Deck 14: Introduction to Time Series Regression and Forecasting
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/36
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 14: Introduction to Time Series Regression and Forecasting
1
Departures from stationarity
A)jeopardize forecasts and inference based on time series regression.
B)occur often in cross-sectional data.
C)can be made to have less severe consequences by using log-log specifications.
D)cannot be fixed
A)jeopardize forecasts and inference based on time series regression.
B)occur often in cross-sectional data.
C)can be made to have less severe consequences by using log-log specifications.
D)cannot be fixed
A
2
The Times Series Regression with Multiple Predictors 

A
3
Negative autocorrelation in the change of a variable implies that
A)the variable contains only negative values.
B)the series is not stable.
C)an increase in the variable in one period is, on average, associated with a decrease in the next.
D)the data is negatively trended
A)the variable contains only negative values.
B)the series is not stable.
C)an increase in the variable in one period is, on average, associated with a decrease in the next.
D)the data is negatively trended
C
4
The random walk model is an example of a
A)deterministic trend model.
B)binomial model.
C)stochastic trend model.
D)stationary model.
A)deterministic trend model.
B)binomial model.
C)stochastic trend model.
D)stationary model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The Granger Causality Test 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The forecast is
A)made for some date beyond the data set used to estimate the regression.
B)another word for the OLS predicted value.
C)equal to the residual plus the OLS predicted value.
D)close to 1.96 times the standard deviation of Y during the sample.
A)made for some date beyond the data set used to estimate the regression.
B)another word for the OLS predicted value.
C)equal to the residual plus the OLS predicted value.
D)close to 1.96 times the standard deviation of Y during the sample.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Pseudo out of sample forecasting can be used for the following reasons with the exception of
A)giving the forecaster a sense of how well the model forecasts at the end of the sample.
B)estimating the RMSFE.
C)analyzing whether or not a time series contains a unit root.
D)evaluating the relative forecasting performance of two or more forecasting models.
A)giving the forecaster a sense of how well the model forecasts at the end of the sample.
B)estimating the RMSFE.
C)analyzing whether or not a time series contains a unit root.
D)evaluating the relative forecasting performance of two or more forecasting models.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
In order to make reliable forecasts with time series data, all of the following conditions are needed with the exception of
A)coefficients having been estimated precisely.
B)the regression having high explanatory power.
C)the regression being stable.
D)the presence of omitted variable bias.
A)coefficients having been estimated precisely.
B)the regression having high explanatory power.
C)the regression being stable.
D)the presence of omitted variable bias.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
To choose the number of lags in either an autoregression or in a time series regression model with multiple predictors, you can use any of the following test statistics with the
Exception of the
A)F-statistic.
B)Akaike Information Criterion.
C)Bayes Information Criterion.
D)Augmented Dickey-Fuller test.
Exception of the
A)F-statistic.
B)Akaike Information Criterion.
C)Bayes Information Criterion.
D)Augmented Dickey-Fuller test.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Autoregressive distributed lag models include
A)current and lagged values of the error term.
B)lags of the dependent variable, and lagged values of additional predictor variables.
C)current and lagged values of the residuals.
D)lags and leads of the dependent variable.
A)current and lagged values of the error term.
B)lags of the dependent variable, and lagged values of additional predictor variables.
C)current and lagged values of the residuals.
D)lags and leads of the dependent variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
One of the sources of error in the RMSFE in the AR(1) model is
A) the error in estimating the coefficients
B) due to measuring variables in logarithms.
C) that the value of the explanatory variable is not known with certainty when making a forecast.
D) the model only looks at the previous period's value of Y when the entire history should be taken into account.
A) the error in estimating the coefficients
B) due to measuring variables in logarithms.
C) that the value of the explanatory variable is not known with certainty when making a forecast.
D) the model only looks at the previous period's value of Y when the entire history should be taken into account.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Problems caused by stochastic trends include all of the following with the exception of
A)the estimator of an AR(1)is biased towards zero if its true value is one.
B)the model can no longer be estimated by OLS.
