being less than accounting income.
D)A deferred tax asset is the amount of income tax recoverable in future periods as a result of deductible temporary differences, losses carried forward, or tax credits carried forward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
What is a deferred tax asset?
A)A deductible temporary difference that results in future taxable income being less than accounting income.
B)The amount of income tax recoverable in future periods as a result of deductible temporary differences, losses carried forward, or tax credits carried forward.
C)A deductible temporary difference that results in future taxable income being higher than accounting income.
D)The amount of income tax payable in future periods as a result of taxable temporary differences.
A)A deductible temporary difference that results in future taxable income being less than accounting income.
B)The amount of income tax recoverable in future periods as a result of deductible temporary differences, losses carried forward, or tax credits carried forward.
C)A deductible temporary difference that results in future taxable income being higher than accounting income.
D)The amount of income tax payable in future periods as a result of taxable temporary differences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
SEG Company reported $490,000 in income tax expense for the year under the accrual method. Its balance sheet reported an overall increase in deferred income tax liability of $20,000 and a decrease in income tax payable of $25,000. How much would SEG report as income tax expense had it used the taxes payable method?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which statement is correct?
A)A deductible temporary difference results in future taxable income being higher than accounting income.
B)A deductible temporary difference results in future taxable income being less than accounting income.
C)A deductible temporary difference refers to the amount of income tax payable in the current year.
D)A deductible temporary difference results from an event affecting accounting and taxable income in the same periods.
A)A deductible temporary difference results in future taxable income being higher than accounting income.
B)A deductible temporary difference results in future taxable income being less than accounting income.
C)A deductible temporary difference refers to the amount of income tax payable in the current year.
D)A deductible temporary difference results from an event affecting accounting and taxable income in the same periods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
What is an "originating difference"?
A)The net carrying amount of a capital asset or capital asset class for tax purposes in Canada.
B)A temporary item that narrows that gap between accounting and tax values of an asset or liability.
C)A temporary item that widens the gap between accounting and tax values of an asset or liability.
D)The terminology used for depreciation of capital assets under for tax purposes in Canada.
A)The net carrying amount of a capital asset or capital asset class for tax purposes in Canada.
B)A temporary item that narrows that gap between accounting and tax values of an asset or liability.
C)A temporary item that widens the gap between accounting and tax values of an asset or liability.
D)The terminology used for depreciation of capital assets under for tax purposes in Canada.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
What is the ending balance of the current year deferred tax liability? Opening deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(400,000)
Current year deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(100,000)
Tax rate (prior year)
40%
Tax rate (current year)
30%
A)30,000 debit
B)30,000 credit
C)150,000 credit
D)190,000 credit
(400,000)
Current year deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(100,000)
Tax rate (prior year)
40%
Tax rate (current year)
30%
A)30,000 debit
B)30,000 credit
C)150,000 credit
D)190,000 credit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which statement is correct?
A)The income tax system treats income and losses symmetrically.
B)The income tax system treats income and losses asymmetrically.
C)When a company has a loss, a refund is received equal to the loss multiplied by the tax rate.
D)A loss carryforward has immediate cash flow benefits to a company.
A)The income tax system treats income and losses symmetrically.
B)The income tax system treats income and losses asymmetrically.
C)When a company has a loss, a refund is received equal to the loss multiplied by the tax rate.
D)A loss carryforward has immediate cash flow benefits to a company.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A company has a deferred tax liability of $20,000 at the beginning of the fiscal year relating to a taxable temporary difference of $80,000. The current year tax rate is 20%.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The following summarizes information relating to Gonzalez Corporation's operations for the current year. 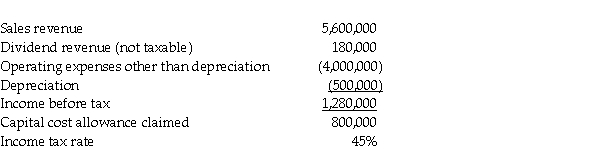 Required:
Required:
Compute the amount of taxes payable and income tax expense for Gonzalez Corporation.
