Deck 19: The Identification Problem
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/17
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 19: The Identification Problem
1
Show that the two definitions of the order condition of identification (see Section 19.3) are equivalent.
Identification:
Identification problem exists in the model, in spite of change in the value of parameter(s). Therefore, it does not modify the relative probability of different possible data sets.
Definition 1 of identification:
To estimate the equation's parameters, under the system of M simultaneous equation model, M -1 variable must be absent from the equation, which is the necessary condition for identification. This can be expressed in the form of equation as follows: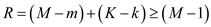 Definition 2 of identification:
Definition 2 of identification:
The model to be identified in the model M simultaneous equation model, the prearranged variables omitted from model must be less than the number of endogenous variables included in equation less 1. This is expressed equation form as follows: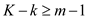
Identification problem exists in the model, in spite of change in the value of parameter(s). Therefore, it does not modify the relative probability of different possible data sets.
Definition 1 of identification:
To estimate the equation's parameters, under the system of M simultaneous equation model, M -1 variable must be absent from the equation, which is the necessary condition for identification. This can be expressed in the form of equation as follows:
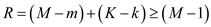 Definition 2 of identification:
Definition 2 of identification: The model to be identified in the model M simultaneous equation model, the prearranged variables omitted from model must be less than the number of endogenous variables included in equation less 1. This is expressed equation form as follows:
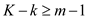
2
Deduce the structural coefficients from the reduced-form coefficients given in Eqs. (19.2.25) and (19.2.27).
The objective is to deduce structural coefficient from the reduced forms in (19.2.25) and (19.2.27).
Dividing (19.2.27) first equation by (19.2.25) first equation and solving these further gives us: and
and  Similarly, dividing (19.2.27) second equation by (19.2.25) second equation gives us:
Similarly, dividing (19.2.27) second equation by (19.2.25) second equation gives us: 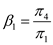 And dividing (19.2.27) third equation by (19.2.25) third equation gives us:
And dividing (19.2.27) third equation by (19.2.25) third equation gives us: 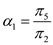 Now, subtract (19.2.25) third equation from (19.2.27) third equation and then replacing
Now, subtract (19.2.25) third equation from (19.2.27) third equation and then replacing 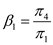 gives us:
gives us:  Similarly, subtract (19.2.25) second equation from (19.2.27) second equation and then replacing
Similarly, subtract (19.2.25) second equation from (19.2.27) second equation and then replacing 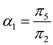 gives us:
gives us: 
Dividing (19.2.27) first equation by (19.2.25) first equation and solving these further gives us:
 and
and  Similarly, dividing (19.2.27) second equation by (19.2.25) second equation gives us:
Similarly, dividing (19.2.27) second equation by (19.2.25) second equation gives us: 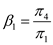 And dividing (19.2.27) third equation by (19.2.25) third equation gives us:
And dividing (19.2.27) third equation by (19.2.25) third equation gives us: 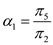 Now, subtract (19.2.25) third equation from (19.2.27) third equation and then replacing
Now, subtract (19.2.25) third equation from (19.2.27) third equation and then replacing 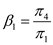 gives us:
gives us:  Similarly, subtract (19.2.25) second equation from (19.2.27) second equation and then replacing
Similarly, subtract (19.2.25) second equation from (19.2.27) second equation and then replacing 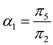 gives us:
gives us: 
3
Obtain the reduced form of the following models and determine in each case whether the structural equations are unidentified, just identified, or overidentified:
a. Chap. 18, Example 18.2.
b. Chap. 18, Example 18.3.
c. Chap. 18, Example 18.6.
a. Chap. 18, Example 18.2.
b. Chap. 18, Example 18.3.
c. Chap. 18, Example 18.6.
The given information:
The regression model for consumption function is represented as given below: …… (1)
…… (1)
The regression model for the income identity is represented as given below: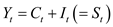 …… (2)
…… (2)
Here,
The consumption expenditure is C.
The income is Y.
The investment (assumed exogenous) is I.
