Deck 12: Instrumental Variables Regression
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 12: Instrumental Variables Regression
1
Two Stage Least Squares is calculated as follows;in the first stage
A)Y is regressed on the exogenous variables only.The predicted value of Y is then regressed on the instrumental variables.
B)the unknown coefficients in the reduced form equation are estimated by OLS, and the predicted values are calculated.In the second stage, Y is regressed on these
Predicted values and the other exogenous variables.
C)the exogenous variables are regressed on the instruments.The predicted value of the exogenous variables is then used in the second stage, together with the
Instruments, to predict the dependent variable.
D)the unknown coefficients in the reduced form equation are estimated by weighted least squares, and the predicted values are calculated.In the second stage, Y is
Regressed on these predicted values and the other exogenous variables.
A)Y is regressed on the exogenous variables only.The predicted value of Y is then regressed on the instrumental variables.
B)the unknown coefficients in the reduced form equation are estimated by OLS, and the predicted values are calculated.In the second stage, Y is regressed on these
Predicted values and the other exogenous variables.
C)the exogenous variables are regressed on the instruments.The predicted value of the exogenous variables is then used in the second stage, together with the
Instruments, to predict the dependent variable.
D)the unknown coefficients in the reduced form equation are estimated by weighted least squares, and the predicted values are calculated.In the second stage, Y is
Regressed on these predicted values and the other exogenous variables.
B
2
In the case of the simple regression model when X and u are correlated, then
A) the OLS estimator is biased in small samples only.
B) OLS and TSLS produce the same estimate.
C) X is exogenous.
D) the OLS estimator is inconsistent.
A) the OLS estimator is biased in small samples only.
B) OLS and TSLS produce the same estimate.
C) X is exogenous.
D) the OLS estimator is inconsistent.
the OLS estimator is inconsistent.
3
The two conditions for a valid instrument are 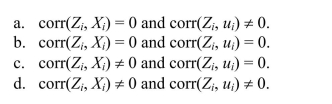
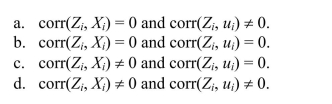
C
4
The J-statistic 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The following will not cause correlation between X and u in the simple regression model:
A)simultaneous causality.
B)omitted variables.
C)irrelevance of the regressor.
D)errors in variables.
A)simultaneous causality.
B)omitted variables.
C)irrelevance of the regressor.
D)errors in variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The IV regression assumptions include all of the following with the exception of 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Having more relevant instruments
A)is a problem because instead of being just identified, the regression now becomes overidentified.
B)is like having a larger sample size in that the more information is available for use in the IV regressions.
C)typically results in larger standard errors for the TSLS estimator.
D)is not as important for inference as having the same number of endogenous variables as instruments.
A)is a problem because instead of being just identified, the regression now becomes overidentified.
B)is like having a larger sample size in that the more information is available for use in the IV regressions.
C)typically results in larger standard errors for the TSLS estimator.
D)is not as important for inference as having the same number of endogenous variables as instruments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The reduced form equation for X
A)regresses the endogenous variable X on the smallest possible subset of regressors.
B)relates the endogenous variable X to all the available exogenous variables, both those included in the regression of interest and the instruments.
C)uses the predicted values of X from the first stage as a regressor in the original equation.
D)uses smaller standard errors, such as homoskedasticity-only standard errors, for inference.
A)regresses the endogenous variable X on the smallest possible subset of regressors.
B)relates the endogenous variable X to all the available exogenous variables, both those included in the regression of interest and the instruments.
C)uses the predicted values of X from the first stage as a regressor in the original equation.
D)uses smaller standard errors, such as homoskedasticity-only standard errors, for inference.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The TSLS estimator is
A)consistent and has a normal distribution in large samples.
B)unbiased.
C)efficient in small samples.
D)F-distributed.
A)consistent and has a normal distribution in large samples.
