Deck 21: The Theory of Consumer Choice
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/209
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 21: The Theory of Consumer Choice
1
If a consumer experiences a decrease in income, the new budget constraint will have the same slope as the old budget constraint.
True
2
The slope of the budget constraint reveals the relative price of good X compared to good Y.
True
3
For a typical consumer, indifference curves can intersect if they satisfy the property of transitivity.
False
4
The marginal rate of substitution is the slope of the budget constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The slope at any point on an indifference curve equals the absolute price at which a consumer is willing to substitute one good for the other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
For a typical consumer, most indifference curves are bowed inward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A consumer's budget constraint for goods X and Y is determined by how much the consumer likes good X relative to good Y.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
If goods A and B are perfect substitutes, then the marginal rate of substitution of good A for good B is constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
For a typical consumer, most indifference curves are downward sloping.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The indifference curves for perfect substitutes are straight lines.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A budget constraint illustrates bundles that a consumer prefers equally, while an indifference curve illustrates bundles that are equally affordable to a consumer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The indifference curves for left gloves and right gloves are straight lines.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The indifference curves for left shoes and right shoes are right angles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
When two goods are perfect complements, the indifference curves are right angles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A typical indifference curve is upward sloping.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The theory of consumer choice illustrates that people face tradeoffs, which is one of the Ten Principles of Economics.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The indifference curves for perfect substitutes are right angles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The indifference curves for nickels and dimes are straight lines.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The marginal rate of substitution between goods A and B measures the price of A relative to the price of B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The slope of a consumer's budget constraint is unaffected by a change in income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
If a consumer purchases more of good A when her income falls, good A is an inferior good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A typical consumer consumes both coffee and donuts. After the consumer's income decreases, the consumer consumes more coffee but fewer donuts than before. For this consumer, coffee is a normal good, but donuts are an inferior good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Giffen goods are inferior goods for which the income effect dominates the substitution effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
At a consumer's optimal choice, the consumer chooses the combination of goods that equates the marginal rate of substitution and the price ratio.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
All points on a demand curve are optimal consumption points.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When indifference curves are downward sloping, the marginal rate of substitution is usually constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
If consumers purchase more of a good when their income rises, the good is a normal good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The marginal rate of substitution is the slope of the indifference curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The income effect of a price change is the change in consumption that results from the movement to a new indifference curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The income effect of a price change is unaffected by whether the good is a normal or inferior good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A typical consumer consumes both coffee and donuts. After the consumer's income decreases, the consumer consumes more coffee but fewer donuts than before. For this consumer, donuts are a normal good, but coffee is an inferior good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
If a consumer purchases more of good X and good Y after her income increases, then neither good X nor good Y is an inferior good for her.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Economists have found evidence of a Giffen good when studying the consumption of rice in the Chinese province of Hunan.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
If a consumer purchases more of good B when his income rises, good B is an inferior good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The substitution effect of a price change is the change in consumption that results from the movement to a new indifference curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The direction of the substitution effect is not influenced by whether the good is normal or inferior.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Giffen goods violate the law of demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
At a consumer's optimal choice, the consumer chooses the combination of goods such that the ratio of the marginal utilities equals the ratio of the prices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
When indifference curves are bowed inward, the marginal rate of substitution varies at each point on the indifference curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A consumer's optimal choice is affected by income, prices of goods, and preferences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Figure 21-17
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.
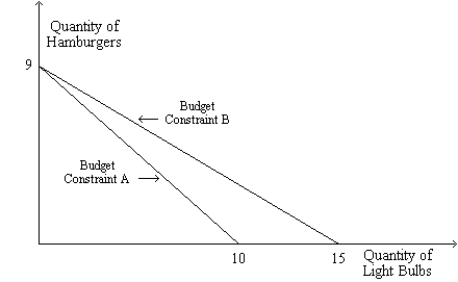
Refer to Figure 21-17. Suppose the price of a hamburger is $10 and Budget Constraint A applies. What is the consumer's income? What is the price of a light bulb?
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. Suppose the price of a hamburger is $10 and Budget Constraint A applies. What is the consumer's income? What is the price of a light bulb?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A rational person can have a negatively-sloped labor supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Katie wins $3 million in her state's lottery. If Katie drastically reduces the number of hours she works after she wins the money, we can infer that the income effect is larger than the substitution effect for her.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The theory of consumer choice is representative of how consumers make decisions but is not intended to be a literal account of the process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Consumers face tradeoffs except at the point where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget line.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Susie wins $2 million in her state's lottery. If Susie keeps working after she wins the money, we can infer that the income effect is larger than the substitution effect for her.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Consumer will always consume more of a good if their income increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Figure 21-17
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. Suppose the consumer's income is $90 and Budget Constraint A applies. What is the price of a light bulb?
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. Suppose the consumer's income is $90 and Budget Constraint A applies. What is the price of a light bulb?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The substitution effect in the work-leisure model induces a person to work less in response to higher wages, which tends to make the labor-supply curve slope upward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Figure 21-17
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. Suppose Budget Constraint B applies. If the consumer's income is $90 and if he is buying 5 light bulbs, then how much money is he spending on hamburgers?
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. Suppose Budget Constraint B applies. If the consumer's income is $90 and if he is buying 5 light bulbs, then how much money is he spending on hamburgers?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
An increase in the interest rate today leading to a decrease in consumption today violates the law of demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A decrease in the price of the good on the horizontal axis rotates the budget constraint counterclockwise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The income effect in the work-leisure model induces a person to work less in response to higher wages, which tends to make the labor-supply curve slope backward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
A rise in the interest rate will generally result in people consuming less when they are old if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Figure 21-17
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. What particular change would result in a rotation of the budget constraint from Budget Constraint A to Budget Constraint B?
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. What particular change would result in a rotation of the budget constraint from Budget Constraint A to Budget Constraint B?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A worker with a backward-bending labor supply curve responds to an increase in wages by working more hours.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A consumer maximizes utility at a point where multiple indifference curves intersect the budget line.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
A rise in the interest rate will generally result in people consuming more when they are old if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Figure 21-17
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. Suppose the price of a light bulb is $3 and Budget Constraint B applies. What is the consumer's income? What is the price of a hamburger?
The graph shows two budget constraints for a consumer.

