Deck 9: Basic Oligopoly Models
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/23
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: Basic Oligopoly Models
1
The graph that accompanies this question illustrates two demand curves for a firm opreating in a differentiated product oligopoly. Initially, the firm charges a price of $60 and produces 10units of output. One of the demand curves is relevant when rivals match the firm's price changes; the other demand curve is relevants when rivals do not match price changes.
a. Which demand curve is relevant when rivals will match any price changes
b. Which demand curve is relevant when rivals will not match any price changes
c. Suppose the manager believes that rivals will match price cuts but will not match price increases 11eb4f3d_2afc_ec13_a4ce_45796b8432fc
(1)What price will the firm be able to charge if it produces 20 units
(2)How many units will the firm sell if it charges a price of $70
(3)For what range in marginal cost will the firm continue to charge a price of $60
a. Which demand curve is relevant when rivals will match any price changes
b. Which demand curve is relevant when rivals will not match any price changes
c. Suppose the manager believes that rivals will match price cuts but will not match price increases 11eb4f3d_2afc_ec13_a4ce_45796b8432fc
(1)What price will the firm be able to charge if it produces 20 units
(2)How many units will the firm sell if it charges a price of $70
(3)For what range in marginal cost will the firm continue to charge a price of $60
The two demand curves  and
and 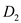 are drawn with respect to the behavior of the firms towards a price change. Demand is said to be more elastic when a price change is not matched by the rival firms.
are drawn with respect to the behavior of the firms towards a price change. Demand is said to be more elastic when a price change is not matched by the rival firms.
a)Given the two demand curves and
and 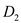 , the more inelastic demand curve is relevant when rivals will match any change in the price level.
, the more inelastic demand curve is relevant when rivals will match any change in the price level.
Note that for a particular demand curve, when there is a price change, rivals match such price change instantaneously so that there is apparently no change in the output produced and consumed. This clearly implies that the demand curve should be inelastic. Hence, in the case given, the more inelastic demand curve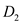 is relevant.
is relevant.
b)Given the two demand curves and
and 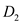 , the more elastic demand curve is relevant when rivals will not match any change in the price level.
, the more elastic demand curve is relevant when rivals will not match any change in the price level.
For a particular demand curve, when there is a price change, it happens that the rivals do not match the price change. Thus there is a significant change in the output produced and consumed. This clearly implies that the demand curve should be elastic in nature. Hence, in the case given, the more elastic demand curve is relevant.
is relevant.
c)In case when rival firms match a price cut so as to prevent sales (and profits) from falling but do not match a price rise, the Sweezy model of oligopoly assumes that the market operates at a kink. The kinked demand curve so formed comprises of upper portion of the demand curve (till the point of kink) and lower portion of the demand curve
(till the point of kink) and lower portion of the demand curve  0
0
(from the point of kink).
(1) If a typical firm in this market produces 20 units of output, then it faces the lower portion of the demand curve 1
1
(from the point of kink). The price charged at this quantity is $20 per unit.
(2) For a price level above $60, the relevant portion of the kinked demand curve is the upper portion of the demand curve 2
2
(till the point of kink). When the price is $70, the quantity produced is zero.
(3) There is a definite range over which changes in the marginal cost do not influence the profit-maximizing level of output (which occurs when firm produces 10 units at $60.) Drawing the respective marginal revenue curve for the two demand curves reveal that in range of $20 to $50 of the marginal cost, the firm can continue to charge a price of $60.
 and
and 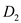 are drawn with respect to the behavior of the firms towards a price change. Demand is said to be more elastic when a price change is not matched by the rival firms.
are drawn with respect to the behavior of the firms towards a price change. Demand is said to be more elastic when a price change is not matched by the rival firms. a)Given the two demand curves
 and
and 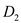 , the more inelastic demand curve is relevant when rivals will match any change in the price level.
, the more inelastic demand curve is relevant when rivals will match any change in the price level. Note that for a particular demand curve, when there is a price change, rivals match such price change instantaneously so that there is apparently no change in the output produced and consumed. This clearly implies that the demand curve should be inelastic. Hence, in the case given, the more inelastic demand curve
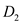 is relevant.
is relevant.b)Given the two demand curves
 and
and 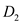 , the more elastic demand curve is relevant when rivals will not match any change in the price level.
