Deck 7: Conic Sections
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/120
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 7: Conic Sections
1
Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin
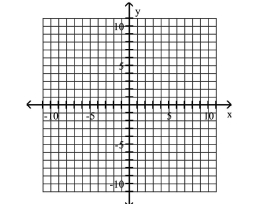
A)
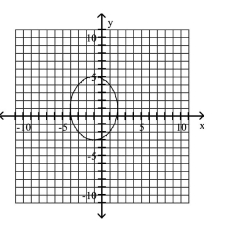
B)
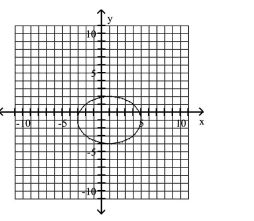
C)
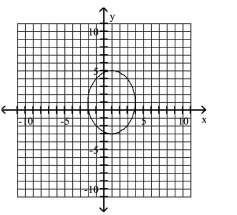
D)
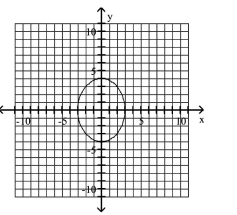

A)

B)

C)

D)

A
2
Write Equations of Ellipses in Standard Form
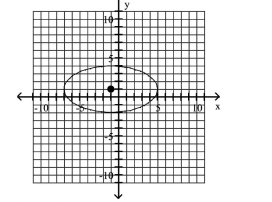
Center at
A)
foci at and
B)
foci at and
C)
foci at and
D)
foci at and

Center at
A)
foci at and
B)
foci at and
C)
foci at and
D)
foci at and
A
3
Find the standard form of the equation of the ellipse satisfying the given conditions.
Major axis vertical with length 14; length of minor axis = 6; center (0, 0) A)
B)
C)
D)
Major axis vertical with length 14; length of minor axis = 6; center (0, 0) A)
B)
C)
D)
A
4
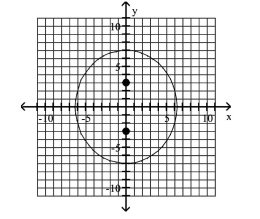
Graph the ellipse and locate the foci.
A) foci at and
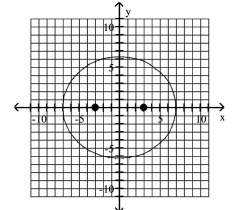
B) foci at and
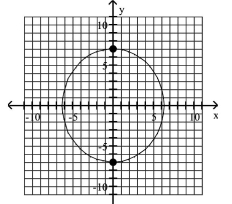
C) foci at and
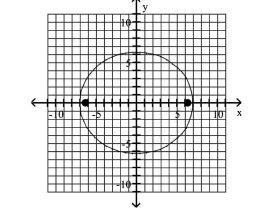
D) foci at and

A) foci at and

B) foci at and

C) foci at and

D) foci at and


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin
A)
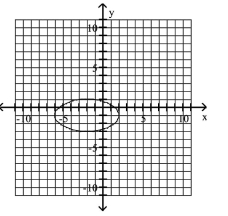
B)
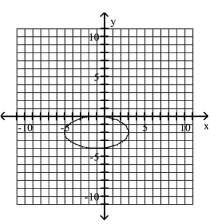
C)
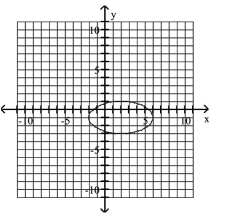
D)
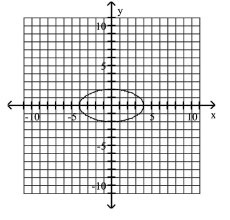

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Graph the ellipse and locate the foci.
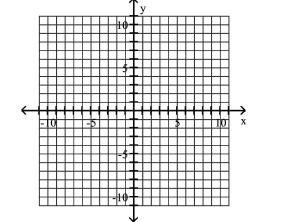
A) foci at and
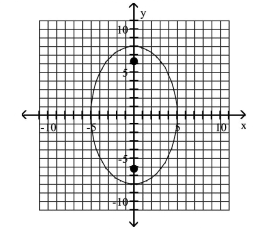
B) foci at and
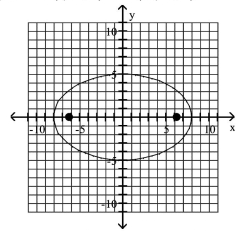
C) foci at and
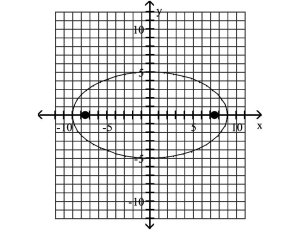
D) foci at and
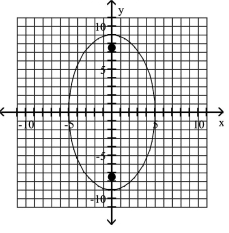

A) foci at and

B) foci at and

C) foci at and

D) foci at and


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Find the standard form of the equation of the ellipse satisfying the given conditions.
Major axis horizontal with length 20; length of minor axis = 16; center (0, 0) A)
B)
C)
D)
Major axis horizontal with length 20; length of minor axis = 16; center (0, 0) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Write Equations of Ellipses in Standard Form
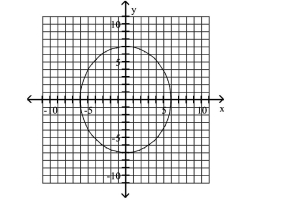
A)
foci at and
B)
foci at and
C)
foci at and
D)
foci at and

