Deck 13: Experiments and Quasi-Experiments
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Experiments and Quasi-Experiments
1
The following are reasons for studying randomized controlled experiment in an econometrics course, with the exception of
A)at a conceptual level, the notion of an ideal randomized controlled experiment provides a benchmark against which to judge estimates of causal effects in
Practice.
B)when experiments are actually conducted, their results can be very influential, so it is important to understand the limitations and threats to validity of actual
Experiments as well as their strength.
C)randomized controlled experiments in economics are common.
D)external circumstances sometimes produce what appears to be randomization.
A)at a conceptual level, the notion of an ideal randomized controlled experiment provides a benchmark against which to judge estimates of causal effects in
Practice.
B)when experiments are actually conducted, their results can be very influential, so it is important to understand the limitations and threats to validity of actual
Experiments as well as their strength.
C)randomized controlled experiments in economics are common.
D)external circumstances sometimes produce what appears to be randomization.
C
2
In a quasi-experiment 

B
3
The following estimation methods should not be used to test for randomization when is binary:
A) linear probability model (OLS) with homoskedasticity-only standard errors.
B) probit.
C) logit.
D) linear probability model (OLS) with heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.
A) linear probability model (OLS) with homoskedasticity-only standard errors.
B) probit.
C) logit.
D) linear probability model (OLS) with heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.
linear probability model (OLS) with homoskedasticity-only standard errors.
4
Experimental effects, such as the Hawthorne effect,
A)generally are not germane in quasi-experiments.
B)typically require instrumental variable estimation in quasi-experiments.
C)can be dealt with using binary variables in quasi-experiments.
D)are the most important threat to internal validity in quasi-experiments.
A)generally are not germane in quasi-experiments.
B)typically require instrumental variable estimation in quasi-experiments.
C)can be dealt with using binary variables in quasi-experiments.
D)are the most important threat to internal validity in quasi-experiments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In the context of a controlled experiment, consider the simple linear regression formulation be the outcome, the treatment level, and contain all the additional determinants of the outcome. Then
A) the OLS estimator of the slope will be inconsistent in the case of a randomly assigned since there are omitted variables present.
B) will be independently distributed if the be are randomly assigned.
C) represents the causal effect of X on Y when X is zero.
D) is the expected value for the treatment group.
A) the OLS estimator of the slope will be inconsistent in the case of a randomly assigned since there are omitted variables present.
B) will be independently distributed if the be are randomly assigned.
C) represents the causal effect of X on Y when X is zero.
D) is the expected value for the treatment group.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In the context of a controlled experiment, consider the simple linear regression formulation
Let the be the outcome, the treatment level when the treatment is binary, and ui contain all the additional determinants of the outcome. Then calling a differences estimator
A) makes sense since it is the difference between the sample average outcome of the treatment group and the sample average outcome of the control group.
B) and the level estimator is standard terminology in randomized controlled experiments.
C) does not make sense, since neither Y nor X are in differences.
D) is not quite accurate since it is actually the derivative of Y on X .
Let the be the outcome, the treatment level when the treatment is binary, and ui contain all the additional determinants of the outcome. Then calling a differences estimator
A) makes sense since it is the difference between the sample average outcome of the treatment group and the sample average outcome of the control group.
B) and the level estimator is standard terminology in randomized controlled experiments.
C) does not make sense, since neither Y nor X are in differences.
D) is not quite accurate since it is actually the derivative of Y on X .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The following is not a threat to external validity:
A)the experimental sample is not representative of the population of interest.
B)the treatment being studied is not representative of the treatment that would be implemented more broadly.
C)experimental participants are volunteers.
D)partial compliance with the treatment protocol.
A)the experimental sample is not representative of the population of interest.
B)the treatment being studied is not representative of the treatment that would be implemented more broadly.
C)experimental participants are volunteers.
D)partial compliance with the treatment protocol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
With panel data, the causal effect
A)cannot be estimated since correlation does not imply causation.
B)is typically estimated using the probit regression model.
C)can be estimated using the "differences-in-differences" estimator.
D)can be estimated by looking at the difference between the treatment and the control group after the treatment has taken place.