Refer to Figure 21-17. Suppose the price of a light bulb is $3 and Budget Constraint B applies. What is the consumer's income? What is the price of a hamburger?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Shelley wins $1 million in her state's lottery. If Shelley keeps working after she wins the money, we can infer that the substitution effect must exactly offset the income effect for her.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
What does the slope of a consumer's indifference curve represent?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Figure 21-18
The figure shows two indifference curves and two budget constraints for a consumer named Kevin.
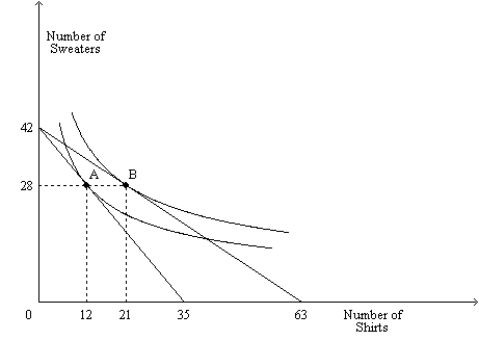
Refer to Figure 21-18. If Kevin's income is $1,260, then what is the price of a sweater?
The figure shows two indifference curves and two budget constraints for a consumer named Kevin.

Refer to Figure 21-18. If Kevin's income is $1,260, then what is the price of a sweater?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
A consumer's budget constraint is drawn on a graph with the number of sandwiches measured along the horizontal axis and the number of bowls of soup measured along the vertical axis. Hold the consumer's income and the price of a sandwich fixed, and increase the price of a bowl of soup. Describe the effect on the budget constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Teresa faces prices of $6.00 for a unit of good X and $1.50 for a unit of good Y. At her optimum, Teresa is willing to give up 1 unit of good X for __________ units of good Y.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
A consumer's budget constraint is drawn with the quantity of pizza measured along the horizontal axis and the price of Pepsi measured along the vertical axis. If the market is offering the consumer the trade-off of 3 pints of Pepsi for 1 pizza, then what is the slope of the consumer's budget constraint?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Goods x and y are available to Jeff. At Jeff's optimum, the marginal utility per dollar spent on good x equals __________________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
When we draw Katie's indifference curves to represent her preferences for books and movies, we find that her indifference curves are upward-sloping. What does this tell us about Katie's preferences?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Using our model of consumer choice, is it possible for a consumer to buy less of a particular good when his income rises? Briefly explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
What does the slope of a budget constraint represent?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
A consumer's indifference curves are right angles when, for the consumer, the goods in question are __________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
What is significant about a point on a graph at which an indifference curve is tangent to a budget constraint?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
A consumer's indifference curves are straight lines when, for the consumer, the goods in question are __________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
In order to represent a consumer's choices on a graph, we draw her budget constraint as well as her __________ curves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Because people are more willing to trade away goods that they have in abundance and less willing to trade away goods of which they have little, indifference curves are ___________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The rate at which a consumer is willing to trade off one good for another is called the __________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Thomas faces prices of $6 for a unit of good X and $30 for a unit of good Y. At his optimum, Thomas is willing to give up 1 unit of good Y for __________ units of good X.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
If the market is offering consumers the trade-off of 3 pints of Pepsi for 1 pizza, and if the price of a pizza is $9, then what is the price of a pint of Pepsi?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Figure 21-18
The figure shows two indifference curves and two budget constraints for a consumer named Kevin.

Refer to Figure 21-18. Suppose point A was Kevin's optimum last week, and point B is his optimum this week. What happened between last week and this week?
The figure shows two indifference curves and two budget constraints for a consumer named Kevin.

Refer to Figure 21-18. Suppose point A was Kevin's optimum last week, and point B is his optimum this week. What happened between last week and this week?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
If goods X and Y are both normal goods for Brenda, then an increase in Brenda's income will lead her to __________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Figure 21-18
The figure shows two indifference curves and two budget constraints for a consumer named Kevin.

Refer to Figure 21-18. If point A is Kevin's optimum, then at that optimum, what is his opportunity cost of a shirt in terms of sweaters?
The figure shows two indifference curves and two budget constraints for a consumer named Kevin.

Refer to Figure 21-18. If point A is Kevin's optimum, then at that optimum, what is his opportunity cost of a shirt in terms of sweaters?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 209 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








