Deck 2: The Rectangular Coordinate System, Lines, and Circles
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/140
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: The Rectangular Coordinate System, Lines, and Circles
1
Sketch the graph for the equation by plotting points.
A)Yes
B)No
A)Yes
B)No
A
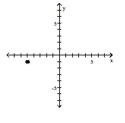
2
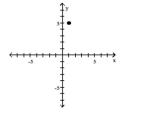
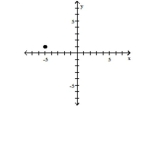
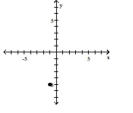
Plot the ordered pair in the Cartesian plane, and state in which quadrant or on which axis it lies.
(1, -5) A) Quadrant I
A) Quadrant I
B) Quadrant II
C) Quadrant III
D) Quadrant IV
(1, -5)
 A) Quadrant I
A) Quadrant I
B) Quadrant II

C) Quadrant III

D) Quadrant IV

D
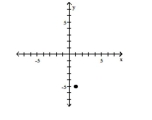
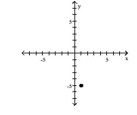
3
Plot the ordered pair in the Cartesian plane, and state in which quadrant or on which axis it lies.
(-1, -5)
A) Quadrant III
B) Quadrant IV
C) Quadrant II
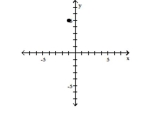
D) Quadrant III
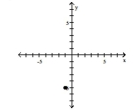
(-1, -5)

A) Quadrant III

B) Quadrant IV

C) Quadrant II

D) Quadrant III

D
4
Determine whether the indicated ordered pair lies on the graph of the given equation.
A = (3, 5); B = (9, 3) A)
В)
C)
D)
A = (3, 5); B = (9, 3) A)
В)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Determine whether the indicated ordered pair lies on the graph of the given equation.
y = |x|, (3, -3)
A)Yes
B)No
y = |x|, (3, -3)
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Determine whether the indicated ordered pair lies on the graph of the given equation.
A = (7, 1); B = (-16, -16) A)
B)
C)
D)
A = (7, 1); B = (-16, -16) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Sketch the graph for the equation by plotting points.
A)Yes
B)No
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Plot the ordered pair in the Cartesian plane, and state in which quadrant or on which axis it lies.
(-4, 6)
A) Quadrant II
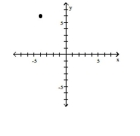
B) Quadrant I
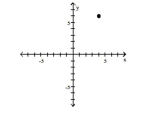
C) Quadrant III
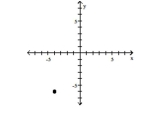
D) Quadrant IV
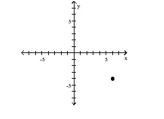
(-4, 6)

A) Quadrant II

B) Quadrant I

C) Quadrant III

D) Quadrant IV


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Sketch the graph for the equation by plotting points.
x2 + 9y = 9
A)
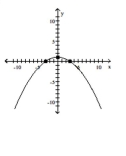
B)
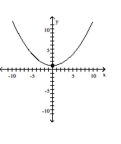
C)
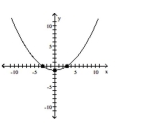
D)
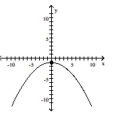
x2 + 9y = 9

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Sketch the graph for the equation by plotting points.
A)Yes
B)No
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
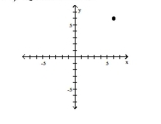
The function f is one-to-one. State the domain and the range of f and f-1. Write the domain and range in set-builder notation.
(6, 0)
A) Quadrant II
B) -axis
C) -axis
D) -axis
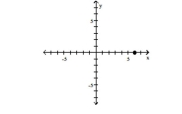
(6, 0)

A) Quadrant II

B) -axis

C) -axis

D) -axis


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Sketch the graph for the equation by plotting points.
A)Yes
B)No
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
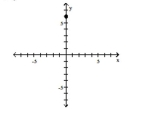
Plot the ordered pair in the Cartesian plane, and state in which quadrant or on which axis it lies.
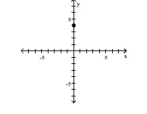
(0, 4)
A) -axis
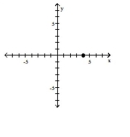
B) Quadrant II
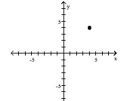
C) -axis
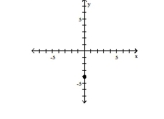
D) -axis
(0, 4)