A)cannot be estimated since correlation does not imply causation.
B)is typically estimated using the probit regression model.
C)can be estimated using the "differences-in-differences" estimator.
D)can be estimated by looking at the difference between the treatment and the control group after the treatment has taken place.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Assume that data are available on other characteristics of the subjects that are relevant to determining the experimental outcome.Then including these determinants explicitly
Results in
A)the limited dependent variable model.
B)the differences in means test.
C)the multiple regression model.
D)large scale equilibrium effects.
Results in
A)the limited dependent variable model.
B)the differences in means test.
C)the multiple regression model.
D)large scale equilibrium effects.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Heterogeneous population
A)implies that heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors must be used.
B)suggest that multiple characteristics must be used to describe the population.
C)effects can be captured through interaction terms.
D)refers to circumstances in which there is unobserved variation in the causal effect with the population.
A)implies that heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors must be used.
B)suggest that multiple characteristics must be used to describe the population.
C)effects can be captured through interaction terms.
D)refers to circumstances in which there is unobserved variation in the causal effect with the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A repeated cross-sectional data set 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Program evaluation
A)is conducted for most departments in your university/college about every seven years.
B)is the field of study that concerns estimating the effect of a program, policy, or some other intervention or "treatment."
C)tries to establish whether EViews, SAS or Stata work best for your econometrics course.
D)establishes rating systems for television programs in a controlled experiment framework.
A)is conducted for most departments in your university/college about every seven years.
B)is the field of study that concerns estimating the effect of a program, policy, or some other intervention or "treatment."
C)tries to establish whether EViews, SAS or Stata work best for your econometrics course.
D)establishes rating systems for television programs in a controlled experiment framework.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The Hawthorne effect refers to
A)subjects dropping out of the study after being randomly assigned to the treatment or control group.
B)the failure of individuals to follow completely the randomized treatment protocol.
C)the phenomenon that subjects in an experiment can change their behavior merely by being included in the experiment.
D)assigning individuals, in part, as a result of their characteristics or preferences.
A)subjects dropping out of the study after being randomly assigned to the treatment or control group.
B)the failure of individuals to follow completely the randomized treatment protocol.
C)the phenomenon that subjects in an experiment can change their behavior merely by being included in the experiment.
D)assigning individuals, in part, as a result of their characteristics or preferences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Your textbooks gives several examples of quasi experiments that were conducted.The following is not an example of a quasi experiment:
A)labor market effects of immigration.
B)effects on civilian earnings of military service.
C)the effect of cardiac catheterization.
D)the effect of unemployment on the inflation rate.
A)labor market effects of immigration.
B)effects on civilian earnings of military service.
C)the effect of cardiac catheterization.
D)the effect of unemployment on the inflation rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
For quasi-experiments,
A)there is a particularly important potential threat to internal validity, namely whether the "as if" randomization in fact can be treated reliably as true
Randomization.
B)there are the same threats to internal validity as for true randomized controlled experiments, without modifications.
C)there is little threat to external validity, since the populations are typically already different.
D)OLS estimation should not be used.
A)there is a particularly important potential threat to internal validity, namely whether the "as if" randomization in fact can be treated reliably as true
Randomization.
B)there are the same threats to internal validity as for true randomized controlled experiments, without modifications.
C)there is little threat to external validity, since the populations are typically already different.
D)OLS estimation should not be used.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Experimental data are often
A)observational data.
B)binary data, in that the subject either does or does not respond to the treatment.
C)panel data.
D)time series data.
A)observational data.
B)binary data, in that the subject either does or does not respond to the treatment.
C)panel data.
D)time series data.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The following does not represent a threat to internal validity of randomized controlled experiments:
A)attrition.
B)failure to follow the treatment protocol.
C)experimental effects.
D)a large sample size.
A)attrition.
B)failure to follow the treatment protocol.
C)experimental effects.
D)a large sample size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
To test for randomization when is binary,
A) you regress on all W 's and compute the F -statistic for testing that all the coefficients on the W 's are zero. (The W 's measure characteristics of individuals, and these are not affected by the treatment.)