, the more elastic demand curve is relevant when rivals will not match any change in the price level. For a particular demand curve, when there is a price change, it happens that the rivals do not match the price change. Thus there is a significant change in the output produced and consumed. This clearly implies that the demand curve should be elastic in nature. Hence, in the case given, the more elastic demand curve
 is relevant.
is relevant.c)In case when rival firms match a price cut so as to prevent sales (and profits) from falling but do not match a price rise, the Sweezy model of oligopoly assumes that the market operates at a kink. The kinked demand curve so formed comprises of upper portion of the demand curve
 (till the point of kink) and lower portion of the demand curve
(till the point of kink) and lower portion of the demand curve  0
0(from the point of kink).
(1) If a typical firm in this market produces 20 units of output, then it faces the lower portion of the demand curve
 1
1(from the point of kink). The price charged at this quantity is $20 per unit.
(2) For a price level above $60, the relevant portion of the kinked demand curve is the upper portion of the demand curve
 2
2(till the point of kink). When the price is $70, the quantity produced is zero.
(3) There is a definite range over which changes in the marginal cost do not influence the profit-maximizing level of output (which occurs when firm produces 10 units at $60.) Drawing the respective marginal revenue curve for the two demand curves reveal that in range of $20 to $50 of the marginal cost, the firm can continue to charge a price of $60.
2
The inverse market demand in a homogeneous-product Cournot duopoly is P= 100 2( Q 1 + Q₂ ) and costs are C 1 ( Q 1 ) = 12 Q 1 and C 2 ( Q₂ ) = 20 Q₂.
a. Determine the reaction function for each firm.
b. Calculate each firm's equilibrium output.
c. Calculate the equilibrium market price.
d. Calculate the profit each firm earns in equilibrium.
a. Determine the reaction function for each firm.
b. Calculate each firm's equilibrium output.
c. Calculate the equilibrium market price.
d. Calculate the profit each firm earns in equilibrium.
Total revenue for a firm is defined as the product of price and quantity of the product. It refers to the total sales by the firm or the total income of the firm.
Total cost is the overall costs of the production and it includes variable costs and fixed costs.
Profit is the difference between the total revenue and total cost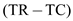 The inverse market demand in the Cournot monopoly is given as:
The inverse market demand in the Cournot monopoly is given as:  The costs in the Cournot monopoly are given as:
The costs in the Cournot monopoly are given as:  It is required to compute the reaction curves for firms 1 and 2.
It is required to compute the reaction curves for firms 1 and 2.
a.
The total revenue for firm 1 can be computed as: The marginal revenue for firm 1 can be computed as:
The marginal revenue for firm 1 can be computed as:  The marginal cost for firm 1 can be computed as:
The marginal cost for firm 1 can be computed as:  Equating MR and MC, the following results can be obtained:
Equating MR and MC, the following results can be obtained:  The reaction curve for firms 1 is
The reaction curve for firms 1 is 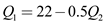 .
.
Similarly, the reaction curve for firm 2 cam be written as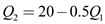 .
.
The equilibrium quantity can be computed as shown below: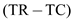 0
0
Hence,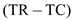 1
1
and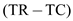 2
2
.
b.
The price can be computed as shown below: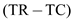 3
3
Hence, price is $44.
c.
The profits for firm 1 can be computed as shown below: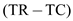 4
4
The profits for firm 2 can be computed as shown below: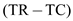 5
5
Hence, the profits for firm 1 are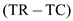 6
6
and for firm 2 are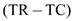 7
7
.
Total cost is the overall costs of the production and it includes variable costs and fixed costs.
Profit is the difference between the total revenue and total cost
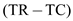 The inverse market demand in the Cournot monopoly is given as:
The inverse market demand in the Cournot monopoly is given as:  The costs in the Cournot monopoly are given as:
The costs in the Cournot monopoly are given as:  It is required to compute the reaction curves for firms 1 and 2.
It is required to compute the reaction curves for firms 1 and 2.a.
The total revenue for firm 1 can be computed as:
 The marginal revenue for firm 1 can be computed as:
The marginal revenue for firm 1 can be computed as:  The marginal cost for firm 1 can be computed as:
The marginal cost for firm 1 can be computed as:  Equating MR and MC, the following results can be obtained:
Equating MR and MC, the following results can be obtained:  The reaction curve for firms 1 is
The reaction curve for firms 1 is 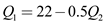 .
. Similarly, the reaction curve for firm 2 cam be written as
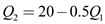 .
.The equilibrium quantity can be computed as shown below:
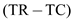 0
0Hence,
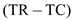 1
1and
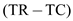 2
2.
b.
The price can be computed as shown below:
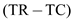 3
3Hence, price is $44.
c.
The profits for firm 1 can be computed as shown below:
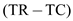 4
4The profits for firm 2 can be computed as shown below:
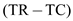 5
5Hence, the profits for firm 1 are
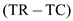 6
6and for firm 2 are
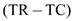 7
7.
