Deck 21: Consumer Choice: Maximizing Utility and Behavioral Economics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/176
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 21: Consumer Choice: Maximizing Utility and Behavioral Economics
1
Suppose you are eating buffalo wings at a local happy hour.The total utils from doing so after the fourth,fifth,sixth,and seventh wings are 30,50,65,72,respectively.In this situation we have __________ marginal utility,which is generally __________ in the analysis of consumer choice.
A) increasing; assumed
B) increasing; not assumed
C) diminishing; assumed
D) diminishing; not assumed
A) increasing; assumed
B) increasing; not assumed
C) diminishing; assumed
D) diminishing; not assumed
C
2
We take one dollar from a millionaire and give it to a pauper.Assuming a diminishing marginal utility of money,
A) total utility in the economy must rise.
B) total utility in the economy must fall.
C) total utility in the economy must remain the same.
D) we cannot say whether or not total utility changes.
A) total utility in the economy must rise.
B) total utility in the economy must fall.
C) total utility in the economy must remain the same.
D) we cannot say whether or not total utility changes.
D
3
Suppose Alice receives 250 utils from consuming one hamburger and 90 utils from consuming a second hamburger.What is the marginal utility of the second hamburger?
A) 340 utils
B) 170 utils
C) 90 utils
D) 0 utils
E) none of the above
A) 340 utils
B) 170 utils
C) 90 utils
D) 0 utils
E) none of the above
C
4
The diamond-water paradox is the observation that
A) those things that have the greatest price often have little value in exchange and those things that have the lowest price often have the greatest value in exchange.
B) those things that have the greatest value in use often have little value in exchange and those things that have little value in use often have the greatest value in exchange.
C) those things that have the least value in use often have little value in exchange and those things that have the greatest value in use often have the greatest value in exchange.
D) those things that have the least price often have little value in exchange and those things that have the greatest price often have the greatest value in exchange.
A) those things that have the greatest price often have little value in exchange and those things that have the lowest price often have the greatest value in exchange.
B) those things that have the greatest value in use often have little value in exchange and those things that have little value in use often have the greatest value in exchange.
C) those things that have the least value in use often have little value in exchange and those things that have the greatest value in use often have the greatest value in exchange.
D) those things that have the least price often have little value in exchange and those things that have the greatest price often have the greatest value in exchange.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Suppose you just finished your third plateful of Thanksgiving dinner and it yielded zero units of additional satisfaction.Should you go back for more?
A) Why not? Since the third plateful gave you zero units, the fourth can't give you any less than zero.
B) No way. You could get negative utility from the fourth plateful.
C) Yes or no. It won't make any difference because your total utility is at its peak.
D) Yes. If you received zero units of satisfaction from the third, then obviously the law of diminishing marginal utility is not working in this case.
A) Why not? Since the third plateful gave you zero units, the fourth can't give you any less than zero.
B) No way. You could get negative utility from the fourth plateful.
C) Yes or no. It won't make any difference because your total utility is at its peak.
D) Yes. If you received zero units of satisfaction from the third, then obviously the law of diminishing marginal utility is not working in this case.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Total utility is defined as the
A) change in marginal utility a person derives from the consumption of a good.
B) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the price of that good.
C) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the change in the consumption of that good.
D) sum of the amounts of satisfaction a person receives from consuming a good.
E) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good.
A) change in marginal utility a person derives from the consumption of a good.
B) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the price of that good.
C) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the change in the consumption of that good.
D) sum of the amounts of satisfaction a person receives from consuming a good.
E) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A util is an artificial construct used as a means of measuring the
A) price of a good.
B) satisfaction one receives from the consumption of a good.
C) costs of producing a good.
D) difference between the price and the value of a good.
A) price of a good.
B) satisfaction one receives from the consumption of a good.
C) costs of producing a good.
D) difference between the price and the value of a good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The law of diminishing marginal utility says that
A) the marginal utility gained by consuming equal successive units of a good will decline as the amount consumed increases.
B) the more of a particular good one consumes, the greater is the utility received from the consumption of that good.
C) the marginal utility gained by consuming equal successive units of a good will increase as the amount consumed increases.
D) the more of a particular product one sells, the less utility one receives from selling.
E) none of the above
A) the marginal utility gained by consuming equal successive units of a good will decline as the amount consumed increases.
B) the more of a particular good one consumes, the greater is the utility received from the consumption of that good.
C) the marginal utility gained by consuming equal successive units of a good will increase as the amount consumed increases.
D) the more of a particular product one sells, the less utility one receives from selling.