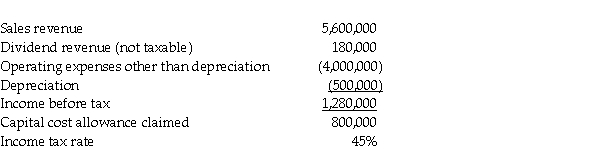 Required:
Required:Compute the amount of taxes payable and income tax expense for Gonzalez Corporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A company has a deferred tax liability of $60,000 at the beginning of the fiscal year relating to a taxable temporary difference of $300,000. The tax rate for the year increased from 20% to 25%.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
What adjustment is required to the opening deferred taxes as a result of the rate change? Opening deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(400,000)
Current year deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(100,000)
Tax rate (prior year)
30%
Tax rate (current year)
40%
A)40,000 debit
B)40,000 credit
C)130,000 credit
D)190,000 credit
(400,000)
Current year deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(100,000)
Tax rate (prior year)
30%
Tax rate (current year)
40%
A)40,000 debit
B)40,000 credit
C)130,000 credit
D)190,000 credit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which is correct regarding the effect of tax rate changes on income tax expense, assets and liabilities?
A)When a company makes no sales and has no expenses such that its pre-tax income is zero, a change in tax rate always results in zero net income.
B)Enterprises need to take account of changes in future tax rates legislation only if it has been passed into legislation and not if it is only considered "substantively enacted."
C)When the tax rate decreases, the decrease in deferred tax liabilities creates a tax expense.
D)When the tax rate increases, the increase in deferred tax liabilities creates tax expense.
A)When a company makes no sales and has no expenses such that its pre-tax income is zero, a change in tax rate always results in zero net income.
B)Enterprises need to take account of changes in future tax rates legislation only if it has been passed into legislation and not if it is only considered "substantively enacted."
C)When the tax rate decreases, the decrease in deferred tax liabilities creates a tax expense.
D)When the tax rate increases, the increase in deferred tax liabilities creates tax expense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What is the opening balance of the deferred tax liability account considering the rate change? Opening deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(400,000)
Current year deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(100,000)
Tax rate (prior year)
30%
Tax rate (current year)
40%
A)100,000 credit
B)160,000 credit
C)120,000 credit
D)200,000 credit
(400,000)
Current year deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(100,000)
Tax rate (prior year)
30%
Tax rate (current year)
40%
A)100,000 credit
B)160,000 credit
C)120,000 credit
D)200,000 credit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
A company has a deferred tax liability of $20,000 at the beginning of the fiscal year relating to a taxable temporary difference of $80,000. The current year tax rate is 30%.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
What is the opening balance of the deferred tax liability account considering the rate change? Opening taxable temporary differences
400,000
Tax rate (prior year)
25%
Tax rate (current year)
30%
A)100,000 debit
B)100,000 credit
C)120,000 debit
D)120,000 credit
400,000
Tax rate (prior year)
25%
Tax rate (current year)
30%
A)100,000 debit
B)100,000 credit
C)120,000 debit
D)120,000 credit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
A company has a deferred tax liability of $120,000 at the beginning of the fiscal year relating to a taxable temporary difference of $300,000. The current year tax rate is 50%.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What adjustment is required to the opening deferred taxes as a result of the rate change? Opening deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(400,000)
Current year deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(100,000)
Tax rate (prior year)
40%
Tax rate (current year)
30%
A)30,000 credit
B)90,000 credit
C)40,000 credit
D)40,000 debit
(400,000)
Current year deductible (taxable)temporary differences
(100,000)
Tax rate (prior year)
40%
Tax rate (current year)
30%
A)30,000 credit
B)90,000 credit
C)40,000 credit
D)40,000 debit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A company has a deferred tax liability of $120,000 at the beginning of the fiscal year relating to a taxable temporary difference of $300,000. The current year tax rate is 20%.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which statement is true?
A)A company should carry forward losses when they have had prior years' taxable income.
B)A company might carry their tax losses forward if they have exhausted the ability to carry losses backward.
C)Carrying forward tax losses results in immediate cash flow to the company.
D)Canadian tax laws allow corporations to carry an operating loss backward for 3 years and forward indefinitely, and capital losses backward for 3 years and forward indefinitely.
A)A company should carry forward losses when they have had prior years' taxable income.
B)A company might carry their tax losses forward if they have exhausted the ability to carry losses backward.
C)Carrying forward tax losses results in immediate cash flow to the company.