A)
foci at and
B)
foci at and
C)
foci at and
D)
foci at and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Graph the ellipse and locate the foci.
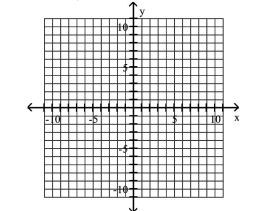
A) foci at and
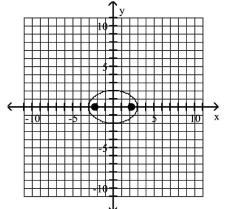
B) foci at and
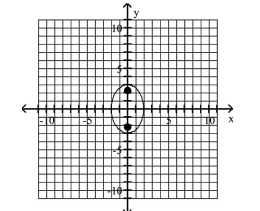
C) foci at and
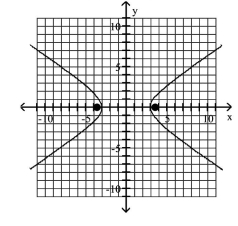
D) foci at and

A) foci at and

B) foci at and

C) foci at and

D) foci at and


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
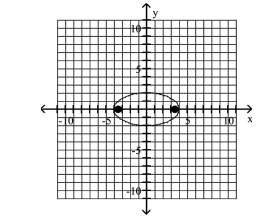
Graph the ellipse and locate the foci.
A) foci at and
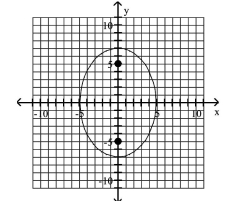
B) foci at and
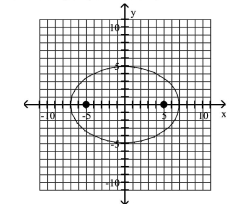
C) foci at and
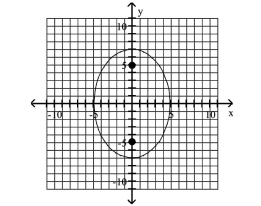
D) foci at and
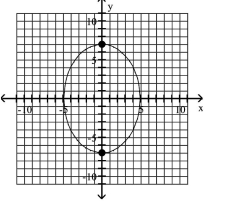

A) foci at and

B) foci at and

C) foci at and

D) foci at and


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Find the standard form of the equation of the ellipse satisfying the given conditions.
Foci: ; vertices:
A)
B)
C)
D)
Foci: ; vertices:
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
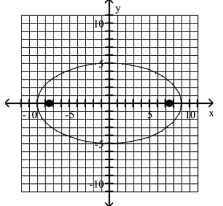
Graph the ellipse and locate the foci.
A)
foci at and
B) foci at and
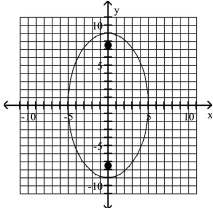
C) foci at and
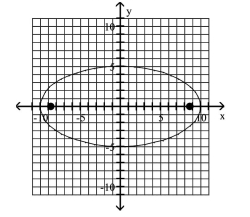
D) foci at and
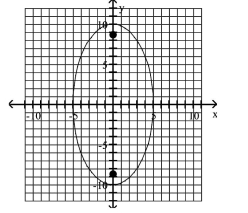

A)
foci at and

B) foci at and

C) foci at and

D) foci at and


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Find the standard form of the equation of the ellipse satisfying the given conditions.
Endpoints of major axis: (2, -8)and (2, 0); endpoints of minor axis: (0, -4)and (4, -4); A)
B)
C)
D)
Endpoints of major axis: (2, -8)and (2, 0); endpoints of minor axis: (0, -4)and (4, -4); A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Write Equations of Ellipses in Standard Form
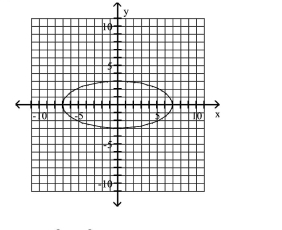
A)
foci at and
B)
foci at and
C)
foci at and
D)
foci at and

A)
foci at and
B)
foci at and
C)
foci at and
D)
foci at and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin
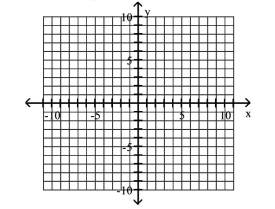
A)
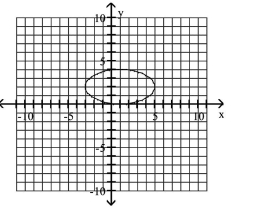
B)
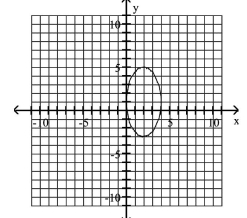
C)
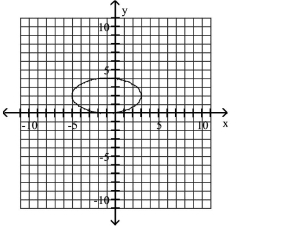
D)
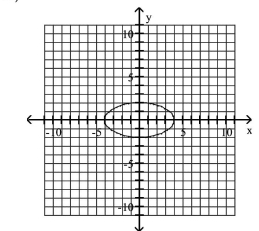

