Deck 20: Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy, and Reaction Direction
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 20: Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy, and Reaction Direction
1
Which of the following is always true for an exothermic process?
A)q sys > 0, Δ S surr < 0
B)q sys < 0, Δ S surr > 0
C)q sys < 0, Δ S surr < 0
D)q sys > 0, Δ S surr > 0
E)w < 0
A)q sys > 0, Δ S surr < 0
B)q sys < 0, Δ S surr > 0
C)q sys < 0, Δ S surr < 0
D)q sys > 0, Δ S surr > 0
E)w < 0
q sys < 0, Δ S surr > 0
2
A certain process has ΔSuniv > 0 at 25°C. What does one know about the process?
A)It is exothermic.
B)It is endothermic.
C)It is spontaneous at 25°C.
D)It will move rapidly toward equilibrium.
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)It is exothermic.
B)It is endothermic.
C)It is spontaneous at 25°C.
D)It will move rapidly toward equilibrium.
E)None of these choices are correct.
It is spontaneous at 25°C.
3
Which of the following should have the greatest molar entropy at 298 K?
A)CH 4( g)
B)H 2O( l)
C)NaCl( s)
D)N 2O 4( g)
E)H 2( g)
A)CH 4( g)
B)H 2O( l)
C)NaCl( s)
D)N 2O 4( g)
E)H 2( g)
N 2O 4( g)
4
As a chemical reaction proceeds toward equilibrium, the free energy of the system decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following values is based on the Third Law of Thermodynamics?
A)Δ H° f = 0 for Al( s)at 298 K
B)Δ G° f = 0 for H 2( g)at 298 K
C)S° = 51.446 J/(mol·K)for Na( s)at 298 K
D)q sys < 0 for H 2O( l)→ H 2O(s)at 0°C
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)Δ H° f = 0 for Al( s)at 298 K
B)Δ G° f = 0 for H 2( g)at 298 K
C)S° = 51.446 J/(mol·K)for Na( s)at 298 K
D)q sys < 0 for H 2O( l)→ H 2O(s)at 0°C
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Under a given set of conditions, all microstates of a system are equally probable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The free energy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero, is zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following is always true for an endothermic process?
A)q sys > 0, Δ S surr < 0
B)q sys < 0, Δ S surr > 0
C)q sys < 0, Δ S surr < 0
D)q sys > 0, Δ S surr > 0
E)w < 0
A)q sys > 0, Δ S surr < 0
B)q sys < 0, Δ S surr > 0
C)q sys < 0, Δ S surr < 0
D)q sys > 0, Δ S surr > 0
E)w < 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
For any reaction, if ΔG° > 0, then K < 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The higher the pressure of a gas sample, the greater is its entropy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In some spontaneous processes, the entropy of the surroundings decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The term microstate refers to the energy state of a single molecule in a system of many molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In a spontaneous process, the entropy of the system always increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
For a reaction at equilibrium, ΔSuniv = 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following is true for a system at equilibrium?
A)Δ S° sys = Δ S° surr
B)Δ S° sys = −Δ S° surr
C)Δ S° sys = Δ S° surr = 0
D)Δ S° univ > 0
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)Δ S° sys = Δ S° surr
B)Δ S° sys = −Δ S° surr
C)Δ S° sys = Δ S° surr = 0
D)Δ S° univ > 0
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The entropy of one mole of oxygen gas in a 0.5-L container is less than it would be in a 22.4-L container at the same temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
For a given reaction, a change in the pressure may result in a change in the sign of ΔG.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following is true for pure oxygen gas, O2(g) at 25°C?
A)Δ H° f > 0
B)Δ H° f < 0
C)Δ G° f > 0
D)Δ G° f < 0
E)S° > 0
A)Δ H° f > 0
B)Δ H° f < 0
C)Δ G° f > 0
D)Δ G° f < 0
E)S° > 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following results in a decrease in the entropy of the system?
A)O 2( g), 300 K → O 2( g), 400 K
B)H 2O( s), 0°C → H 2O( l), 0°C
C)N 2( g), 25°C → N 2( aq), 25°C
D)NH 3( l), −34.5°C → NH 3( g), −34.5°C
E)2H 2O 2( g)→ 2H 2O( g)+ O 2( g)
A)O 2( g), 300 K → O 2( g), 400 K
B)H 2O( s), 0°C → H 2O( l), 0°C
C)N 2( g), 25°C → N 2( aq), 25°C
D)NH 3( l), −34.5°C → NH 3( g), −34.5°C
E)2H 2O 2( g)→ 2H 2O( g)+ O 2( g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following is necessary for a process to be spontaneous?
A)Δ H sys < 0
B)Δ S sys > 0
C)Δ S surr < 0
D)Δ S univ > 0
E)Δ G sys = 0
A)Δ H sys < 0
B)Δ S sys > 0
C)Δ S surr < 0
D)Δ S univ > 0
E)Δ G sys = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? KCl(s) → K+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In which one of these pairs will the entropy of the first substance be greater than that of the second? Assume P and T are the same for each pair, unless stated otherwise.
A)1 mole of F 2( g); 1 mole of Cl 2( g)
B)1 mole of I 2( s); 1 mole of I 2( g)
C)1 mole of CaCO 3( s); 1 mole of CaO( s)plus 1 mole of CO 2( g)
D)1 mole of H 2( g)at 25°C; 1 mole of H 2( g)at 50°C
E)1 mole of O 3( g); 1 mole of O 2( g)
A)1 mole of F 2( g); 1 mole of Cl 2( g)
B)1 mole of I 2( s); 1 mole of I 2( g)
C)1 mole of CaCO 3( s); 1 mole of CaO( s)plus 1 mole of CO 2( g)
D)1 mole of H 2( g)at 25°C; 1 mole of H 2( g)at 50°C
E)1 mole of O 3( g); 1 mole of O 2( g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? 2NH3(g) + 2ClF3(g) → 6HF(g) + N2(g) + Cl2(g)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following pairs has the member with the greater molar entropy listed first? All systems are at 25°C.
A)CO( g), CO 2( g)
B)NaCl( s), NaCl( aq)
C)H 2S( g), H 2S( aq)
D)Li( s), Pb( s)
E)H 2( g), H 2O( g)
A)CO( g), CO 2( g)
B)NaCl( s), NaCl( aq)
C)H 2S( g), H 2S( aq)
D)Li( s), Pb( s)
E)H 2( g), H 2O( g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which one of the following phase changes decreases the entropy of the system?