B) is not possible, since binary variables can only be regressors.
C) requires reordering the observations randomly and re-estimating the model. If the coefficients remain the same, then this is evidence of randomization.
D) requires seeking external validity for your study.
A) you regress on all W 's and compute the F -statistic for testing that all the coefficients on the W 's are zero. (The W 's measure characteristics of individuals, and these are not affected by the treatment.)
B) is not possible, since binary variables can only be regressors.
C) requires reordering the observations randomly and re-estimating the model. If the coefficients remain the same, then this is evidence of randomization.
D) requires seeking external validity for your study.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
All of the following are reasons for using the differences estimator with additional regressors, with the exception of
A)efficiency.
B)providing a check for randomization.
C)providing an adjustment for "conditional" randomization.
D)making the difference estimator easier to calculate than in the case of the differences estimator without the additional regressors.
A)efficiency.
B)providing a check for randomization.
C)providing an adjustment for "conditional" randomization.
D)making the difference estimator easier to calculate than in the case of the differences estimator without the additional regressors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Causal effects that depend on the value of an observable variable, say
A) cannot be estimated.
B) can be estimate by interacting the treatment variable with
C) result in the OLS estimator being inefficient.
D) requires use of homoskedasticity-only standard errors.
A) cannot be estimated.
B) can be estimate by interacting the treatment variable with
C) result in the OLS estimator being inefficient.
D) requires use of homoskedasticity-only standard errors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
 (a)Explain why employment changes of the "high wage" and "low wage" restaurants might
(a)Explain why employment changes of the "high wage" and "low wage" restaurants mightconstitute a quasi-experiment.Which is the treatment group and which the control group?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
 W
W(a)
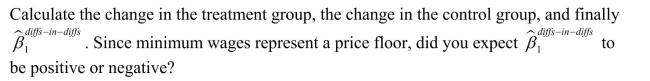

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Canada and the United States had approximately the same aggregate unemployment rates
from the 1920s to 1981.In 1982, a two percentage point gap appears, which has roughly
persisted until today, with the Canadian unemployment rate in the third quarter of 2002
being 7.6 percent while the American rate stood at 5.9 percent in the same period.
Several authors have investigated this phenomenon.One study, published in 1990,
contained the following statement: "It is a clichė that, as compared to analysis in the
physical sciences, economic analysis is hampered by the lack of controlled experiments.
In this regard, study of the Canadian economy can be much facilitated by comparison
with the behaviour of the US …" Discuss what the authors may have had in mind.List
some potential threats to internal and external validity when comparing aggregate
unemployment rate behavior between countries.
from the 1920s to 1981.In 1982, a two percentage point gap appears, which has roughly
persisted until today, with the Canadian unemployment rate in the third quarter of 2002
being 7.6 percent while the American rate stood at 5.9 percent in the same period.
Several authors have investigated this phenomenon.One study, published in 1990,
contained the following statement: "It is a clichė that, as compared to analysis in the
physical sciences, economic analysis is hampered by the lack of controlled experiments.
In this regard, study of the Canadian economy can be much facilitated by comparison
with the behaviour of the US …" Discuss what the authors may have had in mind.List
some potential threats to internal and external validity when comparing aggregate
unemployment rate behavior between countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Define the 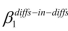 in terms of observable differences in the treatment and control group, before and after the treatment. Explain why this presentation is the equivalent of calculating the coefficient in a regression framework.
in terms of observable differences in the treatment and control group, before and after the treatment. Explain why this presentation is the equivalent of calculating the coefficient in a regression framework.
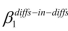 in terms of observable differences in the treatment and control group, before and after the treatment. Explain why this presentation is the equivalent of calculating the coefficient in a regression framework.
in terms of observable differences in the treatment and control group, before and after the treatment. Explain why this presentation is the equivalent of calculating the coefficient in a regression framework.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Describe the major differences between a randomized controlled experiment and a quasi-
experiment.
experiment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26

 Use a figure similar to the textbook to explain what this reviewer meant.
