Deck 16: Kinetics: Rates and Mechanisms of Chemical Reactions
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 16: Kinetics: Rates and Mechanisms of Chemical Reactions
1
A transition state is a species (or state) corresponding to an energy maximum on a reaction energy diagram.
True
2
An elementary reaction is a simple, one-step process.
True
3
All bimolecular reactions are second-order reactions.
True
4
All second-order reactions are bimolecular reactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The half-life of a first-order reaction does not depend on the initial concentration of reactant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A reaction intermediate is a species corresponding to a local energy maximum on a reaction energy diagram.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Chlorine atoms act as heterogeneous catalysts in the destruction of ozone in the stratosphere.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The greater the energy of activation, Ea, the faster will be the reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Consider the following reaction 8A(g) + 5B(g) → 8C(g) + 6D(g)
If [C] is increasing at the rate of 4.0 mol L−1s−1, at what rate is [B] changing?
A)−0.40 mol L −1s −1
B)−2.5 mol L −1s −1
C)−4.0 mol L −1s −1
D)−6.4 mol L −1s −1
E)None of these choices are correct.
If [C] is increasing at the rate of 4.0 mol L−1s−1, at what rate is [B] changing?
A)−0.40 mol L −1s −1
B)−2.5 mol L −1s −1
C)−4.0 mol L −1s −1
D)−6.4 mol L −1s −1
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The half-life of a second-order reaction does not depend on the initial concentration of reactant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In the lock and key model of enzyme action, the active site on the enzyme provides an exact fit for the substrate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Consider the reaction 2NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3H2(g)
If the rate Δ[H2]/Δt is 0.030 mol L−1s−1, then Δ[NH3 ]/Δt is
A)−0.045 mol L −1 s −1
B)−0.030 mol L −1 s −1
C)−0.020 mol L −1 s −1
D)−0.010 mol L −1 s −1
E)None of these choices are correct.
If the rate Δ[H2]/Δt is 0.030 mol L−1s−1, then Δ[NH3 ]/Δt is
A)−0.045 mol L −1 s −1
B)−0.030 mol L −1 s −1
C)−0.020 mol L −1 s −1
D)−0.010 mol L −1 s −1
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Consider the general reaction 5Br−(aq) + BrO3−(aq) + 6H+(aq) → 3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(aq)
For this reaction, the rate when expressed as Δ[Br2]/Δt is the same as
A)−Δ[H 2O]/Δt
B)3Δ[BrO 3 −]/Δt
C)−5Δ[Br −]/Δt
D)−0.6Δ[Br −]/Δt
E)None of these choices are correct.
For this reaction, the rate when expressed as Δ[Br2]/Δt is the same as
A)−Δ[H 2O]/Δt
B)3Δ[BrO 3 −]/Δt
C)−5Δ[Br −]/Δt
D)−0.6Δ[Br −]/Δt
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The units of the rate constant depend on the order of the reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A catalyst lowers the activation energy but does not affect the mechanism of a reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The compound RX3 decomposes according to the equation 3RX3 → R + R2X3 + 3X2
In an experiment the following data were collected for the decomposition at 100°C. What is the average rate at which RX3 is disappearing over the entire experiment?

A)0.011 mol L −1s −1
B)0.019 mol L −1s −1
C)0.044 mol L −1s −1
D)0.049 mol L −1s −1
E)0.069 mol L −1s −1
In an experiment the following data were collected for the decomposition at 100°C. What is the average rate at which RX3 is disappearing over the entire experiment?

