Deck 2: The Key Principles of Economics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/144
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: The Key Principles of Economics
1
The opportunity cost of something is
A)the cost of the labor used to produce it.
B)what you sacrifice to get it.
C)the price charged for it.
D)the search cost required to find it.
A)the cost of the labor used to produce it.
B)what you sacrifice to get it.
C)the price charged for it.
D)the search cost required to find it.
what you sacrifice to get it.
2
An unemployed individual decides to spend the day fishing. The opportunity cost of fishing is equal to
A)the cost of bait and any other monetary expenses.
B)zero, because the person doesnʹt have a job.
C)the cost of bait, any other monetary expenses, and the value of the individualʹs wages while he was working.
D)the cost of bait, any other monetary expenses, and the value of the best alternative use of the individualʹs time.
A)the cost of bait and any other monetary expenses.
B)zero, because the person doesnʹt have a job.
C)the cost of bait, any other monetary expenses, and the value of the individualʹs wages while he was working.
D)the cost of bait, any other monetary expenses, and the value of the best alternative use of the individualʹs time.
the cost of bait, any other monetary expenses, and the value of the best alternative use of the individualʹs time.
3
You rent a DVD of Iron Man II. The rental is for seven days and you watch the movie on the first day. You tell a friend about the film and your friend asks to come over and watch the movie with you before it is due back. What is your opportunity cost if you decide to watch the movie a second time instead of going to a football game?
A)the entire cost of the movie rental, since you have already watched the movie
B)one half the rental cost, because you have already watched the movie one time
C)The answer depends on how much you liked the movie in the first place.
D)the football game you forego by watching the movie again
A)the entire cost of the movie rental, since you have already watched the movie
B)one half the rental cost, because you have already watched the movie one time
C)The answer depends on how much you liked the movie in the first place.
D)the football game you forego by watching the movie again
the football game you forego by watching the movie again
4
The opportunity cost of going to college
A)is zero if your parents pay your tuition.
B)is equal to the cost of tuition, room and board, and other expenses.
C)includes wages you lose by going to school instead of working.
D)is the same for all students at a particular school who pay full tuition.
A)is zero if your parents pay your tuition.
B)is equal to the cost of tuition, room and board, and other expenses.
C)includes wages you lose by going to school instead of working.
D)is the same for all students at a particular school who pay full tuition.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Angelina, age seven, decides to dress up like Princess Fiona for Halloween. What is her opportunity cost of this decision?
A)the cost of the costume
B)the fact that she canʹt dress up like Dora the Explorer, her second choice
C)zero, because seven-year-olds donʹt have opportunity costs
D)the cost of the Lady Gaga costume which she did not want
A)the cost of the costume
B)the fact that she canʹt dress up like Dora the Explorer, her second choice
C)zero, because seven-year-olds donʹt have opportunity costs
D)the cost of the Lady Gaga costume which she did not want

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Suppose that you own a house. What is the opportunity cost of living in the house?
A)There is no opportunity cost because you own the house.
B)There is no opportunity cost unless you could set up a business in the house.
C)The opportunity cost is the rent you could have received from a tenant if you didnʹt live there.
D)The opportunity cost is the cost of your monthly mortgage payment plus bills.
A)There is no opportunity cost because you own the house.
B)There is no opportunity cost unless you could set up a business in the house.
C)The opportunity cost is the rent you could have received from a tenant if you didnʹt live there.
D)The opportunity cost is the cost of your monthly mortgage payment plus bills.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Table 2.1
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. The opportunity cost of grooming the third dog in a day is bathing _______ (dogs).
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)18
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. The opportunity cost of grooming the third dog in a day is bathing _______ (dogs).
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)18

