Deck 18: Advanced Time Series Topics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 18: Advanced Time Series Topics
1
Which of the following statements is true of spurious regressions?
A)The OLS estimates of the population parameters are efficient and unbiased and the t statistic is valid.
B)Even if the explanatory variables and the dependent variable are independent times series processes, the R2 can be large.
C)Spurious regressions are limited to I(0) processes, and are not possible in case of I(1) processes.
D)Spurious regressions are limited to I(1) processes, and are not possible in case of I(0) processes.
A)The OLS estimates of the population parameters are efficient and unbiased and the t statistic is valid.
B)Even if the explanatory variables and the dependent variable are independent times series processes, the R2 can be large.
C)Spurious regressions are limited to I(0) processes, and are not possible in case of I(1) processes.
D)Spurious regressions are limited to I(1) processes, and are not possible in case of I(0) processes.
B
2
The Koyck distributed lag model is an example of:
A)a moving average model.
B)an autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity model.
C)an infinite distributed lag model.
D)a finite distributed lag model.
A)a moving average model.
B)an autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity model.
C)an infinite distributed lag model.
D)a finite distributed lag model.
C
3
A spurious correlation refers to a situation where:
A)two variables are related through their correlation with a third variable.
B)the correlation coefficient between two variables cannot be estimated.
C)there is direct causal relationship between two variables but tests for correlations reject this relationship.
D)the correlation between two variables is positive till the sample size reaches a threshold, and negative after the sample size crosses the threshold.
A)two variables are related through their correlation with a third variable.
B)the correlation coefficient between two variables cannot be estimated.
C)there is direct causal relationship between two variables but tests for correlations reject this relationship.
D)the correlation between two variables is positive till the sample size reaches a threshold, and negative after the sample size crosses the threshold.
A
4
Which of the following tests can be used to check for cointegration between two series?
A)Wald test
B)Breush-Pagan test
C)White test
D)Engle-Granger test
A)Wald test
B)Breush-Pagan test
C)White test
D)Engle-Granger test

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If two series have means that are not trending, a simple regression involving two independent I(1) series will often result in a significant _____ statistic.
A)F
B)t
C)z
D)χ2
A)F
B)t
C)z
D)χ2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is true?
A)The calculated t statistic is valid and efficient in case of a spurious regression.
B)If an explanatory variable or a dependent variable is integrated of the order one, the OLS estimators are asymptotically normally distributed.
C)An error correction model can be used to study the short-run dynamics in the relationship between the dependent variable and the explanatory variables in a time series model.
D)The Dickey-Fuller test can be used to test for heteroskedasticity in the error terms.
A)The calculated t statistic is valid and efficient in case of a spurious regression.
B)If an explanatory variable or a dependent variable is integrated of the order one, the OLS estimators are asymptotically normally distributed.
C)An error correction model can be used to study the short-run dynamics in the relationship between the dependent variable and the explanatory variables in a time series model.
D)The Dickey-Fuller test can be used to test for heteroskedasticity in the error terms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If ft denotes the forecast of yt+1 made at time t, then the forecast error is given by:
A)et+1 = ft/yt+1.
B)et+1 = yt+1/ft.
C)et+1 = yt+1 + ft.
D)et+1 = yt+1 - ft.
A)et+1 = ft/yt+1.
B)et+1 = yt+1/ft.
C)et+1 = yt+1 + ft.
D)et+1 = yt+1 - ft.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The value of the parameter α in the exponential smoothing method lies between _____.
A)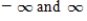
B)-1 and 1
C)0 and 1
D)0 and
A)
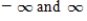
B)-1 and 1
C)0 and 1
D)0 and


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Let {(yt, zt): t = …, −2,−1, 0, 1, 2, …} be a bivariate time series process. The model: yt =  +
+  0zt +
0zt +  1zt - 1 +
1zt - 1 +  2zt - 2 + ….. + ut, represents a(n):
2zt - 2 + ….. + ut, represents a(n):
A)moving average model.
