Deck 46: Ecosystems
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 46: Ecosystems
1
Which term describes the process whereby toxic substances increase along trophic levels of an ecosystem?
A) biomassification
B) biomagnification
C) bioentropy
D) heterotrophy
A) biomassification
B) biomagnification
C) bioentropy
D) heterotrophy
Trophic level is the placement of organisms in a food chain where organisms eat other organisms and in turn are eaten by other organisms. This is how organisms generate their energy. The energy obtained by the organisms' decrease as they go up the trophic level.
Biomassification process does not occur anywhere in the biological process.
Bioentropy can be termed as the gradual decline of the process due to external disturbances.
Heterotrophy is a condition where an organism gains its complex organic material (energy) from another organism as it cannot synthesize its own food.
Hence, the options a., c. and d. are incorrect.
Biomagnification is a process in which toxic substances are accumulated and its concentration increased with each trophic level. The effect of this accumulation will affect those organisms placed at the highest trophic level. One classic example of biomagnification is spraying of DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane), a very harmful pesticide which is persistent, and non-biodegradable gets accumulated in the lower organisms which upon eaten by higher organisms causes harmful effects as the concentration becomes much more.
Hence, the correct answer is option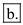
Biomassification process does not occur anywhere in the biological process.
Bioentropy can be termed as the gradual decline of the process due to external disturbances.
Heterotrophy is a condition where an organism gains its complex organic material (energy) from another organism as it cannot synthesize its own food.
Hence, the options a., c. and d. are incorrect.
Biomagnification is a process in which toxic substances are accumulated and its concentration increased with each trophic level. The effect of this accumulation will affect those organisms placed at the highest trophic level. One classic example of biomagnification is spraying of DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane), a very harmful pesticide which is persistent, and non-biodegradable gets accumulated in the lower organisms which upon eaten by higher organisms causes harmful effects as the concentration becomes much more.
Hence, the correct answer is option
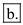
2
What are the factors that cause dead zones? Describe eutrophication, in particular, as a cause.
Dead zones are the areas in oceans and lakes that are hypoxic (low oxygen content). In these areas, mostly marine life cannot survive due to deficient oxygen conditions. There are many areas in the world where dead zones occur namely; East Coast, Gulf of Mexico and the Great Lakes.
Many chemical, physical, and biological factors are the cause of occurrence of dead zones. These factors include climatic changes, garbage dumbing into oceans, toxic waste spills, and oil spills.
Most importantly, the prime cause is the run-off excess nutrients from human made resources like industries and artificial fertilizers that are rich in phosphorus and nitrogen that have a severe effect on the water system. This phenomenon is termed as eutrophication.
Eutrophication occurs when there is excess of nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorous) entering the aquatic systems thereby, causing harmful effects that destroy the marine life. When eliminated in normal concentration, these nutrients act as a feeder system for blue-green algae (cyanobacteria).
When the nutrients are eliminated in excess, cyanobacteria, and other microorganisms may over-grow and damage the nearby organisms and environment too. This leads to the depletion of the dissolved oxygen which harms the aquatic life. This is primarily due to human activities around coastlines. This impact is called the algal blooms.
This excessive growth of algae affects the phytoplanktons, seaweeds, and others by preventing sunlight to reach them. It also affects many filter-feeder organisms like shellfish (oysters) that absorb harmful microbes present in algal blooms which are toxic for them, and in turn affect the humans who consume these oysters.
Many marine animals and birds in the shore that depend on fish for survival are affected too. Thus, algal blooms are a serious threat to marine life.
Hypoxia is another impact of eutrophication. It occurs due to lack of oxygen, and nutrient availability. Marine animals travel to the bottom of the sea, and later are decomposed by bacteria. This decomposition leads to oxygen depletion creating dead zones in the water which kills aquatic species thus, destroying marine life.
Many chemical, physical, and biological factors are the cause of occurrence of dead zones. These factors include climatic changes, garbage dumbing into oceans, toxic waste spills, and oil spills.
Most importantly, the prime cause is the run-off excess nutrients from human made resources like industries and artificial fertilizers that are rich in phosphorus and nitrogen that have a severe effect on the water system. This phenomenon is termed as eutrophication.
Eutrophication occurs when there is excess of nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorous) entering the aquatic systems thereby, causing harmful effects that destroy the marine life. When eliminated in normal concentration, these nutrients act as a feeder system for blue-green algae (cyanobacteria).
When the nutrients are eliminated in excess, cyanobacteria, and other microorganisms may over-grow and damage the nearby organisms and environment too. This leads to the depletion of the dissolved oxygen which harms the aquatic life. This is primarily due to human activities around coastlines. This impact is called the algal blooms.
This excessive growth of algae affects the phytoplanktons, seaweeds, and others by preventing sunlight to reach them. It also affects many filter-feeder organisms like shellfish (oysters) that absorb harmful microbes present in algal blooms which are toxic for them, and in turn affect the humans who consume these oysters.
Many marine animals and birds in the shore that depend on fish for survival are affected too. Thus, algal blooms are a serious threat to marine life.
Hypoxia is another impact of eutrophication. It occurs due to lack of oxygen, and nutrient availability. Marine animals travel to the bottom of the sea, and later are decomposed by bacteria. This decomposition leads to oxygen depletion creating dead zones in the water which kills aquatic species thus, destroying marine life.
3
Organisms that can make their own food using inorganic molecules are called:
A) autotrophs
B) heterotrophs
C) photoautotrophs
D) chemoautotrophs
A) autotrophs
B) heterotrophs
C) photoautotrophs
D) chemoautotrophs
Autotrophs are mainly of two types, namely photosynthetic autotrophs which use sunlight (organic molecule) as the source of energy to synthesize their food and chemosynthetic autotrophs which use inorganic molecules as the source of energy to synthesize their food. Therefore, all organisms that make their food using inorganic molecules cannot be called autotrophs.
Heterotrophs are organisms which are dependent on other organisms for their food requirement sin the form of complex organic substances as they cannot synthesize their own food.
Photoautotrophs or photosynthetic autotrophs use sunlight which is an organic molecule and not inorganic molecules to synthesize their food.
Hence, the options a., b. and c. are incorrect.
Chemoautotrophs or chemosynthetic autotrophs are the type of autotrophs that utilize inorganic molecules like ammonia, hydrogen sulfide and others in order to synthesize their food.
Hence, the correct answer is option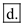
Heterotrophs are organisms which are dependent on other organisms for their food requirement sin the form of complex organic substances as they cannot synthesize their own food.
Photoautotrophs or photosynthetic autotrophs use sunlight which is an organic molecule and not inorganic molecules to synthesize their food.
Hence, the options a., b. and c. are incorrect.
Chemoautotrophs or chemosynthetic autotrophs are the type of autotrophs that utilize inorganic molecules like ammonia, hydrogen sulfide and others in order to synthesize their food.
Hence, the correct answer is option
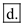
4
Why are drinking water supplies still a major concern for many countries?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In the English Channel ecosystem, the number of primary producers is smaller than the number of primary consumers because________.
A) the apex consumers have a low turnover rate
B) the primary producers have a low turnover rate
C) the primary producers have a high turnover rate
D) the primary consumers have a high turnover rate
A) the apex consumers have a low turnover rate
B) the primary producers have a low turnover rate
C) the primary producers have a high turnover rate
D) the primary consumers have a high turnover rate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What law of chemistry determines how much energy can be transferred when it is converted from one form to another?
A) the first law of thermodynamics
B) the second law of thermodynamics
C) the conservation of matter
D) the conservation of energy
A) the first law of thermodynamics
B) the second law of thermodynamics
C) the conservation of matter
D) the conservation of energy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The movement of mineral nutrients through organisms and their environment is called a ________ cycle.
A) biological
B) bioaccumulation
C) biogeochemical
D) biochemical
A) biological
B) bioaccumulation
C) biogeochemical
D) biochemical