A)Melting
B)Heating a gas
C)Vaporization
D)Condensation
E)Sublimation
A)Melting
B)Heating a gas
C)Vaporization
D)Condensation
E)Sublimation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? O3(g) + NO(g) → O2(g) + NO2(g)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = ΔH°/T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = ΔH°/T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
You are given pure samples of ammonia, NH3(g), and nitrogen trifluoride, NF3(g). What prediction would you make concerning their standard molar entropies at 298 K?
A)S° ammonia > S° nitrogen trifluoride
B)S° ammonia < S° nitrogen trifluoride
C)S° ammonia ≈ S° nitrogen trifluoride
D)Other conditions need to be specified before a reliable prediction can be made.
E)Even if more conditions are specified, a reliable prediction cannot be made.
A)S° ammonia > S° nitrogen trifluoride
B)S° ammonia < S° nitrogen trifluoride
C)S° ammonia ≈ S° nitrogen trifluoride
D)Other conditions need to be specified before a reliable prediction can be made.
E)Even if more conditions are specified, a reliable prediction cannot be made.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which relationship best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? 8H2(g) + S8(s) → 8H2S(g)
A)Δ S° = Δ H°
B)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
C)Δ S° ≈ 0
D)Δ S° < 0
E)Δ S° > 0
A)Δ S° = Δ H°
B)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
C)Δ S° ≈ 0
D)Δ S° < 0
E)Δ S° > 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which, if any, of the following processes is spontaneous under the specified conditions?
A)H 2O( l)→ H 2O( s)at 25°C
B)CO 2( s)→ CO 2( g)at 0°C
C)2H 2O( g)→ 2H 2(g)+ O 2( g)
D)C(graphite)→ C(diamond)at 25°C and 1 atm pressure
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)H 2O( l)→ H 2O( s)at 25°C
B)CO 2( s)→ CO 2( g)at 0°C
C)2H 2O( g)→ 2H 2(g)+ O 2( g)
D)C(graphite)→ C(diamond)at 25°C and 1 atm pressure
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
You are given pure samples of ethane, C2H6(g), and toluene, C7H8(l). What prediction would you make concerning their standard molar entropies at 298 K?
A)S° ethane > S° toluene
B)S° ethane < S° toluene
C)S° ethane ≈ ( S° toluene)÷ 3
D)S° ethane ≈ S° toluene
E)Since toluene is much more complex than ethane, but ethane is in the gas phase while toluene is a liquid, any of these predictions can be confidently made without further information or calculations.
A)S° ethane > S° toluene
B)S° ethane < S° toluene
C)S° ethane ≈ ( S° toluene)÷ 3
D)S° ethane ≈ S° toluene
E)Since toluene is much more complex than ethane, but ethane is in the gas phase while toluene is a liquid, any of these predictions can be confidently made without further information or calculations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
When a sky diver free-falls through the air, the process is
A)non-spontaneous because he is accelerating due to the force applied by gravity.
B)non-spontaneous because he is losing potential energy.
C)non-spontaneous, if he had planned the jump for two weeks.
D)spontaneous.
E)in equilibrium.
A)non-spontaneous because he is accelerating due to the force applied by gravity.
B)non-spontaneous because he is losing potential energy.
C)non-spontaneous, if he had planned the jump for two weeks.
D)spontaneous.
E)in equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) → 2H2O(g) + 2SO2(g)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? Pb(s) + Cl2(g) → PbCl2(s)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
You are given pure samples of pentane, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3(l), and 1,3-pentadiene, CH2=CHCH=CHCH3(l). What prediction would you make concerning their standard molar entropies at 298 K?
A)S° pentane > S° 1, 3-pentadiene
B)S° pentane < S° 1, 3-pentadiene
C)S° pentane ≈ S° 1, 3-pentadiene
D)S° pentane = S° 1, 3-pentadiene + 2 S°H 2
E)More information is needed to make reasonable predictions.
A)S° pentane > S° 1, 3-pentadiene
B)S° pentane < S° 1, 3-pentadiene
C)S° pentane ≈ S° 1, 3-pentadiene
D)S° pentane = S° 1, 3-pentadiene + 2 S°H 2
E)More information is needed to make reasonable predictions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which relationship best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? CO(g) + H2O(g) → CO2(g) + H2(g)
A)Δ S° = Δ H°
B)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° < 0
E)Δ S° ≈ 0
A)Δ S° = Δ H°
B)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° < 0
E)Δ S° ≈ 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? HgS(s) + O2(g) → Hg(l) + SO2(g)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? CaO(s) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = Δ H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which relationship or statement best describes ΔS° for the following reaction? BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.
A)Δ S° ≈ 0
B)Δ S° < 0
C)Δ S° > 0
D)Δ S° = H°/ T
E)More information is needed to make a reasonable prediction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
In which one of the following pairs will the first system have a higher entropy than the second? Assume P and T are the same for each pair, unless stated otherwise.
A)1 mole He( g); 1 mole Kr( g)
B)1 mole O 2( g); 2 mole O( g)
C)1 mole CH 4( g); 1 mole C 2H 6( g)
D)1 mole Xe( g)at 1 atmosphere; 1 mole Xe( g)at 0.5 atmosphere
E)20 one-dollar bills distributed randomly among 20 people; 20 one-dollar bills distributed randomly among 10 people
A)1 mole He( g); 1 mole Kr( g)
B)1 mole O 2( g); 2 mole O( g)
C)1 mole CH 4( g); 1 mole C 2H 6( g)
D)1 mole Xe( g)at 1 atmosphere; 1 mole Xe( g)at 0.5 atmosphere
E)20 one-dollar bills distributed randomly among 20 people; 20 one-dollar bills distributed randomly among 10 people