The savings is S.
The time is t.
The stochastic disturbance is u.
The parameters are 0 and 1.
The regression model for money wage is represented as given below: …… (3)
…… (3)
The regression model for the price determination is represented as given below: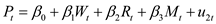 …… (4)
…… (4)
Here,
The rate of change of money wages is W.
The unemployment rate % is UN.
The rate of change of prices is P.
The rate of change of cost of capital is R.
The rate of change of price of imported raw material is M.
The time is t.
The stochastic disturbances are u 1, and u 2.
The regression model for the consumption function is represented as given below: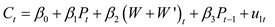 …… (5)
…… (5)
The regression model for the investment function is represented as given below …… (6)
…… (6)
The regression model for the demand for labor is represented as given below: …… (7)
…… (7)
Here,
The consumption expenditure is C.
The investment expenditure is I.
The government expenditure is G.
The profits are P.
The private wage bill is W.
The government wage bill is W'.
The capital stock is K.
The taxes are T.
The income after tax is Y.
The time is t.
The stochastic disturbances are u 1, u 2, and u 3.
The identity of the consumption function is represented as give below: …… (8)
…… (8)
The identity of the investment function is represented as given below: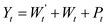 …… (9)
…… (9)
The identity of the demand for labor is represented as given below: 0
0
…… (10)
Reduced form equation:
The reduced form equation is a model that expresses an endogenous variable solely in term of the predetermined variables and the stochastic disturbances. To determine the reduced form, it is necessary to ensure the equation is identified or not. The coefficient of the reduced form is expressed as 1
1
, 2
2
, 3
3
, 4
4
, 5
5
, 6
6
, and 7
7
.
The necessary condition of the identification:
The necessary condition of the identification is explained as follows:
Identification:
Identification problem exists in the model in spite of change in the value of parameter(s), it does not modify the relative probability of different possible data sets.
Definition 1 of identification:
To estimate the equation's parameters, under the system of M simultaneous equation model, the M -1 variable must be absent from the equation which is the necessary condition for identification. This can be expressed in the form of equation which is as follows: 8
8
…… (11)
Definition 2 of identification:
The model to be identified in the model M simultaneous equation model, the prearranged variables omitted from model must be less than the number of endogenous variables included in equation less 1, this expressed equation form is as follows: 9
9
…… (12)
Just identified:
If the model is just identified then it can form unique values for the structural coefficients.
Under identified:
If the model is under identified then it is not possible to form the structural coefficients.
Over identified:
If it is over identified then it produces more than one value for the structural coefficients.
The general form of the reduced model is represented as follows: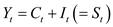 0
0
…… (13)
a.
Reduce form:
The reduced form of the model-1 and 2 is represented as follows: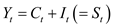 1
1
…… (14)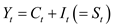 2
2
…… (15)
From the reduced form model-14 and 15, the endogenous variable M is 2, which are C and Y. The number variable K is 1, which is I. According to identification condition (12) the model 14 and 15 is exactly identified.
b.
Reduced form:
The reduced form for the model-3 and 4 is represented as follows: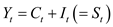 3
3
…… (16)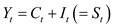 4
4
…… (17)
From the reduced form model- 16 and 17, the endogenous variable M is 2, which are W and P. The number of the variable K is 3, which are UN, R, M. According to the first order condition (12) the model-16 is over identified and model 17 is just identified.
c.
Reduced form:
The reduced form for the model- 5, 6 and 77 is represented as follows: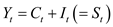 5
5
…… (18)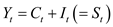 6
6
…… (19)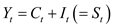 7
7
…… (20)
From the reduced form model- 18, 19, and 20, the endogenous variable M is 3, which are C , I , and W. The number of the variable K is 7, which are P , W , P t-1 , K t-1 , t, Y , T. In this case, applying first order condition (12), the model- 18, 19 and 20 are over identified.
The regression model for consumption function is represented as given below:
 …… (1)
…… (1)The regression model for the income identity is represented as given below:
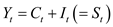 …… (2)
…… (2)Here,
The consumption expenditure is C.