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Carbon is present in the atmosphere as ________.
A) carbon dioxide
B) carbonate ion
C) carbon dust
D) carbon monoxide
A) carbon dioxide
B) carbonate ion
C) carbon dust
D) carbon monoxide

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Figure 46.8 Why do you think the value for gross productivity of the primary producers is the same as the value for total heat and respiration (20,810 kcal/m 2 /yr)? 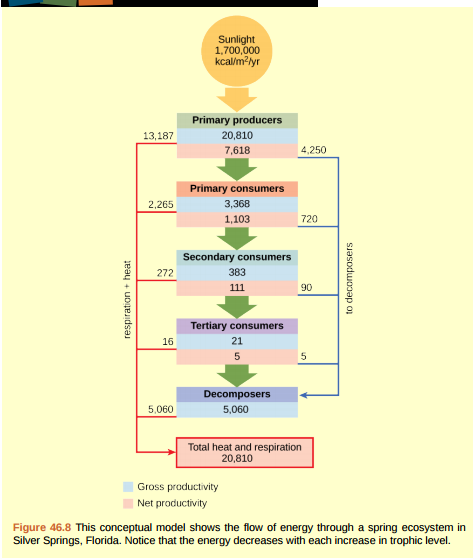


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The majority of water found on Earth is:
A) ice
B) water vapor
C) fresh water
D) salt water
A) ice
B) water vapor
C) fresh water
D) salt water

