Deck 41: Quantum Mechanics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/33
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 41: Quantum Mechanics
1
When a particle approaching a potential step has a total energy that is greater than the potential step, what is the probability that the particle will be reflected?
A) P < 0.
B) P = 0.
C) P = 1.
D) P > 0.
E) P = ∞.
A) P < 0.
B) P = 0.
C) P = 1.
D) P > 0.
E) P = ∞.
P > 0.
2
When the potential energy of a system is independent of time, the wave function of the system
A) is a constant.
B) is directly proportional to the time.
C) cannot be normalized.
D) depends only on the center of mass,
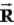 , of the system.
, of the system.
E) depends on the vector positions,
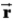
i, of each particle in the system.
A) is a constant.
B) is directly proportional to the time.
C) cannot be normalized.
D) depends only on the center of mass,
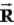 , of the system.
, of the system.E) depends on the vector positions,
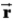
i, of each particle in the system.
depends on the vector positions,
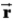
i, of each particle in the system.
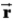
i, of each particle in the system.
3
A particle is in the first excited state of a one-dimensional box of length 1.0 m. What is the minimum value of its momentum (in kg ⋅ m/s)?
A) 3.3 × 10−34
B) 6.6 × 10−34
C) 9.9 × 10−34
D) 13 × 10−34
E) 22 × 10−34
A) 3.3 × 10−34
B) 6.6 × 10−34
C) 9.9 × 10−34
D) 13 × 10−34
E) 22 × 10−34
6.6 × 10−34
4
The fact that we can only calculate probabilities for values of physical quantities in quantum measurements means that
A) radiation and matter are not described by mathematical relations between measurements.
B) the probabilities cannot be calculated from mathematical relationships.
C) the results of physical measurements bear no relationship to theory.
D) the average values of a large number of measurements correspond to the calculated probabilities.
E) the average of the values calculated in a large number of different theories corresponds to the results of a measurement.
A) radiation and matter are not described by mathematical relations between measurements.
B) the probabilities cannot be calculated from mathematical relationships.
C) the results of physical measurements bear no relationship to theory.
D) the average values of a large number of measurements correspond to the calculated probabilities.
E) the average of the values calculated in a large number of different theories corresponds to the results of a measurement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A particle is in the ground state of a one-dimensional box of length 1.0 m. What is the minimum value of its momentum (in kg ⋅ m/s)?
A) 9.9 × 10−34
B) 6.6 × 10−34
C) 3.3 × 10−34
D) 13 × 10−34
E) cannot be solved unless mass of particle is known.
A) 9.9 × 10−34
B) 6.6 × 10−34
C) 3.3 × 10−34
D) 13 × 10−34
E) cannot be solved unless mass of particle is known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The ground state energy of a harmonic oscillator is
A)
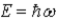
B)
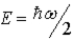
C)
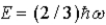
D) E = 0
E)
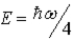
A)
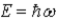
B)
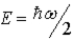
C)
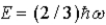
D) E = 0
E)
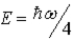

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A particle has a total energy that is less than that of a potential barrier. When the particle penetrates the barrier, its wave function is
A) a positive constant.
B) exponentially increasing.
C) oscillatory.
D) exponentially decreasing.
E) none of the above.
A) a positive constant.
B) exponentially increasing.
C) oscillatory.
D) exponentially decreasing.
E) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A particle is in the second excited state of a one-dimensional box of length 1.0 m. What is its momentum (in kg ⋅ m/s)?
A) 6.6 × 10−34
B) 3.3 × 10−34
C) 9.9 × 10−34
D) 13 × 10−34
E) cannot be solved unless mass of particle is known
A) 6.6 × 10−34
B) 3.3 × 10−34
C) 9.9 × 10−34
D) 13 × 10−34
E) cannot be solved unless mass of particle is known

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The average position, or expectation value, of a particle whose wave function ψ(x) depends only on the value of x, is given by < x > =
A)
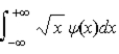 .
.
B)
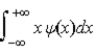 .
.
C)
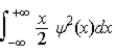 .
.
D)
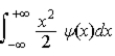 .
.
E)
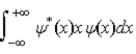 .
.
A)
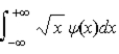 .
.B)
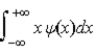 .
.C)
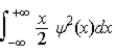 .
.D)
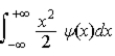 .
.E)
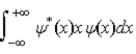 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A 15-kg mass, attached to a massless spring whose force constant is 2500 N/m, has an amplitude of 4 cm. Assuming the energy is quantized, find the quantum number of the system, n, if En = nhf.
A) 1.5 × 1033
B) 3.0 × 1033
C) 4.5 × 1033
D) 5.4 × 1033
E) 1.0 × 1033
A) 1.5 × 1033
B) 3.0 × 1033
C) 4.5 × 1033
D) 5.4 × 1033
E) 1.0 × 1033