The income is Y.
The investment (assumed exogenous) is I.
The savings is S.
The time is t.
The stochastic disturbance is u.
The parameters are 0 and 1.
The regression model for money wage is represented as given below:
 …… (3)
…… (3)The regression model for the price determination is represented as given below:
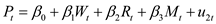 …… (4)
…… (4)Here,
The rate of change of money wages is W.
The unemployment rate % is UN.
The rate of change of prices is P.
The rate of change of cost of capital is R.
The rate of change of price of imported raw material is M.
The time is t.
The stochastic disturbances are u 1, and u 2.
The regression model for the consumption function is represented as given below:
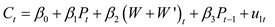 …… (5)
…… (5)The regression model for the investment function is represented as given below
 …… (6)
…… (6)The regression model for the demand for labor is represented as given below:
 …… (7)
…… (7)Here,
The consumption expenditure is C.
The investment expenditure is I.
The government expenditure is G.
The profits are P.
The private wage bill is W.
The government wage bill is W'.
The capital stock is K.
The taxes are T.
The income after tax is Y.
The time is t.
The stochastic disturbances are u 1, u 2, and u 3.
The identity of the consumption function is represented as give below:
 …… (8)
…… (8)The identity of the investment function is represented as given below:
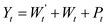 …… (9)
…… (9)The identity of the demand for labor is represented as given below:
 0
0…… (10)
Reduced form equation:
The reduced form equation is a model that expresses an endogenous variable solely in term of the predetermined variables and the stochastic disturbances. To determine the reduced form, it is necessary to ensure the equation is identified or not. The coefficient of the reduced form is expressed as
 1
1,
 2
2,
 3
3,
 4
4,
 5
5,
 6
6, and
 7
7.
The necessary condition of the identification:
The necessary condition of the identification is explained as follows:
Identification:
Identification problem exists in the model in spite of change in the value of parameter(s), it does not modify the relative probability of different possible data sets.
Definition 1 of identification:
To estimate the equation's parameters, under the system of M simultaneous equation model, the M -1 variable must be absent from the equation which is the necessary condition for identification. This can be expressed in the form of equation which is as follows:
 8
8…… (11)
Definition 2 of identification:
The model to be identified in the model M simultaneous equation model, the prearranged variables omitted from model must be less than the number of endogenous variables included in equation less 1, this expressed equation form is as follows:
 9
9…… (12)
Just identified:
If the model is just identified then it can form unique values for the structural coefficients.
Under identified:
If the model is under identified then it is not possible to form the structural coefficients.
Over identified:
If it is over identified then it produces more than one value for the structural coefficients.
The general form of the reduced model is represented as follows:
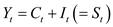 0
0…… (13)
a.
Reduce form:
The reduced form of the model-1 and 2 is represented as follows:
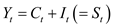 1
1…… (14)
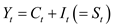 2
2…… (15)
From the reduced form model-14 and 15, the endogenous variable M is 2, which are C and Y. The number variable K is 1, which is I. According to identification condition (12) the model 14 and 15 is exactly identified.
b.
Reduced form:
The reduced form for the model-3 and 4 is represented as follows:
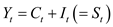 3
3…… (16)
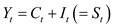 4
4…… (17)
From the reduced form model- 16 and 17, the endogenous variable M is 2, which are W and P. The number of the variable K is 3, which are UN, R, M. According to the first order condition (12) the model-16 is over identified and model 17 is just identified.
c.
Reduced form:
The reduced form for the model- 5, 6 and 77 is represented as follows:
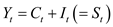 5
5…… (18)
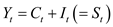 6
6…… (19)
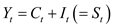 7
7…… (20)
From the reduced form model- 18, 19, and 20, the endogenous variable M is 3, which are C , I , and W. The number of the variable K is 7, which are P , W , P t-1 , K t-1 , t, Y , T. In this case, applying first order condition (12), the model- 18, 19 and 20 are over identified.