B)unbiased.
C)efficient in small samples.
D)F-distributed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The conditions for a valid instruments do not include the following: 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Consider a competitive market where the demand and the supply depend on the current price of the good.Then fitting a line through the quantity-price outcomes will
A)give you an estimate of the demand curve.
B)estimate neither a demand curve nor a supply curve.
C)enable you to calculate the price elasticity of supply.
D)give you the exogenous part of the demand in the first stage of TSLS.
A)give you an estimate of the demand curve.
B)estimate neither a demand curve nor a supply curve.
C)enable you to calculate the price elasticity of supply.
D)give you the exogenous part of the demand in the first stage of TSLS.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Weak instruments are a problem because
A)the TSLS estimator may not be normally distributed, even in large samples.
B)they result in the instruments not being exogenous.
C)the TSLS estimator cannot be computed.
D)you cannot predict the endogenous variables any longer in the first stage.
A)the TSLS estimator may not be normally distributed, even in large samples.
B)they result in the instruments not being exogenous.
C)the TSLS estimator cannot be computed.
D)you cannot predict the endogenous variables any longer in the first stage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
When there is a single instrument and single regressor, the TSLS estimator for the slope can be calculated as follows 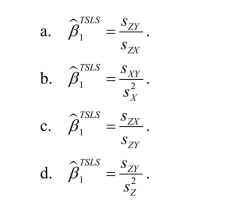
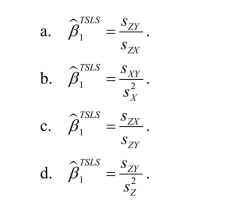

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Instrument relevance 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
If the instruments are not exogenous,
A)you cannot perform the first stage of TSLS.
B)then, in order to conduct proper inference, it is essential that you use heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.
C)your model becomes overidentified.
D)then TSLS is inconsistent.
A)you cannot perform the first stage of TSLS.
B)then, in order to conduct proper inference, it is essential that you use heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.
C)your model becomes overidentified.
D)then TSLS is inconsistent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The distinction between endogenous and exogenous variables is
A)that exogenous variables are determined inside the model and endogenous variables are determined outside the model.
B)dependent on the sample size: for n > 100, endogenous variables become exogenous.
C)depends on the distribution of the variables: when they are normally distributed, they are exogenous, otherwise they are endogenous.
D)whether or not the variables are correlated with the error term.
A)that exogenous variables are determined inside the model and endogenous variables are determined outside the model.
B)dependent on the sample size: for n > 100, endogenous variables become exogenous.
C)depends on the distribution of the variables: when they are normally distributed, they are exogenous, otherwise they are endogenous.
D)whether or not the variables are correlated with the error term.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
When calculating the TSLS standard errors
A)you do not have to worry about heteroskedasticity, since it was eliminated in the first stage
B)you can use the standard errors reported by OLS estimation of the second stage regression.
C)the critical values from the standard normal table should be adjusted for the proper degrees of freedom.
D)you should use heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.
A)you do not have to worry about heteroskedasticity, since it was eliminated in the first stage
B)you can use the standard errors reported by OLS estimation of the second stage regression.
C)the critical values from the standard normal table should be adjusted for the proper degrees of freedom.
D)you should use heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
(requires Appendix material) The relationship between the TSLS slope and the corresponding population parameter is:
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Estimation of the IV regression model
A)requires exact identification.
B)allows only one endogenous regressor, which is typically correlated with the error term.
C)requires exact identification or overidentification.
D)is only possible if the number of instruments is the same as the number of regressors.
A)requires exact identification.
B)allows only one endogenous regressor, which is typically correlated with the error term.
C)requires exact identification or overidentification.
