Deck 44: Nuclear Structure
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 44: Nuclear Structure
1
What value of Z (atomic number) and A (mass number) result in the following β-decay? 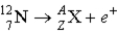
A) Z = 6; A = 12
B) Z = 5; A = 8
C) Z = 6; A = 11
D) Z = 8; A = 12
E) Z = 8; A = 11
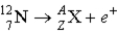
A) Z = 6; A = 12
B) Z = 5; A = 8
C) Z = 6; A = 11
D) Z = 8; A = 12
E) Z = 8; A = 11
Z = 6; A = 12
2
The isotope, tritium, has a half-life of 12.3 years. Assume we have 10 kg of the substance. How much tritium will be left after 30 years?
A) 0.20 kg
B) 1.8 kg
C) 0.18 kg
D) 1.7 kg
E) 4.1 kg
A) 0.20 kg
B) 1.8 kg
C) 0.18 kg
D) 1.7 kg
E) 4.1 kg
1.8 kg
3
What value of Z (atomic number) and A (mass number) result in the following β-decay? 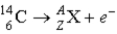
A) Z = 5; A = 14
B) Z = 4; A = 10
C) Z = 6; A = 14
D) Z = 7; A = 14
E) Z = 7; A = 13
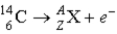
A) Z = 5; A = 14
B) Z = 4; A = 10
C) Z = 6; A = 14
D) Z = 7; A = 14
E) Z = 7; A = 13
Z = 7; A = 14
4
How many radioactive atoms are present in a sample that has an activity of 0.5 μCi and a half-life of 10 years? (1 curie = 3.7 × 1010 decays/s)
A) 9.5 × 1012 atoms
B) 8.4 × 1012 atoms
C) 7.3 × 1012 atoms
D) 6.5 × 1012 atoms
E) 2.7 × 105 atoms
A) 9.5 × 1012 atoms
B) 8.4 × 1012 atoms
C) 7.3 × 1012 atoms
D) 6.5 × 1012 atoms
E) 2.7 × 105 atoms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The half-life of 131I is 8.04 days. Three days after it was prepared, its activity was 0.50 μCi. How many curies (in μCi) were initially prepared?
A) .60
B) .70
C) .65
D) .55
E) .39
A) .60
B) .70
C) .65
D) .55
E) .39

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The isotope, tritium, has a half-life of 12.3 years. Assume we have 10 kg of the substance. What will be the initial decay rate, at t = 0 (in decays/s)?
A) 1.09 × 1014
B) 1.8 × 10−9
C) 5.6 × 108
D) 3.6 × 1018
E) 3.6 × 1017
A) 1.09 × 1014
B) 1.8 × 10−9
C) 5.6 × 108
D) 3.6 × 1018
E) 3.6 × 1017

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Find the binding energy per nucleon (in MeV/nucleon) of carbon-12. Assume:
MC = 12.000 000 u
M p = 1.007 825 u
M n = 1.008 665 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 1.2
B) 4.2 × 10−2
C) 7.4
D) 7.7
E) 5.6
MC = 12.000 000 u
M p = 1.007 825 u
M n = 1.008 665 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 1.2
B) 4.2 × 10−2
C) 7.4
D) 7.7
E) 5.6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Naturally radioactive nuclei can decay spontaneously by emitting the following particles:
A) helium nuclei, electrons, photons
B) electrons, neutrons, protons
C) helium nuclei, electrons, protons
D) electrons, neutrons, photons
E) quarks and leptons
A) helium nuclei, electrons, photons
B) electrons, neutrons, protons
C) helium nuclei, electrons, protons
D) electrons, neutrons, photons
E) quarks and leptons

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Find the ratio of the binding energy per nucleon for helium ( 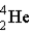 ) to uranium-238 (
) to uranium-238 ( 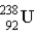 ). Assume:
). Assume:
M p = 1.007 825 u
M n = 1.008 665 u
MHe = 4.002 603 u
MU = 238.050 786 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 1.07
B) 0.934
C) 63.7
D) 1.6 × 10−2
E) 3.24
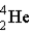 ) to uranium-238 (
) to uranium-238 ( 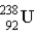 ). Assume:
). Assume:M p = 1.007 825 u
M n = 1.008 665 u
MHe = 4.002 603 u
MU = 238.050 786 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 1.07
B) 0.934
C) 63.7
D) 1.6 × 10−2
E) 3.24

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The radius of a nucleus of 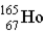 (in fm) is
(in fm) is
A) 15.4
B) 5.5
C) 12.8
D) 6.6
E) 4.9
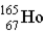 (in fm) is
(in fm) isA) 15.4
B) 5.5
C) 12.8
D) 6.6
E) 4.9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
44 g of petrified wood was found in a petrified forest. A sample showed a 14C activity of 100 decays/minute. How long has the tree been dead (in years)? (The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years and freshly cut wood contains 6.5 × 1010 atoms of 14C per gram.)
A) 12300
B) 15600
C) 8500
D) 4700
E) 2400
A) 12300
B) 15600
C) 8500
D) 4700
E) 2400

