Deck 14: Taxes on the Financial Statements
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 14: Taxes on the Financial Statements
1
Temporary differences are book-tax differences that appear in both the GAAP financial statements and the Federal income tax return but not in the same reporting period.
True
2
A deferred tax liability represents a potential future tax benefit associated with income reported in the current-year
GAAP financial statements.
GAAP financial statements.
False
3
The valuation allowance can reduce either a deferred tax asset or a deferred tax liability.
False
4
Yahr, Inc., is a domestic corporation with no subsidiaries. It operates in almost every U.S. state. Yahr records no permanent or temporary book-tax differences this year. It's tax expense on its GAAP financial statements and its tax liability reported on its Federal income tax return are identical.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
An example of a deferred tax asset is the excess of accelerated MACRS depreciation over GAAP straight-line depreciation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A deferred tax asset is the expected future tax benefit savings) associated with income reported in the current-year
GAAP financial statements.
GAAP financial statements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If a valuation allowance is decreased released) in the current year, the corporation's effective tax rate is lower than had the valuation allowance not decreased.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A valuation allowance expresses on the GAAP balance sheet that there exists uncertainty that the taxpayer will be able to recover a deferred tax asset.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Permanent differences include items that appear in the Federal income tax return as income or deduction and in the
GAAP financial statements as revenue or expense but in different reporting periods.
GAAP financial statements as revenue or expense but in different reporting periods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A deferred tax liability represents a current tax liability associated with income or expense to be reported in future year GAAP financial statements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If a corporation has no operations outside the United States, its GAAP book and taxable income are identical.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Giant uses the equity method to account for the operations of its 40% owned subsidiary Little. A portion of Little's profits for the year are included in Giant's GAAP book income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The income tax footnote to the GAAP financial statements includes a reconciliation of a corporation's hypothetical tax on book income to its book-tax expense as if it were taxed in full at the applicable U.S. income tax rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Schedule UTP of the Form 1120 reconciles financial statement net income after tax with a large corporation's taxable income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In general, the purpose of ASC 740 is to compute and disclose the taxes payable by a business entity to state, local, Federal, and foreign governments for the current year and all future years.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
In the rate reconciliation of GAAP tax footnotes, temporary book-tax differences are reconciled between book income as if taxed at U.S. tax rates and the actual book income tax expense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A partnership owned at least 80% by a corporation is included in a consolidated group's U.S. income tax return.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The operations of 80% or more owned domestic subsidiaries can be included in the parent corporation's consolidated tax return if a proper election is made.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The current tax expense reported on the GAAP financial statements generally represents the taxes actually payable to domestic or foreign governmental authorities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Only U.S. corporations are included in a combined GAAP financial statement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Gravel, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $600,000. Gravel puts into service a depreciable asset this year, and its first-year tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation by $120,000. Gravel has recorded no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21%, what is Gravel's current income tax expense reported on its GAAP financial statements?
A) $151,200
B) $126,000
C) $100,800
D) $25,200
A) $151,200
B) $126,000
C) $100,800
D) $25,200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following items represents a temporary book-tax difference?
A) Municipal bond interest.
B) Federal income tax paid.
C) Addition to bad debt allowance.
D) Nondeductible penalties.
A) Municipal bond interest.
B) Federal income tax paid.
C) Addition to bad debt allowance.
D) Nondeductible penalties.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Never, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $500,000. In computing its book income, Never deducts $50,000 more in warranty expense for book purposes than is allowed for tax purposes. Never records no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21% and no valuation allowance is required, what is Never's deferred income tax asset reported on its GAAP financial statements?
A) $115,500
B) $105,000
C) $94,500
D) $10,500
A) $115,500
B) $105,000
C) $94,500
D) $10,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Create, Inc., a domestic corporation, owns 100% of Vinyl, Ltd., a foreign corporation and Digital, Inc., a domestic corporation. Create also owns 12% of Record, Inc., a domestic corporation. Create receives no distributions from any of these corporations. Which of these entities' net income is included in Create's income statement for current-year financial reporting purposes?
A) Create, Vinyl, and Digital.
B) Create, Vinyl, and Record.
C) Create, Digital, and Record.
D) Create, Vinyl, Digital, and Record.
A) Create, Vinyl, and Digital.
