Deck 30: Plants
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 30: Plants
1
Choose the best answer for each question.
The spores produced by a plant are
A) haploid and genetically different from each other.
B) haploid and genetically identical to each other.
C) diploid and genetically different from each other.
D) diploid and genetically identical to each other.
The spores produced by a plant are
A) haploid and genetically different from each other.
B) haploid and genetically identical to each other.
C) diploid and genetically different from each other.
D) diploid and genetically identical to each other.
Plants undergo a special form of reproduction called the alteration of generations. There are two major forms - a diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte. Diploid and haploid refer to the number of chromosomal copies each cell contains. A diploid cell contains two copies, whereas a haploid cell contains one copy.
The sporophyte is a diploid plant form that produces haploid spores by meiosis. During meiosis, recombination results in a rearrangement of the two chromosomal copies, followed by two cell divisions. This results in the development of genetically distinct spores that have a single copy of the chromosome.
Each spore is capable of mitosis, or cell division, that results in the formation of a gametophyte. The cells of the gametophyte are genetically identical. The gametophyte will produce gametes (egg or sperm) via mitosis. These gametes will be genetically identical to one another.
During the fertilization process, a gamete from one individual will fuse with another gamete from another individual. This fusion will result in an embryo, which will eventually grow and differentiate into the adult form.
Plant spores are haploid. All of the cells of the gametophyte are also haploid. As such, options (C) and (D) are incorrect.
Plant spores form via meiosis, which results in genetically distinct haploid cells. Thus, the spores that are generated from the sporophyte are not genetically identical. As such, option (A) is incorrect.
Meiosis is the process by which plant spores are created. During meiosis, the two chromosomal copies are recombined to produce different combinations of genes. As such, the resultant spores are not genetically identical. Thus, the correct answer is A. Note that this answer differs from the book answer.
The sporophyte is a diploid plant form that produces haploid spores by meiosis. During meiosis, recombination results in a rearrangement of the two chromosomal copies, followed by two cell divisions. This results in the development of genetically distinct spores that have a single copy of the chromosome.
Each spore is capable of mitosis, or cell division, that results in the formation of a gametophyte. The cells of the gametophyte are genetically identical. The gametophyte will produce gametes (egg or sperm) via mitosis. These gametes will be genetically identical to one another.
During the fertilization process, a gamete from one individual will fuse with another gamete from another individual. This fusion will result in an embryo, which will eventually grow and differentiate into the adult form.
Plant spores are haploid. All of the cells of the gametophyte are also haploid. As such, options (C) and (D) are incorrect.
Plant spores form via meiosis, which results in genetically distinct haploid cells. Thus, the spores that are generated from the sporophyte are not genetically identical. As such, option (A) is incorrect.
Meiosis is the process by which plant spores are created. During meiosis, the two chromosomal copies are recombined to produce different combinations of genes. As such, the resultant spores are not genetically identical. Thus, the correct answer is A. Note that this answer differs from the book answer.
2
The gametophyte is the dominant generation in
A) ferns.
B) mosses
C) gymnosperms.
D) angiosperms.
A) ferns.
B) mosses
C) gymnosperms.
D) angiosperms.
Plants undergo a special form of reproduction called the alteration of generations. There are two major forms - a diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte. Diploid and haploid refer to the number of chromosomal copies each cell contains. A diploid cell contains two copies, whereas a haploid cell contains one copy.
The sporophyte is a diploid plant form that produces haploid spores by meiosis. Each spore divides by mitosis, or cell division, to form a multi-cellular gametophyte. The cells of the gametophyte are genetically identical. The gametophyte will produce gametes (egg or sperm) via mitosis.
During the fertilization process, a gamete from one individual will fuse with another gamete from another individual. This fusion will result in an embryo, which will divide by mitosis to form a multi-cellular sporophyte. Depending on the plant, either the gametophyte or the sporophyte will be the more dominant, visible form. For example, the pine tree is a sporophyte.
The fern is a seedless, vascular plant. The predominant form of the fern is the sporophyte. Thus, option (A) is incorrect.
Conifers, cycads, and gingkoes are examples of gymnosperms. The sporophyte is the predominant form of the gymnosperm. Thus, option (C) is incorrect.
The angiosperms are a diverse group of plants, which include flowers and trees such as the eucalyptus. The predominant form of the angiosperm is the sporophyte. Thus, option (D) is incorrect.
Mosses are nonvascular plants. This means that they lack tubular structures that carry water and nutrients throughout the plant. The major form of nonvascular plants, such as mosses, is the gametophyte. Thus, the correct answer is B, mosses.