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The ratio of the radius of a classical electron (re = kee2/mec2 = 2.8 × 10−15 m) to the radius of a 4He nucleus (r = r0A1/3) is
A) 2.0
B) 0.68
C) 1.5
D) 0.92
E) 2.4
A) 2.0
B) 0.68
C) 1.5
D) 0.92
E) 2.4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The isotope, tritium, has a half-life of 12.3 years. Assume we have 10 kg of the substance. What will be the disintegration constant (in s−1)?
A) 5.6 × 10−2
B) 5.6 × 108
C) 3.2 × 107
D) 1.8 × 10−9
E) 1.6 × 106
A) 5.6 × 10−2
B) 5.6 × 108
C) 3.2 × 107
D) 1.8 × 10−9
E) 1.6 × 106

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
An alpha particle is emitted from a radioactive source with an energy of 5 MeV. How fast is it moving (in m/s)? (m = 4.002 603 u, 1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg.)
A) 2.4 × 107
B) 1.6 × 107
C) 3.7 × 107
D) 4.6 × 107
E) 2.1 × 107
A) 2.4 × 107
B) 1.6 × 107
C) 3.7 × 107
D) 4.6 × 107
E) 2.1 × 107

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The ratio of the density of a neutron (r = r0A1/3) to the density of a classical electron (re = ke2/mec2 = 2.8 × 10−15 m) is
A) 4.3 × 102
B) 2.3 × 104
C) 1.4 × 102
D) 6.9 × 10−3
E) 4.3 × 103
A) 4.3 × 102
B) 2.3 × 104
C) 1.4 × 102
D) 6.9 × 10−3
E) 4.3 × 103

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What value of Z (atomic number) and A (mass number) result in the following alpha decay? 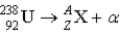
A) Z = 92; A = 238
B) Z = 91; A = 238
C) Z = 90; A = 234
D) Z = 93; A = 238
E) Z = 88; A = 236
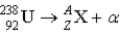
A) Z = 92; A = 238
B) Z = 91; A = 238
C) Z = 90; A = 234
D) Z = 93; A = 238
E) Z = 88; A = 236

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
For large mass number nuclei which are stable, the ratio of protons to neutrons is
A) equal to 1
B) greater than 1
C) less than 1
D) unrelated to the stability of nuclei
E) almost 2 to 1
A) equal to 1
B) greater than 1
C) less than 1
D) unrelated to the stability of nuclei
E) almost 2 to 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Two isotopes of uranium have the same
A) mass number
B) neutron number
C) atomic number
D) nucleon number
E) nucleon number and neutron number
A) mass number
B) neutron number
C) atomic number
D) nucleon number
E) nucleon number and neutron number