A) -axis

B) Quadrant II

C) -axis

D) -axis


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The function f is one-to-one. State the domain and the range of f and f-1. Write the domain and range in set-builder notation.
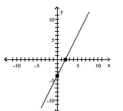
4x + 2y = 8
A)
B)
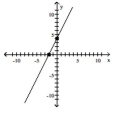
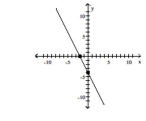
C)
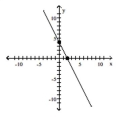
D)
4x + 2y = 8

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Determine whether the indicated ordered pair lies on the graph of the given equation.
A = (y, 2); B = (0, 8) A)
B)
C)
D)
A = (y, 2); B = (0, 8) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The function f is one-to-one. State the domain and the range of f and f-1. Write the domain and range in set-builder notation.
y = x + 3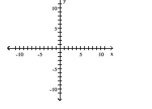
A)
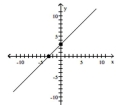
B)
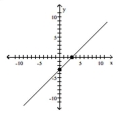
C)
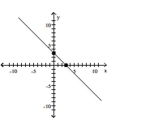
D)
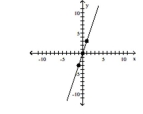
y = x + 3

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Determine whether the indicated ordered pair lies on the graph of the given equation.
A = (5, -9); B = (-2, -3) A)
B)
C)
D)
A = (5, -9); B = (-2, -3) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The function f is one-to-one. State the domain and the range of f and f-1. Write the domain and range in set-builder notation.
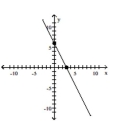
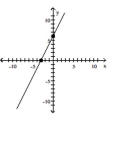
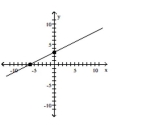
y = 2x - 6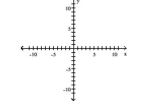
A)
B)
C)
D)
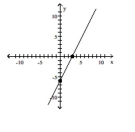
y = 2x - 6

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
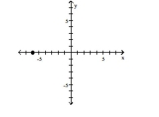
19
Plot the ordered pair in the Cartesian plane, and state in which quadrant or on which axis it lies.
(2, 3)
A) Quadrant II
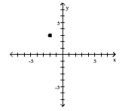
B) Quadrant IV
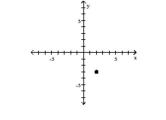
C) Quadrant I
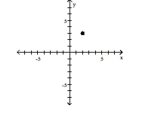
D) Quadrant I
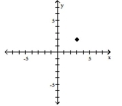
(2, 3)

A) Quadrant II

B) Quadrant IV

C) Quadrant I

D) Quadrant I


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Sketch the graph for the equation by plotting points.
A)Yes
B)No
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Find the distance d(A, B)between the points A and B.
A = (-6, -7); B = (0, -5); C = (-1, -10)
A)Yes
B)No
A = (-6, -7); B = (0, -5); C = (-1, -10)
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Determine whether the points A, B, and C form a right triangle.
Center (0, -5), r = 7 A)
В)
C)
D)
Center (0, -5), r = 7 A)
В)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Find the midpoint of the line segment joining the points A and B.
A = (9y, 9); B = (10y, 8) A)
B)
C)
D)
A = (9y, 9); B = (10y, 8) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Determine whether the points A, B, and C form a right triangle.
A = (-7, -3); B = (-1, -1); C = (5, -8)
A)Yes
B)No
A = (-7, -3); B = (-1, -1); C = (5, -8)
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Find the center and radius of the circle with the given equation.
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Determine whether the points A, B, and C form a right triangle.
Center (5, 7), r = 12 A)
B)
C)
D)
Center (5, 7), r = 12 A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Find the distance d(A, B)between the points A and B.
A = (-6, 7); B = (-4, 11); C = (-2, 10)
A)Yes
B)No
A = (-6, 7); B = (-4, 11); C = (-2, 10)
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Find the midpoint of the line segment joining the points A and B.
A(-1, 6); B(2, 9); C( 4, 1); D(7, 4)
A)Yes
B)No
A(-1, 6); B(2, 9); C( 4, 1); D(7, 4)
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Determine whether the points A, B, C and D form a parallelogram.
A = (4, 4); B = (4, 2)
A)2
B)3
C)1
A = (4, 4); B = (4, 2)
A)2
B)3
C)1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Determine whether the points A, B, C and D form a parallelogram.
A = (0, 0); B = (-2, 5) A)
B)
C) 3
D) 29
A = (0, 0); B = (-2, 5) A)
B)
C) 3
D) 29