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
For a process with ΔS < 0, which one of the following statements is correct?
A)The process will definitely be spontaneous if ΔH < 0.
B)The process will be definitely be spontaneous if Δ H < TΔ S.
C)The process can never be spontaneous.
D)The process will definitely be spontaneous, regardless of Δ H.
E)The process will definitely be spontaneous if Δ S surr > 0.
A)The process will definitely be spontaneous if ΔH < 0.
B)The process will be definitely be spontaneous if Δ H < TΔ S.
C)The process can never be spontaneous.
D)The process will definitely be spontaneous, regardless of Δ H.
E)The process will definitely be spontaneous if Δ S surr > 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which one of the following changes of state increases the entropy of the system?
A)Condensation
B)Cooling a gas
C)Freezing
D)Crystallization
E)Sublimation
A)Condensation
B)Cooling a gas
C)Freezing
D)Crystallization
E)Sublimation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Consider the following quantities used in thermodynamics: E, H, q, w, S, G. How many of them are state functions?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Calculate ΔS° for the combustion of propane. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
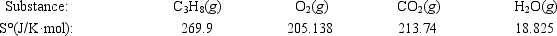
A)−100.9 J/K
B)−72.5 J/K
C)72.5 J/K
D)100.9 J/K
E)877.5 J/K
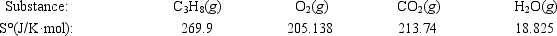
A)−100.9 J/K
B)−72.5 J/K
C)72.5 J/K
D)100.9 J/K
E)877.5 J/K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Given: H2O(l) → H2O(s) ΔH° = −6.02 kJ at 273K Calculate the entropy change of the surroundings (ΔSsurr) when one mole of water freezes at 0°C and a pressure of one atmosphere.
A)22.1 J/K
B)−22.1 J/K
C)397 J/K
D)−397 J/K
E)0.022 J/K
A)22.1 J/K
B)−22.1 J/K
C)397 J/K
D)−397 J/K
E)0.022 J/K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Calculate ΔS° for the reaction 2Cl2(g) + SO2(g) → SOCl2(g) + Cl2O(g)
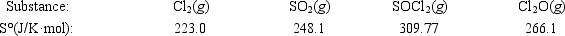
A)−118.2 J/K
B)−104.8 J/K
C)104.8 J/K
D)118.2 J/K
E)1270.0 J/K
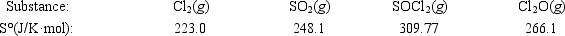
A)−118.2 J/K
B)−104.8 J/K
C)104.8 J/K
D)118.2 J/K
E)1270.0 J/K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Calculate ΔS° for the reaction SiCl4(g) + 2Mg(s) → 2MgCl2(s) + Si(s)