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV/nucleon) for tritium, ( 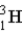 ) a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. Assume:
) a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. Assume:
M p = 1.007 825 u
M n = 1.008 665 u
M t = 3.016 05 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 2.8
B) 3.1
C) 1.0
D) 8.5
E) 2.1
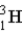 ) a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. Assume:
) a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. Assume:M p = 1.007 825 u
M n = 1.008 665 u
M t = 3.016 05 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 2.8
B) 3.1
C) 1.0
D) 8.5
E) 2.1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Find the binding energy (in MeV) of carbon-12. Assume:
MC = 12.000 000 u
M p = 1.007 825 u
M n = 1.008 665 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 14.8
B) 0.511
C) 9.11
D) 92.3
E) 46.2
MC = 12.000 000 u
M p = 1.007 825 u
M n = 1.008 665 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 14.8
B) 0.511
C) 9.11
D) 92.3
E) 46.2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A glass container holds equal numbers of atoms of phosphorus 30 with a half-life of 2.5 minutes and of nitrogen 13 with a half-life of 10 minutes. After 20 minutes the ratio of the number of nitrogen atoms remaining to the number of phosphorus atoms remaining is
A)
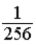 .
.
B)
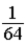 .
.
C)
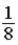 .
.
D) 64.
E) 256.
A)
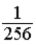 .
.B)
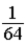 .
.C)
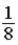 .
.D) 64.
E) 256.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
How can a nucleus be described by particular values of A, Z and N when the mass of the nucleus is not equal to Zmp + Nmn, where mp and mn are the masses of free protons and neutrons?
A) A, Z and N have no intrinsic meaning.
B) A, Z and N describe the number of particles of given types, but mass has no meaning when part of the mass is elsewhere in the universe.
C) A, Z and N describe the number of particles an ideal rather than a real nucleus would have.
D) A, Z and N describe the number of particles of given types in the nucleus, but not their masses in a bound state.
E) A, Z and N describe the number of particles of given types in the nucleus since the missing mass consists of electrons that are also present in the nucleus.
A) A, Z and N have no intrinsic meaning.
B) A, Z and N describe the number of particles of given types, but mass has no meaning when part of the mass is elsewhere in the universe.
C) A, Z and N describe the number of particles an ideal rather than a real nucleus would have.
D) A, Z and N describe the number of particles of given types in the nucleus, but not their masses in a bound state.
E) A, Z and N describe the number of particles of given types in the nucleus since the missing mass consists of electrons that are also present in the nucleus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Two nuclei may have equal Z, but different A, because they contain
A) equal numbers of protons and neutrons.
B) equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
C) different numbers of protons but equal numbers of neutrons.
D) different numbers of protons and neutrons.
E) electrons as well as neutrons.
A) equal numbers of protons and neutrons.
B) equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
C) different numbers of protons but equal numbers of neutrons.
D) different numbers of protons and neutrons.
E) electrons as well as neutrons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
In beta decays
A) a proton changes to a neutron.
B) a neutron changes to a proton.
C) an electron is present in the nucleus before the decay.
D) (a), (b) or (c) may occur.
E) only (a) or (b) may occur.
A) a proton changes to a neutron.
B) a neutron changes to a proton.
C) an electron is present in the nucleus before the decay.
D) (a), (b) or (c) may occur.
E) only (a) or (b) may occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
When a neutron decays, a proton and an electron are observed. When the electrons emitted from a sample of neutrons are observed, they are found to have different kinetic energies. This was accounted for by
A) introducing a different particle, the neutrino.
B) introducing the effect of gravity on the particles.
C) including the kinetic energies of the neutron and proton.
D) modifying the laws of conservation of momentum and energy.
E) taking into account the uncertainties associated with Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle.
A) introducing a different particle, the neutrino.
B) introducing the effect of gravity on the particles.
C) including the kinetic energies of the neutron and proton.
D) modifying the laws of conservation of momentum and energy.
E) taking into account the uncertainties associated with Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The Q value for the following reaction, 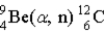 , is (in MeV) m(alpha) = 4.002 603 u
, is (in MeV) m(alpha) = 4.002 603 u
M(Be) = 9.012 182 u
M(n) = 1.008 665 u
M(C) = 12.000 00 u
1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 8.4
B) 6.2
C) 7.3
D) 5.7
E) 3.5
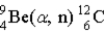 , is (in MeV) m(alpha) = 4.002 603 u
, is (in MeV) m(alpha) = 4.002 603 uM(Be) = 9.012 182 u
M(n) = 1.008 665 u
M(C) = 12.000 00 u
1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 8.4
B) 6.2
C) 7.3
D) 5.7
E) 3.5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Heavy nuclei are unstable because
A) each nucleon is a separate particle that is not acted on by the nuclear force.
B) there are not enough protons present relative to the number of neutrons for the electrical force to be strong enough.
C) the nuclear force dominates the Coulomb repulsive force at distances less than 2 fm, but falls off rapidly at greater distances.
D) nuclei are stable only when the number of neutrons equals the number of protons.
E) nuclei are stable only when the number of protons exceeds the number of neutrons.
A) each nucleon is a separate particle that is not acted on by the nuclear force.
B) there are not enough protons present relative to the number of neutrons for the electrical force to be strong enough.
C) the nuclear force dominates the Coulomb repulsive force at distances less than 2 fm, but falls off rapidly at greater distances.
D) nuclei are stable only when the number of neutrons equals the number of protons.
E) nuclei are stable only when the number of protons exceeds the number of neutrons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the effects listed below is not a major effect influencing the binding energy of the nucleus in the liquid-drop model?
A) The volume effect: the binding energy per nucleon is approximately constant when A > 50.
B) The surface effect: nucleons in the surface have fewer neighbors.
C) The quantum number effect: all nucleons in the nucleus have the same set of quantum numbers.
D) The Coulomb repulsion effect: protons repel protons.
E) The symmetry effect: stable nuclei tend to have N ≈ Z.
A) The volume effect: the binding energy per nucleon is approximately constant when A > 50.
B) The surface effect: nucleons in the surface have fewer neighbors.
C) The quantum number effect: all nucleons in the nucleus have the same set of quantum numbers.
D) The Coulomb repulsion effect: protons repel protons.
E) The symmetry effect: stable nuclei tend to have N ≈ Z.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
What value of Z (atomic number) and A (mass number) result in the following gamma decay? 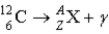
A) Z = 5; A = 12
B) Z = 4; A = 8
C) Z = 7; A = 12
D) Z = 6; A = 12
E) Z = 6; A = 11
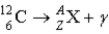
A) Z = 5; A = 12
B) Z = 4; A = 8
C) Z = 7; A = 12
D) Z = 6; A = 12
E) Z = 6; A = 11