B) Create, Vinyl, and Record.
C) Create, Digital, and Record.
D) Create, Vinyl, Digital, and Record.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following taxes are included in the total income tax expense of a corporation as reported on its GAAP financial statements?
A) Federal income taxes.
B) Foreign income taxes.
C) State income taxes.
D) All of these taxes are included.
A) Federal income taxes.
B) Foreign income taxes.
C) State income taxes.
D) All of these taxes are included.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Clipp, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $600,000. Clipp puts into service a depreciable asset this year, and its first-year tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation by $120,000. Clipp has recorded no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21%, what is Clipp's deferred income tax liability reported on its GAAP financial statements?
A) $151,200
B) $126,000
C) $100,800
D) $25,200
A) $151,200
B) $126,000
C) $100,800
D) $25,200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
ASC 740 addresses how an entity should report uncertain tax positions in its financial statements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Purple, Inc., a domestic corporation, owns 80% of Blue, Ltd., a foreign corporation and Yellow, Inc., a domestic corporation. Purple also owns 50% of Green, Inc., a domestic corporation. Purple receives no distributions from any of these corporations. Which of these entities' net income is included in Purple's Federal income tax return for the current year, assuming that Purple elects to include all eligible entities in its consolidated Federal income tax return?
A) Purple, Blue, Yellow, and Green.
B) Purple, Blue, and Yellow.
C) Purple, Blue, and Green.
D) Purple and Yellow.
A) Purple, Blue, Yellow, and Green.
B) Purple, Blue, and Yellow.
C) Purple, Blue, and Green.
D) Purple and Yellow.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
ASC 740 is the GAAP equivalent of the Form 1120 Schedule UTP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Kling Corporation reports a $150,000 cash tax savings from a temporary book-tax difference. This item has the same effect on Kling's current-year effective tax rate as a $150,000 cash tax savings that is a permanent book-tax difference.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which of the following taxes are included in the total income tax liability of a corporation reported on its Federal income tax return?
A) Federal income taxes.
B) Foreign income taxes.
C) State income taxes.
D) All these taxes are included.
A) Federal income taxes.
B) Foreign income taxes.
C) State income taxes.
D) All these taxes are included.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Create, Inc., a domestic corporation, owns 90% of Vinyl, Ltd., a foreign corporation and Digital, Inc., a domestic corporation. Create also owns 60% of Record, Inc., a domestic corporation. Create receives no distributions from any of these corporations. Which of these entities' net income is included in Create's Federal income tax return for the current year, assuming that Create elects to include all eligible entities in its consolidated Federal income tax return?
A) Create, Vinyl, Digital, and Record.
B) Create, Vinyl, and Digital.
C) Create, Vinyl, and Record.
D) Create and Digital.
A) Create, Vinyl, Digital, and Record.
B) Create, Vinyl, and Digital.
C) Create, Vinyl, and Record.
D) Create and Digital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Morrisson, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $500,000. In computing its book income, Morrisson deducts $50,000 more in warranty expense for book purposes than is allowed for tax purposes. Morrisson records no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21% and no valuation allowance is required, what is Morrisson's current income tax expense reported on its GAAP financial statements?
A) $115,500
B) $105,000
C) $94,500
D) $10,500
A) $115,500
B) $105,000
C) $94,500
D) $10,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Qute, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $500,000. In computing its book income, Qute deducts $50,000 more in warranty expense for book purposes than is allowed for tax purposes. Qute records no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21% and no valuation allowance is required, what is Qute's total income tax expense reported on its GAAP financial statements?
A) $115,500
B) $105,000
C) $94,500
D) $10,500
A) $115,500
B) $105,000
C) $94,500
D) $10,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
South, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $400,000 in year 1. It acquires a depreciable asset in year 1, and its first-year tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation by $50,000. At the end of year 1, South's deferred tax liability account balance is $10,500. In year 2, South earns $500,000 book net income before tax, and its book depreciation exceeds tax depreciation by $20,000. South records no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21%, what is South's total provision for income tax expense reported on its GAAP financial statements for year 2?
