Deck 30: Vital Signs
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 30: Vital Signs
1
Match the following terms with the reason for assessing vital signs.
1. Pulse oximeter
2. Doppler ultrasound
3. Stethoscope
4. Tympanic
A. Hard to hear blood pressures
B. Core temperature
C. Non-invasive device for hypoxaemia
D. Assessing apical pulse
1. Pulse oximeter
2. Doppler ultrasound
3. Stethoscope
4. Tympanic
A. Hard to hear blood pressures
B. Core temperature
C. Non-invasive device for hypoxaemia
D. Assessing apical pulse
1C, 2A, 3D, 4B
1
Which of the following factors can affect oxygen saturation readings?
A) Activity.
B) Skin colour.
C) Nutrition.
D) Environmental conditions.
A) Activity.
B) Skin colour.
C) Nutrition.
D) Environmental conditions.
Activity.
2
A patient has returned from having an anaesthetic in a supine position. The RN is monitoring his respiratory rate because the nurse is aware that:
A) narcotics increase the respiratory rate.
B) anaesthetics will block the airway.
C) position will suppress respirations.
D) narcotics can cause wheezing.
A) narcotics increase the respiratory rate.
B) anaesthetics will block the airway.
C) position will suppress respirations.
D) narcotics can cause wheezing.
position will suppress respirations.
3
Which of the following nursing interventions would assure the RN of an accurate temperature reading for a client?
A) Assess that the equipment used is working properly.
B) Take the temperature with a chemical disposable thermometer when the client is perspiring.
C) Wait at least 10 minutes before taking the temperature after a client has been smoking.
D) Place the client in a position that is most comfortable for the health care provider.
A) Assess that the equipment used is working properly.
B) Take the temperature with a chemical disposable thermometer when the client is perspiring.
C) Wait at least 10 minutes before taking the temperature after a client has been smoking.
D) Place the client in a position that is most comfortable for the health care provider.
Assess that the equipment used is working properly.
4
When assessing the temperature of older adults, the nurse needs to be aware that:
A) it is not a reliable indicator of serious infection.
B) older people's core temperature is higher than adults.
C) cerumen build-up won't affect using a tympanic thermometer.
D) older people don't feel the heat or cold.
A) it is not a reliable indicator of serious infection.
B) older people's core temperature is higher than adults.
C) cerumen build-up won't affect using a tympanic thermometer.
D) older people don't feel the heat or cold.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In which phase of Korotkoff's sounds would the nurse hear crisper sounds, increasing in intensity?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Match the following terms with the relevant statement for respiration.
1. Tachypnoea
2. Cheyne-Stokes breathing
3. Orthopnoea
4. Stridor
A. Fluctuating depth and continuity
B. Inspiratory shrill sound
C. Difficulty breathing
D. Quick shallow breaths
1. Tachypnoea
2. Cheyne-Stokes breathing
3. Orthopnoea
4. Stridor
A. Fluctuating depth and continuity
B. Inspiratory shrill sound
C. Difficulty breathing
D. Quick shallow breaths

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following positions would the nurse anticipate suppressed respiratory status?
A) Supine.
B) Lateral.
C) Side-lying.
D) Semi-Fowler's.
A) Supine.
B) Lateral.
C) Side-lying.
D) Semi-Fowler's.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Match the following determinants of Blood Pressure.
1. Pumping action of heart reduced
2. Peripheral Vascular Resistance low
3. Blood volume low
4. Blood viscosity
A. Raised haematocrit
B. Haemorrhage
C. Arteriosclerosis
D. Low cardiac output
1. Pumping action of heart reduced
2. Peripheral Vascular Resistance low
3. Blood volume low
4. Blood viscosity
A. Raised haematocrit
B. Haemorrhage
C. Arteriosclerosis
D. Low cardiac output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following is an appropriate nursing intervention for lowering a client's elevated temperature?
A) Bathe the client with ice water.
B) Increase fluid intake.
C) Lower room temperature.
D) Give the client an antipyretic.
A) Bathe the client with ice water.
B) Increase fluid intake.
C) Lower room temperature.
D) Give the client an antipyretic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A client has returned to the nursing unit from having a cardiac catheterisation. The RN is assessing the client's right pedal pulse (dorsalis pedis) and assesses no pulse present. On further investigation, the extremity is found to be warm and pink, and nail beds blanch well with two to three seconds capillary refilling time. How would the RN explain these findings?
A) The client has thrown a blood clot in that extremity.
B) The RN's watch has stopped working.
C) Too much pressure was applied over the pulse site.
D) A change in the client's health status has occurred.
A) The client has thrown a blood clot in that extremity.
B) The RN's watch has stopped working.
C) Too much pressure was applied over the pulse site.
D) A change in the client's health status has occurred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The RN assesses a client who is recovering from femoral popliteal bypass surgery and discovers that it is difficult to assess the dorsalis pedis pulses. Which of the following nursing interventions would be most appropriate for the nurse to use?
A) Document the findings.
B) Ask another nurse to assess the pulses.
C) Obtain a Doppler ultrasound stethoscope.
D) Wait and just try again later.
A) Document the findings.
B) Ask another nurse to assess the pulses.
C) Obtain a Doppler ultrasound stethoscope.
D) Wait and just try again later.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A client in a motor vehicle crash has arrived at the trauma unit in respiratory distress and unconscious. Knowing that chemoreceptors respond to changes in the concentrations of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen, which of the following circumstances would account for this client's decrease in respiratory rate?