A)0.011 mol L −1s −1
B)0.019 mol L −1s −1
C)0.044 mol L −1s −1
D)0.049 mol L −1s −1
E)0.069 mol L −1s −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The rate of a reaction is determined by the rate of the fastest step in the mechanism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In a reversible reaction, a catalyst will speed up the forward reaction but not affect the reverse reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The units of the rate of reaction depend on the order of the reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The rate law cannot be predicted from the stoichiometry of a reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Sucrose decomposes to fructose and glucose in acid solution. When ln [sucrose] is plotted vs. time, a straight line with slope of −0.208 hr−1 results. What is the rate law for the reaction?
A)Rate = 0.208 hr −1 [sucrose] 2
B)Rate = 0.208 hr −1 [sucrose]
C)Rate = 0.0433 hr [sucrose] 2
D)Rate = 0.0433 hr [sucrose]
E)Rate = 0.208 mol L −1hr −1 [sucrose] 0
A)Rate = 0.208 hr −1 [sucrose] 2
B)Rate = 0.208 hr −1 [sucrose]
C)Rate = 0.0433 hr [sucrose] 2
D)Rate = 0.0433 hr [sucrose]
E)Rate = 0.208 mol L −1hr −1 [sucrose] 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Sulfur trioxide can undergo decomposition according to the equation 2SO3 → 2SO2 + O2
For this reaction, rate = −0.5Δ[SO3 ]/Δt = k[SO3]2. If the reaction rate is 1.75 × 10−7 mol L−1 min−1 when the concentration of sulfur trioxide is 5.4 × 10−3 mol L−1, what is the value of the rate constant k?
A)3.2 × 10 −5 L mol −1 min −1
B)1.6 × 10 −5 L mol −1 min −1
C)6.0 × 10 −3 L mol −1 min −1
D)3.0 × 10 −3 L mol −1 min −1
E)1.6 × 10 −2 L mol −1 min −1
For this reaction, rate = −0.5Δ[SO3 ]/Δt = k[SO3]2. If the reaction rate is 1.75 × 10−7 mol L−1 min−1 when the concentration of sulfur trioxide is 5.4 × 10−3 mol L−1, what is the value of the rate constant k?
A)3.2 × 10 −5 L mol −1 min −1
B)1.6 × 10 −5 L mol −1 min −1
C)6.0 × 10 −3 L mol −1 min −1
D)3.0 × 10 −3 L mol −1 min −1
E)1.6 × 10 −2 L mol −1 min −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Sulfuryl chloride, SO2Cl2(g), decomposes at high temperature to form SO2(g) and Cl2(g). The rate constant at a certain temperature is 4.68 × 10−5s−1. What is the order of the reaction?
A)Zero
B)First
C)Second
D)Third
E)More information is needed to determine the order.
A)Zero
B)First
C)Second
D)Third
E)More information is needed to determine the order.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g)
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.
![<strong>For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A)Rate = k[A] [B] B)Rate = k[A] <sup>2 </sup>[B] C)Rate = k[A] [B] <sup>2</sup> D)Rate = k[A] E)Rate = k[A] <sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8248/11eb6533_8023_a8f2_b0a1_b7e38daa4add_TB8248_00.jpg)
A)Rate = k[A] [B]
B)Rate = k[A] 2 [B]
C)Rate = k[A] [B] 2
D)Rate = k[A]
E)Rate = k[A] 3
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.
![<strong>For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A)Rate = k[A] [B] B)Rate = k[A] <sup>2 </sup>[B] C)Rate = k[A] [B] <sup>2</sup> D)Rate = k[A] E)Rate = k[A] <sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8248/11eb6533_8023_a8f2_b0a1_b7e38daa4add_TB8248_00.jpg)
A)Rate = k[A] [B]
B)Rate = k[A] 2 [B]
C)Rate = k[A] [B] 2
D)Rate = k[A]
E)Rate = k[A] 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g)
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.
![<strong>For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A)Rate = k[A] [B] B)Rate = k[A] <sup>2 </sup>[B] C)Rate = k[A] [B] <sup>2</sup> D)Rate = k[A] E)Rate = k[A] <sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8248/11eb6533_8023_a8f0_b0a1_5d6ff1ecdead_TB8248_00.jpg)
A)Rate = k[A] [B]
B)Rate = k[A] 2 [B]
C)Rate = k[A] [B] 2
D)Rate = k[A]
E)Rate = k[A] 3
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.
![<strong>For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A)Rate = k[A] [B] B)Rate = k[A] <sup>2 </sup>[B] C)Rate = k[A] [B] <sup>2</sup> D)Rate = k[A] E)Rate = k[A] <sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8248/11eb6533_8023_a8f0_b0a1_5d6ff1ecdead_TB8248_00.jpg)
A)Rate = k[A] [B]
B)Rate = k[A] 2 [B]
C)Rate = k[A] [B] 2
D)Rate = k[A]
E)Rate = k[A] 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
A study of the decomposition reaction 3RS2 → 3R + 6S yields the following initial rate data. 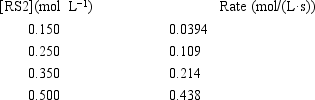 What is the rate constant for the reaction?
What is the rate constant for the reaction?
A)0.0103 L mol −1s −1
B)0.263 L mol −1s −1
C)0.571 L mol −1s −1
D)1.17 L mol −1s −1
E)1.75 L mol −1s −1
 What is the rate constant for the reaction?
What is the rate constant for the reaction?A)0.0103 L mol −1s −1
B)0.263 L mol −1s −1
C)0.571 L mol −1s −1
D)1.17 L mol −1s −1
E)1.75 L mol −1s −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A reaction has the following rate law: Rate = k[A][B]2
In experiment 1, the concentrations of A and B are both 0.10 mol L−1; in experiment 2, the concentrations are both 0.30 mol L−1. If the temperature stays constant, what is the value of the ratio, Rate(2)/Rate(1)?
A)3.0
B)6.0
C)9.0
D)18
E)27
In experiment 1, the concentrations of A and B are both 0.10 mol L−1; in experiment 2, the concentrations are both 0.30 mol L−1. If the temperature stays constant, what is the value of the ratio, Rate(2)/Rate(1)?
A)3.0
B)6.0
C)9.0
D)18
E)27