A) $4,200
B) $94,500
C) $105,000
D) $109,200
A) $4,200
B) $94,500
C) $105,000
D) $109,200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Purple, Inc., a domestic corporation, owns 100% of Blue, Ltd., a foreign corporation and Yellow, Inc., a domestic corporation. Purple also owns 40% of Green, a domestic corporation. Purple receives no distributions from any of these corporations. Which of these entities' net income is included in Purple's GAAP income statement for current- year financial reporting purposes?
A) Purple, Yellow, and Green.
B) Purple, Blue, and Yellow.
C) Purple, Blue, and Green.
D) Purple, Blue, Yellow, and Green.
A) Purple, Yellow, and Green.
B) Purple, Blue, and Yellow.
C) Purple, Blue, and Green.
D) Purple, Blue, Yellow, and Green.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Jogg, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $600,000. It puts into service a depreciable asset this year, and its first-year tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation by $120,000. Jogg has recorded no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21%, and that this is Jogg's first year of operations, what is Jogg's balance in its deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability accounts at year-end?
A) $25,200 and $0.
B) $0 and $0.
C) $0 and $25,200.
D) $25,200 and $25,200.
A) $25,200 and $0.
B) $0 and $0.
C) $0 and $25,200.
D) $25,200 and $25,200.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A chief financial officer CFO) probably prefers a tax planning strategy that produces a temporary book-tax savings difference to one that produces a permanent difference.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Phyllis, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $600,000. Phyllis puts into service a depreciable asset this year, and its first-year tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation by $120,000. Phyllis has recorded no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21%, what is Phyllis's total income tax expense reported on its GAAP financial statements?
A) $151,200
B) $126,000
C) $100,800
D) $25,200
A) $151,200
B) $126,000
C) $100,800
D) $25,200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The release of a valuation allowance may relate to a tax planning strategy adopted by the taxpayer that will produce taxable income in the future.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which of the following items is not included in the GAAP financial statement income tax footnote's effective tax rate reconciliation?
A) Hypothetical tax on book income at U.S. Federal corporate tax rate.
B) Total tax expense per the GAAP financial statements.
C) Tax effect of temporary differences.
D) Tax effect of permanent differences.
A) Hypothetical tax on book income at U.S. Federal corporate tax rate.
B) Total tax expense per the GAAP financial statements.
C) Tax effect of temporary differences.
D) Tax effect of permanent differences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
South, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $400,000 in year 1. It acquires a depreciable asset in year 1, and its first-year tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation by $50,000. At the end of year 1, South's deferred tax liability account balance is $10,500. In year 2, South earns $500,000 book net income before tax, and its book depreciation exceeds tax depreciation by $20,000. South records no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21% in both years, what is South's current income tax expense reported on its GAAP financial statements for year 2?
A) $4,200
B) $94,500
C) $105,000
D) $109,200
A) $4,200
B) $94,500
C) $105,000
D) $109,200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Bunker, Inc., is a domestic corporation. It owns 100% of Texas, Inc., a domestic corporation; 100% of Paris, a foreign corporation and 35% of Iowa, Inc., a domestic corporation.
a. Which entities' incomes are included in Bunker's Federal consolidated income tax return?
b. How would your answer change if Bunker instead owned 15% of Iowa?
a. Which entities' incomes are included in Bunker's Federal consolidated income tax return?
b. How would your answer change if Bunker instead owned 15% of Iowa?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which of the following items is not included in the income tax footnote for a publicly traded company?
A) Rate reconciliation.
B) Analysis of deferred tax assets and liabilities.
C) Breakdown of income tax between foreign and domestic.
D) Breakdown of income tax among U.S. states.
E) Analysis of total tax expense components.
A) Rate reconciliation.
B) Analysis of deferred tax assets and liabilities.
C) Breakdown of income tax between foreign and domestic.
D) Breakdown of income tax among U.S. states.
E) Analysis of total tax expense components.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Ursula, Inc. is a domestic corporation. It owns 100% of Texas, Inc., a domestic corporation; 100% of Paris, a foreign corporation and 45% of Iowa, Inc., a domestic corporation.
a. Which entities' incomes are included in Ursula's combined GAAP financial statements?
b. How would your answer change if Ursula instead owned 15% of Iowa?
a. Which entities' incomes are included in Ursula's combined GAAP financial statements?
b. How would your answer change if Ursula instead owned 15% of Iowa?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A GAAP financial statement includes footnotes that:
A) Give estimates of the dates on which the deferred tax liability will be paid.