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Suppose you are eating buffalo wings at a local happy hour.The total utils from doing so after the fourth,fifth,sixth,and seventh wings are 80,116,136,146,respectively.The marginal utility of the seventh wing is __________ utils.
A) 14
B) 146
C) 10
D) 20.9
A) 14
B) 146
C) 10
D) 20.9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Suppose you are eating slices of pizza and after consuming the first slice you receive 14 utils of total utility,after the second you receive 22 utils of total utility,and after the third 25 utils of total utility.Then
A) the law of diminishing marginal utility is not applicable because your total utility is increasing instead of diminishing.
B) your total utility is 61 utils.
C) your total utility is 25 utils, and the marginal utility of the first slice is 8 utils (22 - 14).
D) your total utility is 25 utils, and the marginal utility of the third slice is 3 utils.
A) the law of diminishing marginal utility is not applicable because your total utility is increasing instead of diminishing.
B) your total utility is 61 utils.
C) your total utility is 25 utils, and the marginal utility of the first slice is 8 utils (22 - 14).
D) your total utility is 25 utils, and the marginal utility of the third slice is 3 utils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Jackson says that his fifth game of chess gave him greater utility than his first,and therefore the law of diminishing marginal utility does not hold.An economist who believes that marginal utility definitely and always declines with the consumption of equal successive units of a good will likely say
A) the fifth game of chess is a different good than the first game of chess.
B) there are exceptions to the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) the law of diminishing marginal utility does not apply to board games.
D) a or b
E) a or c
A) the fifth game of chess is a different good than the first game of chess.
B) there are exceptions to the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) the law of diminishing marginal utility does not apply to board games.
D) a or b
E) a or c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Suppose Will receives 150 utils from consuming one banana and 250 utils from consuming two bananas.What is the marginal utility of the second banana?
A) 50 utils
B) 125 utils
C) 100 utils
D) 58 utils
E) none of the above
A) 50 utils
B) 125 utils
C) 100 utils
D) 58 utils
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Suppose you are eating buffalo wings at a local happy hour.The total utils from doing so after the fourth,fifth,sixth,and seventh wings are 80,116,136,150,respectively.The marginal utility of the sixth wing is __________ utils.
A) 14
B) 136
C) 20
D) 22.7
A) 14
B) 136
C) 20
D) 22.7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
When an economist talks about utility,she is talking about
A) a company that provides electricity, water, gas, etc.
B) the satisfaction, in terms of price, that a producer receives from selling his product.
C) the satisfaction that results from the consumption of a good.
D) the amount of one good that a person is willing to give up in order to get a unit of another good.
E) the satisfaction that results from the consumption of a good minus the price that must be paid to get the good.
A) a company that provides electricity, water, gas, etc.
B) the satisfaction, in terms of price, that a producer receives from selling his product.
C) the satisfaction that results from the consumption of a good.
D) the amount of one good that a person is willing to give up in order to get a unit of another good.
E) the satisfaction that results from the consumption of a good minus the price that must be paid to get the good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Marginal utility is defined as the
A) change in marginal utility a person derives from the consumption of a good.
B) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the price of that good.
C) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the change in the quantity of the good consumed.
D) sum of the amounts of satisfaction a person receives from consuming a good.
E) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the value in use of that good.
A) change in marginal utility a person derives from the consumption of a good.
B) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the price of that good.
C) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the change in the quantity of the good consumed.
D) sum of the amounts of satisfaction a person receives from consuming a good.
E) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the value in use of that good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
You and your roommate are eating pizza and have already consumed all but the last slice.Your roommate claims that he is hungrier than you and therefore should get the last slice of pizza.Your roommate has made
A) a diamond-water paradox.
B) an interpersonal utility comparison.
C) a correct statement.
D) a marginal error.
A) a diamond-water paradox.
B) an interpersonal utility comparison.
C) a correct statement.
D) a marginal error.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The law of diminishing marginal utility can be stated as follows:
A) As the amount of a good consumed increases, the sum of satisfaction received tends to decrease.
B) As the amount of a good consumed increases, the additional satisfaction gained from consuming additional units tends to decrease.
C) As the amount of a good consumed decreases, the additional satisfaction gained from consuming additional units tends to increase.
D) As the amount of a good consumed increases, the sum of satisfaction received tends to increase but at a diminishing rate.
E) b and d
A) As the amount of a good consumed increases, the sum of satisfaction received tends to decrease.
B) As the amount of a good consumed increases, the additional satisfaction gained from consuming additional units tends to decrease.