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following sets of units could be appropriate for a zero-order rate constant?
A)s −1
B)L mol −1s −1
C)L 2 mol −2s −1
D)L 3 mol −3s −1
E)mol L −1s −1
A)s −1
B)L mol −1s −1
C)L 2 mol −2s −1
D)L 3 mol −3s −1
E)mol L −1s −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Ammonium cyanate (NH4CNO) reacts to form urea (NH2CONH2). At 65°C the rate constant, k, is 3.60 L mol−1s−1. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A)Rate = 3.60 L mol −1s −1[NH 4CNO]
B)Rate = 3.60 L mol −1s −1[NH 4CNO] 2
C)Rate = 0.28 mol L −1 s −1[NH 4CNO]
D)Rate = 0.28 mol L −1 s −1[NH 4CNO] 2
E)Rate = 3.60 L mol −1s −1[NH 2CONH 2] −1
A)Rate = 3.60 L mol −1s −1[NH 4CNO]
B)Rate = 3.60 L mol −1s −1[NH 4CNO] 2
C)Rate = 0.28 mol L −1 s −1[NH 4CNO]
D)Rate = 0.28 mol L −1 s −1[NH 4CNO] 2
E)Rate = 3.60 L mol −1s −1[NH 2CONH 2] −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Tetrafluoroethylene, C2F4, can be converted to octafluorocyclobutane which can be used as a refrigerant or an aerosol propellant. A plot of 1/[C2F4] vs. time gives a straight line with a slope of 0.0448 L mol−1s−1. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A)Rate = 0.0448 (L mol −1s −1)[C 2F 4]
B)Rate = 22.3 (mol L −1s)[C 2F 4]
C)Rate = 0.0448 (L mol −1s −1)[C 2F 4] 2
D)Rate = 22.3 (mol L −1s)[C 2F 4] 2
E)Rate = 0.0448 s −1 [C 2F 4]
A)Rate = 0.0448 (L mol −1s −1)[C 2F 4]
B)Rate = 22.3 (mol L −1s)[C 2F 4]
C)Rate = 0.0448 (L mol −1s −1)[C 2F 4] 2
D)Rate = 22.3 (mol L −1s)[C 2F 4] 2
E)Rate = 0.0448 s −1 [C 2F 4]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A reaction is second-order with respect to the reactant R. Which of the following plots will produce a straight line?
A)[R] vs. 1/time
B)1/[R] vs. time
C)[R] 2 vs. time
D)1/[R] 2 vs. time
E)ln[R] vs. time
A)[R] vs. 1/time
B)1/[R] vs. time
C)[R] 2 vs. time
D)1/[R] 2 vs. time
E)ln[R] vs. time