4
Check the identifiability of the models of Exercise 19.3 by applying both the order and rank conditions of identification.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In the model (19.2.22) of the text it was shown that the supply equation was overidentified. What restrictions, if any, on the structural parameters will make this equation just identified Justify the restrictions you impose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
From the model 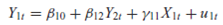
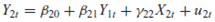
the following reduced-form equations are obtained: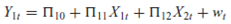
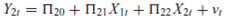
a. Are the structural equations identified
b. What happens to identification if it is known a priori that 11 = 0
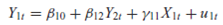
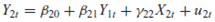
the following reduced-form equations are obtained:
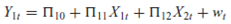
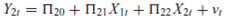
a. Are the structural equations identified
b. What happens to identification if it is known a priori that 11 = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Refer to Exercise 19.6. The estimated reduced-form equations are as follows: 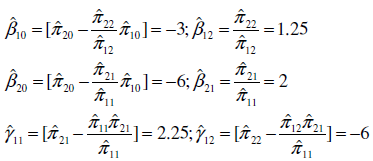
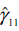
a. Obtain the values of the structural parameters.
b. How would you test the null hypothesis that 11 = 0
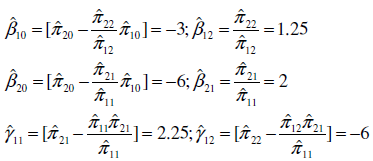
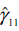
a. Obtain the values of the structural parameters.
b. How would you test the null hypothesis that 11 = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The model 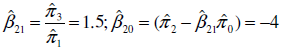
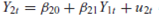
produces the following reduced-form equations: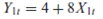
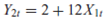
a. Which structural coefficients, if any, can be estimated from the reduced-form coefficients Demonstrate your contention.
b. How does the answer to ( a ) change if it is known a priori that (1) 12 = 0 and (2) 10 = 0
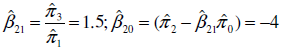
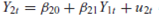
produces the following reduced-form equations:
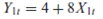
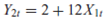
a. Which structural coefficients, if any, can be estimated from the reduced-form coefficients Demonstrate your contention.
b. How does the answer to ( a ) change if it is known a priori that (1) 12 = 0 and (2) 10 = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Determine whether the structural equations of the model given in Exercise 18.8 are identified.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Refer to Exercise 18.7 and find out which structural equations can be identified.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Table 19.3 is a model in five equations with five endogenous variables Y and four exogenous variables X: 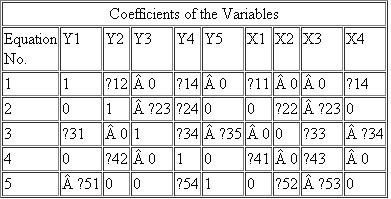 Determine the identifiability of each equation with the aid of the order and rank conditions of identifications.
Determine the identifiability of each equation with the aid of the order and rank conditions of identifications.
 Determine the identifiability of each equation with the aid of the order and rank conditions of identifications.
Determine the identifiability of each equation with the aid of the order and rank conditions of identifications.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Consider the following extended Keynesian model of income determination:
Consumption function:C t = 1 + 2 Y t 3 T t + u 1 t
Investment function:I t = 0 + 1 Y t 1 + u 2 t
Taxation function: T t = 0 + 1 Y t + u 3t
Income identity:Y t = C t + I t + G t
where C = consumption expenditure
Y = income
I = investment
T = taxes
G = government expenditure
u 's = the disturbance terms
In the model the endogenous variables are C , I , T , and Y and the predetermined variables are G and Y t 1.
By applying the order condition, check the identifiability of each of the equations in the system and of the system as a whole. What would happen if r t , the interest rate, assumed to be exogenous, were to appear on the right-hand side of the investment function
Consumption function:C t = 1 + 2 Y t 3 T t + u 1 t
Investment function:I t = 0 + 1 Y t 1 + u 2 t
Taxation function: T t = 0 + 1 Y t + u 3t
Income identity:Y t = C t + I t + G t
where C = consumption expenditure
Y = income
I = investment
T = taxes
G = government expenditure
u 's = the disturbance terms
In the model the endogenous variables are C , I , T , and Y and the predetermined variables are G and Y t 1.