C) As the amount of a good consumed decreases, the additional satisfaction gained from consuming additional units tends to increase.
D) As the amount of a good consumed increases, the sum of satisfaction received tends to increase but at a diminishing rate.
E) b and d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Suppose you are consuming a particular good and you could somehow give back the last unit you consumed.What would happen to total and marginal utility (assuming that the marginal utility of the unit given back is positive)?
A) Both total and marginal utility would decrease.
B) Both total and marginal utility would increase.
C) Total utility would increase but marginal utility would decrease.
D) Total utility would decrease but marginal utility would increase.
E) There would be no change in marginal utility but total utility would decrease.
A) Both total and marginal utility would decrease.
B) Both total and marginal utility would increase.
C) Total utility would increase but marginal utility would decrease.
D) Total utility would decrease but marginal utility would increase.
E) There would be no change in marginal utility but total utility would decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
We take one dollar from a pauper and give it to a millionaire.Assuming a diminishing marginal utility of money,
A) total utility in the economy must rise.
B) total utility in the economy must fall.
C) total utility in the economy must remain the same.
D) we cannot say whether or not total utility changes.
A) total utility in the economy must rise.
B) total utility in the economy must fall.
C) total utility in the economy must remain the same.
D) we cannot say whether or not total utility changes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following is true?
A) It is possible for total utility to rise as marginal utility falls.
B) Marginal utility is the same as total utility.
C) As marginal utility falls, total utility always falls.
D) a and c
A) It is possible for total utility to rise as marginal utility falls.
B) Marginal utility is the same as total utility.
C) As marginal utility falls, total utility always falls.
D) a and c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
We would expect the total utility of water to be high but its marginal utility to be low.Why?
A) Because water is a fluid and we don't need fluids to live as much as we need food.
B) Because we need water to live and there is so much of it.
C) Because we need water to live and there is very little of it.
D) Because water's price is low.
A) Because water is a fluid and we don't need fluids to live as much as we need food.
B) Because we need water to live and there is so much of it.
C) Because we need water to live and there is very little of it.
D) Because water's price is low.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The law of diminishing marginal utility helps to explain
A) why people trade.
B) the law of demand.
C) why the production possibilities frontier is typically bowed-out.
D) a and b
E) all of the above
A) why people trade.
B) the law of demand.
C) why the production possibilities frontier is typically bowed-out.
D) a and b
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Ari is currently consuming 10 hot dogs and 8 hamburgers per week.The last hot dog she consumed yielded 20 utils while the last hamburger she ate gave her 25 utils.If hot dogs cost $2 and hamburgers cost $2.50,is Ari consuming the correct quantities of these two goods to be in consumer equilibrium?
A) No, she should consume more hamburgers and fewer hot dogs.
B) No, she should consume more hot dogs and fewer hamburgers.
C) Yes, so there is no need to change her eating habits.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) No, she should consume more hamburgers and fewer hot dogs.
B) No, she should consume more hot dogs and fewer hamburgers.
C) Yes, so there is no need to change her eating habits.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Because there are so few diamonds in the world,the consumption of diamonds
A) takes priority over the consumption of water.
B) takes place at relatively high marginal utility.
C) takes place at relatively low marginal utility.
D) is more important than the consumption of water.
A) takes priority over the consumption of water.
B) takes place at relatively high marginal utility.
C) takes place at relatively low marginal utility.
D) is more important than the consumption of water.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
In order for an individual to achieve consumer equilibrium through the consumption of two goods,A and B,that individual must fulfill the condition
A) TUA = TUB.
B) TUA/PA = TUB/PB.
C) MUA = MUB.
D) MUA/PA = MUB/PB.
E) MUB/PA = MUA/PB.
A) TUA = TUB.
B) TUA/PA = TUB/PB.
C) MUA = MUB.
D) MUA/PA = MUB/PB.
E) MUB/PA = MUA/PB.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
If a person is receiving greater marginal utility per dollar from consuming one good than another,it follows that he or she is
A) maximizing disutility.
B) not maximizing utility.
C) maximizing utility.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) maximizing disutility.
B) not maximizing utility.
C) maximizing utility.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Suppose the government provides peanut butter to everyone free of charge and everyone consumes it to the point at which he receives no additional satisfaction from another spoonful.Is this necessarily good?
A) Yes, because everyone is satisfied.
B) No, because there might be some cases where the resources used to produce peanut butter could have been better used to produce more of other products.
C) Yes, because the law of diminishing marginal utility indicates that in order to get the greatest amount of satisfaction from the use of resources, people should consume as much of every good as they can.