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Determine whether the points A, B, and C form a right triangle.
The endpoints of a diameter are (3, 6)and (7, 6). A)
B)
C)
D)
The endpoints of a diameter are (3, 6)and (7, 6). A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Find the distance d(A, B)between the points A and B.
A = (-3, -4); B = (3, -6) A)
B) 8
C) 32
D)
A = (-3, -4); B = (3, -6) A)
B) 8
C) 32
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Determine whether the points A, B, C and D form a parallelogram.
A(-2, 10); B(1, 9); C(3, 1); D(6, 4)
A)Yes
B)No
A(-2, 10); B(1, 9); C(3, 1); D(6, 4)
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Find the center and radius of the circle with the given equation.
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Determine whether the points A, B, C and D form a parallelogram.
A = (1, 5); B = (-3, -2) A)
B) 3
C) 28
D)
A = (1, 5); B = (-3, -2) A)
B) 3
C) 28
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Determine whether the points A, B, C and D form a parallelogram.
A = (0, -2); B = (-7, -2)
A)7
C)2
D)49
A = (0, -2); B = (-7, -2)
A)7
C)2
D)49

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Determine whether the points A, B, C and D form a parallelogram.
A = (7, -5); B = (3, -3) A)
B) 6
C) 12
D)
A = (7, -5); B = (3, -3) A)
B) 6
C) 12
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Determine whether the points A, B, C and D form a parallelogram.
A = (4, 2); B = (1, 6)
A)10
B)5
C)25
D)6
A = (4, 2); B = (1, 6)
A)10
B)5
C)25
D)6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Determine whether the points A, B, and C form a right triangle.
Center (0, 0), r = 2 A)
B)
C)
D)
Center (0, 0), r = 2 A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Find the distance d(A, B)between the points A and B.
A = (-8, 3); B = (-5, 3); C = (-5, 12)
A)Yes
B)No
A = (-8, 3); B = (-5, 3); C = (-5, 12)
A)Yes
B)No

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Graph the equation.
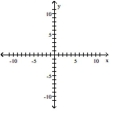
A)
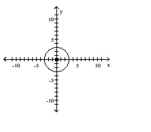
B)
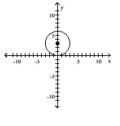
C)
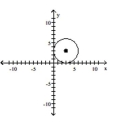
D)
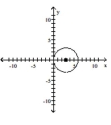

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle.
A)The x-intercept is x = 9, and the y-intercept is y = 9.
B)The two x-intercepts are x = 9 and x = -9, and the two y-intercepts are y = 9 and y = -9.
C)The two x-intercepts are x = 3 and x = -3, and the two y-intercepts are y = 3 and y = -3.
D)The x-intercept is x = 3, and the y-intercept is y = 3.
A)The x-intercept is x = 9, and the y-intercept is y = 9.
B)The two x-intercepts are x = 9 and x = -9, and the two y-intercepts are y = 9 and y = -9.
C)The two x-intercepts are x = 3 and x = -3, and the two y-intercepts are y = 3 and y = -3.
D)The x-intercept is x = 3, and the y-intercept is y = 3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Find the center (h, k)and radius r of the circle. Graph the circle.
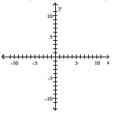
A) Center
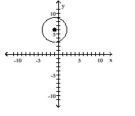
B) Center
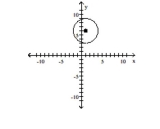
C) Center
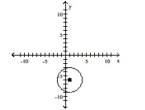
D) Center
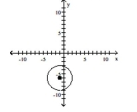