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
In nuclear magnetic resonance, nuclei absorb energy when flipping between nuclear
A) mass states.
B) spin states.
C) charge states.
D) decay states.
E) isotope states.
A) mass states.
B) spin states.
C) charge states.
D) decay states.
E) isotope states.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The chart below shows part of the radioactive series beginning with the isotope 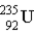 . The isotope marked with an X is
. The isotope marked with an X is 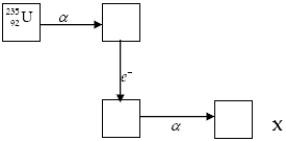
A)
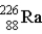 .
.
B)
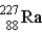 .
.
C)
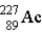 .
.
D)
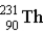 .
.
E)
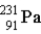 .
.
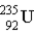 . The isotope marked with an X is
. The isotope marked with an X is 
A)
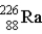 .
.B)
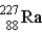 .
.C)
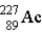 .
.D)
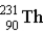 .
.E)
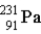 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
What is the disintegration energy (in MeV) associated with this spontaneous decay? 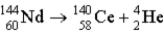 mNd = 143.910 083 u mCe = 139.905 434 u
mNd = 143.910 083 u mCe = 139.905 434 u
MHe = 4.002 603 u
1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 1.54
B) 2.37
C) 1.90
D) 4.13
E) 8.21
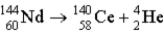 mNd = 143.910 083 u mCe = 139.905 434 u
mNd = 143.910 083 u mCe = 139.905 434 uMHe = 4.002 603 u
1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 1.54
B) 2.37
C) 1.90
D) 4.13
E) 8.21

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Because we know that the half-lives of many radioactive isotopes are millions of years, we can deduce that
A) the longer it exists the more radioactive nuclei Earth produces.
B) the sun is the source of all the radioactive nuclei on Earth.
C) there must have been many more radioactive nuclei on Earth when life began.
D) there must have been far fewer radioactive nuclei on Earth before life began.
E) the natural radioactivity of minerals on the Earth was created by the Earth's internal temperature.
A) the longer it exists the more radioactive nuclei Earth produces.
B) the sun is the source of all the radioactive nuclei on Earth.
C) there must have been many more radioactive nuclei on Earth when life began.
D) there must have been far fewer radioactive nuclei on Earth before life began.
E) the natural radioactivity of minerals on the Earth was created by the Earth's internal temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Two nuclei which share the same atomic number Z always are
A) stable.
B) unstable.
C) isotopes.
D) isobars.
E) radioactive.
A) stable.
B) unstable.
C) isotopes.
D) isobars.
E) radioactive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The radius of an approximately spherical nucleus is given by r =
A) r0Z3.
B) r0Z1/3.
C) r0A3.
D) r0A1/3.
E) r0(A − Z)1/3.
A) r0Z3.
B) r0Z1/3.
C) r0A3.
D) r0A1/3.
E) r0(A − Z)1/3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
It is often possible to use atomic masses when calculating the binding energy of a nucleus. This is not true for calculating the Q value for the e+ decay process since
A) the electron masses do not cancel.
B) a positron is an antiparticle.
C) the electron masses cancel.
D) the mass of a positron cannot be neglected when compared to the mass of a nucleus.
E) none of the above.
A) the electron masses do not cancel.
B) a positron is an antiparticle.
C) the electron masses cancel.
D) the mass of a positron cannot be neglected when compared to the mass of a nucleus.
E) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
According to the shell model, binding energy per nucleon is greater when N or Z is equal to one of the numbers below except for
A) 2.
B) 8.
C) 13.
D) 20.
E) 28.
A) 2.
B) 8.
C) 13.
D) 20.
E) 28.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The reaction energy associated with a nuclear reaction is
A) the total change in rest energy as a result of the reaction.
B) equivalent to the disintegration energy.
C) the minimum energy necessary for such a reaction to occur.
D) called the threshold energy.
E) the binding energy of the nucleons.
A) the total change in rest energy as a result of the reaction.
B) equivalent to the disintegration energy.
C) the minimum energy necessary for such a reaction to occur.
D) called the threshold energy.
E) the binding energy of the nucleons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Rutherford's experiment, in which he fired alpha particles of 7.7 MeV kinetic energy at a thin gold foil, showed that nuclei were very much smaller than the size of an atom because
A) some alpha particles passed through the foil undeflected.
B) some alpha particles were deflected backwards.
C) some alpha particles were captured by the gold nuclei.
D) the alpha particles could not get closer than 10−10 m to the gold nuclei.
E) the alpha particles split into deuterium nuclei when they encountered the gold nuclei.
A) some alpha particles passed through the foil undeflected.
B) some alpha particles were deflected backwards.
C) some alpha particles were captured by the gold nuclei.
D) the alpha particles could not get closer than 10−10 m to the gold nuclei.
E) the alpha particles split into deuterium nuclei when they encountered the gold nuclei.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
It is often possible to use the atomic masses when calculating the binding energy of a nucleus. The reason for this is
A) the electron masses do not cancel.
B) the electron masses cancel.
C) tables of nuclear masses are usually not available.
D) the mass of the electron can usually be neglected when compared to the mass of the neutron.
E) the atomic masses are the same as the nuclear masses.
A) the electron masses do not cancel.
B) the electron masses cancel.
C) tables of nuclear masses are usually not available.
D) the mass of the electron can usually be neglected when compared to the mass of the neutron.
E) the atomic masses are the same as the nuclear masses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Approximately how much uranium (in kg) must undergo fission per day to provide 1 000 MW of power? (Assume an efficiency of 30%). The nuclear reaction is 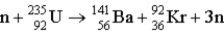 . m(n) = 1.008 665 u
. m(n) = 1.008 665 u
M(U) = 235.043 915 u
M(Ba) = 140.913 9 u
M(Kr) = 91.897 3 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 1.0
B) 3.5
C) 2.3
D) 4.6
E) 0.1
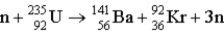 . m(n) = 1.008 665 u
. m(n) = 1.008 665 uM(U) = 235.043 915 u
M(Ba) = 140.913 9 u
M(Kr) = 91.897 3 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 1.0
B) 3.5
C) 2.3
D) 4.6
E) 0.1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
In which of the following decays does the atomic mass number of the daughter nucleus differ from that of the parent nucleus?
A)
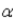
B)
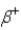
C)
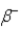
D)
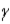
E) Answers (a), (b), and (c) are correct.
A)
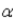
B)
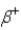
C)
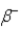
D)
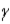
E) Answers (a), (b), and (c) are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The chart below shows part of the radioactive series beginning with the isotope 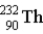 . The isotope marked with an X is
. The isotope marked with an X is 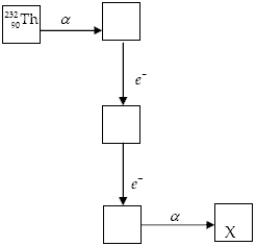
A)
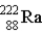 .
.
B)
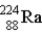 .
.
C)
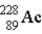 .
.
D)
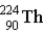 .
.
E)
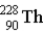 .
.
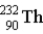 . The isotope marked with an X is
. The isotope marked with an X is 
A)
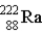 .
.B)
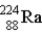 .
.C)
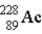 .
.D)
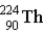 .
.E)
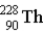 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
What is the average kinetic energy (in keV) of an ion that has a temperature of 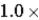 108 K?
108 K?
A) 8.2
B) 13
C) 4.3
D) 16
E) 21
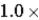 108 K?
108 K?A) 8.2
B) 13
C) 4.3
D) 16
E) 21

