Deck 2: Elementary Programming
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/16
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: Elementary Programming
1
A subclass inherits _____________ from its superclass.
a. private method
b. protected method
c. public method
d. a and c
e. b and c
a. private method
b. protected method
c. public method
d. a and c
e. b and c
b and c
2
What exception type does the following program throw? public class Test {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();
String d = (String)o;
}
}
A) ArithmeticException
B) No exception
C) StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
D) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
E) ClassCastException
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();
String d = (String)o;
}
}
A) ArithmeticException
B) No exception
C) StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
D) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
E) ClassCastException
E
3
What exception type does the following program throw? public class Test {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = null;
System.out.println(o.toString());
}
}
A) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
B) ClassCastException
C) NullPointerException
D) ArithmeticException
E) StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = null;
System.out.println(o.toString());
}
}
A) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
B) ClassCastException
C) NullPointerException
D) ArithmeticException
E) StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
C
4
What is the output of running class C? class A {
Public A() {
System.out.println(
"The default constructor of A is invoked");
}
}
Class B extends A {
Public B(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Public class C {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B("The constructor of B is invoked");
}
}
A) none
B) "The constructor of B is invoked"
C) "The default constructor of A is invoked" "The constructor of B is invoked"
D) "The default constructor of A is invoked"
Public A() {
System.out.println(
"The default constructor of A is invoked");
}
}
Class B extends A {
Public B(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Public class C {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B("The constructor of B is invoked");
}
}
A) none
B) "The constructor of B is invoked"
C) "The default constructor of A is invoked" "The constructor of B is invoked"
D) "The default constructor of A is invoked"

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
What is wrong in the following code?
Test {
main(String[] args) {
Number x = Integer(3);
System.out.println(x.intValue());
System.out.println((Integer)x.compareTo(new Integer(4)));
}
}
Test {
main(String[] args) {
Number x = Integer(3);
System.out.println(x.intValue());
System.out.println((Integer)x.compareTo(new Integer(4)));
}
}

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following possible modifications will fix the errors in this code? public class Test {
Private double code;
Public double getCode() {
Return code;
}
Protected abstract void setCode(double code);
}
A) Remove abstract in the setCode method declaration.
B) Change protected to public.
C)
C) Add abstract in the class declaration.
D) b and
Private double code;
Public double getCode() {
Return code;
}
Protected abstract void setCode(double code);
}
A) Remove abstract in the setCode method declaration.
B) Change protected to public.
C)
C) Add abstract in the class declaration.
D) b and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Write a method to find the max in an array of comparable objects (Assume that the objects in the argument are instances of Comparable). The method signature is as follows:
public static Comparable max(Comparable[] a)
public static Comparable max(Comparable[] a)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What is the output of running the class C. public class C {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] o = {new A(), new B()};
System.out.print(o[0]);
System.out.print(o[1]);
}
}
Class A extends B {
Public String toString() {
Return "A";
}
}
Class B {
Public String toString() {
Return "B";
}
}
A) AB
B) BA
C) AA
D) BB
E) None of above
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] o = {new A(), new B()};
System.out.print(o[0]);
System.out.print(o[1]);
}
}
Class A extends B {
Public String toString() {
Return "A";
}
}
Class B {
Public String toString() {
Return "B";
}
}
A) AB
B) BA
C) AA
D) BB
E) None of above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
What is wrong in the following code?
Test {
main(String[] args) {
Number x = Integer(3);
System.out.println(x.intValue());
System.out.println));
}
}
Test {
main(String[] args) {
Number x = Integer(3);
System.out.println(x.intValue());
System.out.println));
}
}

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Analyze the following code. class Test {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Object x = new Integer(2);
System.out.println(x.toString());
}
}
A) The program has syntax errors because an Integer object is assigned to x.
B) When x.toString() is invoked, the toString() method in the Object class is used.
C) When x.toString() is invoked, the toString() method in the Integer class is used.
D) None of the above.
Public static void main(String[] args) {
Object x = new Integer(2);
System.out.println(x.toString());
}
}
A) The program has syntax errors because an Integer object is assigned to x.
B) When x.toString() is invoked, the toString() method in the Object class is used.
C) When x.toString() is invoked, the toString() method in the Integer class is used.
D) None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The program has a syntax error because the member access operator The java.util.Date class implements java.lang.Cloneable and overrides the equals method to return true if two objects have the same date and time. Show the output of the following code.
import java.util.*;
public class Test extends Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date();
Date d2 = new Date(349324);
Date d3 = d1;
System.out.println("(1) " + (d1 == d2));
System.out.println("(2) " + (d1 == d3));
System.out.println("(3) " + d1.equals(d2));
System.out.println("(4) " + d1.equals(d3));
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Test extends Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date();
Date d2 = new Date(349324);
Date d3 = d1;
System.out.println("(1) " + (d1 == d2));
System.out.println("(2) " + (d1 == d3));
System.out.println("(3) " + d1.equals(d2));
System.out.println("(4) " + d1.equals(d3));
}
}