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Graph the ellipse and locate the foci.
A) foci at and
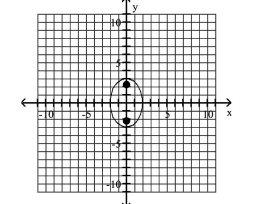
B) foci at and
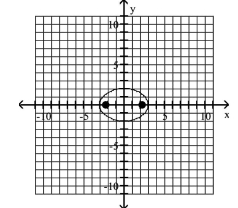
C) foci at and
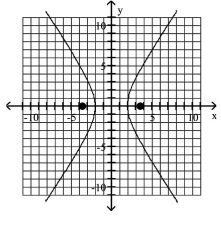
D) foci at and
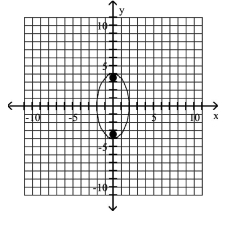

A) foci at and

B) foci at and

C) foci at and

D) foci at and


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Find the standard form of the equation of the ellipse satisfying the given conditions.
Foci: -intercepts: and 5
A)
B)
C)
D)
Foci: -intercepts: and 5
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Find the standard form of the equation of the ellipse satisfying the given conditions.
Endpoints of major axis: (-10, -4)and (6, -4); endpoints of minor axis: (-2, -8)and (-2, 0) A)
B)
C)
D)
Endpoints of major axis: (-10, -4)and (6, -4); endpoints of minor axis: (-2, -8)and (-2, 0) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Find the standard form of the equation of the ellipse satisfying the given conditions.
Foci: -intercepts: and 5
A)
B)
C)
D)
Foci: -intercepts: and 5
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Find the standard form of the equation of the ellipse satisfying the given conditions.
Foci: ; vertices:
A)
B)
C)
D)
Foci: ; vertices:
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Find the foci of the ellipse whose equation is given.
A) foci at and
B) foci at and
C) foci at and
D) foci at and
A) foci at and
B) foci at and
C) foci at and
D) foci at and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Find the vertices and locate the foci for the hyperbola whose equation is given.
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Solve Applied Problems Involving Ellipses
Solve the problem.
The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way roadway passes under the arch. The width of the roadway is 38 feet and the height of the arch over the center of the roadway is 11 feet. Two trucks plan to
Use this road. They are both 8 feet wide. Truck 1 has an overall height of 10 feet and Truck 2 has an overall
Height of 9 feet. Draw a rough sketch of the situation and determine which of the trucks can pass under the
Bridge.
A)Both Truck 1 and Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
B)Neither Truck 1 nor Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
C)Truck 1 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 2 cannot.
D)Truck 2 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 1 cannot.
Solve the problem.
The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way roadway passes under the arch. The width of the roadway is 38 feet and the height of the arch over the center of the roadway is 11 feet. Two trucks plan to
Use this road. They are both 8 feet wide. Truck 1 has an overall height of 10 feet and Truck 2 has an overall
Height of 9 feet. Draw a rough sketch of the situation and determine which of the trucks can pass under the
Bridge.
A)Both Truck 1 and Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
B)Neither Truck 1 nor Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
C)Truck 1 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 2 cannot.
D)Truck 2 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 1 cannot.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Solve Applied Problems Involving Ellipses
Solve the problem.
The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way roadway passes under the arch. The width of the roadway is 30 feet and the height of the arch over the center of the roadway is 13 feet. Two trucks plan to
Use this road. They are both 10 feet wide. Truck 1 has an overall height of 12 feet and Truck 2 has an
Overall height of 13 feet. Draw a rough sketch of the situation and determine which of the trucks can pass
Under the bridge.
A)Truck 1 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 2 cannot.
B)Both Truck 1 and Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
C)Neither Truck 1 nor Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
D)Truck 2 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 1 cannot.
Solve the problem.
The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way roadway passes under the arch. The width of the roadway is 30 feet and the height of the arch over the center of the roadway is 13 feet. Two trucks plan to
Use this road. They are both 10 feet wide. Truck 1 has an overall height of 12 feet and Truck 2 has an
Overall height of 13 feet. Draw a rough sketch of the situation and determine which of the trucks can pass
Under the bridge.
A)Truck 1 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 2 cannot.
B)Both Truck 1 and Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
C)Neither Truck 1 nor Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
D)Truck 2 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 1 cannot.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Find the solution set for the system by graphing both of the system's equations in the same rectangular coordinate
system and finding points of intersection.
A)
B)
C)
D)
system and finding points of intersection.

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Find the foci of the ellipse whose equation is given.
A) foci at and
B) foci at and
C) foci at and
D) foci at and
A) foci at and
B) foci at and
C) foci at and
D) foci at and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Find the solution set for the system by graphing both of the system's equations in the same rectangular coordinate
system and finding points of intersection.
A)
B)
C)
D)
system and finding points of intersection.

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Find the vertices and locate the foci for the hyperbola whose equation is given.
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Find the solution set for the system by graphing both of the system's equations in the same rectangular coordinate
system and finding points of intersection.
A)
B)
C)
D)
system and finding points of intersection.