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Figure 46.10 Pyramids depicting the number of organisms or biomass may be inverted, upright, or even diamond-shaped. Energy pyramids, however, are always upright. Why? 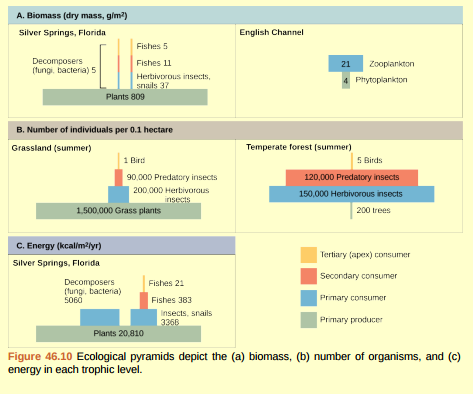


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The average time a molecule spends in its reservoir is known as ________.
A) residence time
B) restriction time
C) resilience time
D) storage time
A) residence time
B) restriction time
C) resilience time
D) storage time

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Figure 46.17 Which of the following statements about the nitrogen cycle is false?
A) Ammonification converts organic nitrogenous matter from living organisms into ammonium (NH 4 + ).
B) Denitrification by bacteria converts nitrates (NO 3 - ) to nitrogen gas (N2 ).
C) Nitrification by bacteria converts nitrates (NO 3 - ) to nitrites (NO2 - ).
D) Nitrogen fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas (N2 ) into organic compounds.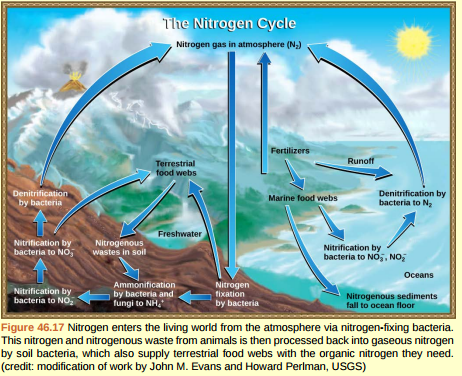
A) Ammonification converts organic nitrogenous matter from living organisms into ammonium (NH 4 + ).
B) Denitrification by bacteria converts nitrates (NO 3 - ) to nitrogen gas (N2 ).
C) Nitrification by bacteria converts nitrates (NO 3 - ) to nitrites (NO2 - ).
D) Nitrogen fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas (N2 ) into organic compounds.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The process whereby oxygen is depleted by the growth of microorganisms due to excess nutrients in aquatic systems is called ________.
A) dead zoning
B) eutrophication
C) retrofication
D) depletion
A) dead zoning
B) eutrophication
C) retrofication
D) depletion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The ability of an ecosystem to return to its equilibrium state after an environmental disturbance is called ________.
A) resistance
B) restoration
C) reformation
D) resilience
A) resistance
B) restoration
C) reformation
D) resilience

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The process whereby nitrogen is brought into organic molecules is called ________.
A) nitrification
B) denitrification
C) nitrogen fixation
D) nitrogen cycling
A) nitrification
B) denitrification
C) nitrogen fixation
D) nitrogen cycling

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A re-created ecosystem in a laboratory environment is known as a ________.
A) mesocosm
B) simulation
C) microcosm
D) reproduction
A) mesocosm
B) simulation
C) microcosm
D) reproduction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Compare and contrast food chains and food webs. What are the strengths of each concept in describing ecosystems?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Decomposers are associated with which class of food web?
A) grazing
B) detrital
C) inverted
D) aquatic
A) grazing
B) detrital
C) inverted
D) aquatic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Describe freshwater, ocean, and terrestrial ecosystems.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The primary producers in an ocean grazing food web are usually ________.
A) plants
B) animals
C) fungi
D) phytoplankton
A) plants
B) animals
C) fungi
D) phytoplankton

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Compare grazing and detrital food webs. Why would they both be present in the same ecosystem?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What term describes the use of mathematical equations in the modeling of linear aspects of ecosystems?
A) analytical modeling
B) simulation modeling
C) conceptual modeling
D) individual-based modeling
A) analytical modeling
B) simulation modeling
C) conceptual modeling
D) individual-based modeling

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Compare the three types of ecological pyramids and how well they describe ecosystem structure. Identify which ones can be inverted and give an example of an inverted pyramid for each.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The position of an organism along a food chain is known as its ________.
A) locus
B) location
C) trophic level
D) microcosm
A) locus
B) location
C) trophic level
D) microcosm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
How does the amount of food a warm blooded-animal (endotherm) eats relate to its net production efficiency (NPE)?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The weight of living organisms in an ecosystem at a particular point in time is called:
A) energy
B) production
C) entropy
D) biomass
A) energy
B) production
C) entropy
D) biomass

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Describe nitrogen fixation and why it is important to agriculture.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 28 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








