Deck 19: Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/96
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 19: Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
1
The direction of heat flow between two objects depends on the amount of internal energy each of the objects has.
False
2
The heat required to change a substance from the solid to the liquid state is referred to as the
A)heat of fusion.
B)heat of vaporization.
C)heat of melting.
D)heat of freezing.
E)heat of condensation.
A)heat of fusion.
B)heat of vaporization.
C)heat of melting.
D)heat of freezing.
E)heat of condensation.
heat of fusion.
3
It is a well-known fact that water has a higher specific heat capacity than iron. Now, consider equal masses of water and iron that are initially in thermal equilibrium. The same amount of heat, 30 calories, is added to each. Which statement is true?
A)They remain in thermal equilibrium.
B)They are no longer in thermal equilibrium; the iron is warmer.
C)They are no longer in thermal equilibrium; the water is warmer.
D)It is impossible to say without knowing the exact mass involved.
E)It is impossible to say without knowing the exact specific heat capacities.
A)They remain in thermal equilibrium.
B)They are no longer in thermal equilibrium; the iron is warmer.
C)They are no longer in thermal equilibrium; the water is warmer.
D)It is impossible to say without knowing the exact mass involved.
E)It is impossible to say without knowing the exact specific heat capacities.
They are no longer in thermal equilibrium; the iron is warmer.
4
Distinguish between heat, internal energy, and temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A thermally isolated system is made up of a hot piece of aluminum and a cold piece of copper; the aluminum and the copper are in thermal contact. The specific heat capacity of aluminum is more than double that of copper. Which object experiences the greater temperature change during the time the system takes to reach thermal equilibrium?
A)the copper
B)the aluminum
C)neither; both experience the same size temperature change
D)it is impossible to tell without knowing the masses
E)it is impossible to tell without knowing the volumes
A)the copper
B)the aluminum
C)neither; both experience the same size temperature change
D)it is impossible to tell without knowing the masses
E)it is impossible to tell without knowing the volumes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A cup of water is scooped up from a swimming pool of water. Compare the temperature T and the internal energy U of the water, in both the cup and the swimming pool.
A)TPool is greater than TCup, and the U is the same.
B)TPool is less than TCup, and the U is the same.
C)TPool is equal to TCup, and UPool is greater than UCup.
D)TPool is equal to TCup, and UPool is less than UCup.
E)TPool is equal to TCup, and UPool is equal to UCup.
A)TPool is greater than TCup, and the U is the same.
B)TPool is less than TCup, and the U is the same.
C)TPool is equal to TCup, and UPool is greater than UCup.
D)TPool is equal to TCup, and UPool is less than UCup.
E)TPool is equal to TCup, and UPool is equal to UCup.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Conductive heat transfer can only occur if solids mediate the energy transfer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Convective heat transfer can only occur if fluids mediate the energy transfer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The heat required to change a substance from the liquid to the vapor state is referred to as the
A)heat of fusion.
B)heat of vaporization.
C)heat of evaporation.
D)heat of condensation.
E)heat of melting.
A)heat of fusion.
B)heat of vaporization.
C)heat of evaporation.
D)heat of condensation.
E)heat of melting.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The internal energy of an ideal gas is changed by adding heat Q to the system and also by doing work W on the gas. What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
A)4.186Q - W
B)Q - 4.186W
C)W - Q
D)Q + W
E)Q - W
A)4.186Q - W
B)Q - 4.186W
C)W - Q
D)Q + W
E)Q - W

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Is it possible to transfer heat from a cold reservoir to a hot reservoir?
A)No.
B)Yes; this will happen naturally.
C)Yes, but work will have to be done.
D)Theoretically yes, but it hasn't been accomplished yet.
A)No.
B)Yes; this will happen naturally.
C)Yes, but work will have to be done.
D)Theoretically yes, but it hasn't been accomplished yet.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
State the First Law of Thermodynamics.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A thermally isolated system is made up of a hot piece of aluminum and a cold piece of copper; the aluminum and the copper are in thermal contact. The specific heat capacity of aluminum is more than double that of copper. Which object experiences the greater magnitude gain or loss of heat during the time the system takes to reach thermal equilibrium?