D)Canadian tax laws allow corporations to carry an operating loss backward for 3 years and forward indefinitely, and capital losses backward for 3 years and forward indefinitely.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
At the beginning of the current fiscal year, Withering Corporation had a deferred income tax liability balance of $20,000, which relates to depreciable assets. During the year, Withering reported the following information:
• Income before income taxes for the year was $300,000 and the tax rate was 45%.
• Depreciation expense was $150,000 and CCA was $130,000.
• Unearned rent revenue was reported at $120,000. Rent revenue is taxable when the cash is received. There was no opening balance in the unearned rent revenue account at the beginning of the year.
• No other items affected deferred tax amounts other than these transactions.
Required:
Prepare the journal entry or entries to record income taxes for the year.
• Income before income taxes for the year was $300,000 and the tax rate was 45%.
• Depreciation expense was $150,000 and CCA was $130,000.
• Unearned rent revenue was reported at $120,000. Rent revenue is taxable when the cash is received. There was no opening balance in the unearned rent revenue account at the beginning of the year.
• No other items affected deferred tax amounts other than these transactions.
Required:
Prepare the journal entry or entries to record income taxes for the year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A company has income before tax of $200,000. The company also has a temporary difference of $80,000 relating to capital cost allowance (CCA)in excess of depreciation expense recorded for the year. There are no other permanent or temporary differences. The income tax rate is 40%.
Required:
Compute the amount of taxes payable and income tax expense.
Required:
Compute the amount of taxes payable and income tax expense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A company has income before tax of $350,000, which includes a permanent difference of $65,000 relating to non-taxable dividend income. There are no other permanent or temporary differences. The income tax rate is 45%.
Required:
Compute the amount of taxes payable and income tax expense.
Required:
Compute the amount of taxes payable and income tax expense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The following information relates to the accounting income for Withering Press Company (WPC)for the current year ended December 31. 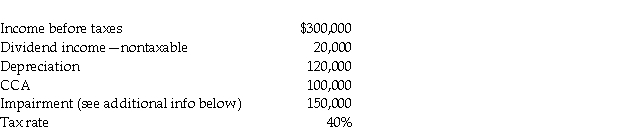 The company had purchased land some years ago for $600,000. Recently, it was discovered that this land is contaminated by industrial pollution. Because of the soil remediation costs required, the value of the land has decreased. For tax purposes, the impairment loss is not currently deductible. In the future when the land is sold, half of any losses is deductible against taxable capital gains (ie., the other half that is not taxable or deductible is a permanent difference).
The company had purchased land some years ago for $600,000. Recently, it was discovered that this land is contaminated by industrial pollution. Because of the soil remediation costs required, the value of the land has decreased. For tax purposes, the impairment loss is not currently deductible. In the future when the land is sold, half of any losses is deductible against taxable capital gains (ie., the other half that is not taxable or deductible is a permanent difference).
The deferred income tax liability account on January 1 had a credit balance of $45,000. This balance is entirely related to property, plant, and equipment (PPE).
Required:
Prepare the journal entries to record income taxes for WPC.
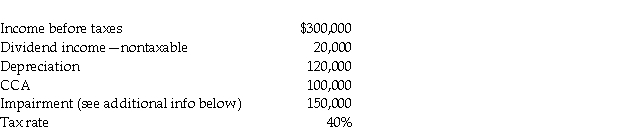 The company had purchased land some years ago for $600,000. Recently, it was discovered that this land is contaminated by industrial pollution. Because of the soil remediation costs required, the value of the land has decreased. For tax purposes, the impairment loss is not currently deductible. In the future when the land is sold, half of any losses is deductible against taxable capital gains (ie., the other half that is not taxable or deductible is a permanent difference).
The company had purchased land some years ago for $600,000. Recently, it was discovered that this land is contaminated by industrial pollution. Because of the soil remediation costs required, the value of the land has decreased. For tax purposes, the impairment loss is not currently deductible. In the future when the land is sold, half of any losses is deductible against taxable capital gains (ie., the other half that is not taxable or deductible is a permanent difference).The deferred income tax liability account on January 1 had a credit balance of $45,000. This balance is entirely related to property, plant, and equipment (PPE).