A)−254.96 J/K
B)−198.02 J/K
C)198.02 J/K
D)254.96 J/K
E)471.86 J/K

A)−254.96 J/K
B)−198.02 J/K
C)198.02 J/K
D)254.96 J/K
E)471.86 J/K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
For a chemical reaction to be spontaneous only at high temperatures, which of the following conditions must be met?
A)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° < 0
C)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° < 0
D)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° > 0
E)Δ G° > 0
A)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° < 0
C)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° < 0
D)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° > 0
E)Δ G° > 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
For a chemical reaction to be non-spontaneous at any temperature, which of the following conditions must be met?
A)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° < 0
C)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° < 0
D)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° > 0
E)All reactions are spontaneous at some temperature.
A)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° < 0
C)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° < 0
D)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° > 0
E)All reactions are spontaneous at some temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In order for a process to be spontaneous,
A)Δ H must be less than zero.
B)Δ S must be greater than zero.
C)Δ G must be greater than zero.
D)it should be rapid.
E)Δ S sys + Δ S surr must be greater than zero.
A)Δ H must be less than zero.
B)Δ S must be greater than zero.
C)Δ G must be greater than zero.
D)it should be rapid.
E)Δ S sys + Δ S surr must be greater than zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
For a chemical reaction to be spontaneous only at low temperatures, which of the following conditions must be met?
A)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° < 0
C)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° < 0
D)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° > 0
E)Δ G° > 0
A)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° < 0
C)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° < 0
D)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° > 0
E)Δ G° > 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which of the following conditions will ensure that a chemical reaction will definitely proceed in the forward direction, toward products?
A)Δ H > 0
B)Δ H < 0
C)Δ S sys > 0
D)Δ S surr > Δ S sys
E)Δ S > Δ H/ T
A)Δ H > 0
B)Δ H < 0
C)Δ S sys > 0
D)Δ S surr > Δ S sys
E)Δ S > Δ H/ T