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
When the reaction A → B + C is studied, a plot of ln[A]t vs. time gives a straight line with a negative slope. What is the order of the reaction?
A)Zero
B)First
C)Second
D)Third
E)More information is needed to determine the order.
A)Zero
B)First
C)Second
D)Third
E)More information is needed to determine the order.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which one of the following sets of units is appropriate for a third-order rate constant?
A)s −1
B)mol L −1s −1
C)L mol −1s −1
D)L 2 mol −2s −1
E)L 3 mol −3s −1
A)s −1
B)mol L −1s −1
C)L mol −1s −1
D)L 2 mol −2s −1
E)L 3 mol −3s −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
When the reaction A → B + C is studied, a plot 1/[A]t vs. time gives a straight line with a positive slope. What is the order of the reaction?
A)Zero
B)First
C)Second
D)Third
E)More information is needed to determine the order.
A)Zero
B)First
C)Second
D)Third
E)More information is needed to determine the order.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which one of the following sets of units is appropriate for a second-order rate constant?
A)s −1
B)mol L −1s −1
C)L mol −1s −1
D)mol 2 L −2s −1
E)L 2 mol −2s −1
A)s −1
B)mol L −1s −1
C)L mol −1s −1
D)mol 2 L −2s −1
E)L 2 mol −2s −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
For the reaction 3A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g)
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.
![<strong>For the reaction 3A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A)Rate = k[A][B] B)Rate = k[A][B] <sup>2</sup> C)Rate = k[A] <sup>3</sup>[B] <sup>2</sup> D)Rate = k[A] <sup>1.5</sup>[B] E)Rate = k[A] <sup>2</sup>[B]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8248/11eb6533_8023_81df_b0a1_fbcbf0e4c940_TB8248_00.jpg)
A)Rate = k[A][B]
B)Rate = k[A][B] 2
C)Rate = k[A] 3[B] 2
D)Rate = k[A] 1.5[B]
E)Rate = k[A] 2[B]
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.
![<strong>For the reaction 3A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A)Rate = k[A][B] B)Rate = k[A][B] <sup>2</sup> C)Rate = k[A] <sup>3</sup>[B] <sup>2</sup> D)Rate = k[A] <sup>1.5</sup>[B] E)Rate = k[A] <sup>2</sup>[B]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8248/11eb6533_8023_81df_b0a1_fbcbf0e4c940_TB8248_00.jpg)
A)Rate = k[A][B]
B)Rate = k[A][B] 2
C)Rate = k[A] 3[B] 2
D)Rate = k[A] 1.5[B]
E)Rate = k[A] 2[B]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
2NOBr(g) → 2NO(g) + Br2(g)  Based on the initial rate data above, what is the value of the rate constant?
Based on the initial rate data above, what is the value of the rate constant?
A)0.0360 L mol −1s −1
B)0.800 L mol −1s −1
C)1.25 L mol −1s −1
D)27.8 L mol −1s −1
E)0.0360 s −1
 Based on the initial rate data above, what is the value of the rate constant?
Based on the initial rate data above, what is the value of the rate constant?A)0.0360 L mol −1s −1
B)0.800 L mol −1s −1
C)1.25 L mol −1s −1
D)27.8 L mol −1s −1
E)0.0360 s −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The reaction X → Y is first-order overall and first-order with respect to the reactant X. The result of doubling the initial concentration of X will be to
A)shorten the half-life of the reaction.
B)increase the rate constant of the reaction.
C)decrease the rate constant of the reaction.
D)shorten the time taken to reach equilibrium.
E)double the initial rate.
A)shorten the half-life of the reaction.
B)increase the rate constant of the reaction.
C)decrease the rate constant of the reaction.
D)shorten the time taken to reach equilibrium.
E)double the initial rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
For the reaction 2A + B + 2C → D + E
The following initial rate data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. All units are arbitrary.
![<strong>For the reaction 2A + B + 2C → D + E The following initial rate data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. All units are arbitrary. </strong> A)Rate = k[A][B][C] B)Rate = k[A] <sup>2</sup>[B][C] C)Rate = k[A] <sup>2</sup>[B][C] <sup>−</sup><sup>1</sup> D)Rate = k[A][B] <sup>2</sup>[C] <sup> </sup><sup>−</sup><sup>1</sup> E)None of these choices are correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8248/11eb6533_8023_a8f1_b0a1_6d7540f79c1b_TB8248_00.jpg)
A)Rate = k[A][B][C]
B)Rate = k[A] 2[B][C]
C)Rate = k[A] 2[B][C] −1
D)Rate = k[A][B] 2[C] −1
E)None of these choices are correct.
The following initial rate data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. All units are arbitrary.
![<strong>For the reaction 2A + B + 2C → D + E The following initial rate data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. All units are arbitrary. </strong> A)Rate = k[A][B][C] B)Rate = k[A] <sup>2</sup>[B][C] C)Rate = k[A] <sup>2</sup>[B][C] <sup>−</sup><sup>1</sup> D)Rate = k[A][B] <sup>2</sup>[C] <sup> </sup><sup>−</sup><sup>1</sup> E)None of these choices are correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8248/11eb6533_8023_a8f1_b0a1_6d7540f79c1b_TB8248_00.jpg)
A)Rate = k[A][B][C]
B)Rate = k[A] 2[B][C]
C)Rate = k[A] 2[B][C] −1
D)Rate = k[A][B] 2[C] −1
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A reaction is first-order with respect to the reactant R. Which of the following plots will produce a straight line?
A)[R] vs. 1/time
B)1/[R] vs. time
C)[R] 2 vs. time
D)1/[R] 2 vs. time
E)ln[R] vs. time
A)[R] vs. 1/time
B)1/[R] vs. time
C)[R] 2 vs. time
D)1/[R] 2 vs. time
E)ln[R] vs. time