D)is only possible if the number of instruments is the same as the number of regressors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The rule-of-thumb for checking for weak instruments is as follows: for the case of a single endogenous regressor, 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Using some of the examples from your textbook, describe econometric studies which
required instrumental variable techniques.In each case emphasize why the need for
instrumental variables arises and how authors have approached the problem.Make sure
to include a discussion of overidentification, the validity of instruments, and testing
procedures in your essay.
required instrumental variable techniques.In each case emphasize why the need for
instrumental variables arises and how authors have approached the problem.Make sure
to include a discussion of overidentification, the validity of instruments, and testing
procedures in your essay.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
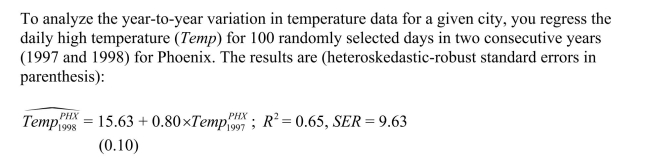 (a)Calculate the predicted temperature for the current year if the temperature in the previous
(a)Calculate the predicted temperature for the current year if the temperature in the previousyear was 400F, 780F, and 1000F.How does this compare with you prior expectation?
Sketch the regression line and compare it to the 45 degree line.What are the
implications?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
In the case of exact identification
A)you can use the J-statistic in a test of overidentifying restrictions.
B)you cannot use TSLS for estimation purposes.
C)you must rely on your personal knowledge of the empirical problem at hand to assess whether the instruments are exogenous.
D)OLS and TSLS yield the same estimate.
A)you can use the J-statistic in a test of overidentifying restrictions.
B)you cannot use TSLS for estimation purposes.
C)you must rely on your personal knowledge of the empirical problem at hand to assess whether the instruments are exogenous.
D)OLS and TSLS yield the same estimate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
In practice, the most difficult aspect of IV estimation is
A)finding instruments that are both relevant and exogenous.
B)that you have to use two stages in the estimation process.
C)calculating the J-statistic.
D)finding instruments that are exogenous.Relevant instruments are easy to find.
A)finding instruments that are both relevant and exogenous.
B)that you have to use two stages in the estimation process.
C)calculating the J-statistic.
D)finding instruments that are exogenous.Relevant instruments are easy to find.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Describe the consequences of estimating an equation by OLS in the presence of an
endogenous regressor.How can you overcome these obstacles? Present an alternative
estimator and state its properties.
endogenous regressor.How can you overcome these obstacles? Present an alternative
estimator and state its properties.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
To calculate the J-statistic you regress the 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Write a short essay about the Overidentifying Restrictions Test.What is meant exactly by
"overidentification?" State the null hypothesis.Describe how to calculate the J-statistic
and what its distribution is.Use an example of two instruments and one endogenous
variable to explain under what situation the test will be likely to reject the null
hypothesis.What does this example tell you about the exactly identified case? If your
variables pass the test, is this sufficient for these variables to be good instruments?
"overidentification?" State the null hypothesis.Describe how to calculate the J-statistic
and what its distribution is.Use an example of two instruments and one endogenous
variable to explain under what situation the test will be likely to reject the null
hypothesis.What does this example tell you about the exactly identified case? If your
variables pass the test, is this sufficient for these variables to be good instruments?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
You started your econometrics course by studying the OLS estimator extensively, first
for the simple regression case and then for extensions of it.You have now learned about
the instrumental variable estimator.Under what situation would you prefer one to the
other? Be specific in explaining under which situations one estimation method generates
superior results.
for the simple regression case and then for extensions of it.You have now learned about
the instrumental variable estimator.Under what situation would you prefer one to the
other? Be specific in explaining under which situations one estimation method generates
superior results.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Consider a model with one endogenous regressor and two instruments.Then the J- statistic will be large
A)if the number of observations are very large.
B)if the coefficients are very different when estimating the coefficients using one instrument at a time.
C)if the TSLS estimates are very different from the OLS estimates.
D)when you use homoskedasticity-only standard errors.
A)if the number of observations are very large.
B)if the coefficients are very different when estimating the coefficients using one instrument at a time.