A)the aluminum
B)the copper
C)neither; both experience the same size gain or loss of heat
D)it is impossible to tell without knowing the masses
E)it is impossible to tell without knowing the volumes
A)the aluminum
B)the copper
C)neither; both experience the same size gain or loss of heat
D)it is impossible to tell without knowing the masses
E)it is impossible to tell without knowing the volumes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Radiative heat transfer requires a fluid to mediate the energy transfer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In the first law of thermodynamics, Q is the heat gained by the system, that is, Q is positive if the system gains heat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Describe the technique know as calorimetry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
FIGURE 19-1 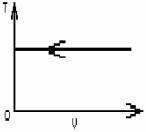
The process shown on the T-V graph in Fig. 19-1 is an
A)adiabatic compression.
B)isothermal compression.
C)isochoric compression.
D)isobaric compression.
E)isovolumetric compression.

The process shown on the T-V graph in Fig. 19-1 is an
A)adiabatic compression.
B)isothermal compression.
C)isochoric compression.
D)isobaric compression.
E)isovolumetric compression.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In the first law of thermodynamics, W is the work done on the system, that is, W is positive if work is done on the system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A chunk of ice (T = -20°C) is added to a thermally insulated container of cold water (T = 0°C). What happens in the container?
A)The ice melts until thermal equilibrium is established.
B)The water cools down until thermal equilibrium is established.
C)Some of the water freezes and the chunk of ice gets larger.
D)none of the above
A)The ice melts until thermal equilibrium is established.
B)The water cools down until thermal equilibrium is established.
C)Some of the water freezes and the chunk of ice gets larger.
D)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Is it possible to transfer heat from a hot reservoir to a cold reservoir?
A)No.
B)Yes; this will happen naturally.
C)Yes, but work will have to be done.
D)Theoretically yes, but it hasn't been accomplished yet.
A)No.
B)Yes; this will happen naturally.
C)Yes, but work will have to be done.
D)Theoretically yes, but it hasn't been accomplished yet.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
When the first law of thermodynamics, Q = ΔU + W, is applied to an ideal gas that is taken through an adiabatic process,
A)ΔU = 0.
B)W = 0.
C)Q = 0.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)ΔU = 0.
B)W = 0.
C)Q = 0.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
When the first law of thermodynamics, Q = ΔU + W, is applied to an ideal gas that is taken through an isothermal process,
A)ΔU = 0
B)W = 0
C)Q = 0
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)ΔU = 0
B)W = 0
C)Q = 0
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Consider two cylinders of gas identical in all respects except that one contains O2 and the other He. Both hold the same volume of gas at STP and are closed by a movable piston at one end. Both gases are now compressed adiabatically to one-third their original volume. Which gas will show the greater temperature increase?
A)the O2
B)the He
C)Neither; both will show the same increase.
D)It's impossible to tell from the information given.
A)the O2
B)the He
C)Neither; both will show the same increase.
D)It's impossible to tell from the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
During which type of process applied to an ideal gas is there no work done by the gas?
A)adiabatic
B)isothermal
C)isochoric
D)isobaric
E)Work is done by the gas during any change to the gas.
A)adiabatic
B)isothermal
C)isochoric
D)isobaric
E)Work is done by the gas during any change to the gas.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
When a gas expands adiabatically,
A)the internal energy of the gas decreases.
B)the internal energy of the gas increases.
C)there is no work done by the gas.
D)work is done on the gas.
E)heat flows out of the system.
A)the internal energy of the gas decreases.
B)the internal energy of the gas increases.
C)there is no work done by the gas.
D)work is done on the gas.
E)heat flows out of the system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When the first law of thermodynamics, Q = ΔU + W, is applied to an ideal gas that is taken through an isochoric process,
A)ΔU = 0.
B)W = 0.
C)Q = 0.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)ΔU = 0.
B)W = 0.
C)Q = 0.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
In an isobaric process, there is no change in
A)pressure.
B)temperature.
C)volume.
D)internal energy.
E)heat.
A)pressure.
B)temperature.
C)volume.
D)internal energy.
E)heat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
FIGURE 19-3 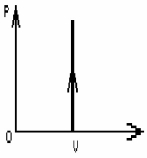
The process shown on the PV diagram in Fig. 19-3 is
A)adiabatic.
B)isothermal.
C)isochoric.
D)isobaric.
E)idealistic.

The process shown on the PV diagram in Fig. 19-3 is
A)adiabatic.
B)isothermal.
C)isochoric.
D)isobaric.
E)idealistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The process whereby heat flows by the mass movement of molecules from one place to another is referred to as
A)conduction.
B)convection.
C)radiation.
D)inversion.
E)evaporation.
A)conduction.
B)convection.
C)radiation.
D)inversion.