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If the interaction of a particle with its environment restricts the particle to a finite region of space, the result is the quantization of ____ of the particle.
A) the momentum
B) the energy
C) the velocity
D) all of the above properties
E) only properties (a) and (b)
A) the momentum
B) the energy
C) the velocity
D) all of the above properties
E) only properties (a) and (b)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Classically, the concept of "tunneling" is impossible. Why?
A) The kinetic energy of the particle would be negative.
B) The velocity of the particle would be negative.
C) The total energy of a particle is equal to the kinetic and potential energies.
D) The kinetic energy must be equal to the potential energy.
E) The total energy for the particle would be negative.
A) The kinetic energy of the particle would be negative.
B) The velocity of the particle would be negative.
C) The total energy of a particle is equal to the kinetic and potential energies.
D) The kinetic energy must be equal to the potential energy.
E) The total energy for the particle would be negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A physically reasonable wave function, ψ(x), for a one-dimensional system must
A) be defined at all points in space.
B) be continuous at all points in space.
C) be single-valued.
D) obey all the constraints listed above.
E) obey only (b) and (c) above.
A) be defined at all points in space.
B) be continuous at all points in space.
C) be single-valued.
D) obey all the constraints listed above.
E) obey only (b) and (c) above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Find the kinetic energy (in terms of Planck's constant) of a baseball (m = 1 kg) confined to a one-dimensional box that is 25 cm wide if the baseball can be treated as a wave in the ground state.
A) 3 h2
B) 2 h2
C) h2
D) 4h2
E) 0.5 h2
A) 3 h2
B) 2 h2
C) h2
D) 4h2
E) 0.5 h2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What is the quantum number n of a particle of mass m confined to a one-dimensional box of length L when its energy is 2 h2/mL2?
A) 2
B) 8
C) 4
D) 1
E) 16
A) 2
B) 8
C) 4
D) 1
E) 16

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The wave function for a particle confined to a one-dimensional box located between x = 0 and x = L is given by Ψ(x) = A sin (nπx/L) + B cos (nπx/L) . The constants A and B are determined to be
A)
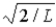 , 0
, 0
B)
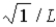 ,
,
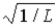
C) 0,
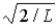
D)
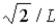 ,
,
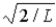
E) 2/L, 0
A)
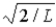 , 0
, 0B)
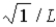 ,
,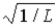
C) 0,
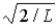
D)
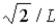 ,
,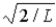
E) 2/L, 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
What is the quantum number n of a particle of mass m confined to a one-dimensional box of length L when its momentum is 4h/L?
A) 1
B) 4
C) 2
D) 8
E) 16
A) 1
B) 4
C) 2
D) 8
E) 16

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Calculate the ground state energy (in eV) for an electron in a box (an infinite well) having a width of 0.050 nm.
A) 10
B) 75
C) 24
D) 150
E) 54
A) 10
B) 75
C) 24
D) 150
E) 54