C)t-statistics on regression coefficients can have a nonnormal distribution, even in large samples.
D)the presence of spurious regression..
A)the estimator of an AR(1)is biased towards zero if its true value is one.
B)the model can no longer be estimated by OLS.
C)t-statistics on regression coefficients can have a nonnormal distribution, even in large samples.
D)the presence of spurious regression..

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The first difference of the logarithm of equals
A) the first difference of Y .
B) the difference between the lead and the lag of Y .
C) approximately the growth rate of Y when the growth rate is small.
D) the growth rate of Y exactly.
A) the first difference of Y .
B) the difference between the lead and the lag of Y .
C) approximately the growth rate of Y when the growth rate is small.
D) the growth rate of Y exactly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The root mean squared forecast error (RMSFE)is defined as 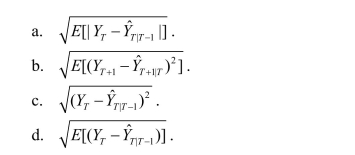
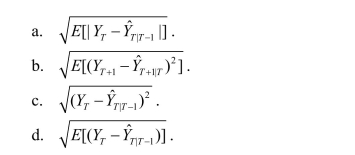

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The time interval between observations can be all of the following with the exception of data collected
A)daily.
B)by decade.
C)bi-weekly.
D)across firms.
A)daily.
B)by decade.
C)bi-weekly.
D)across firms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Stationarity means that the
A)error terms are not correlated.
B)probability distribution of the time series variable does not change over time.
C)time series has a unit root.
D)forecasts remain within 1.96 standard deviation outside the sample period.
A)error terms are not correlated.
B)probability distribution of the time series variable does not change over time.
C)time series has a unit root.
D)forecasts remain within 1.96 standard deviation outside the sample period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
An autoregression is a regression
A)of a dependent variable on lags of regressors.
B)that allows for the errors to be correlated.
C)model that relates a time series variable to its past values.
D)to predict sales in a certain industry.
A)of a dependent variable on lags of regressors.
B)that allows for the errors to be correlated.
C)model that relates a time series variable to its past values.
D)to predict sales in a certain industry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
One reason for computing the logarithms (ln), or changes in logarithms, of economic time series is that
A)numbers often get very large.
B)economic variables are hardly ever negative.
C)they often exhibit growth that is approximately exponential.
D)natural logarithms are easier to work with than base 10 logarithms.
A)numbers often get very large.
B)economic variables are hardly ever negative.
C)they often exhibit growth that is approximately exponential.
D)natural logarithms are easier to work with than base 10 logarithms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Time series variables fail to be stationary when
A)the economy experiences severe fluctuations.
B)the population regression has breaks.
C)there is strong seasonal variation in the data.
D)there are no trends.
A)the economy experiences severe fluctuations.
B)the population regression has breaks.
C)there is strong seasonal variation in the data.
D)there are no trends.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The AR(p) model
A) is defined as
B) represents as a linear function of p of its lagged values.
C) can be represented as follows:
D) can be written as
A) is defined as
B) represents as a linear function of p of its lagged values.
C) can be represented as follows:
D) can be written as

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
 (a)
(a) 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The Augmented Dickey Fuller (ADF)t-statistic
A)has a normal distribution in large samples.
B)has the identical distribution whether or not a trend is included or not.
C)is a two-sided test.
D)is an extension of the Dickey-Fuller test when the underlying model is AR(p) rather than AR(1).
A)has a normal distribution in large samples.
B)has the identical distribution whether or not a trend is included or not.
C)is a two-sided test.
D)is an extension of the Dickey-Fuller test when the underlying model is AR(p) rather than AR(1).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
(Requires Appendix material): Show that the AR(1) process 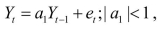
be converted to a process.
process.