The sporophyte is a diploid plant form that produces haploid spores by meiosis. Each spore divides by mitosis, or cell division, to form a multi-cellular gametophyte. The cells of the gametophyte are genetically identical. The gametophyte will produce gametes (egg or sperm) via mitosis.
During the fertilization process, a gamete from one individual will fuse with another gamete from another individual. This fusion will result in an embryo, which will divide by mitosis to form a multi-cellular sporophyte. Depending on the plant, either the gametophyte or the sporophyte will be the more dominant, visible form. For example, the pine tree is a sporophyte.
The fern is a seedless, vascular plant. The predominant form of the fern is the sporophyte. Thus, option (A) is incorrect.
Conifers, cycads, and gingkoes are examples of gymnosperms. The sporophyte is the predominant form of the gymnosperm. Thus, option (C) is incorrect.
The angiosperms are a diverse group of plants, which include flowers and trees such as the eucalyptus. The predominant form of the angiosperm is the sporophyte. Thus, option (D) is incorrect.
Mosses are nonvascular plants. This means that they lack tubular structures that carry water and nutrients throughout the plant. The major form of nonvascular plants, such as mosses, is the gametophyte. Thus, the correct answer is B, mosses.
3
Label the stages in the following diagram of the plant life cycle. 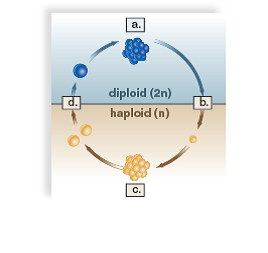

Plants undergo a special form of reproduction called the alteration of generations. There are two major forms of the plant during alteration of generations - a diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte. Diploid and haploid refer to the number of chromosomal copies each cell contains. A diploid cell contains two copies, whereas a haploid cell contains one copy.
a.
The first stage is the sporophyte. The sporophyte is a multi-cellular, diploid plant form. The function of the sporophyte is to produce haploid spores. In plants such as the pine tree and the fern, the dominant form that you typically see is the sporophyte.
b.
The sporophyte produces haploid spores via meiosis. During meiosis, recombination of the two copies of each chromosome occurs. Genetic variation is generated during recombination. Following recombination, there are two cell divisions. The first division results in two diploid cells and the second division results in four haploid cells.
c.
Each spore divides by mitosis, or cell division, to form a multi-cellular gametophyte. The cells of the gametophyte are genetically identical. The gametophyte will produce gametes (egg or sperm) via mitosis.
d.
During the fertilization process, a gamete from one individual will fuse with another gamete from another individual. This fusion will result in an embryo, which will divide by mitosis to form a multi-cellular sporophyte.
a.
The first stage is the sporophyte. The sporophyte is a multi-cellular, diploid plant form. The function of the sporophyte is to produce haploid spores. In plants such as the pine tree and the fern, the dominant form that you typically see is the sporophyte.
b.
The sporophyte produces haploid spores via meiosis. During meiosis, recombination of the two copies of each chromosome occurs. Genetic variation is generated during recombination. Following recombination, there are two cell divisions. The first division results in two diploid cells and the second division results in four haploid cells.
c.
Each spore divides by mitosis, or cell division, to form a multi-cellular gametophyte. The cells of the gametophyte are genetically identical. The gametophyte will produce gametes (egg or sperm) via mitosis.
d.
During the fertilization process, a gamete from one individual will fuse with another gamete from another individual. This fusion will result in an embryo, which will divide by mitosis to form a multi-cellular sporophyte.
4
In mosses, meiosis occurs in
A) antheridia
B) archegonia.
C) capsules.
D) protonema
A) antheridia
B) archegonia.
C) capsules.
D) protonema

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In bryophytes, sperm usually move from the antheridium to the archegonium by
A) swimming.
B) flying.
C) insect pollination.
D) wind pollination.
E) bird pollination.
A) swimming.
B) flying.
C) insect pollination.
D) wind pollination.
E) bird pollination.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Microphylls
A) have a single strand of vascular tissue.
B) evolved before megaphylls.
C) evolved as extensions of the stem.
D) are found in lycophytes.
E) All of these are correct.
A) have a single strand of vascular tissue.
B) evolved before megaphylls.
C) evolved as extensions of the stem.
D) are found in lycophytes.
E) All of these are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
How are ferns different from mosses?
A) Only ferns produce spores as dispersal agents.
B) Ferns have vascular tissue.