A) Increased environmental temperature.
B) Exercise.
C) Stress.
D) Increased intracranial pressure.
A) Increased environmental temperature.
B) Exercise.
C) Stress.
D) Increased intracranial pressure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The following vital signs were taken and given to the RN by the Assistant in Nursing (unlicensed health care worker): 37.2-68-18-130/70. The client from whom these vital signs were obtained is a 75-year-old male. Which of the following rationales would explain this client's low temperature?
A) Loss of subcutaneous fat is noted.
B) Anxiety level of the client has increased.
C) Hormones have fluctuated in this client.
D) Muscle activity has increased during the client's therapy session.
A) Loss of subcutaneous fat is noted.
B) Anxiety level of the client has increased.
C) Hormones have fluctuated in this client.
D) Muscle activity has increased during the client's therapy session.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following sounds will be heard during phase 2 of Korotkoff's sounds?
A) A murmur or swishing sound.
B) Faint, clear tapping sound.
C) Increased intensity of sound.
D) Disappearance of sound.
A) A murmur or swishing sound.
B) Faint, clear tapping sound.
C) Increased intensity of sound.
D) Disappearance of sound.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following arteries is most commonly used to obtain a blood pressure reading?
A) Ulnar.
B) Brachial.
C) Femoral.
D) Radial.
A) Ulnar.
B) Brachial.
C) Femoral.
D) Radial.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Respiratory rate is regulated by all of the following except:
A) diaphragm movement.
B) carotid pressure.
C) chemoreceptors.
D) medulla oblongata.
A) diaphragm movement.
B) carotid pressure.
C) chemoreceptors.
D) medulla oblongata.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In the palpatory method of blood pressure determination, instead of listening for the blood flow sounds, light to moderate pressure is used over the artery as the pressure in the cuff is released. When is the pressure read from the sphygmomanometer?
A) When the cuff is applied.
B) When the second pulsation is felt.
C) When the first pulsation is felt.
D) When the cuff is being deflated.
A) When the cuff is applied.
B) When the second pulsation is felt.
C) When the first pulsation is felt.
D) When the cuff is being deflated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
While assessing a client who has heart failure, the nurse is monitoring the pulse pressure. The nurse can calculate this as the difference between ________ and ________ blood pressures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following sites is recommended for routine clinical use in children and infants?
A) Rectal.
B) Tympanic membrane.
C) Oral.
D) Axilla.
A) Rectal.
B) Tympanic membrane.
C) Oral.
D) Axilla.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which condition would lead the RN to choose the dorsalis pedis pulse as the site for further assessing the client's status?
A) Toes cool to touch.
B) Altered level of consciousness.
C) Irregular radial pulse.
D) Decreased urine output.
A) Toes cool to touch.
B) Altered level of consciousness.
C) Irregular radial pulse.
D) Decreased urine output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following determinants of blood pressure would explain a client's blood pressure reading of 120/100?
A) Pumping action of the heart.
B) Blood viscosity.
C) Blood volume.
D) Peripheral vascular resistance.
A) Pumping action of the heart.
B) Blood viscosity.
C) Blood volume.
D) Peripheral vascular resistance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A client is being treated for congestive heart failure. Which of the following physical findings would lead the RN to believe the client's condition has not improved?
A) Temperature of 37°C.
B) Moderate amount of clear thin mucous.
C) Wheezing of breath sounds in all lobes.
D) Pulse oximetry reading of 96%.
A) Temperature of 37°C.
B) Moderate amount of clear thin mucous.
C) Wheezing of breath sounds in all lobes.
D) Pulse oximetry reading of 96%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
An apical-radial pulse is determined by the RN to be the procedure to use on a client with cardiovascular disorders. Which of the following rationales did the RN use to make this decision?
A) A forceful radial pulse is much too difficult to count correctly.
B) The thrust of blood from the heart is too feeble for the wave to be felt at the peripheral pulse site.
C) The pulse was bounding and easily obliterated.
D) Both arteriole and venous sounds were heard simultaneously.
A) A forceful radial pulse is much too difficult to count correctly.
B) The thrust of blood from the heart is too feeble for the wave to be felt at the peripheral pulse site.
C) The pulse was bounding and easily obliterated.
D) Both arteriole and venous sounds were heard simultaneously.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
When assessing a client's peripheral pulse, the health care provider is also assessing which of the following?
A) Sound.
B) Rhythm.
C) Stress.
D) Depth.
A) Sound.
B) Rhythm.
C) Stress.
D) Depth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
On the diagram below, place an X over the point of maximal impulse (PMI) where the stethoscope is placed to assess the apical pulse. 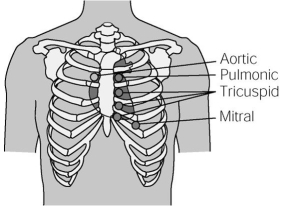


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The RN needs vital signs taken on the four clients that have been assigned. Which of the four clients should be taken by the RN and not the Assistant in Nursing?
A) COPD client on 2 Lpm oxygen via nasal cannula.
B) Client with a pulse deficit requiring one nurse technique.
C) Post-op client of two days from gallbladder surgery.
D) Pneumonia client nearing discharge.
A) COPD client on 2 Lpm oxygen via nasal cannula.
B) Client with a pulse deficit requiring one nurse technique.
C) Post-op client of two days from gallbladder surgery.
D) Pneumonia client nearing discharge.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 30 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