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Convert the equation to the standard form for an ellipse by completing the square on x and y.
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
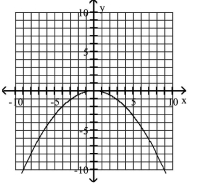
Graph the semi-ellipse.
A)
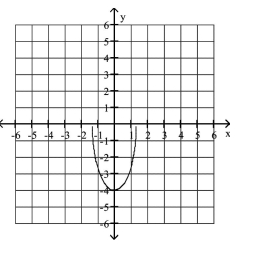
B)
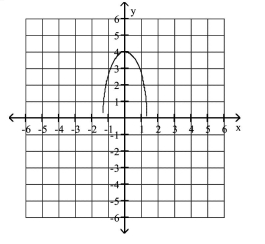
C)
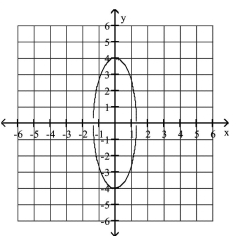
D)
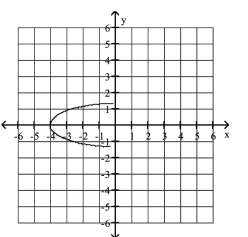

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Find the vertices and locate the foci for the hyperbola whose equation is given.
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin
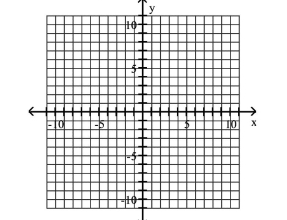
A)
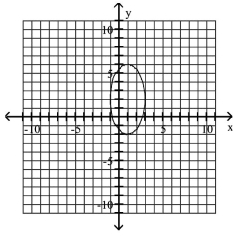
B)
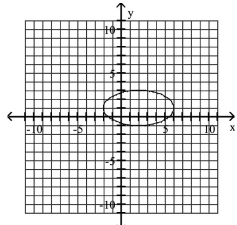
C)
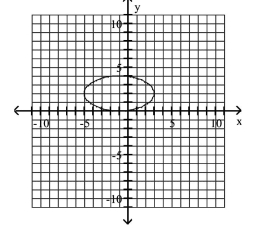
D)
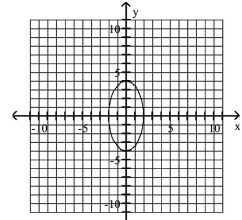

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Solve Applied Problems Involving Ellipses
Solve the problem.
The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way roadway passes under the arch. The width of the roadway is 30 feet and the height of the arch over the center of the roadway is 13 feet. Two trucks plan to
Use this road. They are both 12 feet wide. Truck 1 has an overall height of 12 feet and Truck 2 has an
Overall height of 11 feet. Draw a rough sketch of the situation and determine which of the trucks can pass
Under the bridge.
A)Truck 2 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 1 cannot.
B)Both Truck 1 and Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
C)Neither Truck 1 nor Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
D)Truck 1 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 2 cannot.
Solve the problem.
The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way roadway passes under the arch. The width of the roadway is 30 feet and the height of the arch over the center of the roadway is 13 feet. Two trucks plan to
Use this road. They are both 12 feet wide. Truck 1 has an overall height of 12 feet and Truck 2 has an
Overall height of 11 feet. Draw a rough sketch of the situation and determine which of the trucks can pass
Under the bridge.
A)Truck 2 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 1 cannot.
B)Both Truck 1 and Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
C)Neither Truck 1 nor Truck 2 can pass under the bridge.
D)Truck 1 can pass under the bridge, but Truck 2 cannot.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Find the foci of the ellipse whose equation is given.
A) foci at and
B) foci at and
C) foci at and
D) foci at and
A) foci at and
B) foci at and
C) foci at and
D) foci at and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Find the foci of the ellipse whose equation is given.
A) foci at and
B) foci at and
C) foci at and
D) foci at and
A) foci at and
B) foci at and
C) foci at and
D) foci at and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Convert the equation to the standard form for an ellipse by completing the square on x and y.
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Find the vertices and locate the foci for the hyperbola whose equation is given.
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Write Equations of Hyperbolas in Standard Form
Foci: (-5, 0), (5, 0); vertices: (-2, 0), (2, 0) A)
B)
C)
D)
Foci: (-5, 0), (5, 0); vertices: (-2, 0), (2, 0) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Find the vertices and locate the foci for the hyperbola whose equation is given.
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:
A) vertices:
foci:
B) vertices:
foci:
C) vertices:
foci:
D) vertices:
foci:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Graph Hyperbolas Centered at the Origin
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.
A) Asymptotes:
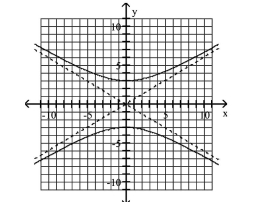
B) Asymptotes:
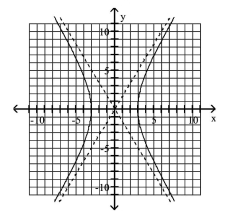
C) Asymptotes:
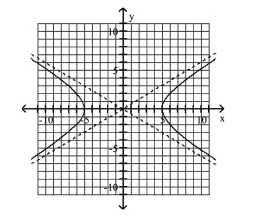
D) Asymptotes:
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.