By applying the order condition, check the identifiability of each of the equations in the system and of the system as a whole. What would happen if r t , the interest rate, assumed to be exogenous, were to appear on the right-hand side of the investment function

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Refer to the data given in Table 18.1 of Chapter 18. Using these data, estimate the reduced-form regressions (19.1.2) and (19.1.4). Can you estimate 0 and 1 Show your calculations. Is the model identified Why or why not

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Suppose we propose yet another definition of the order condition of identifiability:
K m + k 1
which states that the number of predetermined variables in the system can be no less than the number of unknown coefficients in the equation to be identified. Show that this definition is equivalent to the two other definitions of the order condition given in the text.
K m + k 1
which states that the number of predetermined variables in the system can be no less than the number of unknown coefficients in the equation to be identified. Show that this definition is equivalent to the two other definitions of the order condition given in the text.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A simplified version of Suits's model of the watermelon market is as follows:*
Demand equation: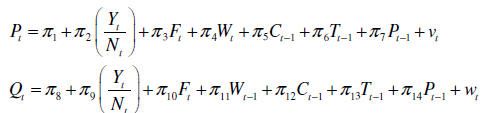
Crop supply function: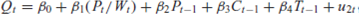
where P = price
( Q / N ) = per capita quantity demanded
( Y / N ) = per capita income
F t = freight costs
( P/ W ) = price relative to the farm wage rate
C = price of cotton
T = price of other vegetables
N = population
P and Q are the endogenous variables.
a. Obtain the reduced form.
b. Determine whether the demand, the supply, or both functions are identified.
Demand equation:
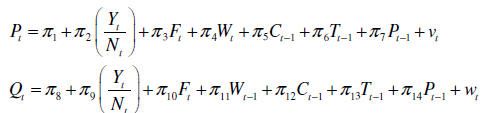
Crop supply function:
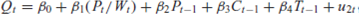
where P = price
( Q / N ) = per capita quantity demanded
( Y / N ) = per capita income
F t = freight costs
( P/ W ) = price relative to the farm wage rate
C = price of cotton
T = price of other vegetables
N = population
P and Q are the endogenous variables.
a. Obtain the reduced form.
b. Determine whether the demand, the supply, or both functions are identified.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Consider the following demand-and-supply model for money:
Money demand: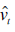
Money supply: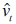
TABLE 19.4 Money, GDP, Interest Rate, and Consumer Price Index, United States, 1970-2006
Source: Economic Report of the President, 2007, Tables B-2, B-60, B-69, B-73.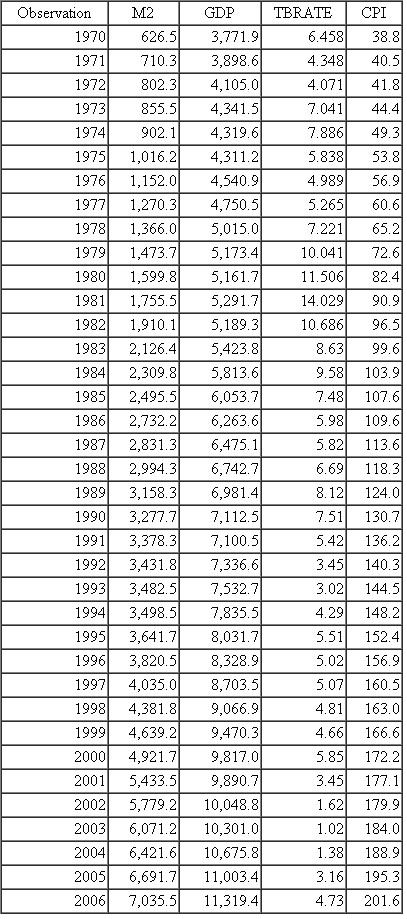 Notes: M 2 = M 2 Money supply (billions of dollars).