3
The following diagram illustrates the reaction functions and isoprofit curves for a homogeneous-product duopoly in which each firm produces at constant marginal cost.
a. If your rival produces 50 units of output, what is your optimal level of output
b. In equilibrium, how much will each firm produce in a Cournot oligopoly
c. In equilibrium, what is the output of the leader and follower in a Stackel-berg oligopoly
d. How much output would be produced if the market were monopolized
e. Suppose you and your rival agree to a collusive arrangement in which each firm produces half of the monopoly output.
(1)What is your output under the collusive arrangement
(2)What is your optimal output if you believe your rival will live up to the agreement 11eb4f3d_2afe_72d1_a4ce_21572f483f9a
a. If your rival produces 50 units of output, what is your optimal level of output
b. In equilibrium, how much will each firm produce in a Cournot oligopoly
c. In equilibrium, what is the output of the leader and follower in a Stackel-berg oligopoly
d. How much output would be produced if the market were monopolized
e. Suppose you and your rival agree to a collusive arrangement in which each firm produces half of the monopoly output.
(1)What is your output under the collusive arrangement
(2)What is your optimal output if you believe your rival will live up to the agreement 11eb4f3d_2afe_72d1_a4ce_21572f483f9a
An economic model named as Cournot competition is used to designate an industry arrangement in which businesses participate on the quantity of output they will produce, which they establish individualistically at the same time.
a.
Given the reaction functions of two firms in a duopoly, if the rival produces 50 units, the optimal level to be produced can be traced by running along the horizontal or vertical line till it reaches the reaction function of the firm. Accordingly, the optimal level of output is 125 units.
b.
The reaction functions of both the firms intersect at a point where they both produce 100 units. Hence the equilibrium occurs at a point where both the firms will produce 100 units each.
c.
From the isoprofit curve of the leader, the optimal level of output produced by the leader is 150 units. The follower produces the remaining output at this level, which corresponds to 75 units.
d.
Had this market been a monopoly with the leader is the sole producer, the optimal level of output produced, given the iso-profit curve, is 150 units.
e.
If the rivals decide to collude and produce half of monopoly's output (which is 150 units) then each of them would be producing 75 units.
If the firm believes that the rival produces 75 units, the optimal level to be produced by this firm can be traced by running along the horizontal line till the firm reaches its reaction function. Accordingly, the optimal level of output is 112.5 units.
a.
Given the reaction functions of two firms in a duopoly, if the rival produces 50 units, the optimal level to be produced can be traced by running along the horizontal or vertical line till it reaches the reaction function of the firm. Accordingly, the optimal level of output is 125 units.
b.
The reaction functions of both the firms intersect at a point where they both produce 100 units. Hence the equilibrium occurs at a point where both the firms will produce 100 units each.
c.
From the isoprofit curve of the leader, the optimal level of output produced by the leader is 150 units. The follower produces the remaining output at this level, which corresponds to 75 units.
d.
Had this market been a monopoly with the leader is the sole producer, the optimal level of output produced, given the iso-profit curve, is 150 units.
e.
If the rivals decide to collude and produce half of monopoly's output (which is 150 units) then each of them would be producing 75 units.
If the firm believes that the rival produces 75 units, the optimal level to be produced by this firm can be traced by running along the horizontal line till the firm reaches its reaction function. Accordingly, the optimal level of output is 112.5 units.
4
The inverse demand for a homogeneous-product Stackelberg duopoly is P = 20,000 - 5 Q. The cost structures for the leader and the follower, respectively, are C L ( Q L ) = 3,000 Q L and C F ( Q F ) = 4,000 Q F
a. What is the follower's reaction function
b. Determine the equilibrium output level for both the leader and the follower.
c. Determine the equilibrium market price.
d. Determine the profits of the leader and the follower.
a. What is the follower's reaction function
b. Determine the equilibrium output level for both the leader and the follower.
c. Determine the equilibrium market price.
d. Determine the profits of the leader and the follower.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Consider a Bertrand oligopoly consisting of four firms that produce an identical product at a marginal cost of $100. The inverse market demand for this product is P= 500 2 Q.
a. Determine the equilibrium level of output in the market.
b. Determine the equilibrium market price.
c. Determine the profits of each firm.
a. Determine the equilibrium level of output in the market.
b. Determine the equilibrium market price.
c. Determine the profits of each firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Provide a real-world example of a market that approximates each oligopoly setting, and explain your reasoning.
a. Cournot oligopoly.
b. Stackelberg oligopoly.
c. Bertrand oligopoly.
a. Cournot oligopoly.
b. Stackelberg oligopoly.