A) Center

B) Center

C) Center

D) Center


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle.
A)The x-intercept is x ≈41.7, and the y-intercept is y ≈40.65.
B)There are no intercepts.
C)The two x-intercepts are x ≈4.12 and x ≈-3.57, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈4.5 and y ≈-3.41.
D)The two x-intercepts are x ≈2.19 and x ≈-1.65, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈2.52 and y ≈-1.43.
A)The x-intercept is x ≈41.7, and the y-intercept is y ≈40.65.
B)There are no intercepts.
C)The two x-intercepts are x ≈4.12 and x ≈-3.57, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈4.5 and y ≈-3.41.
D)The two x-intercepts are x ≈2.19 and x ≈-1.65, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈2.52 and y ≈-1.43.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Find the center and radius of the circle with the given equation.
A)Center (-4, -9), r = 9
B)Center (4, 9), r = 81
C)Center (-9, -4), r = 9
D)Center (9, 4), r = 81
A)Center (-4, -9), r = 9
B)Center (4, 9), r = 81
C)Center (-9, -4), r = 9
D)Center (9, 4), r = 81

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Graph the equation.
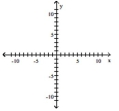
A)
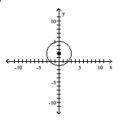
B)
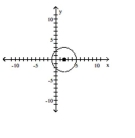
C)
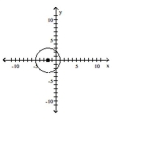
D)
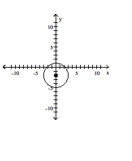

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle.
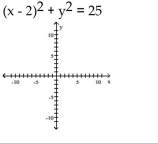 A)
A)
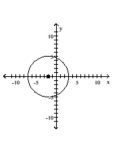
B)
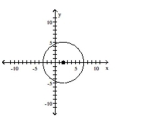
C)
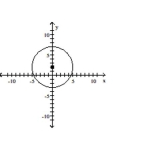
D)
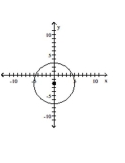
 A)
A)
B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle.
A)The two x-intercepts are x ≈8.9 and x ≈-0.9, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈1.46 and y ≈-5.46.
B)The two x-intercepts are x ≈0.9 and x ≈-8.9, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈5.46 and y ≈-1.46.
C)There are no intercepts.
D)The two x-intercepts are x ≈1.66 and x ≈-9.66, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈8.63 and y ≈-4.63.
A)The two x-intercepts are x ≈8.9 and x ≈-0.9, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈1.46 and y ≈-5.46.
B)The two x-intercepts are x ≈0.9 and x ≈-8.9, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈5.46 and y ≈-1.46.
C)There are no intercepts.
D)The two x-intercepts are x ≈1.66 and x ≈-9.66, and the two y-intercepts are y ≈8.63 and y ≈-4.63.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Find the center and radius of the circle with the given equation.
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle.
A)The two x-intercepts are x = 7 and x = -7, and the two y-intercepts are y = 3 and y = -3.
B)The x-intercept is x = 4, and the y-intercept is y = -9.
C)There are no intercepts.
D)The two x-intercepts are x = 4 and x = -4, and the two y-intercepts are y = 3 and y = -3.
A)The two x-intercepts are x = 7 and x = -7, and the two y-intercepts are y = 3 and y = -3.
B)The x-intercept is x = 4, and the y-intercept is y = -9.
C)There are no intercepts.
D)The two x-intercepts are x = 4 and x = -4, and the two y-intercepts are y = 3 and y = -3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Find the center and radius of the circle with the given equation.
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Find the center and radius of the circle with the given equation.
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Find the slope of the line.
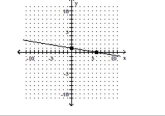 A) 6
A) 6
B)
C)
D)
 A) 6
A) 6B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Find the intercepts of the circle. Round to the nearest hundredth, when necessary.
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Find the intercepts of the circle. Round to the nearest hundredth, when necessary.
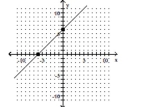
A)-1
B)6
C)1
D)-6