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The principle that the cost of something is equal to what is sacrificed to get it is known as the
A)marginal principle.
B)principle of opportunity cost.
C)principle of diminishing returns.
D)reality principle.
A)marginal principle.
B)principle of opportunity cost.
C)principle of diminishing returns.
D)reality principle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Spending money on a new car instead of a used car when you are on a fixed budget is an example of
A)the incursion of an opportunity cost.
B)isolating variables.
C)a bad thing to do because you run out of money.
D)living on the edge.
A)the incursion of an opportunity cost.
B)isolating variables.
C)a bad thing to do because you run out of money.
D)living on the edge.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The trade-offs made by the U.S. government to fund the war in Iraq
A)prove that the government is spending too much on the war.
B)show that the government is justified in its war spending.
C)exceed the benefits derived from the war.
D)represent what was potentially sacrificed to engage in the war.
A)prove that the government is spending too much on the war.
B)show that the government is justified in its war spending.
C)exceed the benefits derived from the war.
D)represent what was potentially sacrificed to engage in the war.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Suppose that your tuition to attend college is $24,000 per year and you spend $8,000 per year on room and board. If you were working full time, you could earn $30,000 per year. What is your opportunity cost of attending college for one year?
A)$32,000
B)$38,000
C)$54,000
D)$62,000
A)$32,000
B)$38,000
C)$54,000
D)$62,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
According to the possible trade-off example between warships and drinking water in the text, the policy question that should be considered in Malaysia is
A)do the opportunity costs of the warships exceed their nominal costs?
B)do the nominal costs of the warships exceed their real costs?
C)do the benefits of the warships exceed their opportunity costs?
D)do the real costs of the warships exceed their nominal costs?
A)do the opportunity costs of the warships exceed their nominal costs?
B)do the nominal costs of the warships exceed their real costs?
C)do the benefits of the warships exceed their opportunity costs?
D)do the real costs of the warships exceed their nominal costs?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The saying that ʺThereʹs no such thing as a free lunchʺ refers to the
A)marginal principle.
B)spillover principle.
C)principle of opportunity cost.
D)reality principle.
A)marginal principle.
B)spillover principle.
C)principle of opportunity cost.
D)reality principle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The sacrifices made by societies in order to engage in military spending represent
A)the nominal costs of military spending.
B)the real costs of military spending.
C)the opportunity costs of military spending.
D)the excessive costs of military spending.
A)the nominal costs of military spending.
B)the real costs of military spending.
C)the opportunity costs of military spending.
D)the excessive costs of military spending.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
You have an hour between your economics and math classes. What is the opportunity cost of that time if you use it to complete your math homework instead of your economics homework?
A)the economics homework you could have completed
B)the math homework you chose to complete
C)the cost of your calculator and math textbook
D)zero, because it doesnʹt cost any money to do your math homework
A)the economics homework you could have completed
B)the math homework you chose to complete
C)the cost of your calculator and math textbook
D)zero, because it doesnʹt cost any money to do your math homework

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Suppose that your tuition to attend college is $14,000 per year and you spend $5,000 per year on room and board. If you were working full time, you could earn $26,000 per year. What is your opportunity cost of attending college?
A)$19,000
B)$31,000
C)$40,000
D)$45,000
A)$19,000
B)$31,000
C)$40,000
D)$45,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Table 2.1
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. The opportunity cost of grooming the first dog in a day is bathing _______ dog(s).
A)1
B)2
C)24
D)25
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. The opportunity cost of grooming the first dog in a day is bathing _______ dog(s).
A)1
B)2
C)24
D)25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Steven lives in a big city where there is a shortage of parking. He has a parking spot in his driveway where he parks his car. Which of the following statements is most correct?
A)Steven has a lower opportunity cost of owning a car than his neighbor, who must rent a parking spot.
B)The opportunity cost of using the spot is zero, because Steven owns the house.
C)The opportunity cost of using the parking spot is the price he could charge someone else for using the spot.
D)The opportunity cost depends on how much Stevenʹs mortgage payment is.
A)Steven has a lower opportunity cost of owning a car than his neighbor, who must rent a parking spot.
B)The opportunity cost of using the spot is zero, because Steven owns the house.
C)The opportunity cost of using the parking spot is the price he could charge someone else for using the spot.
D)The opportunity cost depends on how much Stevenʹs mortgage payment is.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The principle of opportunity cost
A)is more relevant for firms than for individuals.
B)only refers to monetary payments.
C)is only relevant in economics.
D)is applicable to all decision-making.
A)is more relevant for firms than for individuals.
B)only refers to monetary payments.
C)is only relevant in economics.
D)is applicable to all decision-making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Jacinda quit her job as a blackjack dealer where she made $42,000 per year to start her own florist business. Her business expenses are $14,000 per year on rent, $21,000 per year on supplies, and $9,000 per year on part time help. As for her personal expenses, her apartment costs her $12,000 per year and her personal bills are an extra $6,000 per year. What is Jacindaʹs opportunity cost of running the business?
A)$104,000
B)$86,000
C)$62,000
D)$44,000
A)$104,000
B)$86,000
C)$62,000
D)$44,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A principle is a self-evident truth that most people readily understand and accept.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Recall the Application about the time and invested funds that are involved in starting a decorative
bottle-cap pin business to answer the following question(s).
The time and invested funds involved in starting a decorative bottle-cap pin business address the economic concept of
A)the marginal principle.
B)opportunity cost.
C)the real-nominal principle.
D)the principle of diminishing returns.
bottle-cap pin business to answer the following question(s).
The time and invested funds involved in starting a decorative bottle-cap pin business address the economic concept of
A)the marginal principle.
B)opportunity cost.
C)the real-nominal principle.
D)the principle of diminishing returns.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
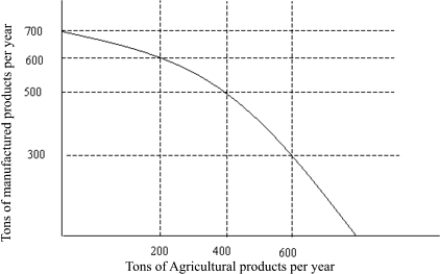 Figure 2.1
Figure 2.1Refer to Figure 2.1. If you choose to produce only agricultural products, what is the maximum quantity you can produce per year?
A)200 tons
B)400 tons
C)600 tons
D)> 600 tons