A) Asymptotes:

B) Asymptotes:

C) Asymptotes:

D) Asymptotes:


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
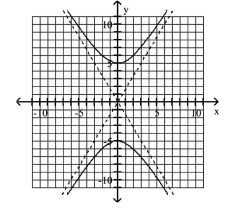
Find the standard form of the equation of the hyperbola.
A)
B)
C)
D)

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Graph Hyperbolas Not Centered at the Origin
Find the location of the center, vertices, and foci for the hyperbola described by the equation.
A) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
B) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
C) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
D) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
Find the location of the center, vertices, and foci for the hyperbola described by the equation.
A) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
B) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
C) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
D) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
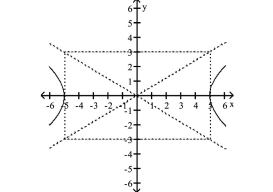
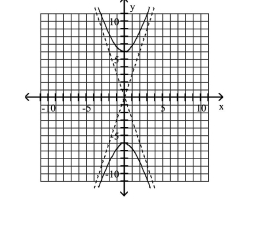
Graph Hyperbolas Centered at the Origin
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.
A) Asymptotes:
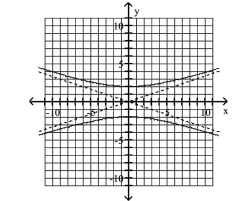
B) Asymptotes:
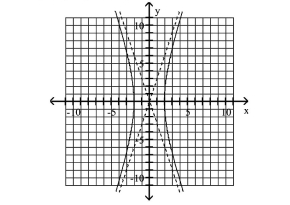
C) Asymptotes:
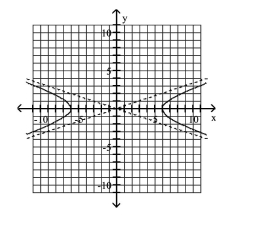
D) Asymptotes:
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.

A) Asymptotes:

B) Asymptotes:

C) Asymptotes:

D) Asymptotes:


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Graph Hyperbolas Centered at the Origin
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.
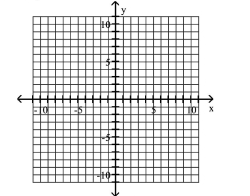
A) Asymptotes:
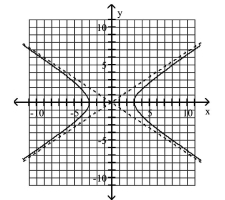
B) Asymptotes:
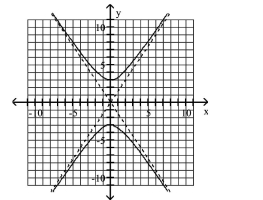
C) Asymptotes:

D) Asymptotes:
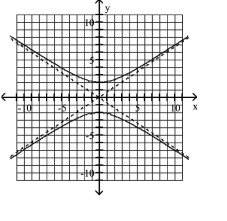
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.

A) Asymptotes:

B) Asymptotes:

C) Asymptotes:

D) Asymptotes:


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Find the standard form of the equation of the hyperbola.
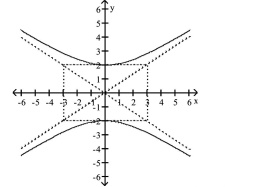
A)
B)
C)
D)

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Write Equations of Hyperbolas in Standard Form
Endpoints of transverse axis: ; asymptote:
A)
B)
C)
D)
Endpoints of transverse axis: ; asymptote:
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Convert the equation to the standard form for a hyperbola by completing the square on x and y.
A)
В)
C)
D)
A)
В)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Write Equations of Hyperbolas in Standard Form
Endpoints of transverse axis: ; foci:
A)
B)
C)
D)
Endpoints of transverse axis: ; foci:
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Convert the equation to the standard form for a hyperbola by completing the square on x and y.
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Convert the equation to the standard form for a hyperbola by completing the square on x and y.
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Graph Hyperbolas Not Centered at the Origin
Find the location of the center, vertices, and foci for the hyperbola described by the equation.
A) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
B) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
C) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
D) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
Find the location of the center, vertices, and foci for the hyperbola described by the equation.
A) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
B) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
C) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
D) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Graph Hyperbolas Not Centered at the Origin
Find the location of the center, vertices, and foci for the hyperbola described by the equation.
A) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
B) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
C) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
D) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
Find the location of the center, vertices, and foci for the hyperbola described by the equation.
A) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
B) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
C) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
D) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Graph Hyperbolas Centered at the Origin
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.
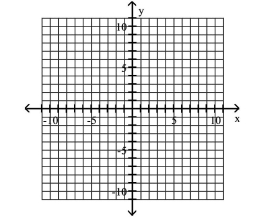
A) Asymptotes:
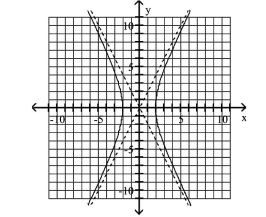
B) Asymptotes:

C) Asymptotes:
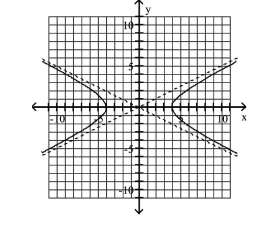
D) Asymptotes:
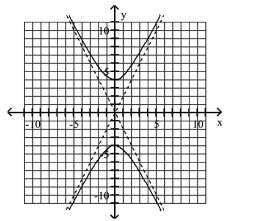
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.