A)-1
B)6
C)1
D)-6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Find the intercepts of the circle. Round to the nearest hundredth, when necessary.
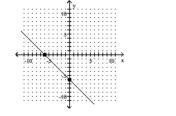
A)1
B)-1
C)-6
D)6

A)1
B)-1
C)-6
D)6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Graph the equation.
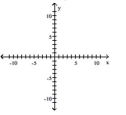
A)
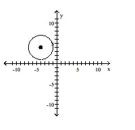
B)
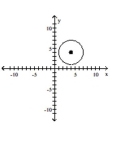
C)

D)
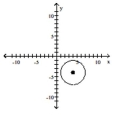

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Find the intercepts of the circle. Round to the nearest hundredth, when necessary.
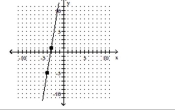 A)
A)
B)
D) 6
 A)
A) B)
D) 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Find the center (h, k)and radius r of the circle. Graph the circle.
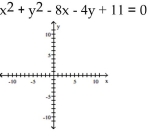 A) Center
A) Center
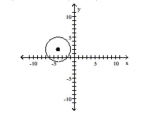
B) Center
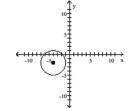
C) Center
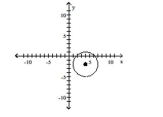
D) Center
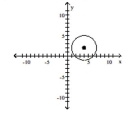
 A) Center
A) Center 
B) Center

C) Center

D) Center


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Find the center and radius of the circle with the given equation.
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center
A) Center
B) Center
C) Center
D) Center

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Find the slope of the line.
(5, 0)and (0, 3) A)
B)
C)
D)
(5, 0)and (0, 3) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
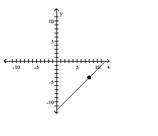
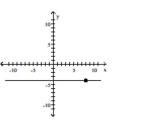
Slope = 0; line passes through the point (8, -4)
A)
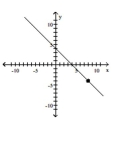
B)
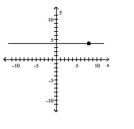
C)
D)
Slope = 0; line passes through the point (8, -4)

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
A)
B)
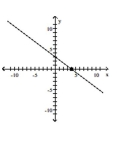
C)
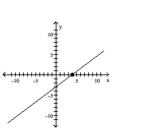
D)
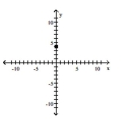

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
(2, -4)and (-3, -4) A) 0
B)
C)
D) undefined
(2, -4)and (-3, -4) A) 0
B)
C)
D) undefined

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Find the slope of the line.
(5, -3)and (6, -5) A)
B) 2
C)
D)
(5, -3)and (6, -5) A)
B) 2
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
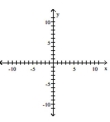
A)
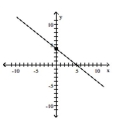
B)
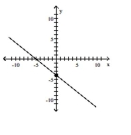
C)
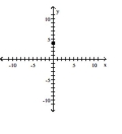
D)
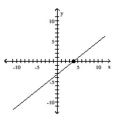

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
Slope = 1; line passes through the point (-4, -6)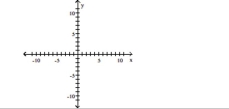 A)
A)
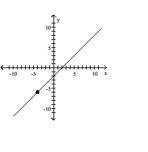
B)
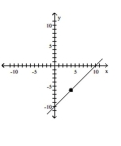
C)
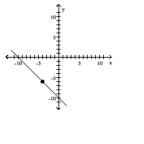
D)
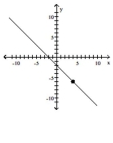
Slope = 1; line passes through the point (-4, -6)
 A)
A)
B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Sketch the line with the given slope that passes through the indicated point.
Slope line passes through the point
A)
B)
C)
D)
Slope line passes through the point
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Find the point-slope equation for the line with the given properties.
Slope line passes through the point
A)
B)
C)
D)
Slope line passes through the point
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Find the slope of the line.
(-5, -3)and (-5, -2)
A)- 1
B)1
C)0
D)undefined
(-5, -3)and (-5, -2)
A)- 1
B)1
C)0
D)undefined