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The reaction CH3NC(g) → CH3CN(g) is first-order with respect to methyl isocyanide, CH3NC. If it takes 10.3 minutes for exactly one quarter of the initial amount of methyl isocyanide to react, what is the rate constant in units of min−1?
A)−0.135 min −1
B)0.0279 min −1
C)0.089 min −1
D)0.135 min −1
E)35.8 min −1
A)−0.135 min −1
B)0.0279 min −1
C)0.089 min −1
D)0.135 min −1
E)35.8 min −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A first-order reaction has a half-life of 20.0 minutes. Starting with 1.00 × 1020 molecules of reactant at time t = 0, how many molecules remain unreacted after 100.0 minutes?
A)1.00 × 10 4 molecules
B)2.00 × 10 19 molecules
C)3.20 × 10 16 molecules
D)5.00 × 10 20 molecules
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)1.00 × 10 4 molecules
B)2.00 × 10 19 molecules
C)3.20 × 10 16 molecules
D)5.00 × 10 20 molecules
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Dinitrogen tetraoxide, N2O4, decomposes to nitrogen dioxide, NO2, in a first-order process. If k = 2.5 × 103 s−1 at −5°C and k = 3.5 × 104 s−1 at 25°C, what is the activation energy for the decomposition?
A)0.73 kJ/mol
B)58 kJ/mol
C)140 kJ/mol
D)580 kJ/mol
E)> 1000 kJ/mol
A)0.73 kJ/mol
B)58 kJ/mol
C)140 kJ/mol
D)580 kJ/mol
E)> 1000 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The radioactive isotope tritium decays with a first-order rate constant k of 0.056 year−1. What fraction of the tritium initially in a sample is still present 30 years later?
A)0.19
B)0.60
C)0.15
D)2.8 × 10 −38
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)0.19
B)0.60
C)0.15
D)2.8 × 10 −38
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The rate constant for the reaction 3A → 4B is 6.00 × 10−3 L mol−1min−1. How long will it take the concentration of A to drop from 0.75 M to 0.25 M?
A)2.2 × 10 −3 min
B)5.5 × 10 −3 min
C)180 min
D)440 min
E)5.0 × 10 2 min
A)2.2 × 10 −3 min
B)5.5 × 10 −3 min
C)180 min
D)440 min
E)5.0 × 10 2 min

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
If the activation energy of a reaction decreases by 10.0 kJ/mol, from 100.0 to 90.0 kJ/mol, what effect will this have on the rate of reaction at 298K?
A)The rate will increase, by a factor of more than 50.
B)The rate will decrease, by a factor of more than 50.
C)The rate will increase, by a factor of less than 50.
D)The rate will decrease, by a factor of less than 50.
E)The rate will not change unless temperature changes.
A)The rate will increase, by a factor of more than 50.
B)The rate will decrease, by a factor of more than 50.
C)The rate will increase, by a factor of less than 50.
D)The rate will decrease, by a factor of less than 50.
E)The rate will not change unless temperature changes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Cyclopropane is converted to propene in a first-order process. The rate constant is 5.4 × 10−2 hr−1. If the initial concentration of cyclopropane is 0.150 M, what will its concentration be after 22.0 hours?
A)0.0457 M
B)0.105 M
C)0.127 M
D)0.492 M
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)0.0457 M
B)0.105 M
C)0.127 M
D)0.492 M
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is a first-order process with a rate constant of 1.06 × 10−3 min−1. How long will it take for the concentration of H2O2 to drop from 0.0200 M to 0.0120 M?
A)< 1 min
B)7.55 min
C)481 min
D)4550 min
E)31,400 min
A)< 1 min
B)7.55 min
C)481 min
D)4550 min
E)31,400 min

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope which decays with a half-life of 5730 years. What is the first-order rate constant for its decay, in units of years−1?
A)5.25 × 10 −5 years −1
B)1.21 × 10 −4 years −1
C)1.75 × 10 −4 years −1
D)3.49 × 10 −4 years −1
E)3.97 × 10 3 years −1
A)5.25 × 10 −5 years −1
B)1.21 × 10 −4 years −1
C)1.75 × 10 −4 years −1
D)3.49 × 10 −4 years −1
E)3.97 × 10 3 years −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The active ingredient in an over the counter pain killer analgesic decomposes with a rate constant, k = 9.05 × 10−4 day−1. How many days does it take for 15% of the original ingredient to decompose?
A)730 days
B)414 days
C)365 days
D)180 days
E)78 days
A)730 days
B)414 days
C)365 days
D)180 days
E)78 days

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
A gas-phase decomposition is first-order with respect to the reactant, R. If the initial concentration of R is 1.0 × 10−4 mol L−1and the rate constant k = 1.08 × 10−6 s−1, what concentration of R remains after 25 days?
A)1.0 × 10 −3 mol L −1
B)1.0 × 10 −4 mol L −1
C)9.6 × 10 −5 mol L −1
D)4.3 × 10 −5 mol L −1
E)9.7 × 10 −6 mol L −1
A)1.0 × 10 −3 mol L −1
B)1.0 × 10 −4 mol L −1
C)9.6 × 10 −5 mol L −1
D)4.3 × 10 −5 mol L −1
E)9.7 × 10 −6 mol L −1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Ammonia will react with oxygen in the presence of a copper catalyst to form nitrogen and water. From 164.5°C to 179.0°C, the rate constant increases by a factor of 4.27. What is the activation energy of this oxidation reaction?
A)24.5 kJ/mol
B)165 kJ/mol
C)242 kJ/mol
D)1630 kJ/mol
E)> 10 4 kJ/mol
A)24.5 kJ/mol
B)165 kJ/mol
C)242 kJ/mol
D)1630 kJ/mol
E)> 10 4 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The rate law for the reaction 3A → C is Rate = 4.36 × 10−2 L mol−1 hr−1 [A]2
What is the half-life for the reaction if the initial concentration of A is 0.250 M?
A)0.0109 hr
B)0.0629 hr
C)15.9 hr
D)23.9 hr
E)91.7 hr
What is the half-life for the reaction if the initial concentration of A is 0.250 M?
A)0.0109 hr
B)0.0629 hr
C)15.9 hr
D)23.9 hr
E)91.7 hr