E)evaporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
In an isochoric process, there is no change in
A)pressure.
B)temperature.
C)volume.
D)internal energy.
E)heat.
A)pressure.
B)temperature.
C)volume.
D)internal energy.
E)heat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
When the first law of thermodynamics, Q = ΔU + W, is applied to an ideal gas that is taken through an isobaric process,
A)ΔU = 0.
B)W = 0.
C)Q = 0.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)ΔU = 0.
B)W = 0.
C)Q = 0.
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The process whereby heat flows in the absence of any medium is referred to as
A)conduction.
B)convection.
C)radiation.
D)inversion.
E)evaporation.
A)conduction.
B)convection.
C)radiation.
D)inversion.
E)evaporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The process whereby heat flows by means of molecular collisions is referred to as
A)conduction.
B)convection.
C)radiation.
D)inversion.
E)evaporation.
A)conduction.
B)convection.
C)radiation.
D)inversion.
E)evaporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
During which type of process applied to an ideal gas is there no change in internal energy of the gas?
A)isobaric
B)isothermal
C)isochoric
D)adiabatic
E)Internal energy changes during any of these processes.
A)isobaric
B)isothermal
C)isochoric
D)adiabatic
E)Internal energy changes during any of these processes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
An ideal gas starts in state A at temperature T. The gas expands to new volume V by an adiabatic process and its final temperature is Tʹ. What is the relationship between T and Tʹ?
A)T = Tʹ
B)T > Tʹ
C)T < Tʹ
D)The answer depends on the heat capacity of the ideal gas.
E)The answer depends on the number of moles of gas and the pressure.
A)T = Tʹ
B)T > Tʹ
C)T < Tʹ
D)The answer depends on the heat capacity of the ideal gas.
E)The answer depends on the number of moles of gas and the pressure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
FIGURE 19-2 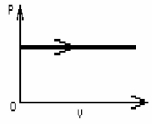
The process shown on the PV diagram in Fig. 19-2 is an
A)adiabatic expansion.
B)isothermal expansion.
C)isometric expansion.
D)isobaric expansion.
E)isovolumetric compression.

The process shown on the PV diagram in Fig. 19-2 is an
A)adiabatic expansion.
B)isothermal expansion.
C)isometric expansion.
D)isobaric expansion.
E)isovolumetric compression.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
In an isothermal process, there is no change in
A)pressure.
B)temperature.
C)volume.
D)heat.
E)internal energy.
A)pressure.
B)temperature.
C)volume.
D)heat.
E)internal energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
During which type of process applied to an ideal gas is there no heat added to the gas?
A)isobaric
B)isochoric
C)isothermal
D)adiabatic
E)A and C
A)isobaric
B)isochoric
C)isothermal
D)adiabatic
E)A and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A gas is quickly compressed in an isolated environment. During the event, the gas exchanged no heat with its surroundings. This process is
A)isothermal.
B)isochoric.
C)isobaric.
D)adiabatic.
E)idealistic.
A)isothermal.
B)isochoric.
C)isobaric.
D)adiabatic.
E)idealistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Consider two cylinders of gas identical in all respects except that one contains O2 and the other He. Both hold the same volume of gas at STP and are closed by a movable piston at one end. Both gases are now compressed adiabatically to one-third their original volume. Which gas will show the greater pressure increase?
A)the O2
B)the He
C)Neither; both will show the same increase.
D)It's impossible to tell from the information given.
A)the O2
B)the He
C)Neither; both will show the same increase.
D)It's impossible to tell from the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The melting point of aluminum is 660°C, the latent heat of fusion is 4.0 × 105 J/kg and its specific heat is 900 J/(kg∙K). How much heat must be added to 500 g of aluminum at 27°C to completely melt it?
A)485 kJ
B)395 kJ
C)273 kJ
D)147 kJ
E)14 kJ
A)485 kJ
B)395 kJ
C)273 kJ
D)147 kJ
E)14 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A camper is about to drink his morning coffee. He pours 400 grams of coffee, initially at 75.0°C, into a 250-g aluminum cup, initially at 16.0°C. What is the equilibrium temperature of the coffee-cup system, assuming no heat is lost to the surroundings? The specific heat of aluminum is 900 J/(kg∙K). Assume that the specific heat of coffee is the same as the specific heat of water.