Notes: M 2 = M 2 Money supply (billions of dollars).
GDP = gross domestic product (billions of dollars).
TBRATE = 3-month Treasury bill rate, %.
CPI = Consumer Price Index (19821984 = 100).
where M = money
Y = income
R = rate of interest
P = price
u 's = error terms
Assume that R and P are exogenous and M and Y are endogenous. Table 19.4 gives data on M ( M 2 definition), Y (GDP), R (3-month Treasury bill rate) and P (Consumer Price Index), for the United States for 1970-2006.
a. Is the demand function identified
b. Is the supply function identified
c. Obtain the expressions for the reduced-form equations for M and Y.
d. Apply the test of simultaneity to the supply function.
e. How would we find out if Y in the money supply function is in fact endogenous
Money demand:
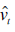
Money supply:
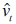
TABLE 19.4 Money, GDP, Interest Rate, and Consumer Price Index, United States, 1970-2006
Source: Economic Report of the President, 2007, Tables B-2, B-60, B-69, B-73.
 Notes: M 2 = M 2 Money supply (billions of dollars).
Notes: M 2 = M 2 Money supply (billions of dollars).GDP = gross domestic product (billions of dollars).
TBRATE = 3-month Treasury bill rate, %.
CPI = Consumer Price Index (19821984 = 100).
where M = money
Y = income
R = rate of interest
P = price
u 's = error terms
Assume that R and P are exogenous and M and Y are endogenous. Table 19.4 gives data on M ( M 2 definition), Y (GDP), R (3-month Treasury bill rate) and P (Consumer Price Index), for the United States for 1970-2006.
a. Is the demand function identified
b. Is the supply function identified
c. Obtain the expressions for the reduced-form equations for M and Y.
d. Apply the test of simultaneity to the supply function.
e. How would we find out if Y in the money supply function is in fact endogenous

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The Hausman test discussed in the text can also be conducted in the following way. Consider Eq. (19.4.7): ![The Hausman test discussed in the text can also be conducted in the following way. Consider Eq. (19.4.7): a. Since P t and v t have the same coefficients, how would you test that in a given application that is indeed the case What are the implications of this b. Since P t is uncorrelated with u 2 t by design (why), one way to find out if P t is exogenous is to see if v t is correlated with u 2 t. How would you go about testing this Which test do you use ( Hint: Substitute P t from [19.4.6] into Eq. [19.4.7].)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/SM2027/11eb5d88_3d86_0230_b078_75973b204608_SM2027_11.jpg)
a. Since P t and v t have the same coefficients, how would you test that in a given application that is indeed the case What are the implications of this
b. Since P t is uncorrelated with u 2 t by design (why), one way to find out if P t is exogenous is to see if v t is correlated with u 2 t. How would you go about testing this Which test do you use ( Hint: Substitute P t from [19.4.6] into Eq. [19.4.7].)
![The Hausman test discussed in the text can also be conducted in the following way. Consider Eq. (19.4.7): a. Since P t and v t have the same coefficients, how would you test that in a given application that is indeed the case What are the implications of this b. Since P t is uncorrelated with u 2 t by design (why), one way to find out if P t is exogenous is to see if v t is correlated with u 2 t. How would you go about testing this Which test do you use ( Hint: Substitute P t from [19.4.6] into Eq. [19.4.7].)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/SM2027/11eb5d88_3d86_0230_b078_75973b204608_SM2027_11.jpg)
a. Since P t and v t have the same coefficients, how would you test that in a given application that is indeed the case What are the implications of this
b. Since P t is uncorrelated with u 2 t by design (why), one way to find out if P t is exogenous is to see if v t is correlated with u 2 t. How would you go about testing this Which test do you use ( Hint: Substitute P t from [19.4.6] into Eq. [19.4.7].)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 17 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