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
When you implement a method that is defined in a superclass, you __________ the original method.
A) overload
B) override
C) copy
D) call
A) overload
B) override
C) copy
D) call

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Show the output of running the class Test in the following code: interface A {
Void print();
}
Class C {}
Class B extends C implements A {
Public void print() { }
}
Public class Test {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
If (b instanceof A)
System.out.println("b is an instance of A");
If (b instanceof C)
System.out.println("b is an instance of C");
}
}
A) Nothing.
B) b is an instance of A.
C) b is an instance of C.
D) b is an instance of A followed by b is an instance of C.
Void print();
}
Class C {}
Class B extends C implements A {
Public void print() { }
}
Public class Test {
Public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
If (b instanceof A)
System.out.println("b is an instance of A");
If (b instanceof C)
System.out.println("b is an instance of C");
}
}
A) Nothing.
B) b is an instance of A.
C) b is an instance of C.
D) b is an instance of A followed by b is an instance of C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Write a class named Hexagon that extends GeometricObject and implements the Comparable interface. Assume all six sides of the hexagon are of equal size. The Hexagon class is defined as follows:
public class Hexagon extends GeometricObject implements Comparable {
private double side;
/** Construct a Hexagon with the specified side */
public Hexagon(double side) {
// Implement it
}
/** Implement the abstract method getArea in
GeometricObject */
public double getArea() {
// Implement it (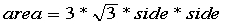 )
)
}
/** Implement the abstract method getPerimeter in
GeometricObject */
public double getPerimeter() {
// Implement it
}
/** Implement the compareTo method in
the Comparable interface to */
public int compareTo(Object obj) {
// Implement it (compare two Hexagons based on their areas)
}
}
public class Hexagon extends GeometricObject implements Comparable {
private double side;
/** Construct a Hexagon with the specified side */
public Hexagon(double side) {
// Implement it
}
/** Implement the abstract method getArea in
GeometricObject */
public double getArea() {
// Implement it (
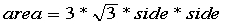 )
)}
/** Implement the abstract method getPerimeter in
GeometricObject */
public double getPerimeter() {
// Implement it
}
/** Implement the compareTo method in
the Comparable interface to */
public int compareTo(Object obj) {
// Implement it (compare two Hexagons based on their areas)
}
}

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The method _____ overrides the following method: protected double xMethod(int x) {…};
A) private double xMethod(int x) {…}
B) protected int xMethod(double x) {…}
C) public double xMethod(double x) {…}
D) public double xMethod(int x) {…}
A) private double xMethod(int x) {…}
B) protected int xMethod(double x) {…}
C) public double xMethod(double x) {…}
D) public double xMethod(int x) {…}

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Analyze the following code: public class Test1 {
Public Object max(Object o1, Object o2) {
If ((Comparable)o1.compareTo(o2) >= 0) {
Return o1;
}
Else {
Return o2;
}
}
}
A) The program has a syntax error because Test1 does not have a main method.
B) The program has a syntax error because o1 is an Object instance and it does not have the compareTo method.
C) The program has a syntax error because you cannot cast an Object instance o1 into Comparable.
D) The program would compile if ((Comparable)o1.compareTo(o2) >= 0) is replaced by (((Comparable)o1).compareTo(o2) >= 0).
E) b and d are both correct.
Public Object max(Object o1, Object o2) {
If ((Comparable)o1.compareTo(o2) >= 0) {
Return o1;
}
Else {
Return o2;
}
}
}
A) The program has a syntax error because Test1 does not have a main method.
B) The program has a syntax error because o1 is an Object instance and it does not have the compareTo method.
C) The program has a syntax error because you cannot cast an Object instance o1 into Comparable.
D) The program would compile if ((Comparable)o1.compareTo(o2) >= 0) is replaced by (((Comparable)o1).compareTo(o2) >= 0).
E) b and d are both correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