A) Asymptotes:

B) Asymptotes:

C) Asymptotes:

D) Asymptotes:


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Write Equations of Hyperbolas in Standard Form
Center: Focus: Vertex:
A)
B)
C)
D)
Center: Focus: Vertex:
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Find the standard form of the equation of the hyperbola.
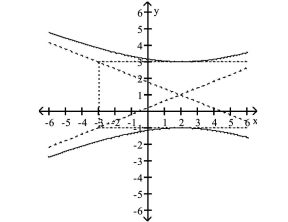
A)
B)
C)
D)

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Graph Hyperbolas Centered at the Origin
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.
A) Asymptotes:
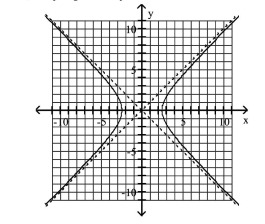
B) Asymptotes:
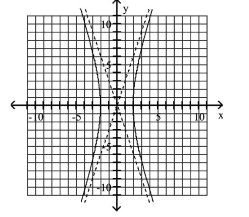
C) Asymptotes:
D) Asymptotes:
Use vertices and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola. Find the equations of the asymptotes.

A) Asymptotes:

B) Asymptotes:

C) Asymptotes:

D) Asymptotes:


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Write Equations of Hyperbolas in Standard Form
Foci: (0, -5), (0, 5); vertices: (0, -3), (0, 3) A)
B)
C)
D)
Foci: (0, -5), (0, 5); vertices: (0, -3), (0, 3) A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Graph Hyperbolas Not Centered at the Origin
Find the location of the center, vertices, and foci for the hyperbola described by the equation.
A) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
B) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
C) Center: ; Vertices: and Foci: and
D) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
Find the location of the center, vertices, and foci for the hyperbola described by the equation.
A) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
B) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and
C) Center: ; Vertices: and Foci: and
D) Center: ; Vertices: and ; Foci: and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Convert the equation to the standard form for a hyperbola by completing the square on x and y.
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
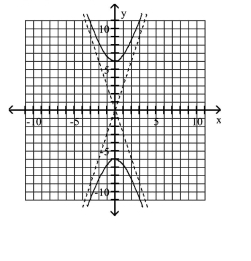
Graph Parabolas with Vertices at the Origin
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A)
B)

C)
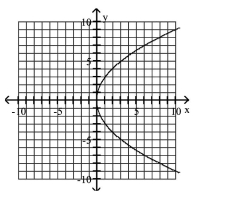
D)
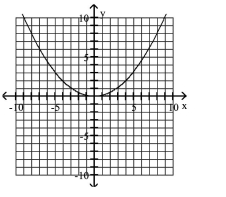
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Solve Applied Problems Involving Hyperbolas
Solve the problem.
Two recording devices are set 2600 feet apart, with the device at point A to the west of the device at point B. At a point on a line between the devices, 400 feet from point B, a small amount of explosive is detonated. The recording devices record the time the sound reaches each one. How far directly north of site B should a second explosion be done so that the measured time difference recorded by the devices is the same as that for the first detonation?
A) feet
B) feet
C) feet
D) feet
Solve the problem.
Two recording devices are set 2600 feet apart, with the device at point A to the west of the device at point B. At a point on a line between the devices, 400 feet from point B, a small amount of explosive is detonated. The recording devices record the time the sound reaches each one. How far directly north of site B should a second explosion be done so that the measured time difference recorded by the devices is the same as that for the first detonation?
A) feet
B) feet
C) feet
D) feet

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
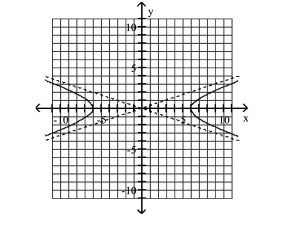
Use the center, vertices, and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola.
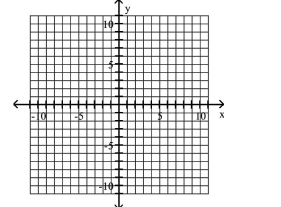
A)
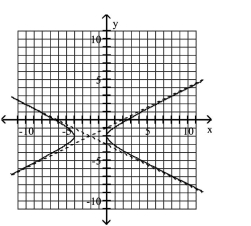
B)
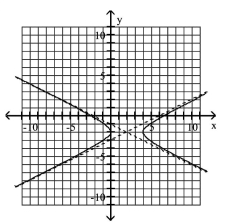
C)
D)

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Graph Parabolas with Vertices at the Origin
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Graph Parabolas with Vertices at the Origin
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Find the solution set for the system by graphing both of the system's equations in the same rectangular coordinate
system and finding points of intersection.
A)
B)
C)
D)
system and finding points of intersection.

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Graph Parabolas with Vertices at the Origin
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
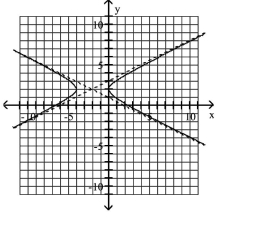
Use the center, vertices, and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola.
A)
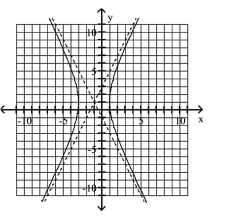
B)
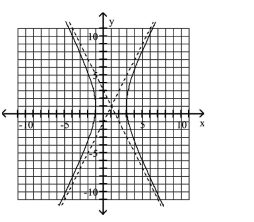
C)
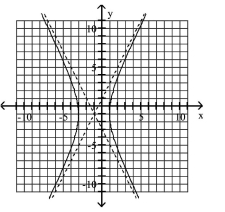
D)
11ecbe12_bedf_f697_88d3_9faa96c6c770_TB1195_11

A)

B)

C)

