Deck 16: Continental Shelves and Neritic Zone
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 16: Continental Shelves and Neritic Zone
1
How do waves and currents affect the types of benthic organisms found on the continental shelf?
The frequency and force of movement of the water on continental shelves controls many aspects of the benthic communities. Organisms strive for stable environments, even if those environments have strong movement of water. For organisms that withstand wave shock, their body size and shape is adapted to those forces. During storms however, waves create an unstable environment for those same, and all other, organisms, and can be responsible for mortality (especially where sediment is unusually disturbed). Currents are also important for the survival of species, as some rely on the movement of water to transport organisms, their gametes, and their larvae. The lack of water movement is also important to some communities that rely on the nutrients that fall from above; these communities also rely on the lack of current to maintain their hold on the bottom.
2
Diagram a simple food web for the continental shelf.
A simple food web of the continental shelf begins with plankton, which are food for deposit feeders and some burrowers. 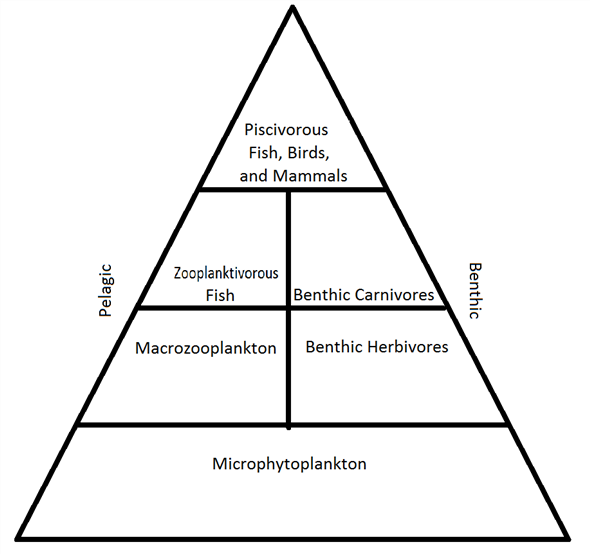

3
Why do disturbances such as landslides have a greater impact on invertebrate populations than on algal populations?
Invertebrate populations that live on the bottom of the continental seas rely on specific types of substrate for shelter and feeding. When a landslide occurs the burrowers are buried in new sediments that are not oxygenated, thus suffocating those that are buried. Other burrowers are displaced either deeper where the sediments are anoxic, or up to the surface where they are unprotected. Landslides also effect epifauna in the same way as those that burrow; they are buried or displaced and often killed. Those that survive may not be able to move to more suitable sediment, or may be exposed to sediment floating in the water column; both situations easily lead to death. Algae populations, on the other hand, have less stringent habitat requirements, and more easily survive a landslide because of their substrate needs, physiology, and reproduction habits. Algae live in hard substrate areas. Where calcareous algae live, a landslide removes invertebrates and makes that space available for the new growth of more algae. Many species of algae are able to photosynthesize with minimal light, similar to the conditions of clarity after a landslide. Algae are very elastic and can withstand the higher current energy produced by a landslide. They also have "floats" as part of their anatomy, and can continue to grow when uprooted.
4
Describe the process of succession that occurs in soft-bottom communities that are disturbed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Although representing only 10% of the ocean, coastal seas provide 90% of the world's commercial catch. The high level of productivity found in coastal seas supports large populations of fish and shellfish, far more than the open ocean.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What are two ecological roles for plankton in the neritic zone?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The uneven distribution of bottom organisms and sediment type on the continental shelf is referred to as
a. reticulation
b. patchiness
c. diversity
d. sediment selection
e. benthic orientation
a. reticulation
b. patchiness
c. diversity
d. sediment selection
e. benthic orientation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Name two important functions of bottom currents in benthic communities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Coastal waters receive nutrient runoff from the land and upwellings bring nutrients from deeper water to the surface. The heavy concentration of nutrients combined with large amounts of sunlight support large populations of phytoplankton which in turn support large numbers of zooplankton and fish.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
In colder waters, ___ dominate the phytoplankton.
a. krill
b. copepods
c. diatoms
d. dinoflagellates
e. kelp
a. krill
b. copepods
c. diatoms
d. dinoflagellates
e. kelp

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Match the following organisms with the appropriate description. 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Explain how the types of bottom sediments influence the diversity of life on the floor of the continental shelf.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Most of the world's harvest of commercial fish comes from
a. estuaries
b. bays
c. coastal seas
d. the open ocean
e. benthic regions
a. estuaries
b. bays
c. coastal seas
d. the open ocean
e. benthic regions

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The most abundant members of the zooplankton are
a. krill
b. copepods
c. jellyfish
d. diatoms
e. dinoflagellates
a. krill
b. copepods
c. jellyfish
d. diatoms
e. dinoflagellates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What are the main sources of nutrient input into coastal seas?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
List three explanations for the patchy distribution of organisms in soft-bottom communities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Currently there is concern about climate change caused by the greenhouse effect. How might this affect the productivity of coastal seas?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Nutrients produced by bacteria in the bottom sediments are returned to the surface waters by
a. gyres
b. upwellings
c. thermoclines
d. Eckman spirals
e. the Coriolis effect
a. gyres
b. upwellings
c. thermoclines
d. Eckman spirals
e. the Coriolis effect

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Hard bottom sediments such as rock support seaweeds and a variety of sessile and sedentary filter feeders. Soft bottom sediments such as sand and mud support many burrowing organisms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Explain how decreases in the size of lobster and cod populations have affected North Atlantic kelp beds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Burrowing organisms would more likely be found where
a. sediments are predominantly gravel
b. the sediments are sand, and the water currents are fast
c. the sediments are silt, and the water currents are slow
d. the sediments are silt, and the water currents are fast
e. landslides frequently disrupt the bottom
a. sediments are predominantly gravel
b. the sediments are sand, and the water currents are fast
c. the sediments are silt, and the water currents are slow
d. the sediments are silt, and the water currents are fast
e. landslides frequently disrupt the bottom

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In soft-bottom communities, suspension feeders and deposit feeders are usually not found in the same areas because
a. they compete with each other for food
b. they compete with each other for space
c. deposit feeders prey on suspension feeders
d. the suspended silt in regions inhabited by deposit feeders clogs the feeding structures of suspension feeders
e. the type of sediments inhabited by deposit feeders will not support suspension feeders
a. they compete with each other for food
b. they compete with each other for space
c. deposit feeders prey on suspension feeders
d. the suspended silt in regions inhabited by deposit feeders clogs the feeding structures of suspension feeders
e. the type of sediments inhabited by deposit feeders will not support suspension feeders

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What factors affect the size of plankton populations?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Why are kelp beds frequently compared to terrestrial rainforests?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Why do so many species of small fish found in coastal seas travel in large schools?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The world's most productive upwelling area is located off the coast of
a. California
b. Peru
c. China
d. South Africa
e. Europe
a. California
b. Peru
c. China
d. South Africa
e. Europe

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Kelp communities are important because they provide a complex three-dimensional habitat for hundreds of species as well as a food source for many species.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Why is the neritic zone such a productive area?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Sedentary and sessile filter feeders and suspension feeders are better adapted to
a. hard bottoms
b. soft bottoms
a. hard bottoms
b. soft bottoms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The dominant alga in southern California kelp forests is
a. Fucus
b. Laminaria
c. Eisenia
d. Sargassum
e. Macrocystis
a. Fucus
b. Laminaria
c. Eisenia
d. Sargassum
e. Macrocystis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