B)ARIMA model.
C)finite distributed lag model.
D)infinite distributed lag model.
 +
+  0zt +
0zt +  1zt - 1 +
1zt - 1 +  2zt - 2 + ….. + ut, represents a(n):
2zt - 2 + ….. + ut, represents a(n):A)moving average model.
B)ARIMA model.
C)finite distributed lag model.
D)infinite distributed lag model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following is used to test whether a time series follows a unit root process?
A)Wald test
B)White test
C)Augmented Dickey-Fuller test
D)Johansen test
A)Wald test
B)White test
C)Augmented Dickey-Fuller test
D)Johansen test

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The long-run propensity measures the long-run change in the expected value of y given a one-unit, permanent increase in z.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In case of forecasts, the root mean squared error is the:
A)average of the forecast errors divided by the variance of the errors.
B)average of the absolute forecast errors.
C)standard deviation of the forecast errors without any degrees of freedom adjustment.
D)standard deviation of the forecast errors with a degrees of freedom adjustment.
A)average of the forecast errors divided by the variance of the errors.
B)average of the absolute forecast errors.
C)standard deviation of the forecast errors without any degrees of freedom adjustment.
D)standard deviation of the forecast errors with a degrees of freedom adjustment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following is true of squared forecast errors?
A)An error of +2 yields a greater loss than an error of −2.
B)An error of −2 yields a greater loss than an error of +2.
C)An error of −2 or +2 yields the same loss.
D)Loss from positive and negative forecast errors cannot be compared.
A)An error of +2 yields a greater loss than an error of −2.
B)An error of −2 yields a greater loss than an error of +2.
C)An error of −2 or +2 yields the same loss.
D)Loss from positive and negative forecast errors cannot be compared.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
If the t statistic for the presence of a unit root in a variable is −7.22 and the 5% critical value is −2.86, there is strong evidence against a unit root in the variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Two series are said to be cointegrated if:
A)both series are I(1) but a linear combination of them is I(0).
B)both series are I(0) but a linear combination of them is I(1).
C)both series have the same set of explanatory variables but a different dependent variable.
D)both series have the same dependent variable but a different set of explanatory variables.
A)both series are I(1) but a linear combination of them is I(0).
B)both series are I(0) but a linear combination of them is I(1).
C)both series have the same set of explanatory variables but a different dependent variable.
D)both series have the same dependent variable but a different set of explanatory variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The model: yt =  0 +
0 +  0zt +
0zt + 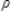 yt - 1 +
yt - 1 +  1zt - 1 +vt, where vt = ut -
1zt - 1 +vt, where vt = ut - 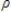 ut - 1 represents a:
ut - 1 represents a:
A)finite distributed lag model.
B)simultaneous equations model.
C)rational distributed lag model.
D)vector error correction model.
 0 +
0 +  0zt +
0zt + 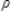 yt - 1 +
yt - 1 +  1zt - 1 +vt, where vt = ut -
1zt - 1 +vt, where vt = ut - 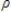 ut - 1 represents a:
ut - 1 represents a:A)finite distributed lag model.
B)simultaneous equations model.
C)rational distributed lag model.
D)vector error correction model.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements correctly identifies the difference between an autoregressive model and a vector autoregressive model?
A)In an autoregressive model, the dependent variable is expressed as a function of its own lag, whereas in a vector autoregressive model, the dependent variable is expressed as a function of the lag of an explanatory variable.
B)In an autoregressive model, the dependent variable is expressed as a function of the lag of an explanatory variable, whereas in a vector autoregressive model, the dependent variable is expressed as a function of its own lag.
C)In an autoregressive model several series are modeled in terms of their own past, whereas in a vector autoregressive model only one series is modeled in terms of its own past.
D)In an autoregressive model one series is modeled in terms of its own past, whereas in a vector autoregressive model several series are modeled in terms of their past.