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The radiocarbon content of 14C decreases after the death of a living system with a half-life of 5730 y. If an archaeologist working a dig finds an ancient firepit containing some partially consumed firewood and the wood contains only 12.5 percent of the 14C content of an equal carbon sample from a present-day tree, what is the age of the ancient site?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A neutron is characterized by the term "thermal neutron" when
A) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 0°C.
B) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 0 K.
C) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 273°C.
D) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 100°C.
E) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 0°R.
A) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 0°C.
B) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 0 K.
C) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 273°C.
D) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 100°C.
E) its energy is of the order kT, where T is on the order of 0°R.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A self-sustained chain reaction occurs when the reproduction constant, K, is equal to
A) 3.0
B) 2.0
C) 2.5
D) 1.0
E) 0.5
A) 3.0
B) 2.0
C) 2.5
D) 1.0
E) 0.5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
One of the naturally occurring radioactive series begins with 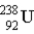 . Which of the following isotopes is the stable isotope at the end of this series?
. Which of the following isotopes is the stable isotope at the end of this series?
A)
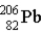
B)
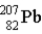
C)
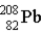
D)
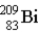
E) None of the above choices can be correct.
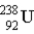 . Which of the following isotopes is the stable isotope at the end of this series?
. Which of the following isotopes is the stable isotope at the end of this series?A)
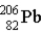
B)
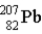
C)
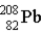
D)
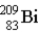
E) None of the above choices can be correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Find the unknown atomic number and mass number respectively, for the following reaction 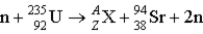
A) 141, 53
B) 140, 54
C) 53, 41
D) 54, 140
E) 54, 141
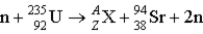
A) 141, 53
B) 140, 54
C) 53, 41
D) 54, 140
E) 54, 141

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
A pure sample of 226Ra contains 2.0 × 1014 atoms of the isotope. If the half-life of 226Ra = 1.6 × 103 years, what is the decay rate of this sample? (1 Ci = 3.7 × 1010 decays/s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Find the number of nuclei per unit volume (n = nuclei/cm3) for lead. atomic weight = 202.7
Density = 11.5 g/cm3
Avogadro's number = 6.02 × 1023
A) 2.51 × 1022
B) 3.42 × 1022
C) 2.93 × 1022
D) 2.94 × 1023
E) 2.05 × 1021
Density = 11.5 g/cm3
Avogadro's number = 6.02 × 1023
A) 2.51 × 1022
B) 3.42 × 1022
C) 2.93 × 1022
D) 2.94 × 1023
E) 2.05 × 1021