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
If an economy is fully utilizing its resources, it can produce more of one product only if it
A)doubles manufacturing of the product.
B)produces less of another product.
C)adds more people to the labor force.
D)reduces the prices of the most expensive products.
A)doubles manufacturing of the product.
B)produces less of another product.
C)adds more people to the labor force.
D)reduces the prices of the most expensive products.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
 Figure 2.1
Figure 2.1The production possibilities curve in Figure 2.1 illustrates the notion of
A)increased factory goods production.
B)increased farm produce production.
C)diminishing resources.
D)opportunity cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Table 2.1
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. The opportunity cost of grooming the sixth dog in a day is bathing _______ (dogs).
A)0
B)5
C)6
D)7
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. The opportunity cost of grooming the sixth dog in a day is bathing _______ (dogs).
A)0
B)5
C)6
D)7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The opportunity cost of something is the gain you receive as a result of your sacrifice.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
All else equal, if income continues to remain flat, the only way for consumer spending to increase is for personal savings to
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain unchanged.
D)remain flat.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain unchanged.
D)remain flat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Table 2.1
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. As they groom more dogs, the opportunity cost of bathing additional dogs
A)falls.
B)rises.
C)remains constant.
D)depends on the prices being charged.
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. As they groom more dogs, the opportunity cost of bathing additional dogs
A)falls.
B)rises.
C)remains constant.
D)depends on the prices being charged.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Reflecting what is being referred to as the ʺnew normalʺ, consumer spending is down, home sales have
declined, and personal savings has risen since the start of the recession in 2007, and the continuation of this
trend is threatening the economic recovery in the United States. In June 2010, factory orders fell for the
second consecutive month, home sales fell by nearly 19 percent compared to June 2009, and personal
spending and income remained relatively flat. The personal savings rate, however, has continued to increase,
reaching a level of 6.4 percent of after-tax income in June 2010, which is more than three times higher than
the average savings rate prior to the start of the recession in 2007. The increase in savings is coming at the
expense of consumer spending, and economists worry that households’ financial problems could cause a
further decline in spending for the second half of 2010.
According to the Application, a tradeoff exists between
A)consumer spending and home sales.
B)home sales in 2009 and home sales in 2010.
C)consumer spending and personal savings.
D)income levels and the savings rate.
declined, and personal savings has risen since the start of the recession in 2007, and the continuation of this
trend is threatening the economic recovery in the United States. In June 2010, factory orders fell for the
second consecutive month, home sales fell by nearly 19 percent compared to June 2009, and personal
spending and income remained relatively flat. The personal savings rate, however, has continued to increase,
reaching a level of 6.4 percent of after-tax income in June 2010, which is more than three times higher than
the average savings rate prior to the start of the recession in 2007. The increase in savings is coming at the
expense of consumer spending, and economists worry that households’ financial problems could cause a
further decline in spending for the second half of 2010.
According to the Application, a tradeoff exists between
A)consumer spending and home sales.
B)home sales in 2009 and home sales in 2010.
C)consumer spending and personal savings.
D)income levels and the savings rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Recall the Application about the time and invested funds that are involved in starting a decorative
bottle-cap pin business to answer the following question(s).
The current income Betty would sacrifice to start her own decorative bottle-cap pin business reflects the
A)opportunity cost of invested funds.
B)opportunity cost of her starting a business.
C)cost of doing business.
D)present value of her initial investment.
bottle-cap pin business to answer the following question(s).
The current income Betty would sacrifice to start her own decorative bottle-cap pin business reflects the
A)opportunity cost of invested funds.
B)opportunity cost of her starting a business.
C)cost of doing business.
D)present value of her initial investment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Table 2.1
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. As they groom more dogs, the opportunity cost of grooming additional dogs
A)falls.
B)rises.
C)remains constant.
D)depends on the prices being charged.
-Kaitlyn and Larissa have formed a dog bathing and grooming business business. The number of dogs they can bathe or groom in any given day is depicted in Table 2.1. As they groom more dogs, the opportunity cost of grooming additional dogs
A)falls.
B)rises.
C)remains constant.
D)depends on the prices being charged.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Opportunity cost is the difference between the nominal and real cost of some action.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
 Figure 2.1
Figure 2.1Referring to Figure 2.1, if you increase the production of farm goods, what other area is affected?
A)the price of produce
B)the production of manufactured goods
C)how much people can purchase
D)the wages earned by farm workers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
 Figure 2.1
Figure 2.1Refer to Figure 2.1. What is the opportunity cost of increasing production of manufactured products from 500 tons to 600 tons per year?
A)200 tons of agricultural products per year
B)400 tons of agricultural products per year
C)500 tons of agricultural products per year
D)600 tons of agricultural products per year