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The expectations value of a function f(x) of x when the wave function depends only on x is given by < f(x) > =
A)
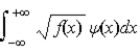 .
.
B)
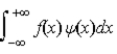 .
.
C)
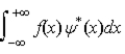 .
.
D)
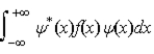 .
.
E)
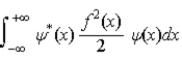 .
.
A)
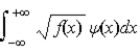 .
.B)
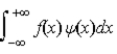 .
.C)
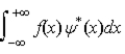 .
.D)
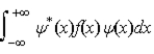 .
.E)
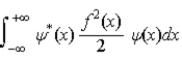 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The wave function for a particle in a one-dimensional box is  . Which statement is correct?
. Which statement is correct?
A) This wavefunction gives the probability of finding the particle at x.
B) |Ψ(x)|2 gives the probability of finding the particle at x.
C) |Ψ(x)|2 Δx gives the probability of finding the particle between x and x + Δx.
D)
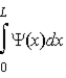 gives the probability of finding the particle at a particular value of x.
gives the probability of finding the particle at a particular value of x.
E)
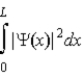 gives the probability of finding the particle between x and x + Δx.
gives the probability of finding the particle between x and x + Δx.
 . Which statement is correct?
. Which statement is correct?A) This wavefunction gives the probability of finding the particle at x.
B) |Ψ(x)|2 gives the probability of finding the particle at x.
C) |Ψ(x)|2 Δx gives the probability of finding the particle between x and x + Δx.
D)
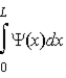 gives the probability of finding the particle at a particular value of x.
gives the probability of finding the particle at a particular value of x.E)
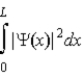 gives the probability of finding the particle between x and x + Δx.
gives the probability of finding the particle between x and x + Δx.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The wave function for a particle in a box of length L is given by 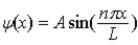 . If the box extends from x = 0 to x = L, at which of the following positions is the highest probability for finding the particle?
. If the box extends from x = 0 to x = L, at which of the following positions is the highest probability for finding the particle?
A) x = 0.33 L
B) x = 0.04 L
C) x = 0.60 L
D) Both (a) and (b).
E) Both (b) and (c).
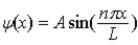 . If the box extends from x = 0 to x = L, at which of the following positions is the highest probability for finding the particle?
. If the box extends from x = 0 to x = L, at which of the following positions is the highest probability for finding the particle?A) x = 0.33 L
B) x = 0.04 L
C) x = 0.60 L
D) Both (a) and (b).
E) Both (b) and (c).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Quantum tunneling occurs in
A) nuclear fusion.
B) radioactive decay by emission of alpha particles.
C) the scanning tunneling microscope.
D) all of the above.
E) only (b) and (c) above.
A) nuclear fusion.
B) radioactive decay by emission of alpha particles.
C) the scanning tunneling microscope.
D) all of the above.
E) only (b) and (c) above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The wave function ψ(x) of a particle confined to 0 ≤ x ≤ L is given by ψ(x) = Ax. ψ(x) = 0 for x < 0 and x > L. When the wave function is normalized, the probability density at coordinate x has the value
A)
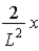 .
.
B)
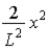 .
.
C)
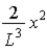 .
.
D)
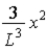 .
.
E)
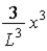 .
.
A)
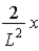 .
.B)
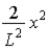 .
.C)
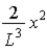 .
.D)
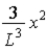 .
.E)
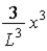 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Frank says that quantum mechanics does not apply to baseballs because they do not jump from quantum state to quantum state when being thrown. Francine agrees with him. She says that there is no uncertainty in a baseball's position or momentum. Are they correct, or not, and why?
A) They are correct because the first excited state of a baseball is at a higher energy that any baseball ever receives. Therefore we cannot determine whether or not there is uncertainty in its position or momentum.
B) They are correct because the first excited state of a baseball is at a higher energy that any baseball ever receives. Therefore its position and momentum are completely uncertain until it is caught.
C) They are wrong because the baseball goes through so many quantum states in being thrown that we cannot observe the transitions. The uncertainties in its position and momentum are too small to observe.
D) They are wrong because the baseball goes through so many quantum states in being thrown that we cannot observe the transitions. Because of the number of transitions its position and momentum are completely uncertain until it is caught.
E) Quantum mechanics states that they are correct as long as they do not make any observations, but wrong as soon as they begin to make observations.
A) They are correct because the first excited state of a baseball is at a higher energy that any baseball ever receives. Therefore we cannot determine whether or not there is uncertainty in its position or momentum.
B) They are correct because the first excited state of a baseball is at a higher energy that any baseball ever receives. Therefore its position and momentum are completely uncertain until it is caught.
C) They are wrong because the baseball goes through so many quantum states in being thrown that we cannot observe the transitions. The uncertainties in its position and momentum are too small to observe.
D) They are wrong because the baseball goes through so many quantum states in being thrown that we cannot observe the transitions. Because of the number of transitions its position and momentum are completely uncertain until it is caught.
E) Quantum mechanics states that they are correct as long as they do not make any observations, but wrong as soon as they begin to make observations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A particle in a finite potential well has energy E, as shown below. 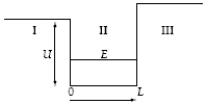 The wave function in region I where x < 0 has the form ψI =
The wave function in region I where x < 0 has the form ψI =
A) Ae−Cx.
B) AeCx.
C) F sin kx.
D) G cos kx.
E) F sin kx + G cos kx.
 The wave function in region I where x < 0 has the form ψI =
The wave function in region I where x < 0 has the form ψI =A) Ae−Cx.
B) AeCx.
C) F sin kx.
D) G cos kx.
E) F sin kx + G cos kx.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When U(x) is infinitely large elsewhere, the wave function of a particle restricted to the region 0 < x < L where U(x) = 0, may have the form ψ(x) =
A)
 .
.
B)
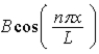 .
.
C) Aenπx / L.
D)
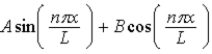 .
.
E)
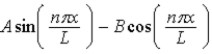 .
.
A)
 .
.B)
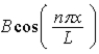 .
.C) Aenπx / L.
D)
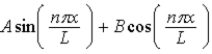 .
.E)
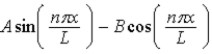 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The graph below shows the value of the probability density |ψ(x)|2 in the region −3.00 m ≤ x ≤ +3.00 m. The value of the constant A is 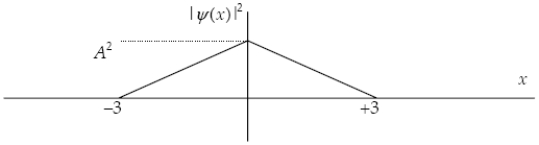
A)
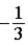 .
.
B)
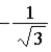 .
.
C)
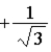 .
.
D)
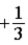 .
.
E) either
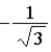 or
or
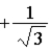 .
.