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A beam of 1-MeV gamma rays incident on a piece of 0.50-cm thick lead is reduced by 50% of its initial value. How thick must the lead be to reduce the beam to one percent of its initial value?
A) 1.1 cm
B) 2.2 cm
C) 3.3 cm
D) 4.4 cm
E) 8.4 cm
A) 1.1 cm
B) 2.2 cm
C) 3.3 cm
D) 4.4 cm
E) 8.4 cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Linus claims that the added gravitational force of neutrons holds the particles in a nucleus together. Linnea says that they stick together because they lose their electric charge when they form a nucleus. Which one, if either, is correct, and why?
A) Linus, because more particles exert gravitational forces on one another than exert electromagnetic forces.
B) Linus, because the numerical magnitude of G/ke is 7.42 × 10−21.
C) Linnea, because the numerical magnitude of G/ke is 7.42 × 10−21.
D) Both, because electric charge is lost and then gravity holds the nucleus together.
E) Neither, because gravity is not lost, and the numerical magnitude of ke/G is 1.35 × 1020.
A) Linus, because more particles exert gravitational forces on one another than exert electromagnetic forces.
B) Linus, because the numerical magnitude of G/ke is 7.42 × 10−21.
C) Linnea, because the numerical magnitude of G/ke is 7.42 × 10−21.
D) Both, because electric charge is lost and then gravity holds the nucleus together.
E) Neither, because gravity is not lost, and the numerical magnitude of ke/G is 1.35 × 1020.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
How much energy (in MeV) is released when a 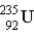 fissions to
fissions to 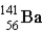 and
and 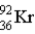 in the reaction
in the reaction 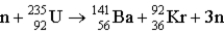 m(n) = 1.008665 u m(U) = 235.043915 u
m(n) = 1.008665 u m(U) = 235.043915 u
M(Ba) = 140.9139 u
M(Kr) = 91.8973 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 100
B) 50
C) 200
D) 150
E) 250
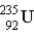 fissions to
fissions to 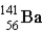 and
and 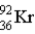 in the reaction
in the reaction 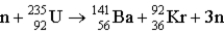 m(n) = 1.008665 u m(U) = 235.043915 u
m(n) = 1.008665 u m(U) = 235.043915 uM(Ba) = 140.9139 u
M(Kr) = 91.8973 u
U = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
A) 100
B) 50
C) 200
D) 150
E) 250

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A neutron is known to undergo beta decay (n → p + e− + 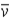 ). A reasonable mean lifetime for free neutrons is
). A reasonable mean lifetime for free neutrons is
A) 10 years
B) 10 hours
C) 10 days
D) 10 minutes
E) 10−23 s
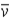 ). A reasonable mean lifetime for free neutrons is
). A reasonable mean lifetime for free neutrons isA) 10 years
B) 10 hours
C) 10 days
D) 10 minutes
E) 10−23 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A thermal neutron has an energy (in eV) on the order of
A) 40
B) 0.4
C) 4
D) 0.04
E) 400
A) 40
B) 0.4
C) 4
D) 0.04
E) 400

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The mass of 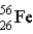 is 55.9349 u and the mass of
is 55.9349 u and the mass of 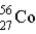 is 55.939 9 u. Which isobar decays into the other, and by what 2 possible processes?
is 55.939 9 u. Which isobar decays into the other, and by what 2 possible processes?
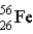 is 55.9349 u and the mass of
is 55.9349 u and the mass of 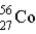 is 55.939 9 u. Which isobar decays into the other, and by what 2 possible processes?
is 55.939 9 u. Which isobar decays into the other, and by what 2 possible processes?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Homer says that we can safely use nuclear power because all radioactive nuclei are gone after two half-lives. Marge says that only the decay rate is zero after two half-lives. Which one, if either, is correct, and why?
A) Homer, because half of the nuclei disintegrate in each half-life.
B) Marge, because the number of decays per unit time is halved in each half-life.
C) Homer, because it's safe to handle radioactive substances after two half-lives.
D) Both, because when all nuclei disintegrate the decay rate is also zero.
E) Neither, because one quarter of the nuclei are left after two half-lives.
A) Homer, because half of the nuclei disintegrate in each half-life.
B) Marge, because the number of decays per unit time is halved in each half-life.
C) Homer, because it's safe to handle radioactive substances after two half-lives.
D) Both, because when all nuclei disintegrate the decay rate is also zero.
E) Neither, because one quarter of the nuclei are left after two half-lives.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The half-life of 131I is 8 days. On a certain day, the activity of an 131I sample is 6.4 mCi. What is its activity 40 days later?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The nuclear probability of interacting with neutrons depends most strongly on the neutron's
A) mass
B) area
C) volume
D) speed
E) charge
A) mass
B) area
C) volume
D) speed
E) charge

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The reaction 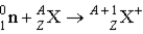 is known as a ____ reaction.
is known as a ____ reaction.
A) beta capture
B) beta emission
C) neutron capture
D) neutron emission
E) photon emission
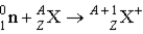 is known as a ____ reaction.
is known as a ____ reaction.A) beta capture
B) beta emission
C) neutron capture
D) neutron emission
E) photon emission