C)if the TSLS estimates are very different from the OLS estimates.
D)when you use homoskedasticity-only standard errors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Here are some examples of the instrumental variables regression model.In each case you
are given the number of instruments and the J-statistic.Find the relevant value from the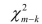 distribution, using a 1% and 5% significance level, and make a decision whether or
distribution, using a 1% and 5% significance level, and make a decision whether or
not to reject the null hypothesis.
(a)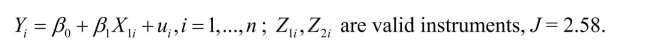
are given the number of instruments and the J-statistic.Find the relevant value from the
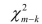 distribution, using a 1% and 5% significance level, and make a decision whether or
distribution, using a 1% and 5% significance level, and make a decision whether ornot to reject the null hypothesis.
(a)
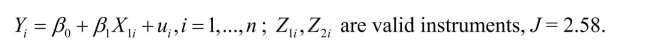

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
To study the determinants of growth between the countries of the world, researchers have
used panels of countries and observations spanning over long periods of time (e.g.1965-
1975, 1975-1985, 1985-1990).Some of these studies have focused on the effect that
inflation has on growth and found that although the effect is small for a given time
period, it accumulates over time and therefore has an important negative effect.
(a)Explain why the OLS estimator may be biased in this case.
used panels of countries and observations spanning over long periods of time (e.g.1965-
1975, 1975-1985, 1985-1990).Some of these studies have focused on the effect that
inflation has on growth and found that although the effect is small for a given time
period, it accumulates over time and therefore has an important negative effect.
(a)Explain why the OLS estimator may be biased in this case.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Consider the following model of demand and supply of coffee: 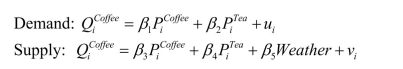 (variables are measure in deviations from means, so that the constant is omitted).
(variables are measure in deviations from means, so that the constant is omitted).
What are the expected signs of the various coefficients this model? Assume that the price
of tea and Weather are exogenous variables.Are the coefficients in the supply equation
identified? Are the coefficients in the demand equation identified? Are they
overidentified? Is this result surprising given that there are more exogenous regressors in
the second equation?
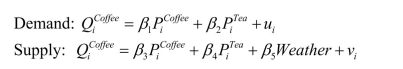 (variables are measure in deviations from means, so that the constant is omitted).
(variables are measure in deviations from means, so that the constant is omitted).What are the expected signs of the various coefficients this model? Assume that the price
of tea and Weather are exogenous variables.Are the coefficients in the supply equation
identified? Are the coefficients in the demand equation identified? Are they
overidentified? Is this result surprising given that there are more exogenous regressors in
the second equation?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Your textbook gave an example of attempting to estimate the demand for a good in a
market, but being unable to do so because the demand function was not identified.Is this
the case for every market? Consider, for example, the demand for sports events.One of
your peers estimated the following demand function after collecting data over two years
for every one of the 162 home games of the 2000 and 2001 season for the Los Angeles
Dodgers. Where Attend is announced stadium attendance, Temperat it the average temperature on
Where Attend is announced stadium attendance, Temperat it the average temperature on
game day, DodgNetWin are the net wins of the Dodgers before the game (wins-losses),
OppNetWin is the opposing team's net wins at the end of the previous season, and
DFSaSu, Drain, D150m, Ddiv, and D2001 are binary variables, taking a value of 1 if the
game was played on a weekend, it rained during that day, the opposing team was within a
150 mile radius, plays in the same division as the Dodgers, and during 2001, respectively.
Numbers in parenthesis are heteroskedasticity- robust standard errors.
Even if there is no identification problem, is it likely that all regressors are uncorrelated
with the error term? If not, what are the consequences?
market, but being unable to do so because the demand function was not identified.Is this
the case for every market? Consider, for example, the demand for sports events.One of
your peers estimated the following demand function after collecting data over two years
for every one of the 162 home games of the 2000 and 2001 season for the Los Angeles
Dodgers.