A)45.5°C
B)62.0°C
C)65.0°C
D)68.0°C
E)71.0°C
A)45.5°C
B)62.0°C
C)65.0°C
D)68.0°C
E)71.0°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
An insulated container is filled with a mix of 400 g of water at 20.0°C and 60 g of ice at 0.00°C. Assuming negligible heat is exchanged with the container, what is the temperature of the mixture when it reaches thermal equilibrium?
A)7.0°C
B)6.0°C
C)0.0°C
D)4.0°C
E)5.0°C
A)7.0°C
B)6.0°C
C)0.0°C
D)4.0°C
E)5.0°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The type of heat transfer that occurs between a stove and a pot placed on it is
A)convective.
B)conductive.
C)radiative.
D)countercurrent.
E)evaporation.
A)convective.
B)conductive.
C)radiative.
D)countercurrent.
E)evaporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The type of heat transfer that occurs between the radiator of a car and the atmosphere, when the car is in motion, is principally
A)convective.
B)conductive.
C)radiative.
D)countercurrent.
E)evaporation.
A)convective.
B)conductive.
C)radiative.
D)countercurrent.
E)evaporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
How much heat must be removed from 456 g of water at 25.0°C to change it into ice at -10.0°C? The specific heat of ice is 2090 J/(kg∙K) and the latent heat of fusion of water is 33.5 × 104 J/kg.
A)105 kJ
B)153 kJ
C)57.3 kJ
D)47.7 kJ
E)210 kJ
A)105 kJ
B)153 kJ
C)57.3 kJ
D)47.7 kJ
E)210 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A 425-g piece of metal at 100°C is dropped into a 100-g aluminum cup containing 500 g of water at 15°C. The final temperature of the system is 40°C. What is the specific heat of the metal, assuming no heat is exchanged with the surroundings? The specific heat of aluminum is 900 J/(kg∙K).
A)1900 J/(kg∙K)
B)2140 J/(kg∙K)
C)3300 J/(kg∙K)
D)3800 J/(kg∙K)
E)4280 J/(kg∙K)
A)1900 J/(kg∙K)
B)2140 J/(kg∙K)
C)3300 J/(kg∙K)
D)3800 J/(kg∙K)
E)4280 J/(kg∙K)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If 40 kcal of heat is added to 2.0 kg of water, what is the resulting temperature change?
A)80C°
B)60C°
C)40C°
D)20C°
E)0.05C°
A)80C°
B)60C°
C)40C°
D)20C°
E)0.05C°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
330 g of water at 55°C are poured into an 855 g aluminum container with an initial temperature of 10°C. The specific heat of aluminum is 900 J/(kg∙K). What is the final temperature of the system, assuming no heat is exchanged with the surroundings?
A)28°C
B)39°C
C)31°C
D)33°C
E)35°C
A)28°C
B)39°C
C)31°C
D)33°C
E)35°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
150 kcal of heat raises the temperature of 2.0 kg of material by 400 F°. What is the material's specific heat capacity?
A)1.35 kcal/kg∙C°
B)1.31 kcal/kg∙C°
C)0.75 kcal/kg∙C°
D)0.34 kcal/kg∙C°
E)0.19 kcal/kg∙C°
A)1.35 kcal/kg∙C°
B)1.31 kcal/kg∙C°
C)0.75 kcal/kg∙C°
D)0.34 kcal/kg∙C°
E)0.19 kcal/kg∙C°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
An athlete doing push-ups performs 650 kJ of work and loses 425 kJ of heat. What is the change in the internal energy of the athlete?
A)-225 kJ
B)-1075 kJ
C)1075 kJ
D)225 kJ
E)276 kJ
A)-225 kJ
B)-1075 kJ
C)1075 kJ
D)225 kJ
E)276 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The type of heat transfer that occurs between warm food and the air in the room is principally
A)convective.
B)conductive.
C)radiative.
D)countercurrent.
E)evaporation.
A)convective.
B)conductive.
C)radiative.
D)countercurrent.
E)evaporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Convection can occur
A)only in solids.
B)only in liquids.
C)only in gases.
D)only in liquids and gases.
E)in solids, liquids, and gases.
A)only in solids.
B)only in liquids.
C)only in gases.
D)only in liquids and gases.
E)in solids, liquids, and gases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The type of heat transfer that occurs between a heating lamp and the food that it is keeping warm is
A)convective.
B)conductive.
C)radiative.
D)countercurrent.
E)evaporation.
A)convective.
B)conductive.
C)radiative.
D)countercurrent.