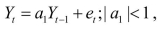
be converted to a
 process.
process.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The following two graphs give you a plot of the United States aggregate unemployment
rate for the sample period 1962:I to 1999:IV, and the (log)level of real United States
GDP for the sample period 1962:I to 1995:IV.You want test for stationarity in both
cases.Indicate whether or not you should include a time trend in your Augmented
Dickey-Fuller test and why.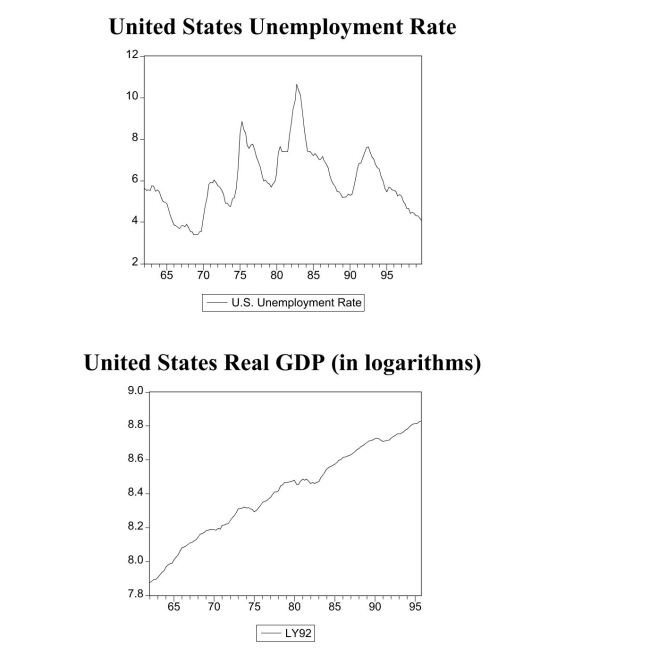
rate for the sample period 1962:I to 1999:IV, and the (log)level of real United States
GDP for the sample period 1962:I to 1995:IV.You want test for stationarity in both
cases.Indicate whether or not you should include a time trend in your Augmented
Dickey-Fuller test and why.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
You want to determine whether or not the unemployment rate for the United States has a
stochastic trend using the Augmented Dickey Fuller Test (ADF).The BIC suggests using
3 lags, while the AIC suggests 4 lags.
(a)Which of the two will you use for your choice of the optimal lag length?
stochastic trend using the Augmented Dickey Fuller Test (ADF).The BIC suggests using
3 lags, while the AIC suggests 4 lags.
(a)Which of the two will you use for your choice of the optimal lag length?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
 (a)
(a) 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
If a "break" occurs in the population regression function, then
A)inference and forecasting are compromised when neglecting it.
B)an Augmented Dickey Fuller test, rather than the Dickey Fuller test, should be used to test for stationarity.
C)this suggests the presence of a deterministic trend in addition to a stochastic trend.
D)forecasting, but not inference, is unaffected, if the break occurs during the first half of the sample period.
A)inference and forecasting are compromised when neglecting it.
B)an Augmented Dickey Fuller test, rather than the Dickey Fuller test, should be used to test for stationarity.
C)this suggests the presence of a deterministic trend in addition to a stochastic trend.