 Where Attend is announced stadium attendance, Temperat it the average temperature on
Where Attend is announced stadium attendance, Temperat it the average temperature ongame day, DodgNetWin are the net wins of the Dodgers before the game (wins-losses),
OppNetWin is the opposing team's net wins at the end of the previous season, and
DFSaSu, Drain, D150m, Ddiv, and D2001 are binary variables, taking a value of 1 if the
game was played on a weekend, it rained during that day, the opposing team was within a
150 mile radius, plays in the same division as the Dodgers, and during 2001, respectively.
Numbers in parenthesis are heteroskedasticity- robust standard errors.
Even if there is no identification problem, is it likely that all regressors are uncorrelated
with the error term? If not, what are the consequences?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
(Requires Matrix Algebra)The population multiple regression model can be written in
matrix form as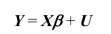
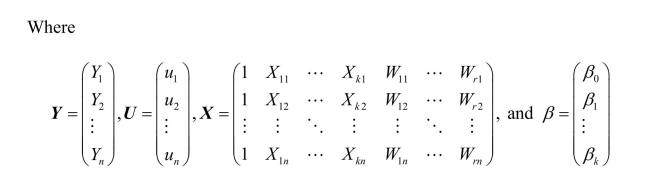 Note that the X matrix contains both k endogenous regressors and (r +1)included
Note that the X matrix contains both k endogenous regressors and (r +1)included
exogenous regressors (the constant is obviously exogenous).
The instrumental variable estimator for the overidentified case is
matrix form as
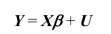
 Note that the X matrix contains both k endogenous regressors and (r +1)included
Note that the X matrix contains both k endogenous regressors and (r +1)includedexogenous regressors (the constant is obviously exogenous).
The instrumental variable estimator for the overidentified case is


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Earnings functions, whereby the log of earnings is regressed on years of education, years
of on the job training, and individual characteristics, have been studied for a variety of
reasons.Some studies have focused on the returns to education, others on discrimination,
union non-union differentials, etc.For all these studies, a major concern has been the fact
that ability should enter as a determinant of earnings, but that it is close to impossible to
measure and therefore represents an omitted variable.
Assume that the coefficient on years of education is the parameter of interest.Given that
education is positively correlated to ability, since, for example, more able students attract
scholarships and hence receive more years of education, the OLS estimator for the
returns to education could be upward biased.To overcome this problem, various authors have used instrumental variable estimation techniques.For each of the instruments
potential instruments listed below briefly discuss instrument validity.
(a)The individual's postal zip code.
Answer (b)The individual's IQ or testscore on a work related exam.
(b)The individual's IQ or testscore on a work related exam.
Answer: There is instrument relevance in this case, since, on average, individuals who
do well in intelligence scores or other work related test scores, will have more
years of education.Unfortunately there is bound to be a high correlation with
the omitted variable ability, since this is what these tests are supposed to
measure.
(c)Years of education for the individual's mother or father.
Answer: A non-zero correlation between the mother's or father's years of education and
the individual's years of education can be expected.Hence this is a relevant
instrument.However, it is not clear that the parent's years of education are
uncorrelated with parent's ability, which in turn, can be a major determinant of
the individual's ability.If this is the case, then years of education of the mother
or father is not a valid instrument.
(d)Number of siblings the individual has.
of on the job training, and individual characteristics, have been studied for a variety of
reasons.Some studies have focused on the returns to education, others on discrimination,
union non-union differentials, etc.For all these studies, a major concern has been the fact
that ability should enter as a determinant of earnings, but that it is close to impossible to
measure and therefore represents an omitted variable.