Required:
Prepare the journal entries to record income taxes for WPC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The following summarizes information relating to Gonzalez Corporation's operations for the current year. 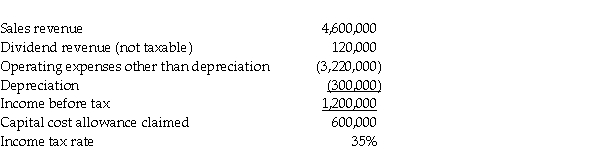 Required:
Required:
Compute the amount of taxes payable and income tax expense for Gonzalez Corporation.
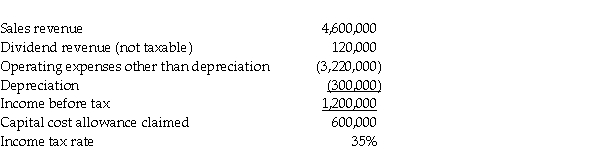 Required:
Required:Compute the amount of taxes payable and income tax expense for Gonzalez Corporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A company has a deferred tax liability of $112,500 at the beginning of the fiscal year relating to a taxable temporary difference of $450,000. The tax rate for the year increased from 25% to 35%.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.
Required:
Provide the journal entry to reflect the tax rate change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Summarize the rules covering presentation and disclosure of the following items according to IFRS using the following template:
Item
Presentation and Disclosure
Income Tax Expense
Composition of Income Tax Expense
Taxes on discontinued operations
Comprehensive income
Permanent Differences
Offsetting
Different jurisdiction and component entities
According to source
Tax losses carried forward
Item
Presentation and Disclosure
Income Tax Expense
Composition of Income Tax Expense
Taxes on discontinued operations
Comprehensive income
Permanent Differences
Offsetting
Different jurisdiction and component entities
According to source
Tax losses carried forward

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A company had taxable income of $2 million in fiscal 2020 and paid taxes of .7 million; the company incurred a loss of $8 million in fiscal 2021 when the tax rate is 50%. How much refund is the company entitled to?
A)Nil
B)$0.7 million
C)$3.85 million
D)$4 million
A)Nil
B)$0.7 million
C)$3.85 million
D)$4 million

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
A company had taxable income of $12 million in fiscal 2019 and paid taxes of 4.8 million; the company incurred a loss of $7 million in fiscal 2020 when the tax rate is 50%. How much refund is the company entitled to?
A)Nil
B)$2.8 million
C)$3.5 million
D)$4.8 million
A)Nil
B)$2.8 million
C)$3.5 million
D)$4.8 million

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Explain why a company should carry back losses and why a company might choose to carry losses forward instead.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Which statement is true?
A)IAS 12 states the following: Deferred tax assets and liabilities shall be discounted.
B)Enterprises are expected to keep very detailed scheduling of the timing of the reversal of each temporary difference.
C)To permit, but not require discounting would result in deferred tax assets and liabilities which would be comparable between entities.
D)The rationale for not discounting is based on considerations of costs and benefits as well as comparability among enterprises.
A)IAS 12 states the following: Deferred tax assets and liabilities shall be discounted.
B)Enterprises are expected to keep very detailed scheduling of the timing of the reversal of each temporary difference.
C)To permit, but not require discounting would result in deferred tax assets and liabilities which would be comparable between entities.
D)The rationale for not discounting is based on considerations of costs and benefits as well as comparability among enterprises.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
State whether or not discounting of deferred assets and liabilities is required or permitted and explain why or why not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
A company had taxable income of $2 million in fiscal 2020 and paid taxes of 0.6 million; the company incurred a loss of $7 million in fiscal 2021 when the tax rate is 50%. How much refund is the company entitled to?
A)Nil
B)$0.6 million
C)$1.0 million
D)$3.5 million
A)Nil
B)$0.6 million
C)$1.0 million
D)$3.5 million

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
A company had taxable income of $2 million in fiscal 2019 and paid taxes of 0.4 million; the company incurred a loss of $0.5 million in fiscal 2021 when the tax rate is 30%. How much refund is the company entitled to?
A)$0.2 million
B)$0.1 million
C)$0.4 million
D)$0.6 million
A)$0.2 million
B)$0.1 million
C)$0.4 million
D)$0.6 million

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
In the first two years of operations, a company reports taxable income of $115,000 and $165,000, respectively. In the first two years, the tax rates were 38% and 32% respectively. It is now the end of the third year, and the company has a loss of $160,000 for tax purposes. The company carries losses to the earliest year possible. The tax rate is currently 25%.