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
For a chemical reaction to be spontaneous at all temperatures, which of the following conditions must be met?
A)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° < 0
C)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° < 0
D)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° > 0
E)It is not possible for a reaction to be spontaneous at all temperatures.
A)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0, Δ H° < 0
C)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° < 0
D)Δ S° < 0, Δ H° > 0
E)It is not possible for a reaction to be spontaneous at all temperatures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The second law of thermodynamics tells us that
A)the entropy of the universe is constant.
B)entropy is neither created nor destroyed.
C)the universe proceeds toward a state of lower entropy.
D)the universe proceeds toward a state of higher entropy.
E)the universe cannot create entropy.
A)the entropy of the universe is constant.
B)entropy is neither created nor destroyed.
C)the universe proceeds toward a state of lower entropy.
D)the universe proceeds toward a state of higher entropy.
E)the universe cannot create entropy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Elemental boron can be formed by reaction of boron trichloride with hydrogen. BCl3(g) + 1.5H2(g) → B(s) + 3HCl(g)
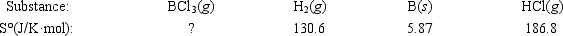 If ΔS° = 80.3 J/K for the reaction above, what is S° for BCl3(g)?
If ΔS° = 80.3 J/K for the reaction above, what is S° for BCl3(g)?
A)−18.2 J/K·mol
B)18.2 J/K·mol
C)290.1 J/K·mol
D)355.4 J/K.mol
E)450.6 J/K·mol
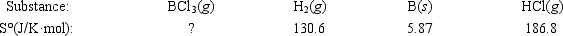 If ΔS° = 80.3 J/K for the reaction above, what is S° for BCl3(g)?
If ΔS° = 80.3 J/K for the reaction above, what is S° for BCl3(g)?A)−18.2 J/K·mol
B)18.2 J/K·mol
C)290.1 J/K·mol
D)355.4 J/K.mol
E)450.6 J/K·mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A certain process has ΔH° > 0, ΔS° < 0, and ΔG° > 0. The values of ΔH° and ΔS° do not depend on the temperature. Which of the following is a correct conclusion about this process?
A)It is non-spontaneous at all T.
B)It is spontaneous at high T.
C)It is spontaneous at low T.
D)It is spontaneous at all T.
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)It is non-spontaneous at all T.
B)It is spontaneous at high T.
C)It is spontaneous at low T.
D)It is spontaneous at all T.
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
In order for a process to be spontaneous,
A)the entropy of the system must increase.
B)the entropy of the surroundings must increase.
C)the entropy of the universe must decrease.
D)the entropy of the surroundings must decrease.
E)the entropy change of the surroundings plus the entropy change of the system must be positive.
A)the entropy of the system must increase.
B)the entropy of the surroundings must increase.
C)the entropy of the universe must decrease.
D)the entropy of the surroundings must decrease.
E)the entropy change of the surroundings plus the entropy change of the system must be positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
A sample of water is heated at a constant pressure of one atmosphere. Initially, the sample is ice at 260 K, and at the end the sample consists of steam at 400 K. In which of the following 5K temperature intervals would there be the greatest increase in the entropy of the sample?
A)From 260 K to 265 K
B)From 275 K to 280 K
C)From 360 K to 365 K
D)370 K to 375 K
E)From 395 K to 400 K
A)From 260 K to 265 K
B)From 275 K to 280 K
C)From 360 K to 365 K
D)370 K to 375 K
E)From 395 K to 400 K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Calculate ΔS° for the reaction 4Cr(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Cr2O3(s)
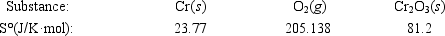
A)−548.1 J/K
B)−147.7 J/K
C)147.7 J/K
D)310.1 J/K
E)548.1 J/K
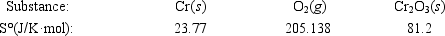
A)−548.1 J/K
B)−147.7 J/K
C)147.7 J/K
D)310.1 J/K
E)548.1 J/K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Given: H2O(l) → H2O(g) ΔH° = 40.7 kJ at 373K What is the entropy change in the system (ΔS) when one mole of water vaporizes at 100°C and a pressure of one atmosphere?
A)407 J/K
B)−407 J/K
C)109 J/K
D)−109 J/K
E)J/K
A)407 J/K
B)−407 J/K
C)109 J/K
D)−109 J/K
E)J/K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
"A diamond is forever" is one of the most successful advertising slogans of all time. But is it true? For the reaction shown below, calculate the standard free energy change at 298K and determine whether or not a diamond is "forever". C(diamond) → C(graphite)
Data: ΔHf°(diamond) = 1.895 kJ/mol; S°(diamond) = 2.337 J mol−1K−1; S°(graphite) = 5.740 J mol−1K−1.
A)Δ G° = 2.19 kJ; forever
B)Δ G° = −1.90 kJ; not forever
C)Δ G° = −2.90 kJ; not forever
D)Δ G° = 1.90 kJ; forever
E)Δ G° = < −1000 kJ; not forever
Data: ΔHf°(diamond) = 1.895 kJ/mol; S°(diamond) = 2.337 J mol−1K−1; S°(graphite) = 5.740 J mol−1K−1.
A)Δ G° = 2.19 kJ; forever
B)Δ G° = −1.90 kJ; not forever
C)Δ G° = −2.90 kJ; not forever
D)Δ G° = 1.90 kJ; forever
E)Δ G° = < −1000 kJ; not forever