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The rate law for the rearrangement of CH3NC to CH3CN at 800 K is Rate = (1300 s−1)[CH3NC]. What is the half-life for this reaction?
A)7.69 × 10 −4 s
B)5.3 × 10 −4 s
C)1.9 × 10 −3 s
D)520 s
E)1920 s
A)7.69 × 10 −4 s
B)5.3 × 10 −4 s
C)1.9 × 10 −3 s
D)520 s
E)1920 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The rate law for the reaction 3A → 2B is rate = k[A] with a rate constant of 0.0447 hr−1. What is the half-life of the reaction?
A)0.0224 hr
B)0.0645 hr
C)15.5 hr
D)22.4 hr
E)44.7 hr
A)0.0224 hr
B)0.0645 hr
C)15.5 hr
D)22.4 hr
E)44.7 hr

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The decomposition of SOCl2 is first-order in SOCl2. If the half-life for the reaction is 4.1 hr, how long would it take for the concentration of SOCl2 to drop from 0.36 M to 0.045 M?
A)0.52 hr
B)1.4 hr
C)12 hr
D)33 hr
E)> 40 hr
A)0.52 hr
B)1.4 hr
C)12 hr
D)33 hr
E)> 40 hr

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A reactant R is being consumed in a first-order reaction. What fraction of the initial R is consumed in 4.0 half-lives?
A)0.94
B)0.87
C)0.75
D)0.13
E)0.063
A)0.94
B)0.87
C)0.75
D)0.13
E)0.063