D)
11ecbe12_bedf_f697_88d3_9faa96c6c770_TB1195_11

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Solve Applied Problems Involving Hyperbolas
Solve the problem.
Two LORAN stations are positioned 278 miles apart along a straight shore. A ship records a time difference of 0.00086 seconds between the LORAN signals. (The radio signals travel at 186,000 miles per
Second.)Where will the ship reach shore if it were to follow the hyperbola corresponding to this time
Difference? If the ship is 200 miles offshore, what is the position of the ship?
A)59 miles from the master station, (161.9, 200)
B)80 miles from the master station, (200, 161.9)
C)59 miles from the master station, (200, 161.9)
D)80 miles from the master station, (161.9, 200)
Solve the problem.
Two LORAN stations are positioned 278 miles apart along a straight shore. A ship records a time difference of 0.00086 seconds between the LORAN signals. (The radio signals travel at 186,000 miles per
Second.)Where will the ship reach shore if it were to follow the hyperbola corresponding to this time
Difference? If the ship is 200 miles offshore, what is the position of the ship?
A)59 miles from the master station, (161.9, 200)
B)80 miles from the master station, (200, 161.9)
C)59 miles from the master station, (200, 161.9)
D)80 miles from the master station, (161.9, 200)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Additional Concepts
Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range.
![<strong>Additional Concepts Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range. \frac { x ^ { 2 } } { 16 } + \frac { y ^ { 2 } } { 4 } = 1 </strong> A) Domain: [ - 4,4 ] Range: [ - 2,2 ] B) Domain: [ - 2,2 ] Range: [ - 4,4 ] C) Domain: ( - 4,4 ) Range: ( - 2,2 ) D) Domain: [ - 4,4 ] \text { Range: }(-\infty, \infty)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1195/11ecbe13_9913_0892_88d3_699014baaf7c_TB1195_11.jpg)
A) Domain:
Range:
B) Domain:
Range:
C) Domain:
Range:
D) Domain:
Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range.
![<strong>Additional Concepts Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range. \frac { x ^ { 2 } } { 16 } + \frac { y ^ { 2 } } { 4 } = 1 </strong> A) Domain: [ - 4,4 ] Range: [ - 2,2 ] B) Domain: [ - 2,2 ] Range: [ - 4,4 ] C) Domain: ( - 4,4 ) Range: ( - 2,2 ) D) Domain: [ - 4,4 ] \text { Range: }(-\infty, \infty)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1195/11ecbe13_9913_0892_88d3_699014baaf7c_TB1195_11.jpg)
A) Domain:
Range:
B) Domain:
Range:
C) Domain:
Range:
D) Domain:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Graph Parabolas with Vertices at the Origin
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
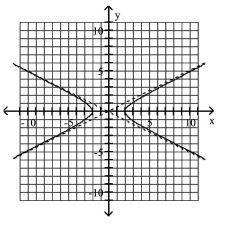
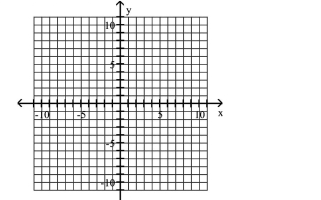
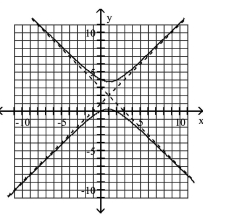
Use the center, vertices, and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola.
A)
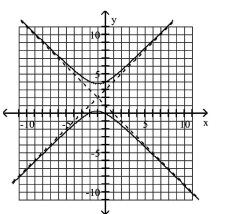
B)
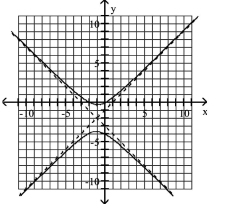
C)
D)
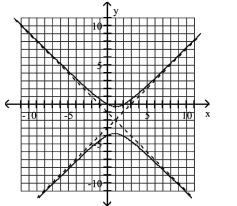

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Use the center, vertices, and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola.
A)
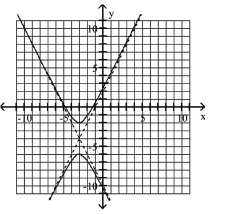
B)
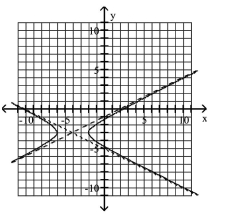
C)
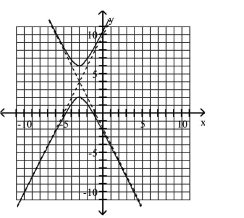
D)
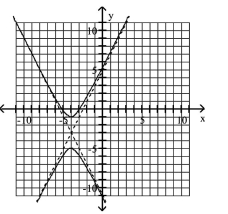