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The opportunity cost of something is the nominal price paid for the product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If you remove resources from factory production, the quantity of factory goods will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same but their price will decrease.
D)be diverted to other production.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same but their price will decrease.
D)be diverted to other production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Reflecting what is being referred to as the ʺnew normalʺ, consumer spending is down, home sales have
declined, and personal savings has risen since the start of the recession in 2007, and the continuation of this
trend is threatening the economic recovery in the United States. In June 2010, factory orders fell for the
second consecutive month, home sales fell by nearly 19 percent compared to June 2009, and personal
spending and income remained relatively flat. The personal savings rate, however, has continued to increase,
reaching a level of 6.4 percent of after-tax income in June 2010, which is more than three times higher than
the average savings rate prior to the start of the recession in 2007. The increase in savings is coming at the
expense of consumer spending, and economists worry that households’ financial problems could cause a
further decline in spending for the second half of 2010.
The relationship between consumer spending and saving discussed in the Application addresses the economic principle of
A)opportunity cost.
B)diminishing returns.
C)thinking at the margin.
D)real versus nominal.
declined, and personal savings has risen since the start of the recession in 2007, and the continuation of this
trend is threatening the economic recovery in the United States. In June 2010, factory orders fell for the
second consecutive month, home sales fell by nearly 19 percent compared to June 2009, and personal
spending and income remained relatively flat. The personal savings rate, however, has continued to increase,
reaching a level of 6.4 percent of after-tax income in June 2010, which is more than three times higher than
the average savings rate prior to the start of the recession in 2007. The increase in savings is coming at the
expense of consumer spending, and economists worry that households’ financial problems could cause a
further decline in spending for the second half of 2010.
The relationship between consumer spending and saving discussed in the Application addresses the economic principle of
A)opportunity cost.
B)diminishing returns.
C)thinking at the margin.
D)real versus nominal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
 Figure 2.1
Figure 2.1Refer to Figure 2.1. If you are producing 600 tons of agricultural products per year, what is the maximum amount of manufactured products you can produce per year?
A)300 tons
B)500 tons
C)600 tons
D)700 tons

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
If you have $10,000 to start a decorative bottle-cap pin business, the interest rate is 4 percent, your annual cost of raw materials are $3,000, and the earnings you sacrifice from working at another job are $32,000, your yearly cost of doing business would be
A)$13,000.
B)$13,400.
C)$35,400.
D)$45,000.
A)$13,000.
B)$13,400.
C)$35,400.
D)$45,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
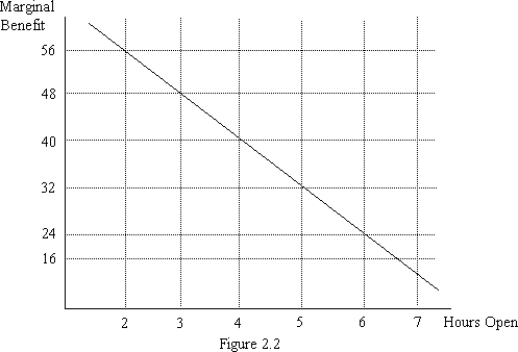
Joe runs a business and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Figure 2.2 illustrates his marginal benefit of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Joe staying open 3 hours per day. If he is following the marginal principle, what must his marginal cost per hour be?
A)$24
B)$32
C)$40
D)$48