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
A boiled egg can be cooked at 100.0°C in exactly 5 minutes. At an altitude of around 2000 m where the boiling point of water is 93.0°C, it takes exactly 7.5 minutes to cook the egg to the same amount. What is the activation energy for the reaction involved when an egg is boiled?
A)0.5 kJ/mol
B)4.5 kJ/mol
C)7.9 kJ/mol
D)66 kJ/mol
E)>100 kJ/mol
A)0.5 kJ/mol
B)4.5 kJ/mol
C)7.9 kJ/mol
D)66 kJ/mol
E)>100 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
In going from room temperature (25.0°C) to 10°C above room temperature, the rate of a reaction doubles. Calculate the activation energy for the reaction.
A)157.2 kJ/mol
B)103.8 kJ/mol
C)52.9 kJ/mol
D)6.4 kJ/mol
E)<1 kJ/mol
A)157.2 kJ/mol
B)103.8 kJ/mol
C)52.9 kJ/mol
D)6.4 kJ/mol
E)<1 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Butadiene, C4H6 (used to make synthetic rubber and latex paints) reacts to C8H12 with a rate law of rate = 0.014 L/(mol·s) [C4H6]2. What will be the concentration of C4H6 after 3.0 hours if the initial concentration is 0.025 M?
A)0.0052 M
B)0.024 M
C)43 M
D)190 M
E)0.0000 M
A)0.0052 M
B)0.024 M
C)43 M
D)190 M
E)0.0000 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The decomposition of dinitrogen pentaoxide to nitrogen dioxide and oxygen follows first-order kinetics and has an activation energy of 102 kJ/mol. By what factor will the fraction of collisions with energy greater than or equal to the activation energy increase if the reaction temperature goes from 30°C to 60°C?
A)1.00
B)1.10
C)2.00
D)4.00
E)38.4
A)1.00
B)1.10
C)2.00
D)4.00
E)38.4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The decomposition of dinitrogen pentaoxide has an activation energy of 102 kJ/mol and ΔH°rxn = + 55 kJ/mol. What is the activation energy for the reverse reaction?
A)27 kJ/mol
B)47 kJ/mol
C)55 kJ/mol
D)102 kJ/mol
E)More information is needed, since this is a Hess's law calculation.
A)27 kJ/mol
B)47 kJ/mol
C)55 kJ/mol
D)102 kJ/mol
E)More information is needed, since this is a Hess's law calculation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Consider the reaction 2A + 2B + C → 2D + E
If the rate law for this reaction is Rate = k[A][B]2, what will be the effect on the rate if the concentrations of A, B and C are all doubled at the same time?
A)The rate will increase by a factor of 2.
B)The rate will increase by a factor of 4.
C)The rate will increase by a factor of 6.
D)The rate will increase by a factor of 8.
E)More information is needed before this question can be answered.
If the rate law for this reaction is Rate = k[A][B]2, what will be the effect on the rate if the concentrations of A, B and C are all doubled at the same time?
A)The rate will increase by a factor of 2.
B)The rate will increase by a factor of 4.
C)The rate will increase by a factor of 6.
D)The rate will increase by a factor of 8.
E)More information is needed before this question can be answered.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The kinetics of the decomposition of dinitrogen pentaoxide is studied at 50°C and at 75°C. Which of the following statements concerning the studies is correct?
A)The rate at 75°C will be greater than the rate at 50°C because the activation energy will be lower at 75°C than at 50°C.
B)The rate at 75°C will be greater than the rate at 50°C because the activation energy will be higher at 75°C than at 50°C.
C)The rate at 75°C will be less than the rate at 50°C because the molecules at higher speeds do not interact as well as those at lower speeds.
D)The rate at 75°C will be greater than at 50°C because the concentration of a gas increases with increasing temperature.
E)The rate at 75°C will be greater than the rate at 50°C because the number of molecules with enough energy to react increases with increasing temperature.
A)The rate at 75°C will be greater than the rate at 50°C because the activation energy will be lower at 75°C than at 50°C.
B)The rate at 75°C will be greater than the rate at 50°C because the activation energy will be higher at 75°C than at 50°C.
C)The rate at 75°C will be less than the rate at 50°C because the molecules at higher speeds do not interact as well as those at lower speeds.
D)The rate at 75°C will be greater than at 50°C because the concentration of a gas increases with increasing temperature.
E)The rate at 75°C will be greater than the rate at 50°C because the number of molecules with enough energy to react increases with increasing temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
When a catalyst is added to a reaction mixture, it
A)increases the rate of collisions between reactant molecules.
B)provides reactant molecules with more energy.
C)slows down the rate of the back reaction.
D)provides a new pathway (mechanism)for the reaction.
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)increases the rate of collisions between reactant molecules.
B)provides reactant molecules with more energy.
C)slows down the rate of the back reaction.
D)provides a new pathway (mechanism)for the reaction.
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
An increase in temperature increases the reaction rate because
A)a greater fraction of the collisions have the correct orientation of molecules.
B)the activation energy of the reaction will increase.
C)the activation energy of the reaction will decrease.
D)temperature acts as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
E)more collisions will have enough energy to exceed the activation energy.
A)a greater fraction of the collisions have the correct orientation of molecules.
B)the activation energy of the reaction will increase.
C)the activation energy of the reaction will decrease.
D)temperature acts as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
E)more collisions will have enough energy to exceed the activation energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
What is the molecularity of the following elementary reaction? NH2Cl(aq) + OH− (aq) → NHCl− (aq) + H2O(l)
A)Unimolecular
B)Bimolecular
C)Termolecular
D)Tetramolecular
E)Need to know the reaction order before molecularity can be determined.
A)Unimolecular
B)Bimolecular
C)Termolecular
D)Tetramolecular
E)Need to know the reaction order before molecularity can be determined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
In order to obtain the activation energy of a reaction using a graphical method, __________ is plotted against __________, giving a straight line whose slope is equal to __________.
A)k; T; −E a
B)k; 1/T; −E a
C)lnk; T; −E a/R
D)k; 1/T; −E a/R
E)lnk; 1/T; −E a/R
A)k; T; −E a
B)k; 1/T; −E a
C)lnk; T; −E a/R
D)k; 1/T; −E a/R
E)lnk; 1/T; −E a/R