Use a figure similar to the textbook to explain what this reviewer meant.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
(Requires Appendix material)Discuss how the differences-in-differences estimator can
be extended to multiple time periods.In particular, assume that there are n individuals
and T time periods.What do the individual and time effects control for?
be extended to multiple time periods.In particular, assume that there are n individuals
and T time periods.What do the individual and time effects control for?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The New Jersey-Pennsylvania study on the effect of minimum wages on employment
mentioned in your textbook used a comparison in means "before" and "after" analysis.
The difference-in-difference estimate turned out to be 2.76 with a standard error of 1.36.
The authors also used a difference-in-differences estimator with additional regressors of
the type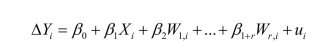
 (a)Given that there are four chains and the possibility of a company ownership, why did the
(a)Given that there are four chains and the possibility of a company ownership, why did the
authors not include five W-variables?
mentioned in your textbook used a comparison in means "before" and "after" analysis.
The difference-in-difference estimate turned out to be 2.76 with a standard error of 1.36.
The authors also used a difference-in-differences estimator with additional regressors of
the type
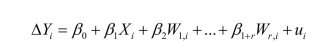
 (a)Given that there are four chains and the possibility of a company ownership, why did the
(a)Given that there are four chains and the possibility of a company ownership, why did theauthors not include five W-variables?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Consider the simple population regression model where the treatment is the same for the
members of the treatment group, and hence X is a binary variable.Explain why the
coefficient on X represents the difference between two means.How is the test for the
statistical significance of the coefficient on X related to the test for differences in means
between two populations, when their variances are different? Write down the null and
alternative hypothesis in each case.
members of the treatment group, and hence X is a binary variable.Explain why the
coefficient on X represents the difference between two means.How is the test for the
statistical significance of the coefficient on X related to the test for differences in means
between two populations, when their variances are different? Write down the null and
alternative hypothesis in each case.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
One of the major lessons learned in the chapter on experiments and quasi-experiments
A)is that there are almost no true experiments in economics and that quasi- experiments are a poor substitute.
B)you should always use TSLS when estimating causal effects in quasi-experiments.
C)populations are always homogeneous.
D)is that the insights of experimental methods can be applied to quasi-experiments, in which special circumstances make it seem "as if" randomization has occurred.
A)is that there are almost no true experiments in economics and that quasi- experiments are a poor substitute.
B)you should always use TSLS when estimating causal effects in quasi-experiments.
C)populations are always homogeneous.
D)is that the insights of experimental methods can be applied to quasi-experiments, in which special circumstances make it seem "as if" randomization has occurred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Present alternative estimators for causal effects using experimental data when data is
available for a single period or for two periods.Discuss their advantages and
disadvantages.
available for a single period or for two periods.Discuss their advantages and
disadvantages.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Earnings functions provide a measure, among other things, of the returns to education.It
has been argued these regressions contain a serious omitted variable bias due to
differences in abilities.Furthermore, ability is hard to measure and bound to be highly
correlated with years of schooling.Hence the standard estimate of about a 10 percent
return to every year of schooling is upward biased.Suggest some ways to address this
problem.One famous study looked at earnings of identical twins.Explain how this can
be viewed as a quasi-experiment, and mention some of the threats to internal and external
validity that such a study might encounter.
has been argued these regressions contain a serious omitted variable bias due to
differences in abilities.Furthermore, ability is hard to measure and bound to be highly
correlated with years of schooling.Hence the standard estimate of about a 10 percent
return to every year of schooling is upward biased.Suggest some ways to address this
problem.One famous study looked at earnings of identical twins.Explain how this can
be viewed as a quasi-experiment, and mention some of the threats to internal and external
validity that such a study might encounter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
You want to study whether or not the use of computers in the classroom for elementary
students has an effect on performance.Explain in some detail how you would ideally set
up such an experiment and what threats to internal and external validity there might be.
students has an effect on performance.Explain in some detail how you would ideally set
up such an experiment and what threats to internal and external validity there might be.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Quasi-experiments
A)provide a bridge between the econometric analysis of observational data sets and the statistical ideal of a true randomized controlled experiment.