c. Bertrand oligopoly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Two firms compete in a market to sell a homogeneous product with inverse demand function P = 400 2 Q. Each firm produces at a constant marginal cost of $50 and has no fixed costs. Use this information to compare the output levels and profits in settings characterized by Cournot, Stackelberg, Bertrand, and collusive behavior.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Consider a homogeneous-product duopoly where each firm initially produces at a constant marginal cost of $100 and there are no fixed costs. Determine what would happen to each firm's equilibrium output and profits if firm 2's marginal cost increased to $110 but firm l's marginal cost remained constant at $100 in each of the following settings:
a. Cournot duopoly.
b. Sweezy oligopoly.
a. Cournot duopoly.
b. Sweezy oligopoly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Determine whether each of the following scenarios best reflects features of Sweezy, Cournot, Stackelberg, or Bertrand duopoly:
a. Neither manager expects her own output decision to impact the other manager's output decision.
b. Each manager charges a price that is a best response to the price charged by the rival.
c. The manager of one firm gets to observe the output of the rival firm before making its own output decision.
d. The managers perceive that rivals will match price reductions but not price increases.
a. Neither manager expects her own output decision to impact the other manager's output decision.
b. Each manager charges a price that is a best response to the price charged by the rival.
c. The manager of one firm gets to observe the output of the rival firm before making its own output decision.
d. The managers perceive that rivals will match price reductions but not price increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Suppose a single firm produces all of the output in a contestable market. The market inverse demand function is P = 100 Q, and the firm's cost function is C ( Q ) = 2 Q. Determine the firm's equilibrium price and corresponding profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Ford executive announced that the company would extend its most dramatic consumer incentive program in the company's long history the Ford Drive America Program.The program provides consumers with either cash back or zero percent financing for new Ford vehicles. As the manager of a Ford/Lincoln/Mercury franchise, how would you expect this program to impact your firm's bottom line Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
You are the manager of BlackSpot Computers, which competes directly with Condensed Computers to sell high-powered computers to businesses. From the two businesses' perspectives, the two products are indistinguishable. The large investment required to build production facilities prohibits other firms from entering this market, and existing firms operate under the assumption that the rival will hold output constant. The inverse market demand for computers is P = 5,100 -. 5 Q and both firms produce at a marginal cost of $750 per computer Currently, BlackSpot earns revenues of $6.38 million and profits (net of investment, R D, and other fixed costs) of $1 million. The engineering department at BlackSpot has been steadily working on developing an assembly method that would dramatically reduce the marginal cost of producing these high-powered computers and has found a process that allows it to manufacture each computer at a marginal cost of $500. How will this technological advance impact your production and pricing plans How will it impact BlackSpot's bottom line

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The Hull Petroleum Company and Inverted V are retail gasoline franchises that compete in a local market to sell gasoline to consumers. Hull and Inverted V are located across the street from each other and can observe the prices posted on each other's marquees. Demand for gasoline in this market is Q = 50 10 P, and both franchises obtain gasoline from their supplier at $1.25 per gallon. On the day that both franchises opened for business, eacli owner was observed changing the price of gasoline advertised on its marquee more than 10 times; the owner of Hull lowered its price to slightly undercut Inverted V's price, and the owner of Inverted V lowered its advertised price to beat Hull's price. Since then, prices appear to have stabilized. Under current conditions, how many gallons of gasoline are sold in the market, and at what price Would your answer differ if Hull had service attendants available to fill consumers' tanks but Inverted V was only a self-service station Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
You are the manager of the only firm worldwide that specializes in exporting fish products to Japan. Your firm competes against a handful of Japanese firms that enjoy a significant first-mover advantage. Recently, one of your Japanese customers has called to inform you that the Japanese legislature is considering imposing a quota that would reduce the number of pounds of fish products you are permitted to ship to Japan each year. Your first instinct is to call the trade representative of your country to lobby against the import quota. Is following through with your first instinct necessarily the best decision Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The opening statement on the Web site of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) says, "... OPEC's eleven members are all developing countries whose economies are heavily reliant on oil export revenues. They therefore seek stable oil prices that are fair and reasonable for both producers and consumers of oil." To achieve this goal, OPEC attempts to coordinate and unify petroleum policies by raising or lowering their collective oil production. However, increased production by Russia, Oman, Mexico, Norway, and other non-OPEC countries has caused the price of crude oil to fall dramatically in recent years. To achieve its goal of stable and fair oil prices, what must OPEC do to maintain the price of oil at its desired level Do you think this will be easy for OPEC to do Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Semi-Salt Industries began its operation in 1975 and remains the only firm in the world that produces and sells commercial-grade polyglutamate. While virtually anyone with a degree in college chemistry could replicate the firm's formula, due to the relatively high cost, Semi-Salt has decided not to apply for a patent. Despite the absence of patent protection, Semi-Salt has averaged accounting profits of 5.5 percent on investment since it began producing polyglutamate-a rate comparable to the average rate of interest that large banks paid on deposits over this period. Do you think Semi-Salt is earning monopoly profits Why