E)evaporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
How much heat is required to change 456 g of ice at -25.0°C into water at 25.0°C? The specific heat of ice is 2090 J/(kg∙K)and the latent heat of fusion of water is 33.5 × 104 J/kg.
A)224 kJ
B)153 kJ
C)112 kJ
D)71.5 kJ
E)72.5 kJ
A)224 kJ
B)153 kJ
C)112 kJ
D)71.5 kJ
E)72.5 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A 50.0-g sample of a material at 80.0°C is dropped into a calorimeter containing 100.0 g of water at 20.0°C. When the mixture reaches thermal equilibrium, it is at a temperature 24.0°C. If heat transfer to the walls of the calorimeter is negligible, what is the specific heat of the material?
A)0.143 cal/(g∙C°)
B)0.322 cal/(g∙C°)
C)0.221 cal/(g∙C°)
D)0.437 cal/(g∙C°)
E)0.0714 cal/(g∙C°)
A)0.143 cal/(g∙C°)
B)0.322 cal/(g∙C°)
C)0.221 cal/(g∙C°)
D)0.437 cal/(g∙C°)
E)0.0714 cal/(g∙C°)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Ice has a latent heat of fusion of 80 kcal/kg. How much heat is required to melt 200 g of ice?
A)400 J
B)160 J
C)67 kJ
D)32 kJ
E)16 kJ
A)400 J
B)160 J
C)67 kJ
D)32 kJ
E)16 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
By what primary heat transfer mechanism does one end of an iron bar become hot when the other end is placed in a flame?
A)natural convection
B)conduction
C)radiation
D)forced convection
E)countercurrent.
A)natural convection
B)conduction
C)radiation
D)forced convection
E)countercurrent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A 400-g piece of metal at 100°C is dropped into a cup containing 450 g of water at 15.0°C. The final temperature of the system is 40.0°C. What is the specific heat of the metal, assuming no heat is exchanged with the surroundings or the cup?
A)1960 J/(kg∙K)
B)2830 J/(kg∙K)
C)3420 J/(kg∙K)
D)3780 J/(kg∙K)
E)4280 J/(kg∙K)
A)1960 J/(kg∙K)
B)2830 J/(kg∙K)
C)3420 J/(kg∙K)
D)3780 J/(kg∙K)
E)4280 J/(kg∙K)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
A person tries to heat up her bath water by adding 5.0 L of water at 80°C to 60 L of water at 30°C. What is the final temperature of the water?
A)34°C
B)36°C
C)38°C
D)40°C
E)65°C
A)34°C
B)36°C
C)38°C
D)40°C
E)65°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A person makes ice tea by adding ice to 1.8 kg of hot tea, initially at 80°C. How many kilograms of ice, initially at 0°C, are required to bring the mixture to 10°C?
A)1.0 kg
B)1.2 kg
C)1.4 kg
D)1.5 kg
E)1.7 kg
A)1.0 kg
B)1.2 kg
C)1.4 kg
D)1.5 kg
E)1.7 kg

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
During an isothermal process, 5.0 J of heat is removed from an ideal gas. What is the change in internal energy?
A)zero
B)2.5 J
C)5.0 J
D)7.5 J
E)10 J
A)zero
B)2.5 J
C)5.0 J
D)7.5 J
E)10 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
How much heat energy is needed to change 10 kg of water at 50°C to steam at 120°C?
A)4.2 × 105 J
B)2.3 × 107 J
C)4.2 × 106 J
D)3.6 × 106 J
E)2.5 × 107 J
A)4.2 × 105 J
B)2.3 × 107 J
C)4.2 × 106 J
D)3.6 × 106 J
E)2.5 × 107 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
During an isothermal process, 5.0 J of heat is removed from an ideal gas. What is the work done in the process?
A)zero
B)2.0 J
C)5.0 J
D)-5.0 J
E)none of the above
A)zero
B)2.0 J
C)5.0 J
D)-5.0 J
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
An ideal gas undergoes an adiabatic process while doing 25 J of work. What is the change in internal energy?
A)zero
B)50 J
C)25 J
D)-25 J
E)none of the above
A)zero
B)50 J
C)25 J
D)-25 J
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
200 g of ice at 0°C is dropped into a calorimeter of negligible heat capacity containing 350 g of water at 20°C. What is the temperature of the system when it reaches equilibrium? The latent heat of fusion of water is 80 cal/g.
A)0°C
B)24°C
C)-13°C
D)13°C
E)-24°C
A)0°C
B)24°C
C)-13°C
D)13°C
E)-24°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
If 2.0 kg of water at 0°C is to be vaporized, how much heat must be added?