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Radioactive technetium, a gamma emitter, is taken up by the heart muscle in a medical test. The detector for the radiation emitted from the heart could be a
A) Tokamak.
B) quarter-wavelength antenna.
C) Geiger counter.
D) photoelectric tube.
E) diffraction grating.
A) Tokamak.
B) quarter-wavelength antenna.
C) Geiger counter.
D) photoelectric tube.
E) diffraction grating.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
How fast must two deuterium atoms be moving so they can overcome the Coulomb force of repulsion, and attain the necessary 10−14 m for fusion? (m( 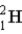 ) = 2.014 1 u)
) = 2.014 1 u)
A) 3.9 × 106 m/s
B) 1.3 × 106 m/s
C) 2.6 × 106 m/s
D) 5.2 × 106 m/s
E) 3.7 × 106 m/s
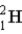 ) = 2.014 1 u)
) = 2.014 1 u)A) 3.9 × 106 m/s
B) 1.3 × 106 m/s
C) 2.6 × 106 m/s
D) 5.2 × 106 m/s
E) 3.7 × 106 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
When a fast neutron collides with a hydrogen or deuterium nucleus, the most likely result is that
A) the neutron has an appreciable gain in kinetic energy, the gain being greatest for head-on collisions.
B) the neutron has an appreciable gain in kinetic energy, the gain being greatest for oblique collisions.
C) the neutron has an appreciable loss in kinetic energy, the loss being greatest for head-on collisions.
D) the neutron has an appreciable loss in kinetic energy, the loss being greatest for oblique collisions.
E) the neutron is absorbed by the hydrogen or deuterium nucleus.
A) the neutron has an appreciable gain in kinetic energy, the gain being greatest for head-on collisions.
B) the neutron has an appreciable gain in kinetic energy, the gain being greatest for oblique collisions.
C) the neutron has an appreciable loss in kinetic energy, the loss being greatest for head-on collisions.
D) the neutron has an appreciable loss in kinetic energy, the loss being greatest for oblique collisions.
E) the neutron is absorbed by the hydrogen or deuterium nucleus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Which of the following is not a radiation detector?
A) cloud chamber
B) Geiger counter
C) scintillation counter
D) neutron activation
E) spark chamber
A) cloud chamber
B) Geiger counter
C) scintillation counter
D) neutron activation
E) spark chamber

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
When a nucleus at rest spontaneously splits into fragments of mass m1 and m2, the ratio of the momentum of m1 to the momentum of m2 is
A)
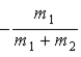 .
.
B)
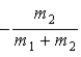 .
.
C) −1.
D)
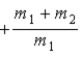 .
.
E)
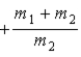 .
.
A)
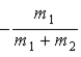 .
.B)
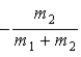 .
.C) −1.
D)
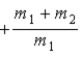 .
.E)
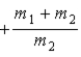 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Background radiation from cosmic rays and radioactive nuclei in our surroundings is about 0.13 rem/year. Suppose we assume this all comes from cosmic rays which have an RBE factor of 1.0. The RBE factor for the most dangerous types of radiation is 20. How many rads of the most dangerous radiation could a 100-year-old person have been exposed to in her lifetime without having gone over the recommended limit of 0.5 rem/year?
A) 0.37
B) 0.50
C) 1.85
D) 13
E) 37
A) 0.37
B) 0.50
C) 1.85
D) 13
E) 37

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Calculate the half-value thickness (in mm) of lead if it reduces the intensity of a beam of x-rays whose wavelength is 10 pm by a factor of two. (Assume the linear absorption coefficient of lead is 43 cm−1 for x-rays of wavelength 10 × 10−12 m.)
A) 0.24
B) 0.20
C) 0.12
D) 0.16
E) 0.18
A) 0.24
B) 0.20
C) 0.12
D) 0.16
E) 0.18