B) Show the journal entries to determine the deferred income tax expense.
C) Break down the state-by-state profitability of the entity.
D) Include a reconciliation of the book effective tax rate with the applicable statutory tax rate.
A) Give estimates of the dates on which the deferred tax liability will be paid.
B) Show the journal entries to determine the deferred income tax expense.
C) Break down the state-by-state profitability of the entity.
D) Include a reconciliation of the book effective tax rate with the applicable statutory tax rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Van Dyke, Inc., hopes to report a total book-tax expense of $150,000 in the current year. This amount consists of $200,000 in current tax expense and a $50,000 tax benefit related to the expected future use of an NOL by Van Dyke. If the auditors determine that a valuation allowance of $20,000 must be placed against Van Dyke's deferred tax
Assets, what is Van Dyke's total book-tax expense?
A) $150,000
B) $170,000
C) $200,000
D) $250,000
Assets, what is Van Dyke's total book-tax expense?
A) $150,000
B) $170,000
C) $200,000
D) $250,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The best estimate of the actual current-year income tax liability i.e., perhaps the amount of the checks that the taxpayer will write to taxing jurisdictions) is the:
A) Change in the deferred tax asset account balance.
B) Change in the deferred tax liability account balance.
C) Current tax expense.
D) Current E&P.
A) Change in the deferred tax asset account balance.
B) Change in the deferred tax liability account balance.
C) Current tax expense.
D) Current E&P.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
JuarezCo constructs the following table in determining how to apply ASC 740-10 to its filing position for its domestic production activities deduction. Its book-tax provision for the year, including $3 million for the uncertain transfer pricing issue, is $10 million. Under ASC 740-10, JuarezCo's book income tax expense for this item is:
A) $13 million.
B) $12 million.
C) $11.4 million.
D) $11 million.
A) $13 million.
B) $12 million.
C) $11.4 million.
D) $11 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements best describes considerations regarding a company's tax expense that users of GAAP financial statements may make?
A) The breakdown of tax expense between current and deferred may provide useful information regarding the comparison of tax burdens between companies.
B) An analysis of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization EBITDA) is often a better approach to comparing the operating results of two companies.
C) One-time effects within a company's effective tax rate should be removed before comparing the effective tax rates across companies or across years for the same company).
D) All these observations are correct.
A) The breakdown of tax expense between current and deferred may provide useful information regarding the comparison of tax burdens between companies.
B) An analysis of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization EBITDA) is often a better approach to comparing the operating results of two companies.
C) One-time effects within a company's effective tax rate should be removed before comparing the effective tax rates across companies or across years for the same company).
D) All these observations are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Black, Inc., is a domestic corporation with the following balance sheet for book and tax purposes at the end of the year. Assume a 21% corporate tax rate and no valuation allowance. 
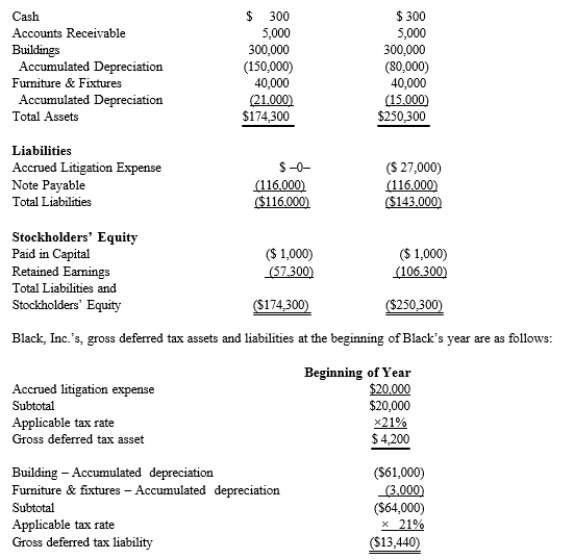 Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest, and it incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Determine the change in Black's deferred tax assets for the current year.

 Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest, and it incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Determine the change in Black's deferred tax assets for the current year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Cold, Inc., reported a $100,000 total tax expense for financial statement purposes in year 1. This total expense consisted of $150,000 in current tax expense and a deferred tax benefit of $50,000. The deferred tax benefit consisted of $90,000 in deferred tax assets reduced by a valuation allowance of $40,000. In year 2, Cold reports $600,000 in book net income before tax. Cold records no other permanent or temporary book-tax differences. At the end of year 2, Cold's auditors determine that the existing valuation allowance of $40,000 should be reduced to zero. What is Cold's total tax expense for year 2?
A) $250,000
B) $126,000
C) $86,000
D) $40,000
A) $250,000
B) $126,000
C) $86,000
D) $40,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Black, Inc., is a domestic corporation with the following balance sheet for book and tax purposes at the end of the year. Assume a 21% corporate tax rate and no valuation allowance. 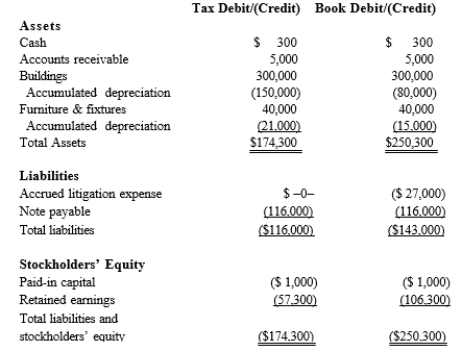 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are listed below.
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are listed below. 
 Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest and incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Determine the change in Black's deferred tax liabilities for the current year.
 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are listed below.
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are listed below. 
 Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest and incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Determine the change in Black's deferred tax liabilities for the current year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
South, Inc., earns book net income before tax of $400,000 in year 1. It acquires a depreciable asset in year 1, and its first-year tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation by $50,000. At the end of year 1, South's deferred tax liability account balance is $10,500. In year 2, South earns $500,000 book net income before tax, and its book depreciation exceeds tax depreciation by $20,000. South records no other temporary or permanent book-tax differences. Assuming that the U.S. tax rate is 21% in both years, what is South's balance in its deferred tax liability account at the end of year 2?
A) $0
B) $4,200
C) $6,300
D) $10,500
A) $0
B) $4,200
C) $6,300
D) $10,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Budlow, Inc., reported the following results for the current year.  Determine Budlow's taxable income for the current year. Identify any temporary or permanent book-tax differences.
Determine Budlow's taxable income for the current year. Identify any temporary or permanent book-tax differences.
 Determine Budlow's taxable income for the current year. Identify any temporary or permanent book-tax differences.
Determine Budlow's taxable income for the current year. Identify any temporary or permanent book-tax differences.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Hot, Inc.'s primary competitor is Cold, Inc. When comparing relative deferred tax asset and liability accounts with Cold, which of the following benchmarking activities should Hot undertake?
A) Scale the deferred tax assets and liabilities by total sales or total assets.
B) Compare raw dollar amounts of deferred tax assets and liabilities.
C) Ignore deferred tax assets and liabilities and focus on overall effective tax rate.
D) Ignore all tax information other than the current tax expense.
A) Scale the deferred tax assets and liabilities by total sales or total assets.
B) Compare raw dollar amounts of deferred tax assets and liabilities.
C) Ignore deferred tax assets and liabilities and focus on overall effective tax rate.
D) Ignore all tax information other than the current tax expense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
JiangCo constructs the following table in determining how to apply ASC 740-10 to its filing position for a transfer pricing issue. Its book-tax provision for the year, including $3 million for the uncertain transfer pricing issue, is $10 million. Under ASC 740-10, JiangCo's book income tax expense for this item is:
A) $13 million.
B) $11.6 million.
C) $11.4 million.
D) $10 million.
A) $13 million.
B) $11.6 million.
C) $11.4 million.
D) $10 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
In the typical case, the taxpayer would prefer to see an):
A) Increase in the current tax expense.
B) Increase in the deferred tax asset account balance.
C) Decrease in the deferred tax liability account balance.
D) Increase in the deferred tax liability account balance.
A) Increase in the current tax expense.
B) Increase in the deferred tax asset account balance.
C) Decrease in the deferred tax liability account balance.
D) Increase in the deferred tax liability account balance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Healy, Inc., reports an effective tax rate in its income tax footnote of 6%. The only reconciling item with regard to the hypothetical tax at 21% is a valuation allowance reversal of negative 15%. Which of the following statements is true concerning comparing Healy's effective tax rate with its competitors, all of whom have an effective tax rate between 20 and 24%?