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42

Joe runs a business and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Figure 2.2 illustrates his marginal benefit of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that Joeʹs marginal cost of staying open per hour is $32. How many hours should Joe stay open?
A)4 hours
B)5 hours
C)6 hours
D)7 hours

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Table 2.2
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that Krystalʹs marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $30. If she is following the marginal principle, how many hours should Krystal stay open?
A)4 hours
B)5 hours
C)6 hours
D)7 hours
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that Krystalʹs marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $30. If she is following the marginal principle, how many hours should Krystal stay open?
A)4 hours
B)5 hours
C)6 hours
D)7 hours

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The notion of opportunity cost allows the measurement of tradeoffs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The cost of a bachelorʹs degree in philosophy equals the tuition plus the cost of room and board.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The additional cost resulting from a small increase in some activity is called the
A)opportunity cost.
B)marginal benefit.
C)marginal cost.
D)diminishing returns of the activity.
A)opportunity cost.
B)marginal benefit.
C)marginal cost.
D)diminishing returns of the activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What is an opportunity cost?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
What is the opportunity cost of your college degree?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Suppose that you lend $5,000 to a friend who pays you back $5,400 the next year. Suppose that prices that year rose by six percent and the real rate of return in the stock market was five percent. Your friend says that he or she was being more than fair by giving you more than the rate of inflation as a return. What do you think?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In order to get his bachelorʹs degree, Timothy gave up an offer for a full time job as a bartender. Therefore, Timothy incurred an opportunity cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The extra benefit resulting from a small increase in an activity is called the
A)opportunity cost.
B)marginal benefit.
C)marginal cost.
D)diminishing returns of the activity.
A)opportunity cost.
B)marginal benefit.
C)marginal cost.
D)diminishing returns of the activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52

Joe runs a business and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Figure 2.2 illustrates his marginal benefit of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Joe staying open 6 hours per day. If he is following the marginal principle, what must his marginal cost per hour be?
A)$16
B)$24
C)$32
D)$48

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The principle that individuals and firms pick the activity level where the incremental benefit of that activity equals the incremental cost of that activity is known as the
A)marginal principle.
B)principle of opportunity cost.
C)principle of diminishing returns.
D)spillover principle.
A)marginal principle.
B)principle of opportunity cost.
C)principle of diminishing returns.
D)spillover principle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The opportunity cost of going to a particular college is not the same for everyone.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
What do economists mean when they say that there is no such thing as a free lunch?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56

Joe runs a business and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Figure 2.2 illustrates his marginal benefit of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that Joeʹs marginal cost of staying open per hour is $24. How many hours should Joe stay open?
A)3 hours
B)4 hours
C)5 hours
D)6 hours

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Tradeoffs involve an exchange of one thing for another because resources are limited and can be used in different ways.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What is the opportunity cost of investing $10,000 of your own money in a business you wish to start?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59

Joe runs a business and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Figure 2.2 illustrates his marginal benefit of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Joe staying open 5 hours per day. If he is following the marginal principle, what must his marginal cost per hour be?
A)$16
B)$24
C)$32
D)$40

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The marginal principle implies that an individual should produce or consume where
A)marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost.
B)marginal benefit is less than marginal cost.
C)marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
D)total benefit equals total cost.
A)marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost.
B)marginal benefit is less than marginal cost.
C)marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
D)total benefit equals total cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Table 2.2
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 4 hours per day. If she is following the marginal principle, what must her marginal benefit be?
A)$12
B)$18
C)$24
D)$30
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 4 hours per day. If she is following the marginal principle, what must her marginal benefit be?
A)$12
B)$18
C)$24
D)$30