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Use the thermodynamic data at 298 K below to determine the Ksp for barium carbonate, BaCO3 at this temperature. 
A)5.86
B)6.30 × 10 8
C)1.59 × 10 −9
D)5.47 × 10 −21
E)2.18 × 10 −27

A)5.86
B)6.30 × 10 8
C)1.59 × 10 −9
D)5.47 × 10 −21
E)2.18 × 10 −27

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Use the given data at 298 K to calculate ΔG° for the reaction 2Cl2(g) + SO2(g) → SOCl2(g) + Cl2O(g)
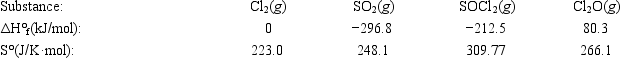
A)129.3 kJ
B)133.6 kJ
C)196.0 kJ
D)199.8 kJ
E)229.6 kJ
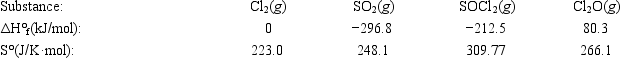
A)129.3 kJ
B)133.6 kJ
C)196.0 kJ
D)199.8 kJ
E)229.6 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
What is the free energy change, ΔG°, for the equilibrium between hydrogen iodide, hydrogen, and iodine at 453°C? Kc = 0.020 2HI(g) ⇄ H2(g) + I2(g)
A)6.4 kJ
B)8.8 kJ
C)15 kJ
D)19 kJ
E)24 kJ
A)6.4 kJ
B)8.8 kJ
C)15 kJ
D)19 kJ
E)24 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Consider the figure that shows ΔG° for a chemical process plotted against absolute temperature. 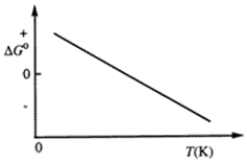 Which one of the following is an incorrect conclusion, based on the information in the diagram?
Which one of the following is an incorrect conclusion, based on the information in the diagram?
A)Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0
C)The reaction is spontaneous at high temperatures.
D)Δ S° increases with temperature while Δ H° remains constant.
E)There exists a certain temperature at which Δ H° = TΔ S°.
 Which one of the following is an incorrect conclusion, based on the information in the diagram?
Which one of the following is an incorrect conclusion, based on the information in the diagram?A)Δ H° > 0
B)Δ S° > 0
C)The reaction is spontaneous at high temperatures.
D)Δ S° increases with temperature while Δ H° remains constant.
E)There exists a certain temperature at which Δ H° = TΔ S°.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The temperature at which the following process reaches equilibrium at 1.0 atm is the normal melting point for phosphoric acid. H3PO4(s)⇄ H3PO4(l)
Use the following thermodynamic information at 298 K to determine this temperature.
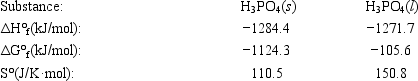
A)286 K
B)305 K
C)315 K
D)347 K
E)3170 K
Use the following thermodynamic information at 298 K to determine this temperature.
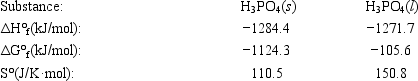
A)286 K
B)305 K
C)315 K
D)347 K
E)3170 K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Sulfuryl dichloride is formed when sulfur dioxide reacts with chlorine. The data refer to 298 K. SO2(g) + Cl2(g) → SO2Cl2(g)
 What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction at 600 K?
What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction at 600 K?
A)−162.8 kJ
B)−40.1 kJ
C)−28.4 kJ
D)28.4 kJ
E)162.8 kJ
 What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction at 600 K?
What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction at 600 K?A)−162.8 kJ
B)−40.1 kJ
C)−28.4 kJ
D)28.4 kJ
E)162.8 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Iron(III) oxide can be reduced by carbon monoxide. Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) ⇄ 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
Use the following thermodynamic data at 298 K to determine the equilibrium constant at this temperature.