D)forecasting, but not inference, is unaffected, if the break occurs during the first half of the sample period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
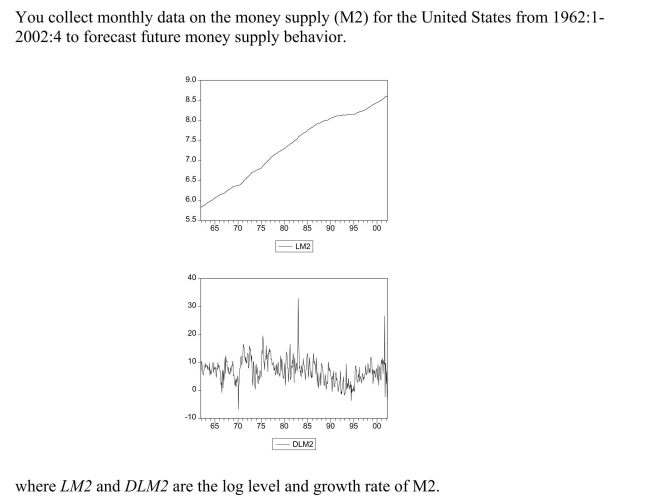 (a)Using quarterly data, when analyzing inflation and unemployment in the United States,
(a)Using quarterly data, when analyzing inflation and unemployment in the United States,the textbook converted log levels of variables into growth rates by differencing the log
levels, and then multiplying these by 400.Given that you have monthly data, how would
you proceed here?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29

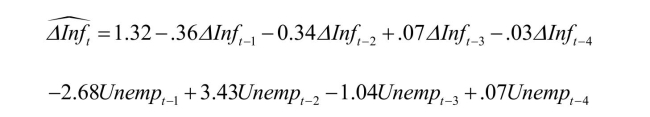 Assume that the inflation rate is constant in the long-run and calculate the resulting
Assume that the inflation rate is constant in the long-run and calculate the resultingunemployment rate.What does the solution represent? Is it reasonable to assume that this
long-run solution is constant over the estimation period 1962-1999? If not, how could
you detect the instability?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
You have decided to use the Dickey Fuller (DF)test on the United States aggregate
unemployment rate (sample period 1962:I - 1995:IV).As a result, you estimate the
following AR(1)model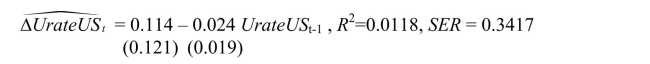 You recall that your textbook mentioned that this form of the AR(1)is convenient
You recall that your textbook mentioned that this form of the AR(1)is convenient
because it allows for you to test for the presence of a unit root by using the t- statistic of
the slope.Being adventurous, you decide to estimate the original form of the AR(1)
instead, which results in the following output
unemployment rate (sample period 1962:I - 1995:IV).As a result, you estimate the
following AR(1)model
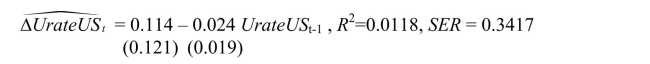 You recall that your textbook mentioned that this form of the AR(1)is convenient
You recall that your textbook mentioned that this form of the AR(1)is convenientbecause it allows for you to test for the presence of a unit root by using the t- statistic of
the slope.Being adventurous, you decide to estimate the original form of the AR(1)
instead, which results in the following output


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Consider the following model 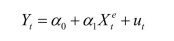 t
t
where the superscript "e" indicates expected values.This may represent an example
where consumption depended on expected, or "permanent," income.Furthermore, let
expected income be formed as follows: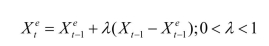 1
1
This particular type of expectation formation is called the "adaptive expectations
hypothesis."
(a)
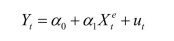 t
twhere the superscript "e" indicates expected values.This may represent an example
where consumption depended on expected, or "permanent," income.Furthermore, let
expected income be formed as follows:
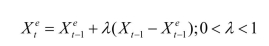 1
1This particular type of expectation formation is called the "adaptive expectations
hypothesis."
(a)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Having learned in macroeconomics that consumption depends on disposable income, you
want to determine whether or not disposable income helps predict future consumption.
You collect data for the sample period 1962:I to 1995:IV and plot the two variables.
(a)To determine whether or not past values of personal disposable income growth rates help
to predict consumption growth rates, you estimate the following relationship.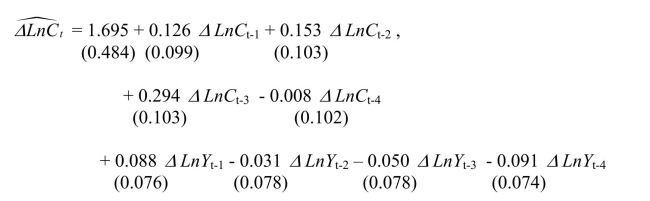 The Granger causality test for the exclusion on all four lags of the GDP growth rate is
The Granger causality test for the exclusion on all four lags of the GDP growth rate is
0.98.Find the critical value for the 1%, the 5%, and the 10% level from the relevant table
and make a decision on whether or not these additional variables Granger cause the
change in the growth rate of consumption.
want to determine whether or not disposable income helps predict future consumption.