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Find the point-slope equation for the line with the given properties.
(5, -6)and (7, 1) A) or
B) or
C) or
D) or
(5, -6)and (7, 1) A) or
B) or
C) or
D) or

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
A)
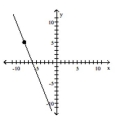
B)
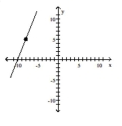
C)
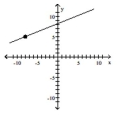
D)
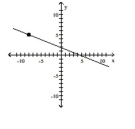

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Find the slope of the line.
(8, -4)and (-7, 9) A)
В)
C)
D)
(8, -4)and (-7, 9) A)
В)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Sketch the line with the given slope that passes through the indicated point.
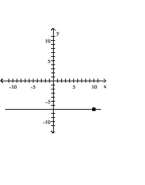
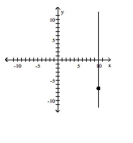
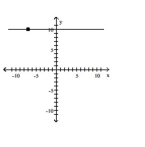
Slope is undefined; line passes through the point (-7, 10)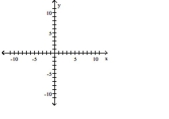
A)
B)
C)
D)
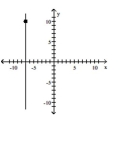
Slope is undefined; line passes through the point (-7, 10)

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Find the point-slope equation for the line with the given properties.
(-2, 15)and (4, -9)
A)y + 15 = -4(x + 2)or y + 9 = -4(x + 4)
B)y - 15 = -4(x + 2)or y + 9 = -4(x - 4)
C)y + 15 = -4(x - 2)or y - 9 = -4(x + 4)
D)y - 15 = -4(x - 2)or y - 9 = -4(x - 4)
(-2, 15)and (4, -9)
A)y + 15 = -4(x + 2)or y + 9 = -4(x + 4)
B)y - 15 = -4(x + 2)or y + 9 = -4(x - 4)
C)y + 15 = -4(x - 2)or y - 9 = -4(x + 4)
D)y - 15 = -4(x - 2)or y - 9 = -4(x - 4)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Find the point-slope equation for the line with the given properties.
(7, 9)and (4, 1) A) or
B) or
C) or
D) or
(7, 9)and (4, 1) A) or
B) or
C) or
D) or

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Find the point-slope equation for the line with the given properties.
(-4, -8)and (2, 16)
A)y - 8 = 4(x - 4)or y - 16 = 4(x - 2)
B)y + 8 = 4(x - 4)or y - 16 = 4(x + 2)
C)y - 8 = 4(x - 4)or y + 16 = 4(x + 2)
D)y + 8 = 4(x + 4)or y - 16 = 4(x - 2)
(-4, -8)and (2, 16)
A)y - 8 = 4(x - 4)or y - 16 = 4(x - 2)
B)y + 8 = 4(x - 4)or y - 16 = 4(x + 2)
C)y - 8 = 4(x - 4)or y + 16 = 4(x + 2)
D)y + 8 = 4(x + 4)or y - 16 = 4(x - 2)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
Slope = - 1; line passes through the point (-2, -4)
A)
B)
C)
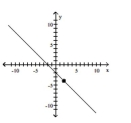
D)
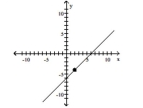
Slope = - 1; line passes through the point (-2, -4)

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
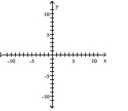
A)
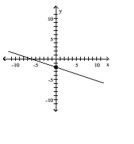
B)
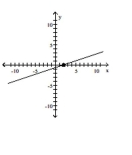
C)
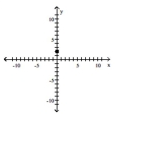
D)
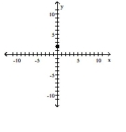

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Find the slope of the line containing the two points.
 A)
A)
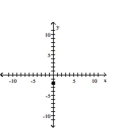
B)
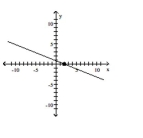
C)
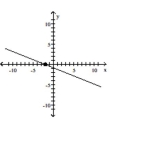
D)
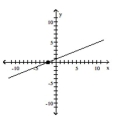
 A)
A)
B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 140 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