A)7.0 × 10 −6
B)1.3 × 10 −3
C)2.2 × 10 4
D)1.4 × 10 5
E)> 2.0 × 10 5
Use the following thermodynamic data at 298 K to determine the equilibrium constant at this temperature.

A)7.0 × 10 −6
B)1.3 × 10 −3
C)2.2 × 10 4
D)1.4 × 10 5
E)> 2.0 × 10 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Hydrogen sulfide decomposes according to the following reaction 2H2S(g) → 2H2(g) + S2(g)
For this reaction at 298K ΔS° = 78.1 J/K, ΔH° = 169.4 kJ, and ΔG° = 146.1 kJ. What is the value of ΔG° at 900 K?
A)−69881 kJ
B)48.4 kJ
C)99.1 kJ
D)240 kJ
E)441 kJ
For this reaction at 298K ΔS° = 78.1 J/K, ΔH° = 169.4 kJ, and ΔG° = 146.1 kJ. What is the value of ΔG° at 900 K?
A)−69881 kJ
B)48.4 kJ
C)99.1 kJ
D)240 kJ
E)441 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The temperature at which the following process reaches equilibrium at 1.0 atm is the normal boiling point of hydrogen peroxide. H2O2(l) ⇄ H2O2(g)
Use the following thermodynamic information at 298 K to determine this temperature.
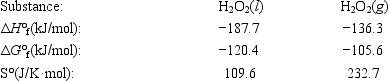
A)120°C
B)144°C
C)196°C
D)418°C
E)585°C
Use the following thermodynamic information at 298 K to determine this temperature.
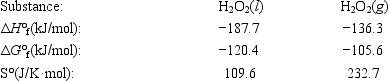
A)120°C
B)144°C
C)196°C
D)418°C
E)585°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25°C for the reaction of methane with water to form carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The data refer to 25°C. CH4(g) + 2H2O(g) ⇄ CO2(g) + 4H2(g)

A)8.2 × 10 19
B)0.96
C)0.58
D)1.2 × 10 −20
E)1.4 × 10 −46

A)8.2 × 10 19
B)0.96
C)0.58
D)1.2 × 10 −20
E)1.4 × 10 −46

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The reaction of methane with water to form carbon dioxide and hydrogen is nonspontaneous at 298 K. At what temperature will this system make the transition from nonspontaneous to spontaneous? The data refer to 298 K. CH4(g) + 2H2O(g) ⇄ CO2(g) + 4H2(g)
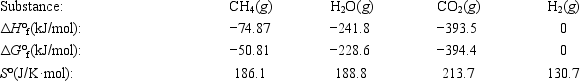
A)658 K
B)683 K
C)955 K
D)1047 K
E)1229 K
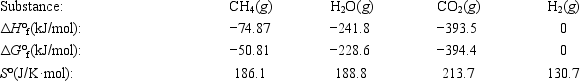
A)658 K
B)683 K
C)955 K
D)1047 K
E)1229 K