B)are not the same as experiments, and lessons learned from the use of the latter can therefore not be applied to them.
C)most often use difference-in-difference estimators, which are quite different from OLS and instrumental variables methods studied in earlier chapters of the book.
D)use the same methods as studied in earlier chapters of the book, and hence the interpretation of these methods is the same.
A)provide a bridge between the econometric analysis of observational data sets and the statistical ideal of a true randomized controlled experiment.
B)are not the same as experiments, and lessons learned from the use of the latter can therefore not be applied to them.
C)most often use difference-in-difference estimators, which are quite different from OLS and instrumental variables methods studied in earlier chapters of the book.
D)use the same methods as studied in earlier chapters of the book, and hence the interpretation of these methods is the same.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
In the case of heterogeneous causal effects, the following is not true: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
If the causal effect is different for different people, then the population regression equation for a binary treatment variable Xi, can be written as 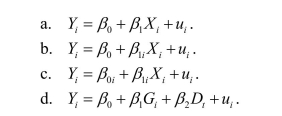
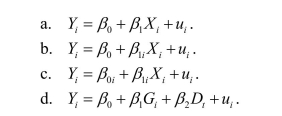

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Specify the multiple regression model that contains the difference-in-difference estimator
(with additional regressors).Explain the circumstances under which this model is
preferable to the simple difference-in-difference estimator.Explain how the W's can be
used to test for randomization.How does the interpretation of the W variables change
compared to the differences estimator with additional regressors?
(with additional regressors).Explain the circumstances under which this model is
preferable to the simple difference-in-difference estimator.Explain how the W's can be
used to test for randomization.How does the interpretation of the W variables change
compared to the differences estimator with additional regressors?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Roughly ten percent of elementary schools in California have a system whereby 4th to 6th graders share a common classroom and a single teacher (multi-age, multi-grade classroom). Suggest an experimental design that would allow you to assess the effect of learning in this environment. Mention some of the threats to internal and external validity and how you would attempt to circumvent these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
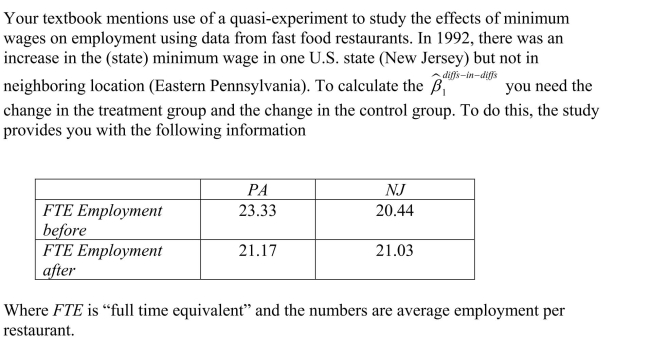
Let the vertical axis of a figure indicate the average employment fast food restaurants. There are two time periods, t=1 and t=2 , where time period is measured on the horizontal axis. The following table presents average employment levels per restaurant for New Jersey (the treatment group) and Eastern Pennsylvania (the control group).
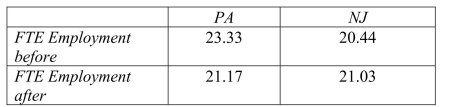
Enter the four points in the figure and label them and
and 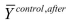 . Connect the points. Finally calculate and indicate the value for
. Connect the points. Finally calculate and indicate the value for 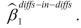

Enter the four points in the figure and label them
 and
and 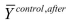 . Connect the points. Finally calculate and indicate the value for
. Connect the points. Finally calculate and indicate the value for 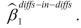

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The major distinction between the experiments and quasi-experiments chapter and earlier chapters is the
A)frequent use of binary variables.
B)type of data analyzed and the special opportunities and challenges posed when analyzing experiments and quasi-experiments.
C)superiority of TSLS over OLS.
D)use of heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.
A)frequent use of binary variables.
B)type of data analyzed and the special opportunities and challenges posed when analyzing experiments and quasi-experiments.
C)superiority of TSLS over OLS.
D)use of heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