A) Healy is managing its tax burden in a more efficient manner than its competitors are.
B) Healy's structural effective tax rate is actually quite close to that of its competitors.
C) Healy earned more cash profits because of its lower effective tax rate.
D) Healy is likely to be engaged in tax shelter activities.
A) Healy is managing its tax burden in a more efficient manner than its competitors are.
B) Healy's structural effective tax rate is actually quite close to that of its competitors.
C) Healy earned more cash profits because of its lower effective tax rate.
D) Healy is likely to be engaged in tax shelter activities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Black, Inc., is a domestic corporation with the following balance sheet for book and tax purposes at the end of the year. Assume a 21% corporate tax rate and no valuation allowance. 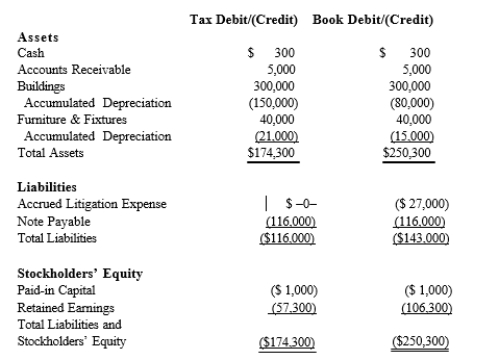 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows: 
 Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest, and it incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Determine the net deferred tax asset or net deferred tax liability at year-end.
 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows: 
 Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest, and it incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Determine the net deferred tax asset or net deferred tax liability at year-end.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
You are the tax adviser to a publicly traded U.S. corporation. How might you use a "benchmarking" analysis to begin your review of the entity's tax situation and planning opportunities?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Book-tax differences can be explained in part by examining the objectives underlying financial accounting and taxable income computations. Evaluate this statement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Bryden Corporation is considering two tax planning strategies. Both would produce a $1 million tax savings. One of
the strategies would structure the plan so that the $1 million would represent a temporary book-tax difference, and the other would generate a permanent difference. In general, which plan would the Bryden CFO prefer? Which would a stock analyst reviewing the Bryden valuation prefer?
the strategies would structure the plan so that the $1 million would represent a temporary book-tax difference, and the other would generate a permanent difference. In general, which plan would the Bryden CFO prefer? Which would a stock analyst reviewing the Bryden valuation prefer?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
At the beginning of the year, the balance sheet of Schrader, Inc., shows a $500,000 deferred tax asset relating to a net operating loss carryforward offset by a $90,000 valuation allowance. At the end of the year, Schrader's auditors
agree to release $20,000 of the allowance. Provide the journal entry to record this change in the valuation allowance.
agree to release $20,000 of the allowance. Provide the journal entry to record this change in the valuation allowance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Black, Inc., is a domestic corporation with the following balance sheet for book and tax purposes at the end of the year. Assume a 21% corporate tax rate and no valuation allowance. 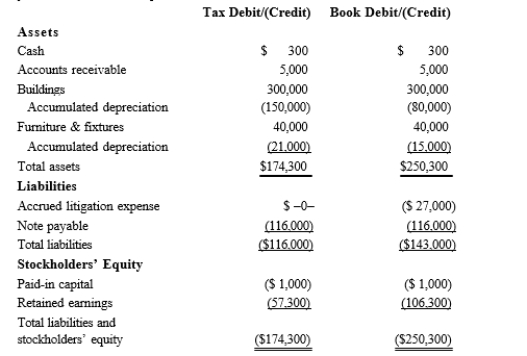 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:  Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest and incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Provide the income tax footnote rate reconciliation for Black, using either
dollars or percentages.
 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:  Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest and incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Provide the income tax footnote rate reconciliation for Black, using either
dollars or percentages.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Black, Inc., is a domestic corporation with the following balance sheet for book and tax purposes at the end of the year. Assume a 21% corporate tax rate and no valuation allowance. 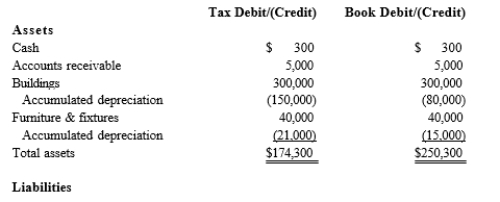
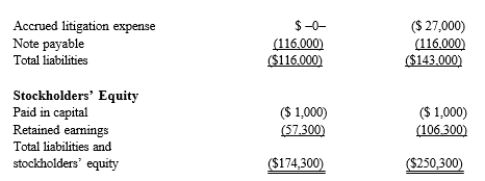 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:  Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest, and it incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Provide the journal entry to record Black's current tax expense.