Assume that the coefficient on years of education is the parameter of interest.Given that
education is positively correlated to ability, since, for example, more able students attract
scholarships and hence receive more years of education, the OLS estimator for the
returns to education could be upward biased.To overcome this problem, various authors have used instrumental variable estimation techniques.For each of the instruments
potential instruments listed below briefly discuss instrument validity.
(a)The individual's postal zip code.
Answer
 (b)The individual's IQ or testscore on a work related exam.
(b)The individual's IQ or testscore on a work related exam.Answer: There is instrument relevance in this case, since, on average, individuals who
do well in intelligence scores or other work related test scores, will have more
years of education.Unfortunately there is bound to be a high correlation with
the omitted variable ability, since this is what these tests are supposed to
measure.
(c)Years of education for the individual's mother or father.
Answer: A non-zero correlation between the mother's or father's years of education and
the individual's years of education can be expected.Hence this is a relevant
instrument.However, it is not clear that the parent's years of education are
uncorrelated with parent's ability, which in turn, can be a major determinant of
the individual's ability.If this is the case, then years of education of the mother
or father is not a valid instrument.
(d)Number of siblings the individual has.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
You have estimated a government reaction function, i.e., a multiple regression equation,
where a government instrument, say the federal funds rate, depends on past government
target variables, such as inflation and unemployment rates.In addition, you added the
previous period's popularity deficit of the government,e.g.the (approval rating of the
president - 50%), as one of the regressors.Your idea is that the Federal Reserve,
although formally independent, will try to expand the economy if the president is
unpopular.One of your peers, a political science student, points out that approval ratings
depend on the state of the economy and thereby indirectly on government instruments.It
is therefore endogenous and should be estimated along with the reaction function.
Initially you want to reply by using a phrase that includes the words "money neutrality"
but are worried about a lengthy debate.Instead you state that as an economist, you are
not concerned about government approval ratings, and that government approval ratings
are determined outside your (the economic)model.Does your whim make the regressor
exogenous? Why or why not?
where a government instrument, say the federal funds rate, depends on past government
target variables, such as inflation and unemployment rates.In addition, you added the
previous period's popularity deficit of the government,e.g.the (approval rating of the
president - 50%), as one of the regressors.Your idea is that the Federal Reserve,
although formally independent, will try to expand the economy if the president is
unpopular.One of your peers, a political science student, points out that approval ratings
depend on the state of the economy and thereby indirectly on government instruments.It
is therefore endogenous and should be estimated along with the reaction function.
Initially you want to reply by using a phrase that includes the words "money neutrality"
but are worried about a lengthy debate.Instead you state that as an economist, you are
not concerned about government approval ratings, and that government approval ratings
are determined outside your (the economic)model.Does your whim make the regressor
exogenous? Why or why not?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
 where Z is a valid instrument for X.
where Z is a valid instrument for X.(a)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The two conditions for instrument validity are 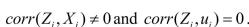
The reason for the inconsistency of OLS is that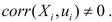
But if X and Z are correlated, and X and u are also correlated, then how can Z and u not be correlated? Explain.
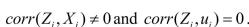
The reason for the inconsistency of OLS is that
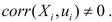
But if X and Z are correlated, and X and u are also correlated, then how can Z and u not be correlated? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
(Requires Chapter 8)When using panel data and in the presence of endogenous regressors
A)the TSLS does not exist.
B)you do not have to worry about the validity of instruments, since there are so many fixed effects.
C)the OLS estimator is consistent.
D)application of the TSLS estimator is straightforward if you use two time periods and difference the data.
A)the TSLS does not exist.
B)you do not have to worry about the validity of instruments, since there are so many fixed effects.
C)the OLS estimator is consistent.
D)application of the TSLS estimator is straightforward if you use two time periods and difference the data.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Write an essay about where valid instruments come from.Part of your explorations must
deal with checking the validity of instruments and what the consequences of weak
instruments are.
deal with checking the validity of instruments and what the consequences of weak
instruments are.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 40 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








