Deck 20: Economic Development and the Environment
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/6
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 20: Economic Development and the Environment
1
Following are illustrative numbers indicating benefits and costs to Country A of taking specific actions on an international treaty to reduce CO₂ emissions. The choice is either to adhere to the CO₂ emissions cutbacks called for by the treaty or to disregard the treaty. 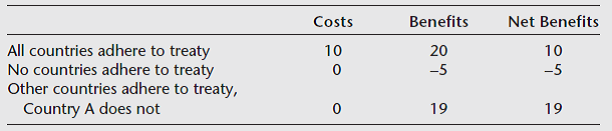
What is the incentive for Country A to free ride on the abatement efforts of other countries? If all countries become free riders, what is the result?

What is the incentive for Country A to free ride on the abatement efforts of other countries? If all countries become free riders, what is the result?
Given information:
Costs, benefits and net benefits associated with the different type of actions of country A towards an international treaty to reduce CO₂ emission are shown in the Table-1.Table-1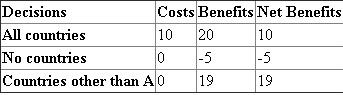 Incentive for country A to free ride:
Incentive for country A to free ride:
When all countries including county A agrees to the international treaty, then the net benefit would be 10. But, if countries other than country A agree to international treaty, then the net benefit would be 19. Now, there is net gain of 9 in the net benefit from the international treaty to reduce CO₂ emissions.
Thus, this net gain of worth 9 in the net benefit from the international treaty to reduce CO₂ emissions would provide incentive for country A to free ride on the abatement efforts of other countries.
All countries are free rider:
In a case, where all countries try to free ride on the abatement effort of others would lead to net loss worth of 5 in the net benefit expected from the international treaty to reduce CO₂ emissions.
Costs, benefits and net benefits associated with the different type of actions of country A towards an international treaty to reduce CO₂ emission are shown in the Table-1.Table-1
 Incentive for country A to free ride:
Incentive for country A to free ride: When all countries including county A agrees to the international treaty, then the net benefit would be 10. But, if countries other than country A agree to international treaty, then the net benefit would be 19. Now, there is net gain of 9 in the net benefit from the international treaty to reduce CO₂ emissions.
Thus, this net gain of worth 9 in the net benefit from the international treaty to reduce CO₂ emissions would provide incentive for country A to free ride on the abatement efforts of other countries.
All countries are free rider:
In a case, where all countries try to free ride on the abatement effort of others would lead to net loss worth of 5 in the net benefit expected from the international treaty to reduce CO₂ emissions.
2
We talked about "side payments" in the form of technology transfers, given to developing countries to lower the costs to them of joining international environmental agreements. What other types of side payments might be effective in this regard?
Types of side payments to reduce cost of joining in global environmental treaty:
Side payments are provided by the international treaties to developing countries in order to induce voluntary cooperation to global environmental treaty to get welfare gains.
•Preferential access to markets for goods produced in developing countries to relax the binding participation constraints in developing countries and improve the efficiency.
•Conventional foreign aid to improve efficiency.
•As equity remains a priority in international pollution control efforts, technical aid in pollution control to achieve equity for developing countries should be provided.
•Straight forward payments in return for adopting certain environmental policies.
•Availability of low cost abatement policies.
Side payments are provided by the international treaties to developing countries in order to induce voluntary cooperation to global environmental treaty to get welfare gains.
•Preferential access to markets for goods produced in developing countries to relax the binding participation constraints in developing countries and improve the efficiency.
•Conventional foreign aid to improve efficiency.
•As equity remains a priority in international pollution control efforts, technical aid in pollution control to achieve equity for developing countries should be provided.
•Straight forward payments in return for adopting certain environmental policies.
•Availability of low cost abatement policies.
3
Suppose Country A imports a product from Country B, and that Country B lacks environmental laws governing the production of the item. Under what conditions might Country A be justified in putting a tariff on the imported item?
Condition for justification in imposition of tariff:
Suppose there are two countries, A and B and assume that country A imports a particular item from the country B. Also assume that country B lacks environmental laws or emission control laws in governing the production of that particular item.
In this case, tariff imposed by country A would be justifiable if and only if, the production of that particular item in country B alters the environmental quality of country A or if the production of that particular item in country B damages the environment quality in country A.
Suppose there are two countries, A and B and assume that country A imports a particular item from the country B. Also assume that country B lacks environmental laws or emission control laws in governing the production of that particular item.
In this case, tariff imposed by country A would be justifiable if and only if, the production of that particular item in country B alters the environmental quality of country A or if the production of that particular item in country B damages the environment quality in country A.
4
If all countries adopted the same emission standards in similar industries, would this tend to equalize production costs and put each country on the same footing with respect to environmental matters?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 6 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
"International environmental agreements are very much shaped by the fact that enforcement on the international level is difficult, if not impossible." Discuss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 6 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In the early 1990s, the United States attempted to put restrictions on the importation of tuna from Mexico because Mexican fishers used methods that destroyed relatively large numbers of dolphin when catching the tuna. These fishing methods are illegal for U.S. tuna fishers. Is this trade restriction efficient? Is it equitable?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 6 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