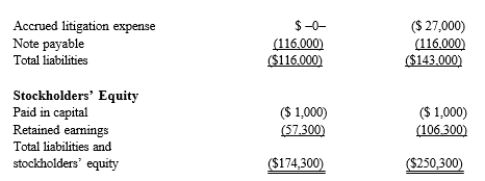 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:  Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest, and it incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Provide the journal entry to record Black's current tax expense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
A corporation's taxable income almost never is the same as its GAAP financial accounting income. Explain why this occurs. Use the terms permanent and temporary book-tax differences in your answer. Give at least two examples of each type of book-tax difference.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Jacobsen Corporation has determined the appropriate changes to its deferred tax accounts. Its auditor now is discussing whether to place a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset on the balance sheet. List some of the factors that the Jacobsen auditor will consider in this regard.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
At the beginning of the year, Schrader, Inc., holds a net operating loss carryforward, and its balance sheet shows a related deferred tax asset of $500,000. At the end of the year, the balance in the deferred tax asset account has not changed, but Schrader's auditors want to record a $90,000 valuation allowance against this amount, because of a persistent downturn in Schrader's profitability. Provide the journal entry to record the valuation allowance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
You are assisting LipidCo, a U.S. corporation subject to GAAP, to determine its current-year book expense for income taxes. The following represent the steps that you will take in making this computation. Put the steps into the correct order.
A. Compute the deferred tax provision.
B. Determine book income before income tax effects. C. Determine the current tax provision.
D. Determine whether a valuation allowance is required, and apply or release it. E. Identify and measure temporary book-tax differences.
F. Prepare the disclosures for the financial statement footnotes. G. Add/Subtract any permanent book-tax differences.
A. Compute the deferred tax provision.
B. Determine book income before income tax effects. C. Determine the current tax provision.
D. Determine whether a valuation allowance is required, and apply or release it. E. Identify and measure temporary book-tax differences.
F. Prepare the disclosures for the financial statement footnotes. G. Add/Subtract any permanent book-tax differences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Black, Inc., is a domestic corporation with the following balance sheet for book and tax purposes at the end of the year. Assume a 21% corporate tax rate and no valuation allowance. 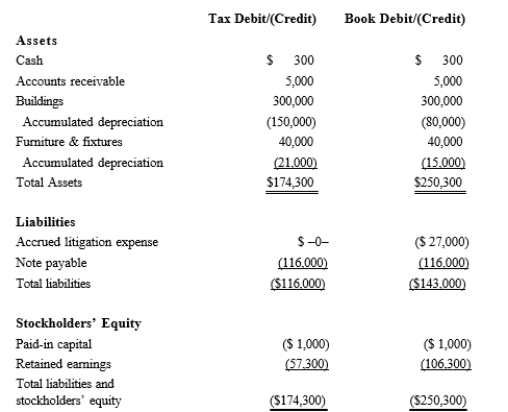 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows: 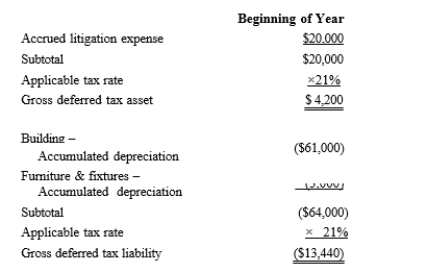 Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest, and it incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Calculate Black's current tax expense.
 Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:
Black, Inc.'s, gross deferred tax assets and liabilities at the beginning of Black's year are as follows:  Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.
Black, Inc.'s, book income before tax is $6,000. Black records two permanent book-tax differences.It earned $250 in tax-exempt municipal bond interest, and it incurred $500 in nondeductible business meals expense. Calculate Black's current tax expense.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