A)1080 cal
B)1080 kcal
C)1140 cal
D)1280 cal
E)1280 kcal
A)1080 cal
B)1080 kcal
C)1140 cal
D)1280 cal
E)1280 kcal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The work done on an ideal gas system in an isothermal process is -400 J. What is the change in internal energy?
A)zero
B)-400 J
C)400 J
D)200 J
E)none of the above
A)zero
B)-400 J
C)400 J
D)200 J
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
In an isochoric process, the internal energy of a system decreases by 50 J. What is the heat exchange?
A)zero
B)25 J
C)50 J
D)-50 J
E)none of the above
A)zero
B)25 J
C)50 J
D)-50 J
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
If you add 900 kJ of heat to 900 g of water at 90.0°C, how much water is left in the container? The latent heat of vaporization of water is 22.6 × 105 J/kg.
A)518 g
B)258 g
C)340 g
D)600 g
E)none
A)518 g
B)258 g
C)340 g
D)600 g
E)none

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
How much heat needs to be removed from 100 g of 85°C water to make -5°C ice?
A)255 cal
B)168 kcal
C)8.5 kcal
D)16.5 kcal
E)16.8 kcal
A)255 cal
B)168 kcal
C)8.5 kcal
D)16.5 kcal
E)16.8 kcal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
200 J of work is done in compressing a gas adiabatically. What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
A)zero
B)100 J
C)150 J
D)200 J
E)There is not enough information to determine.
A)zero
B)100 J
C)150 J
D)200 J
E)There is not enough information to determine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
How much heat is required to change one gram of 0°C ice to 120°C steam?
A)48.7 cal
B)120 cal
C)540 cal
D)730 cal
E)1505 cal
A)48.7 cal
B)120 cal
C)540 cal
D)730 cal
E)1505 cal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Three moles of an ideal gas with a molar heat capacity at constant volume of 4.9 cal/(mol∙K) and a molar heat capacity at constant pressure of 6.9 cal/(mol∙K) starts at 300 K and is heated at constant pressure to 320 K, then cooled at constant volume to its original temperature. How much heat flows into the gas during this two-step process?
A)710 cal
B)-720 cal
C)0 cal
D)120 cal
E)-120 cal
A)710 cal
B)-720 cal
C)0 cal
D)120 cal
E)-120 cal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
A block of ice at 0°C is added to a 150-g aluminum calorimeter cup that holds 200 g of water at 10°C. If all but 2.00 g of ice melt, what was the original mass of the block of ice?
A)31.1 g
B)35.6 g
C)38.8 g
D)42.0 g
E)47.6 g
A)31.1 g
B)35.6 g
C)38.8 g
D)42.0 g
E)47.6 g

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
A quantity of ideal gas requires 800 kJ to raise the temperature of the gas by 10.0 K when the gas is maintained at constant volume. The same quantity of gas requires 900 kJ to raise the temperature of the gas by 10.0 K when the gas is maintained at constant pressure. What is the adiabatic gas constant of this gas?
A)0.889
B)1.13
C)1.22
D)1.67
E)1.40
A)0.889
B)1.13
C)1.22
D)1.67
E)1.40

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
A monatomic gas is cooled by 50 K at constant volume when 831 J of energy is removed from it. How many moles of gas are in the sample?
A)2.50 mol
B)2.15 mol
C)1.50 mol
D)1.33 mol
E)none of the above
A)2.50 mol
B)2.15 mol
C)1.50 mol
D)1.33 mol
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
How much work is done by 3 moles of gas when they triple their volume at a constant temperature of 400 K?
A)12.7 kJ
B)9.97 kJ
C)11.0 kJ
D)15.3 kJ
E)1.20 kJ
A)12.7 kJ
B)9.97 kJ
C)11.0 kJ
D)15.3 kJ
E)1.20 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
A certain amount of a monatomic gas is maintained at constant volume as it is cooled by 50 K. This feat is accomplished by removing 400 J of energy from the gas. How much work is done by the gas?
A)zero
B)200 J
C)400 J
D)-400 J
E)none of the above
A)zero
B)200 J
C)400 J
D)-400 J
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
In an isochoric process, the internal energy of a system decreases by 50 J. What is the work done?
A)zero
B)25 J
C)50 J
D)-50 J
E)none of the above
A)zero
B)25 J
C)50 J
D)-50 J
E)none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 96 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