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
You are the manager of a firm that competes against four other firms by bidding for government contracts. While you believe your product is better than the competition, the government purchasing agent views the products as identical and purchases from the firm offering the best price. Total government demand is Q = 750 8 P arid all five firms produce at a constant marginal cost of $50. For security reasons, the government has imposed restrictions that permit a maximum of five firms to compete in this market; thus entry by new firms is prohibited. A member of Congress is concerned because no restrictions have been placed on the price that the government pays for this product. In response, she has proposed legislation that would award each existing firm 20 percent of a contract for 270 units at a contracted price of $60 per unit. Would you support or oppose this legislation Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The market for a standard-sized cardboard container consists of two firms: CompositeBox and Fiberboard. As the manager of CompositeBox, you enjoy a patented technology that permits your company to produce boxes faster and at a lower cost than Fiberboard. You use this advantage to be the first to choose its profit-maximizing output level in the market. The inverse demand function for boxes is P= 800 4 Q, CompositeBox's costs are C c ( Q c ) = 40 Q C , and Fiberboard's costs are C F ( Q F ) = 80 Q F. Ignoring antitrust considerations, would it be profitable for your firm to merge with Fiberboard If not, explain why not; if so, put together an offer that would permit you to profitably complete the merger.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
You are the manager of Taurus Technologies, and your sole competitor is Spy- der Technologies. The two firms' products are viewed as identical by most consumers. The relevant cost functions are C ( Q i ) = 2 Q i and the inverse market demand curve for this unique product is given by P = 50 Q. Currently, you and your rival simultaneously (but independently) make production decisions, and the price you fetch for the product depends on the total amount produced by each firm. However, by making an unrecoverable fixed investment of $40, Taurus Technologies can bring its product to market before Spyder finalizes production plans. Should you invest the $40 Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
During the 1980s, most of the world's supply of lysine was produced by a Japanese company named Ajinomoto. Lysine is an essential amino acid that is an important livestock feed component. At this time, the United States imported most of the world's supply of lysine-more than 30,000 tons-to use in livestock feed at a price of $1.65 per pound. The worldwide market for lysine, however, fundamentally changed in 1991 when U.S.-based Archer Daniels Midland (ADM) began producing lysine-a move that doubled worldwide production capacity. Experts conjectured that Ajinomoto and ADM had similar cost structures and that the marginal cost of producing and distributing lysine was approximately $0.70 per pound. Despite ADM's entry into the lysine market, suppose demand remained constant at Q = 208 80 P (in millions of pounds). Shortly after ADM began producing lysine, the worldwide price dropped to $0.70. By 1993, however, the price of lysine shot back up to $1.65. Use the the ories discussed in this chapter to provide a potential explanation for what happened in the lysine market. Support your answer with appropriate calculations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
PC Connection and CDW are two online retailers that compete in an Internet market for digital cameras. While the products they sell are similar, the firms attempt to differentiate themselves through their service polices. Over the last couple of months, PC Connection has matched CDW's price cuts, but has not matched its price increases. Suppose that when PC Connection matches CDW's price changes, the inverse demand curve fur CDW's cameras is given by P = 1,250 2 Q. When it does not match price changes, CDW's inverse demand curve is P = 800 0.50 Q Based on this information, determine CDW's inverse demand and marginal revenue functions over the last couple of months. Over what range will changes in marginal cost have no effect on CDW's profit-maximizing level of output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Jones is the manager of an upscale clothing store in a shopping mall that contains only two such stores. While these two competitors do not carry the same brands of clothes, they serve a similar clientele. Jones was recently notified that the mall is going to implement a 10 percent across-the-board increase in rents to all stores in the mall, effective next month. Should Jones raise her prices 10 percent to offset the increase in monthly rent Explain carefully.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
In an attempt to increase tax revenues, legislators in several states have introduced legislation that would increase state excise taxes. Examine the impact of such an increase on the equilibrium prices paid and quantities consumed by consumers in markets characterized by (1) Sweezy oligopoly, (b) Cournot oligopoly, and (c) Bertrand oligopoly, and determine which of these market settings is likely to generate the greatest increase in tax revenues.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 23 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