A)
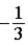 .
.B)
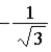 .
.C)
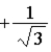 .
.D)
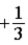 .
.E) either
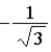 or
or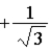 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The wave function for a particle in a box of length L is given by 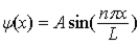 . If the box extends from x = 0 to x = L, What is the probability of finding the particle between x = 0.60 L and x = 0.70 L?
. If the box extends from x = 0 to x = L, What is the probability of finding the particle between x = 0.60 L and x = 0.70 L?
A) 0.10
B) 0.20
C) 0.25
D) 0.05
E) The probability is not given.
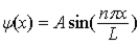 . If the box extends from x = 0 to x = L, What is the probability of finding the particle between x = 0.60 L and x = 0.70 L?
. If the box extends from x = 0 to x = L, What is the probability of finding the particle between x = 0.60 L and x = 0.70 L?A) 0.10
B) 0.20
C) 0.25
D) 0.05
E) The probability is not given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A particle in a finite potential well has energy E, as shown below. 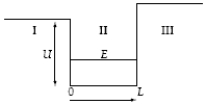 The wave function in region III where x > L has the form ψIII =
The wave function in region III where x > L has the form ψIII =
A) Ae−Cx.
B) AeCx.
C) F sin kx.
D) G cos kx.
E) F sin kx + G cos kx.
 The wave function in region III where x > L has the form ψIII =
The wave function in region III where x > L has the form ψIII =A) Ae−Cx.
B) AeCx.
C) F sin kx.
D) G cos kx.
E) F sin kx + G cos kx.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The graph below represents a wave function ψ(x) for a particle confined to −4.00 m ≤ x ≤ +4.00 m. The magnitude of the normalization constant A is 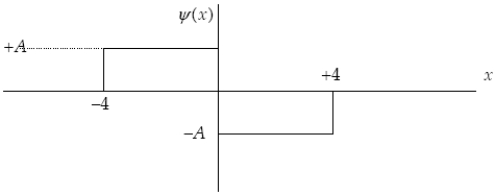
A)
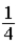 .
.
B)
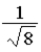 .
.
C)
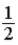 .
.
D)
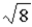 .
.
E) 4.

A)
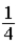 .
.B)
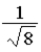 .
.C)
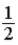 .
.D)
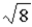 .
.E) 4.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A particle in a finite potential well has energy E, as shown below. 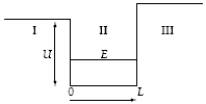 The wave function in region II where x > 0 has the form ψII =
The wave function in region II where x > 0 has the form ψII =
A) Ae−Cx.
B) AeCx.
C) F sin kx.
D) G cos kx.
E) F sin kx + G cos kx.
 The wave function in region II where x > 0 has the form ψII =
The wave function in region II where x > 0 has the form ψII =A) Ae−Cx.
B) AeCx.
C) F sin kx.
D) G cos kx.
E) F sin kx + G cos kx.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The graph below represents a wave function ψ(x) for a particle confined to −2.00 m ≤ x ≤ +2.00 m. The value of the normalization constant A may be 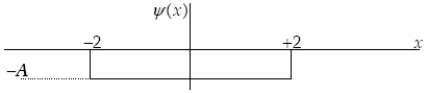
A)
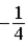 .
.
B)
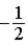 .
.
C)
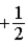 .
.
D)
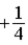 .
.
E) either
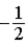 or
or
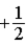 .
.

A)
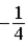 .
.B)
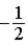 .
.C)
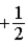 .
.D)
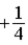 .
.E) either
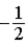 or
or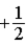 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The graph below represents a wave function ψ(x) for a particle confined to −2.00 m ≤ x ≤ +2.00 m. The value of the normalization constant A may be 
A)
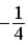 .
.
B)
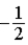 .
.
C)
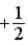 .
.
D)
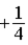 .
.
E) either
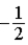 or
or
 .
.

A)
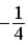 .
.B)
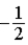 .
.C)
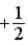 .
.D)
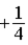 .
.E) either
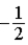 or
or .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 33 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