C) In the fern life cycle, the gametophyte and sporophyte are both independent.
D) Ferns do not have flagellated sperm.
E) Both b and c are correct.
A) Only ferns produce spores as dispersal agents.
B) Ferns have vascular tissue.
C) In the fern life cycle, the gametophyte and sporophyte are both independent.
D) Ferns do not have flagellated sperm.
E) Both b and c are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Ferns have
A) a dominant gametophyte generation.
B) vascular tissue.
C) seeds.
D) Both a and b are correct.
E) Choices a, b, and c are correct.
A) a dominant gametophyte generation.
B) vascular tissue.
C) seeds.
D) Both a and b are correct.
E) Choices a, b, and c are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which statement about the conifer life cycle is false?
A) Meiosis produces spores.
B) The gametophyte is the dominant generation.
C) The seed is a dispersal agent.
D) Male gametophytes are carried by the wind.
A) Meiosis produces spores.
B) The gametophyte is the dominant generation.
C) The seed is a dispersal agent.
D) Male gametophytes are carried by the wind.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of these pairs is mismatched?
A) anther-produces microspores
B) carpel-produces pollen
C) ovule-becomes seed
D) ovary-becomes fruit
E) flower-is a reproductive structure
A) anther-produces microspores
B) carpel-produces pollen
C) ovule-becomes seed
D) ovary-becomes fruit
E) flower-is a reproductive structure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Unlike eudicots, monocots have
A) woody tissue.
B) two seed leaves.
C) scattered vascular bundles in their stems.
D) flower parts in multiples of fours or fives.
A) woody tissue.
B) two seed leaves.
C) scattered vascular bundles in their stems.
D) flower parts in multiples of fours or fives.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Label the parts of the flower in the following diagram. 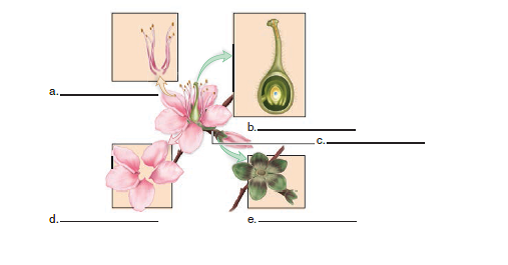


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Why do you think plants are such a good source of drugs for human use? What advantage does this give the plants?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Plants and Humans
Humans derive most of their nourishment from three flowering plants: wheat, corn, and rice. All three of these plants are members of the grass family and are collectively called grains (Fig. 30A). Wheat is commonly used to produce flour and bread. It was first cultivated in the Middle East about 8000 b.c., and is thought to be one of the earliest cultivated plants. Early settlers brought wheat to North America, where many varieties of corn, more properly called maize, were already in existence. Rice originated in southeastern Asia several thousand years ago, where it grew in swamps. Many foods of both plant and animal origin are considered bland or tasteless without seasonings or spices. The Americas were discovered when Columbus was seeking a new route to the Far East to acquire spices, such as nutmeg, oregano, rosemary, and sage. In addition, our primary sweetener, sugar, comes almost exclusively from two plants-sugarcane (grown in South America, Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean) and sugar beets (grown mostly in Europe and North America). Our most popular drinks-coffee, tea, and cola-also come from flowering plants. Coffee originated in Ethiopia, whereas tea is thought to have been first used somewhere in central Asia. Cotton and rubber are two plants that still have many uses today (Fig. 30B). Until a few decades ago, cotton and other natural fibers were our only source of clothing. Interestingly, when Levi Strauss wanted to make a tough pair of jeans, he needed a stronger fiber than cotton, so he used hemp. Hemp comes from a plant that is closely related to marijuana, but unlike marijuana, has extremely small amounts of the chemical tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which causes the hallucinogenic effect when marijuana is smoked. Today, hemp is increasingly used to make clothing due to its toughness and wearability. Rubber had its origin in Brazil from the thick, white sap of the rubber tree. To produce a stronger rubber, such as that in tires, sulfur is added, and the sap is heated in a process called vulcanization. This produces a flexible material less sensitive to temperature changes. However, at present, most rubber is synthetically produced.
Plants have also been used for centuries for a number of important household items, including the house itself. We are most familiar with lumber as the major structural portion in buildings. This wood comes mainly from a variety of conifers: pine, fir, and spruce, among others. In the tropics, trees and even herbs provide important components for houses. In rural parts of Central and South America, palm leaves are preferable to tin for roofs, because they last as long as ten years and are quieter during rainstorms. In the Middle East, numerous houses along rivers are made entirely of reeds.