You collect data for the sample period 1962:I to 1995:IV and plot the two variables.
(a)To determine whether or not past values of personal disposable income growth rates help
to predict consumption growth rates, you estimate the following relationship.
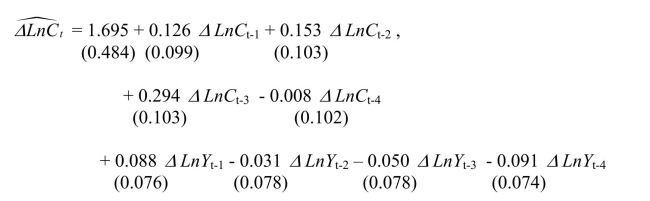 The Granger causality test for the exclusion on all four lags of the GDP growth rate is
The Granger causality test for the exclusion on all four lags of the GDP growth rate is0.98.Find the critical value for the 1%, the 5%, and the 10% level from the relevant table
and make a decision on whether or not these additional variables Granger cause the
change in the growth rate of consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
You set out to forecast the unemployment rate in the United States (UrateUS), using
quarterly data from 1960, first quarter, to 1999, fourth quarter.
(a)The following table presents the first four autocorrelations for the United States
aggregate unemployment rate and its change for the time period 1960 (first quarter)to
1999 (fourth quarter).Explain briefly what these two autocorrelations measure.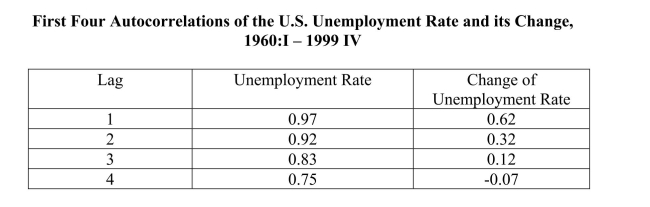
quarterly data from 1960, first quarter, to 1999, fourth quarter.
(a)The following table presents the first four autocorrelations for the United States
aggregate unemployment rate and its change for the time period 1960 (first quarter)to
1999 (fourth quarter).Explain briefly what these two autocorrelations measure.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
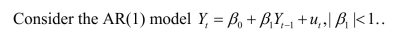 (a)
(a) 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The textbook displayed the accompanying four economic time series with "markedly
different patterns." For each indicate what you think the sample autocorrelations of the
level (Y)and change ( ΔY )will be and explain your reasoning.
(a)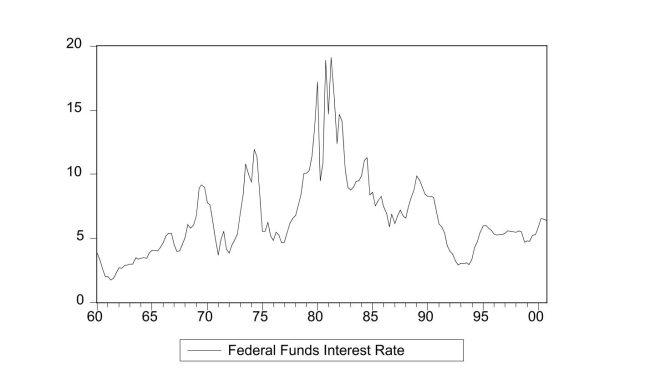
different patterns." For each indicate what you think the sample autocorrelations of the
level (Y)and change ( ΔY )will be and explain your reasoning.
(a)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
You should use the QLR test for breaks in the regression coefficients, when
A)the Chow F-test has a p value of between 0.05 and 0.10.
B)the suspected break data is not known.
C)there are breaks in only some, but not all, of the regression coefficients.
D)the suspected break data is known.
A)the Chow F-test has a p value of between 0.05 and 0.10.
B)the suspected break data is not known.
C)there are breaks in only some, but not all, of the regression coefficients.
D)the suspected break data is known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 36 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