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Additional Concepts
Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range.
![<strong>Additional Concepts Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range. \frac { x ^ { 2 } } { 4 } - \frac { y ^ { 2 } } { 16 } = 1 </strong> A) Domain: ( - \infty , - 2 ] or [ 2 , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty ) B) Domain: ( - \infty , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , - 2 ) or ( 2 , \infty ) C) Domain: ( - \infty , - 2 ] and [ 2 , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty ) D) Domain: ( - \infty , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1195/11ecbe13_8b5f_cd01_88d3_1fc3d71067e2_TB1195_11.jpg)
A) Domain: or
Range:
B) Domain:
Range: or
C) Domain: and
Range:
D) Domain:
Range:
Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range.
![<strong>Additional Concepts Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range. \frac { x ^ { 2 } } { 4 } - \frac { y ^ { 2 } } { 16 } = 1 </strong> A) Domain: ( - \infty , - 2 ] or [ 2 , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty ) B) Domain: ( - \infty , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , - 2 ) or ( 2 , \infty ) C) Domain: ( - \infty , - 2 ] and [ 2 , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty ) D) Domain: ( - \infty , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1195/11ecbe13_8b5f_cd01_88d3_1fc3d71067e2_TB1195_11.jpg)
A) Domain: or
Range:
B) Domain:
Range: or
C) Domain: and
Range:
D) Domain:
Range:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Find the solution set for the system by graphing both of the system's equations in the same rectangular coordinate
system and finding points of intersection.

A)
B)
C)
D)
system and finding points of intersection.

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Use the center, vertices, and asymptotes to graph the hyperbola.
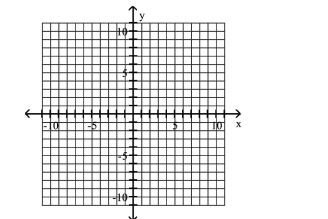
A)
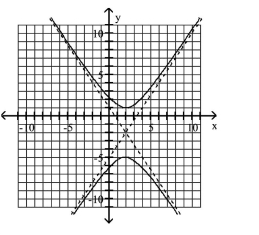
B)
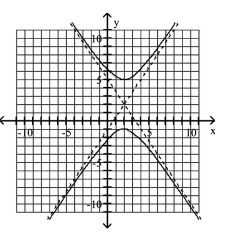
C)
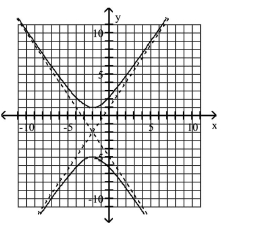
D)
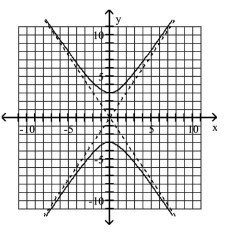

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Solve Applied Problems Involving Hyperbolas
Solve the problem.
A satellite following the hyperbolic path shown in the picture turns rapidly at and then moves closer and closer to the line as it gets farther from the tracking station at the origin. Find the equation that describes the path of the satellite if the center of the hyperbola is at .
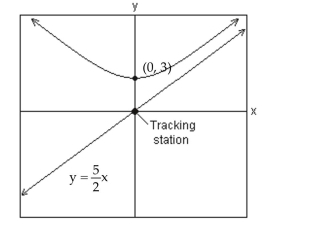
A)
B)
C)
D)
Solve the problem.
A satellite following the hyperbolic path shown in the picture turns rapidly at and then moves closer and closer to the line as it gets farther from the tracking station at the origin. Find the equation that describes the path of the satellite if the center of the hyperbola is at .

A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Additional Concepts
Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range.
![<strong>Additional Concepts Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range. \frac { y ^ { 2 } } { 4 } - \frac { x ^ { 2 } } { 25 } = 1 </strong> A) Domain: ( - \infty , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , - 2 ] or [ 2 , \infty ) B) Domain: ( - \infty , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , - 2 ] and [ 2 , \infty ) C) Domain: ( - \infty , - 2 ] or [ 2 , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty ) D) Domain: ( - \infty , - 2 ] and [ 2 , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1195/11ecbe13_b412_cea3_88d3_1f0b702d85f1_TB1195_11.jpg)
A) Domain:
Range: or
B) Domain:
Range: and
C) Domain: or
Range:
D) Domain: and
Range:
Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range.
![<strong>Additional Concepts Use the relation's graph to determine its domain and range. \frac { y ^ { 2 } } { 4 } - \frac { x ^ { 2 } } { 25 } = 1 </strong> A) Domain: ( - \infty , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , - 2 ] or [ 2 , \infty ) B) Domain: ( - \infty , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , - 2 ] and [ 2 , \infty ) C) Domain: ( - \infty , - 2 ] or [ 2 , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty ) D) Domain: ( - \infty , - 2 ] and [ 2 , \infty ) Range: ( - \infty , \infty )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1195/11ecbe13_b412_cea3_88d3_1f0b702d85f1_TB1195_11.jpg)
A) Domain:
Range: or
B) Domain:
Range: and
C) Domain: or
Range:
D) Domain: and
Range:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Graph Parabolas with Vertices at the Origin
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A) focus:
directrix:
B) focus:
directrix:
C) focus:
directrix:
D) focus:
directrix:

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Graph Parabolas with Vertices at the Origin
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A)
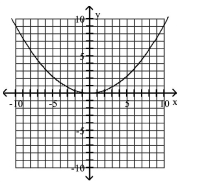
B)
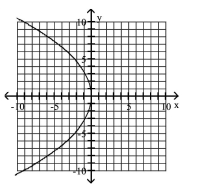
C)
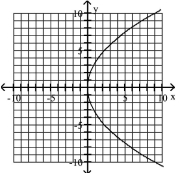
D)
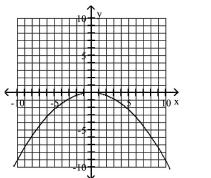
Find the focus and directrix of the parabola with the given equation.
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