Today, plants are increasingly researched for their use in medicinal products. Currently, about 50% of all pharmaceutical drugs originate from plants or are derived from plant products. Some cancers are even treatable with medicinal plants, such as the rosy periwinkle, extracts from which have shown some success in treating childhood leukemia. Indeed, the National Cancer Institute and most pharmaceutical companies have spent millions of dollars to send botanists out to collect and test plant samples from around the world. Tribal medicine men, or shamans, of South America and Africa have already been of great importance in developing numerous drugs. However, plant extracts also continue to be misused for their hallucinogenic or other effects on the human body; examples are coca, the source of cocaine and crack, and the opium poppy, the source of heroin.
In addition to all these uses of plants, we should not forget their aesthetic value. Flowers brighten any yard, ornamental plants accent landscaping, and trees provide cooling shade during the summer as well as shelter from harsh winds during the winter.
Figure 30A Plants used for food.
Figure 30B Plants used commercially.
With over 270,000 species of angiosperms alone, why do you think we get most of our nourishment from only three plants (wheat, corn, and rice)?
Humans derive most of their nourishment from three flowering plants: wheat, corn, and rice. All three of these plants are members of the grass family and are collectively called grains (Fig. 30A). Wheat is commonly used to produce flour and bread. It was first cultivated in the Middle East about 8000 b.c., and is thought to be one of the earliest cultivated plants. Early settlers brought wheat to North America, where many varieties of corn, more properly called maize, were already in existence. Rice originated in southeastern Asia several thousand years ago, where it grew in swamps. Many foods of both plant and animal origin are considered bland or tasteless without seasonings or spices. The Americas were discovered when Columbus was seeking a new route to the Far East to acquire spices, such as nutmeg, oregano, rosemary, and sage. In addition, our primary sweetener, sugar, comes almost exclusively from two plants-sugarcane (grown in South America, Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean) and sugar beets (grown mostly in Europe and North America). Our most popular drinks-coffee, tea, and cola-also come from flowering plants. Coffee originated in Ethiopia, whereas tea is thought to have been first used somewhere in central Asia. Cotton and rubber are two plants that still have many uses today (Fig. 30B). Until a few decades ago, cotton and other natural fibers were our only source of clothing. Interestingly, when Levi Strauss wanted to make a tough pair of jeans, he needed a stronger fiber than cotton, so he used hemp. Hemp comes from a plant that is closely related to marijuana, but unlike marijuana, has extremely small amounts of the chemical tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which causes the hallucinogenic effect when marijuana is smoked. Today, hemp is increasingly used to make clothing due to its toughness and wearability. Rubber had its origin in Brazil from the thick, white sap of the rubber tree. To produce a stronger rubber, such as that in tires, sulfur is added, and the sap is heated in a process called vulcanization. This produces a flexible material less sensitive to temperature changes. However, at present, most rubber is synthetically produced.
Plants have also been used for centuries for a number of important household items, including the house itself. We are most familiar with lumber as the major structural portion in buildings. This wood comes mainly from a variety of conifers: pine, fir, and spruce, among others. In the tropics, trees and even herbs provide important components for houses. In rural parts of Central and South America, palm leaves are preferable to tin for roofs, because they last as long as ten years and are quieter during rainstorms. In the Middle East, numerous houses along rivers are made entirely of reeds.
Today, plants are increasingly researched for their use in medicinal products. Currently, about 50% of all pharmaceutical drugs originate from plants or are derived from plant products. Some cancers are even treatable with medicinal plants, such as the rosy periwinkle, extracts from which have shown some success in treating childhood leukemia. Indeed, the National Cancer Institute and most pharmaceutical companies have spent millions of dollars to send botanists out to collect and test plant samples from around the world. Tribal medicine men, or shamans, of South America and Africa have already been of great importance in developing numerous drugs. However, plant extracts also continue to be misused for their hallucinogenic or other effects on the human body; examples are coca, the source of cocaine and crack, and the opium poppy, the source of heroin.
In addition to all these uses of plants, we should not forget their aesthetic value. Flowers brighten any yard, ornamental plants accent landscaping, and trees provide cooling shade during the summer as well as shelter from harsh winds during the winter.
Figure 30A Plants used for food.

Figure 30B Plants used commercially.

With over 270,000 species of angiosperms alone, why do you think we get most of our nourishment from only three plants (wheat, corn, and rice)?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What are some uses of plants, other than those just discussed?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