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Calculate ΔG° for the reaction of ammonia with fluorine. 2NH3(g) + 5F2(g) → N2F4(g) + 6HF(g)
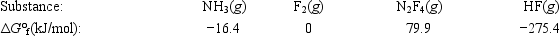
A)179.1 kJ
B)−179.1 kJ
C)1539.7 kJ
D)−1539.7 kJ
E)None of these choices are correct.
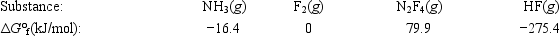
A)179.1 kJ
B)−179.1 kJ
C)1539.7 kJ
D)−1539.7 kJ
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Elemental boron can be formed by reaction of boron trichloride with hydrogen. BCl3(g) + 1.5H2(g) → B(s) + 3HCl(g)
Calculate ΔG° for the reaction.
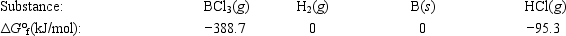
A)−293.4 kJ
B)293.4 kJ
C)−102.8 kJ
D)102.8 kJ
E)None of these choices are correct.
Calculate ΔG° for the reaction.
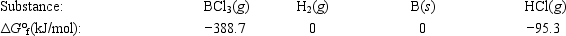
A)−293.4 kJ
B)293.4 kJ
C)−102.8 kJ
D)102.8 kJ
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Calculate ΔG° for the combustion of propane. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
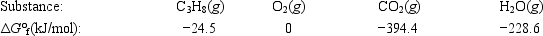
A)−2073.1 kJ
B)−1387.3 kJ
C)−598.5 kJ
D)598.5 kJ
E)2073.1 kJ
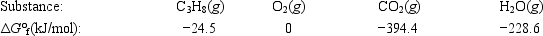
A)−2073.1 kJ
B)−1387.3 kJ
C)−598.5 kJ
D)598.5 kJ
E)2073.1 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Nitric oxide reacts with chlorine to form NOCl. The data refer to 298 K.2NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NOCl(g)  What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction at 550 K?
What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction at 550 K?
A)-143.76 kJ
B)-78.78 kJ
C)-22.24 kJ
D)-10.56 kJ
E)66600 kJ
 What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction at 550 K?
What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction at 550 K?A)-143.76 kJ
B)-78.78 kJ
C)-22.24 kJ
D)-10.56 kJ
E)66600 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Consider the figure that shows ΔG° for a chemical process plotted against absolute temperature. From this plot, it is reasonable to conclude that 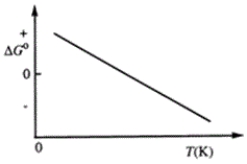
A)Δ H° > 0, Δ S° > 0
B)Δ H° > 0, Δ S° < 0
C)Δ H° < 0, Δ S° > 0
D)Δ H° < 0, Δ S° < 0
E)None of these choices are correct.

A)Δ H° > 0, Δ S° > 0
B)Δ H° > 0, Δ S° < 0
C)Δ H° < 0, Δ S° > 0
D)Δ H° < 0, Δ S° < 0
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Calculate ΔG° for the reaction SiCl4(g) + 2Mg(s) → 2MgCl2(s) + Si(s)
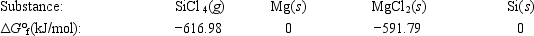
A)566.60 kJ
B)50.38 kJ
C)25.19 kJ
D)−25.19 kJ
E)−566.60 kJ
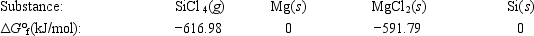
A)566.60 kJ
B)50.38 kJ
C)25.19 kJ
D)−25.19 kJ
E)−566.60 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Consider the figure that shows ΔG° for a chemical process plotted against absolute temperature. From this plot, it is reasonable to conclude that 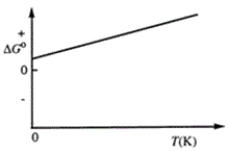
A)Δ H° > 0, Δ S° > 0
B)Δ H° > 0, Δ S° < 0
C)Δ H° < 0, Δ S° > 0
D)Δ H° < 0, Δ S° < 0
E)None of these choices are correct.

A)Δ H° > 0, Δ S° > 0
B)Δ H° > 0, Δ S° < 0
C)Δ H° < 0, Δ S° > 0
D)Δ H° < 0, Δ S° < 0
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
A reaction is proceeding toward equilibrium. At a certain stage, the concentrations of reactants and products are such that ΔG = ΔG°. What conclusion can reasonably be drawn about the reaction at this time?
A)K > Q
B)K < Q
C)K = Q
D)K = 1
E)Q = 1
A)K > Q
B)K < Q
C)K = Q
D)K = 1
E)Q = 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 85 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