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The reaction of ethylene (C2H4) with butadiene (C4H6) to form cyclohexene (C6H10) has an activation energy (Ea) of 115 kJ/mol. The reverse reaction (decomposition of cyclohexene to ethylene and butadiene) has an activation energy of 287 kJ/mol. What is the heat of reaction, Δ Hrxn, for the forward reaction?
A)+115 kJ/mol
B)+287 kJ/mol
C)−287 kJ/mol
D)+172 kJ/mol
E)−172 kJ/mol
A)+115 kJ/mol
B)+287 kJ/mol
C)−287 kJ/mol
D)+172 kJ/mol
E)−172 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Reaction intermediates differ from activated complexes in that
A)they are stable molecules with normal bonds and are frequently isolated.
B)they are molecules with normal bonds rather than partial bonds and can occasionally be isolated.
C)they are intermediate structures which have characteristics of both reactants and products.
D)they are unstable and can never be isolated.
E)all reactions involve reaction intermediates, but not all have activated complexes.
A)they are stable molecules with normal bonds and are frequently isolated.
B)they are molecules with normal bonds rather than partial bonds and can occasionally be isolated.
C)they are intermediate structures which have characteristics of both reactants and products.
D)they are unstable and can never be isolated.
E)all reactions involve reaction intermediates, but not all have activated complexes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
A catalyst accelerates a reaction because
A)it increases the number of molecules with energy equal to or greater than the activation energy.
B)it lowers the activation energy for the reaction.
C)it increases the number of collisions between molecules.
D)it increases the temperature of the molecules in the reaction.
E)it supplies energy to reactant molecules.
A)it increases the number of molecules with energy equal to or greater than the activation energy.
B)it lowers the activation energy for the reaction.
C)it increases the number of collisions between molecules.
D)it increases the temperature of the molecules in the reaction.
E)it supplies energy to reactant molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
A reaction has an activation energy of 195.0 kJ/mol. When the temperature is increased from 200°C to 220°C, the rate constant will increase by a factor of
A)1.1.
B)4.3 × 10 4.
C)3.2.
D)7.5.
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)1.1.
B)4.3 × 10 4.
C)3.2.
D)7.5.
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Consider the following mechanism for the oxidation of bromide ions by hydrogen peroxide in aqueous acid solution. H+ + H2O2 ⇄ H2O+−OH (rapid equilibrium)H2O+−OH + Br− → HOBr + H2O (slow)HOBr + H+ + Br− → Br2 + H2O (fast)
What is the overall reaction equation for this process?
A)2H 2O +−OH + 2Br − → H 2O 2 + Br 2 + 2H 2O
B)2H + + 2Br − + H 2O 2 → Br 2 + 2H 2O
C)2H + + H 2O 2 + Br − + HOBr → H 2O +−OH + Br 2 + H 2O
D)H 2O +−OH + Br − + H + → Br 2 + H 2O
E)None of these choices are correct.
What is the overall reaction equation for this process?
A)2H 2O +−OH + 2Br − → H 2O 2 + Br 2 + 2H 2O
B)2H + + 2Br − + H 2O 2 → Br 2 + 2H 2O
C)2H + + H 2O 2 + Br − + HOBr → H 2O +−OH + Br 2 + H 2O
D)H 2O +−OH + Br − + H + → Br 2 + H 2O
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Which of the following affects the activation energy of a reaction?
A)Temperature of the reactants
B)Concentrations of reactants
C)Presence of a catalyst
D)Surface area of reactants
E)Reaction progress
A)Temperature of the reactants
B)Concentrations of reactants
C)Presence of a catalyst
D)Surface area of reactants
E)Reaction progress

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The gas-phase reaction CH3NC → CH3CN has been studied in a closed vessel, and the rate equation was found to be: Rate = −Δ[CH3NC]/Δt = k[CH3NC]. Which one of the following actions is least likely to cause a change in the rate of the reaction?
A)Lowering the temperature
B)Adding a catalyst
C)Using a larger initial amount of CH 3NC in the same vessel
D)Using a bigger vessel, but the same initial amount of CH 3NC
E)Continuously removing CH 3CN as it is formed
A)Lowering the temperature
B)Adding a catalyst
C)Using a larger initial amount of CH 3NC in the same vessel
D)Using a bigger vessel, but the same initial amount of CH 3NC
E)Continuously removing CH 3CN as it is formed

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
In an exothermic reaction,
A)the forward reaction is slower than the reverse reaction.
B)the reaction rate will speed up with time.
C)the collision energy of the reactants will be greater than that of the products.
D)the forward reaction will have a lower activation energy than the reverse reaction.
E)the activation energy will change as the reaction progresses.
A)the forward reaction is slower than the reverse reaction.
B)the reaction rate will speed up with time.
C)the collision energy of the reactants will be greater than that of the products.
D)the forward reaction will have a lower activation energy than the reverse reaction.
E)the activation energy will change as the reaction progresses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Consider the following mechanism for the oxidation of bromide ions by hydrogen peroxide in aqueous acid solution. H+ + H2O2 ⇄ H2O+−OH (rapid equilibrium)H2O+−OH + Br− → HOBr + H2O (slow)HOBr + H+ + Br− → Br2 + H2O (fast)
Which of the following rate laws is consistent with the mechanism?
A)Rate = k[H 2O 2][H +] 2[Br −]
B)Rate = k[H 2O +−OH][Br −]
C)Rate = k[H 2O 2][H +][Br −]
D)Rate = k[HOBr][H +][Br −][H 2O 2]
E)Rate = k[Br −]
Which of the following rate laws is consistent with the mechanism?
A)Rate = k[H 2O 2][H +] 2[Br −]
B)Rate = k[H 2O +−OH][Br −]
C)Rate = k[H 2O 2][H +][Br −]
D)Rate = k[HOBr][H +][Br −][H 2O 2]
E)Rate = k[Br −]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
A rate constant obeys the Arrhenius equation, the factor A being 2.2 ×1013 s−1 and the activation energy being 150. kJ mol−1. What is the value of the rate constant at 227°C, in s−1?
A)2.1 × 10 13 s −1
B)6.7 × 10 −22 s −1
C)1.5 × 10 11 s −1
D)4.7 × 10 −3 s −1
E)None of these choices are correct.
A)2.1 × 10 13 s −1
B)6.7 × 10 −22 s −1
C)1.5 × 10 11 s −1
D)4.7 × 10 −3 s −1
E)None of these choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 78 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