A)In an autoregressive model, the dependent variable is expressed as a function of its own lag, whereas in a vector autoregressive model, the dependent variable is expressed as a function of the lag of an explanatory variable.
B)In an autoregressive model, the dependent variable is expressed as a function of the lag of an explanatory variable, whereas in a vector autoregressive model, the dependent variable is expressed as a function of its own lag.
C)In an autoregressive model several series are modeled in terms of their own past, whereas in a vector autoregressive model only one series is modeled in terms of its own past.
D)In an autoregressive model one series is modeled in terms of its own past, whereas in a vector autoregressive model several series are modeled in terms of their past.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A spurious regression refers to a situation where:
A)the direction of the relationship between the dependent variable and the explanatory variables is uncertain.
B)even though two variables are independent, the OLS regression of one variable on the other indicates a relationship between them.
C)a few important and necessary explanatory variables are left out of a regression equation, thus leading to inefficient and inconsistent forecasts.
D)at least one of the variables used in a regression equation does not have a unit root and the error terms are heteroskedastic.
A)the direction of the relationship between the dependent variable and the explanatory variables is uncertain.
B)even though two variables are independent, the OLS regression of one variable on the other indicates a relationship between them.
C)a few important and necessary explanatory variables are left out of a regression equation, thus leading to inefficient and inconsistent forecasts.
D)at least one of the variables used in a regression equation does not have a unit root and the error terms are heteroskedastic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A process {yt} is a martingale if _____ is equal to yt for all t ≥ 0.
A)E(yt+1|yt, yt-1, …, y0)
B)E(yt+1|yt-1, …, y0)
C)E(yt+1, yt| yt-1, …, y0)
D)E(yt+1, yt| yt-1, yt-2)
A)E(yt+1|yt, yt-1, …, y0)
B)E(yt+1|yt-1, …, y0)
C)E(yt+1, yt| yt-1, …, y0)
D)E(yt+1, yt| yt-1, yt-2)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In the given AR(1) model, yt =  +
+ 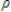 yt - 1 +
yt - 1 +  , t = 1,2…… , the Dickey-Fuller distribution refers to the:
, t = 1,2…… , the Dickey-Fuller distribution refers to the:
A)asymptotic distribution of the t statistic under the hypothesis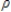 - 1 = 0.
- 1 = 0.
B)asymptotic distribution of the F statistic under the hypothesis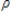 - 1 = 0.
- 1 = 0.
C)asymptotic distribution of the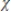 2 statistic under the hypothesis
2 statistic under the hypothesis 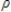 - 1 = 0.
- 1 = 0.
D)asymptotic distribution of the z statistic under the hypothesis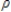 - 1 = 0.
- 1 = 0.
 +
+ 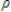 yt - 1 +
yt - 1 +  , t = 1,2…… , the Dickey-Fuller distribution refers to the:
, t = 1,2…… , the Dickey-Fuller distribution refers to the:A)asymptotic distribution of the t statistic under the hypothesis
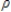 - 1 = 0.
- 1 = 0.B)asymptotic distribution of the F statistic under the hypothesis
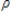 - 1 = 0.
- 1 = 0.C)asymptotic distribution of the
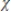 2 statistic under the hypothesis
2 statistic under the hypothesis 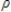 - 1 = 0.
- 1 = 0.D)asymptotic distribution of the z statistic under the hypothesis
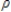 - 1 = 0.
- 1 = 0.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
For 2.5% significance level, the asymptotic critical value for cointegration test with linear time trend is -3.59.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Vector autoregressive models should be used for forecasting if the series being studied are cointegrated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Exponential smoothing is a forecasting method where the weights on the lagged dependent variable decline to zero exponentially.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The R2 calculated in a spurious regression is a valid and efficient estimate of the goodness-of-fit of the regression equation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
In calculation of squared forecast errors, an error of +3 yields a loss three times greater than an error of −1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