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Recall the Application about why people walk up stairs but not escalators to answer the following
question(s).
Walking up an escalator as opposed to standing still on an escalator makes sense if the _______ of walking is less than the _______ of walking.
A)marginal benefit; marginal cost
B)marginal cost; marginal benefit
C)marginal benefit; opportunity cost
D)marginal cost; opportunity cost
question(s).
Walking up an escalator as opposed to standing still on an escalator makes sense if the _______ of walking is less than the _______ of walking.
A)marginal benefit; marginal cost
B)marginal cost; marginal benefit
C)marginal benefit; opportunity cost
D)marginal cost; opportunity cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
What is a marginal benefit?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
When applying the marginal principle, you should pick the level at which the activityʹs marginal benefit is less than its marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
When referring to ʺmarginalʺ changes, the economic focus is on
A)changes which affect only a few people or products.
B)large changes on the low end.
C)graduated changes on the high end.
D)small or incremental changes.
A)changes which affect only a few people or products.
B)large changes on the low end.
C)graduated changes on the high end.
D)small or incremental changes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Basically, the marginal principle teaches us to evaluate the factors involved in taking an action or if doing something is worth the effort.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Considering how a change in one variable affects the value of another variable is called
A)the Peter Principle.
B)the marginal principle.
C)the principle of supply and demand.
D)functional decision making.
A)the Peter Principle.
B)the marginal principle.
C)the principle of supply and demand.
D)functional decision making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
What is a marginal cost?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
If a companyʹs total costs per day increase from $200 to $400 by adding another worker, but its additional benefits are $300, it is sensible to add that additional worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The use of seat belts and other automobile safety features making bicycling more hazardous can be explained by the economic concept known as
A)the principle of opportunity cost.
B)the marginal principle.
C)the principle of voluntary exchange.
D)the principle of diminishing returns.
A)the principle of opportunity cost.
B)the marginal principle.
C)the principle of voluntary exchange.
D)the principle of diminishing returns.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Table 2.2
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 5 hours and her marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $36. If she is following the marginal principle, Krystal should
A)stay open 1 more hour.
B)stay open 2 more hours.
C)stay open 1 fewer hour.
D)stay open 2 fewer hours.
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 5 hours and her marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $36. If she is following the marginal principle, Krystal should
A)stay open 1 more hour.
B)stay open 2 more hours.
C)stay open 1 fewer hour.
D)stay open 2 fewer hours.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Table 2.2
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 5 hours and her marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $18. If she is following the marginal principle, Krystal should
A)stay open 2 more hours.
B)stay open 3 more hours.
C)stay open 2 fewer hours.
D)stay open 3 fewer hours.
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 5 hours and her marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $18. If she is following the marginal principle, Krystal should
A)stay open 2 more hours.
B)stay open 3 more hours.
C)stay open 2 fewer hours.
D)stay open 3 fewer hours.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Economists argue that individuals should continue to consume until total benefit equals total cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
When deciding whether to engage in an activity or how much to do, people should follow
A)the principle of microeconomics.
B)the principle of macroeconomics.
C)the marginal principle.
D)the law of supply and demand.
A)the principle of microeconomics.
B)the principle of macroeconomics.
C)the marginal principle.
D)the law of supply and demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Table 2.2
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that Krystalʹs marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $18. If she is following the marginal principle, how many hours should Krystal stay open?
A)3 hours
B)4 hours
C)6 hours
D)7 hours
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that Krystalʹs marginal benefit of staying open per hour is $18. If she is following the marginal principle, how many hours should Krystal stay open?
A)3 hours
B)4 hours
C)6 hours
D)7 hours

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Table 2.2
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 2 hours per day. If she is following the marginal principle, what must her marginal benefit be?
A)$6
B)$12
C)$15
D)$18
-Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 2 hours per day. If she is following the marginal principle, what must her marginal benefit be?
A)$6
B)$12
C)$15
D)$18

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Saving time by driving faster is an example of a _______ of driving faster. Increasing the severity of injuries from a potential accident due to driving faster is a(n) _______ of driving faster.
A)nominal cost; real cost
B)marginal cost; nominal cost
C)marginal benefit; marginal cost
D)normative benefit; opportunity cost
A)nominal cost; real cost
B)marginal cost; nominal cost
C)marginal benefit; marginal cost
D)normative benefit; opportunity cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
When Lonnie produces 1 pair of cowboy boots his costs total $300. When he produces 2 pairs of cowboy boots his total costs are $500. This means that Lonnieʹs marginal cost of producing the second pair of cowboy boots is $200.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
When applying the marginal principle, you should pick the level at which the activityʹs marginal benefit equals its marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Recall the Application about why people walk up stairs but not escalators to answer the following
question(s).
Weighing the benefits and costs of walking up an escalator versus standing still on an escalator addresses the economic concept known as
A)the principle of opportunity cost.
B)the marginal principle.
C)the principle of voluntary exchange.
D)the principle of diminishing returns.
question(s).
Weighing the benefits and costs of walking up an escalator versus standing still on an escalator addresses the economic concept known as
A)the principle of opportunity cost.
B)the marginal principle.
C)the principle of voluntary exchange.
D)the principle of diminishing returns.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 144 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