Required:
a. How much tax was paid in year 1 and year 2?
b. Compute the amount of income tax payable or receivable in the current (third)year.
Required:
a. How much tax was paid in year 1 and year 2?
b. Compute the amount of income tax payable or receivable in the current (third)year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
A large public company reported that its provision for income taxes was $500 million and that it has a deferred tax liability of 2 billion. A Member of Parliament calls you and says, "I see hundreds of companies who have these huge deferred tax liabilities on their balance sheets. If the government could get even half of what's owed, it could cut the public deficit down to size in a hurry."
Required:
Write a memo to the Member of Parliament explaining the issues.
Required:
Write a memo to the Member of Parliament explaining the issues.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
In the first two years of operations, a company reports taxable income of $125,000 and $165,000, respectively. In the first two years, the tax rates were 44% and 48% respectively. It is now the end of the third year, and the company has a loss of $260,000 for tax purposes. The company carries losses to the earliest year possible. The tax rate is currently 25%.
Required:
a. How much tax was paid in year 1 and year 2?
b. Compute the amount of income tax payable or receivable in the current (third)year.
Required:
a. How much tax was paid in year 1 and year 2?
b. Compute the amount of income tax payable or receivable in the current (third)year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
In its first year of operations, a company reported taxable income of $200,000. In its second year the company incurred a $250,000 loss. During these first two years, the tax rates were 30% and 35% respectively. It is now the end of the third year, and the company a taxable income of $260,000. The company carries losses to the earliest year possible. The tax rate is currently 40%. The amount of income tax receivable or payable in the current (third)year is:
A)$104,000 payable.
B)$27,500 receivable.
C)$76,500 payable.
D)$16,500 payable.
A)$104,000 payable.
B)$27,500 receivable.
C)$76,500 payable.
D)$16,500 payable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Under ASPE, Section 3465 indicates less onerous disclosures as private enterprises are permitted to use the tax payable method. Summarize the rules covering presentation and disclosure of the following items according to ASPE using the following template:
Item
Presentation and Disclosure
Required separate disclosure for companies using the accrual method
No requirement for the following disclosures for companies using the taxes payable method
Reconciliation required
Item
Presentation and Disclosure
Required separate disclosure for companies using the accrual method
No requirement for the following disclosures for companies using the taxes payable method
Reconciliation required

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
In the first year of operations, a company reports taxable income of $225,000 and paid a tax rate of 28%. It is now the end of the second year, and the company has a loss of $375,000 for tax purposes. The company's management believes it is probable the company will be able to use up its tax losses. The tax rate is currently 32%.
Required:
Compute the amounts of income tax receivable and/ or deferred income tax asset in the current (second)year.
Required:
Compute the amounts of income tax receivable and/ or deferred income tax asset in the current (second)year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
In the first two years of operations, a company reports taxable income of $200,000 and $250,000, respectively. During these first two years, the tax rates were 30% and 35% respectively. It is now the end of the third year, and the company has a loss of $260,000 for tax purposes. The company carries losses to the earliest year possible. The tax rate is currently 40%. The amount of income tax receivable in the current (third)year is:
A)$104,000
B)$81,000
C)$147,500
D)$91,000
A)$104,000
B)$81,000
C)$147,500
D)$91,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Summarize the IFRS rules for presentation and disclosure of taxes on discontinued operations and comprehensive income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
In the first year of operations, a company reports taxable income of $125,000 and paid $31,250 of income taxes. It is now the end of the second year, and the company has a loss of $175,000 for tax purposes. The company's management believes it is probable the company will be able to use up its tax losses. The tax rate is currently 40%.
Required:
Compute the amounts of income tax receivable and/ or deferred income tax asset in the current (second)year.
Required:
Compute the amounts of income tax receivable and/ or deferred income tax asset in the current (second)year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
In the first two years of operations, a company reports taxable income of $125,000 and $65,000, respectively. In the first two years, the company paid $50,000 and $13,000. It is now the end of the third year, and the company has a loss of $160,000 for tax purposes. The company carries losses to the earliest year possible. The tax rate is currently 25%.
Required:
Compute the amount of income tax payable or receivable in the current (third)year.
Required:
Compute the amount of income tax payable or receivable in the current (third)year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