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
When a beam of nuclear radiation of initial intensity I0 passes through a thickness x of material, the intensity of the beam exiting the material is I =
A) I0e−μx.
B) I0eμx.
C) I0(e−μx − 1).
D) I0(eμx − 1).
E) I0(1 − e−μx).
A) I0e−μx.
B) I0eμx.
C) I0(e−μx − 1).
D) I0(eμx − 1).
E) I0(1 − e−μx).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
In order to control a nuclear reactor, control rods can be pulled out of or pushed into the reactor core by remote control. These rods control the reactor by
A) slowing down the fast neutrons so the neutrons can be absorbed by 238U.
B) speeding up slow neutrons so the neutrons can be absorbed by 238U.
C) slowing down fast neutrons so they cannot initiate further fusion reactions in 235U.
D) speeding up fast neutrons so they cannot initiate further fusion reactions in 235U.
E) capturing thermal neutrons so they cannot initiate further fission reactions in 235U.
A) slowing down the fast neutrons so the neutrons can be absorbed by 238U.
B) speeding up slow neutrons so the neutrons can be absorbed by 238U.
C) slowing down fast neutrons so they cannot initiate further fusion reactions in 235U.
D) speeding up fast neutrons so they cannot initiate further fusion reactions in 235U.
E) capturing thermal neutrons so they cannot initiate further fission reactions in 235U.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
A radioactive sample with decay rate R and decay energy Q has power output
A)
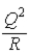 .
.
B) RQ.
C) Q2R.
D) equal to any of the above.
E) equal to (a) or (c) above.
A)
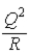 .
.B) RQ.
C) Q2R.
D) equal to any of the above.
E) equal to (a) or (c) above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
In neutron capture by an atomic nucleus, the atomic number changes by
A) −2.
B) −1.
C) 0.
D) +1.
E) +2.
A) −2.
B) −1.
C) 0.
D) +1.
E) +2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
One rad is
A) the amount of radiation that deposits 10−2 J of energy into 1 kg of absorbing material.
B) the amount of ionizing radiation that will produce 1/3 × 10−9 C of electric charge in 1 cm3 of air under standard conditions.
C) the amount of radiation needed for ionization of an atom.
D) the amount of radiation needed for dissociation of a molecule.
E) the amount of radiation that deposits one erg of energy in 1g of material.
A) the amount of radiation that deposits 10−2 J of energy into 1 kg of absorbing material.
B) the amount of ionizing radiation that will produce 1/3 × 10−9 C of electric charge in 1 cm3 of air under standard conditions.
C) the amount of radiation needed for ionization of an atom.
D) the amount of radiation needed for dissociation of a molecule.
E) the amount of radiation that deposits one erg of energy in 1g of material.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
A principal mechanism for energy loss during nuclear fusion is bremsstrahlung. This loss is associated with
A) x-rays emitted due to electron-ion collisions.
B) radiation losses due to T4 losses.
C) conduction losses associated with ΔT.
D) convection losses associated with ΔT.
E) neutron collisions with atoms of moderator.
A) x-rays emitted due to electron-ion collisions.
B) radiation losses due to T4 losses.
C) conduction losses associated with ΔT.
D) convection losses associated with ΔT.
E) neutron collisions with atoms of moderator.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Approximately how fast is an ion of helium moving if it is in a plasma with a temperature of 108 K? m(He) = 4.002 603 u and u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg.
A) 106 m/s
B) 104 m/s
C) 102 m/s
D) 10 m/s
E) 1 m/s
A) 106 m/s
B) 104 m/s
C) 102 m/s
D) 10 m/s
E) 1 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
When a nucleus at rest spontaneously splits into fragments of mass m1 and m2, the ratio of the velocity of m1 to the velocity of m2 is
A)
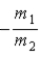 .
.
B)
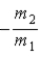 .
.
C) −1.
D)
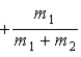 .
.
E)
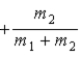 .
.
A)
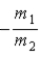 .
.B)
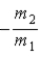 .
.C) −1.
D)
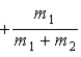 .
.E)
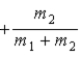 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Radiant energy reaching the Earth from the sun is not sufficient to keep the Earth's surface temperature comfortable for life. Of the following, the most likely source of the additional thermal energy is from
A) fusion of hydrogen nuclei in the Earth's core.
B) fusion of high Z nuclei in the Earth's core.
C) fission of radioactive nuclei inside the Earth.
D) fission of radioactive nuclei in cosmic rays.
E) deflection of radioactive nuclei in cosmic rays.
A) fusion of hydrogen nuclei in the Earth's core.
B) fusion of high Z nuclei in the Earth's core.
C) fission of radioactive nuclei inside the Earth.
D) fission of radioactive nuclei in cosmic rays.
E) deflection of radioactive nuclei in cosmic rays.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
One roentgen is defined as
A) the amount of ionizing radiation that will produce 1/3 × 10−9 C of electric charge in 1 cm3 of air under standard conditions.
B) the amount of radiation that deposits 10−2 J of energy into 1 kg of absorbing material.
C) the amount of radiation needed for ionization of an atom.
D) the amount of radiation needed for dissociation of a molecule.
E) the amount of radiation that deposits 1 erg of energy in 1 g of air.
A) the amount of ionizing radiation that will produce 1/3 × 10−9 C of electric charge in 1 cm3 of air under standard conditions.
B) the amount of radiation that deposits 10−2 J of energy into 1 kg of absorbing material.
C) the amount of radiation needed for ionization of an atom.
D) the amount of radiation needed for dissociation of a molecule.
E) the amount of radiation that deposits 1 erg of energy in 1 g of air.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
What energy is needed (in MeV) so two deuterium atoms moving together will reach the necessary 10−14 m for fusion?
A) 0.511
B) 0.14
C) 2.5
D) 4.3
E) 1.0
A) 0.511
B) 0.14
C) 2.5
D) 4.3
E) 1.0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
A rem (roentgen equivalent in man) is defined as (the product of)
A) the dose in RBE.
B) the dose in roentgen and the RBE factor.
C) the dose in rad times the dose in roentgen.
D) the dose in rad and the RBE factor.
E) the dose in rad and energy of radiation.
A) the dose in RBE.
B) the dose in roentgen and the RBE factor.
C) the dose in rad times the dose in roentgen.
D) the dose in rad and the RBE factor.
E) the dose in rad and energy of radiation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 89 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