D) none of the above
A) Yes, because everyone is satisfied.
B) No, because there might be some cases where the resources used to produce peanut butter could have been better used to produce more of other products.
C) Yes, because the law of diminishing marginal utility indicates that in order to get the greatest amount of satisfaction from the use of resources, people should consume as much of every good as they can.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Rich has $100,000 and Poore has $1,000.Which of these statements is most strongly supported by the theory of consumer choice?
A) An extra dollar given to Rich is worth less to him than his 100,000th dollar.
B) An extra dollar is worth less to Rich than it is to Poore.
C) An extra dollar is worth less to Poore than it is to Rich.
D) Rich's 1,000th dollar is worth more to Rich than Poore's 1,000th dollar is worth to Poore.
E) Rich's 100,000th dollar is worth to Rich exactly what Poore's 1,000th dollar is worth to Poore.
A) An extra dollar given to Rich is worth less to him than his 100,000th dollar.
B) An extra dollar is worth less to Rich than it is to Poore.
C) An extra dollar is worth less to Poore than it is to Rich.
D) Rich's 1,000th dollar is worth more to Rich than Poore's 1,000th dollar is worth to Poore.
E) Rich's 100,000th dollar is worth to Rich exactly what Poore's 1,000th dollar is worth to Poore.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A consumer is in equilibrium if he or she derives the same
A) total utility from each good consumed.
B) total utility per dollar spent on each good consumed.
C) marginal utility from each good consumed.
D) marginal utility per dollar spent on each good consumed.
A) total utility from each good consumed.
B) total utility per dollar spent on each good consumed.
C) marginal utility from each good consumed.
D) marginal utility per dollar spent on each good consumed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Suppose for a consumer the marginal utility (MU)of bread is 20 utils and the MU of milk is 10 utils; the price of bread is $3 and the price of milk is $1.Given this,
A) more utility per dollar is gained from consuming bread than milk.
B) more utility per dollar is gained from consuming milk than bread.
C) the same amount of utility per dollar is gained from consuming milk as bread.
D) the consumer is in consumer equilibrium.
A) more utility per dollar is gained from consuming bread than milk.
B) more utility per dollar is gained from consuming milk than bread.
C) the same amount of utility per dollar is gained from consuming milk as bread.
D) the consumer is in consumer equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
We would expect the total utility of diamonds to be __________ than the total utility of water and the marginal utility of diamonds to be __________ than the marginal utility of water.
A) higher; higher
B) lower; lower
C) higher; lower
D) lower; higher
A) higher; higher
B) lower; lower
C) higher; lower
D) lower; higher

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Dan is currently consuming 10 Cokes and 5 slices of pizza per week such that the marginal utility of the tenth Coke is 12 utils and that of the fifth slice of pizza is also 12 utils.How should Dan redirect his purchases so as to attain consumer equilibrium?
A) He should buy more pizza slices and less Coke.
B) He should buy fewer pizza slices and more Coke.
C) He is currently attaining consumer equilibrium and should not redirect his purchases.
D) He could gain more satisfaction by buying less of both and more of something else.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) He should buy more pizza slices and less Coke.
B) He should buy fewer pizza slices and more Coke.
C) He is currently attaining consumer equilibrium and should not redirect his purchases.
D) He could gain more satisfaction by buying less of both and more of something else.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
In the Texas A & M study of the "buying" behavior of two white rats,as the "relative price" of one beverage was raised,
A) both white rats began to consume more of the higher-priced beverage.
B) both white rats began to consume less of the higher-priced beverage.
C) one white rat began to consume more of the higher-priced beverage and the other began to consume less.
D) both white rats continued consuming the same amount of the beverage as before its price was raised.
E) There was no study done at Texas A & M with white rats.
A) both white rats began to consume more of the higher-priced beverage.
B) both white rats began to consume less of the higher-priced beverage.
C) one white rat began to consume more of the higher-priced beverage and the other began to consume less.
D) both white rats continued consuming the same amount of the beverage as before its price was raised.
E) There was no study done at Texas A & M with white rats.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Suppose you could quantify the amount of satisfaction you receive from consuming ice cream in money terms.You might say,"I expect to get $3 worth of satisfaction from this ice cream cone." According to traditional economic theory,if the price of this ice cream cone were $3.05,would you buy one?
A) Sure, why not? What's a nickel?
B) Absolutely. It's worth it at that price.
C) No way, because it's not worth it.
D) There is no way to answer this question because you really can't compare the price of something and the amount of satisfaction you expect to receive from it.
A) Sure, why not? What's a nickel?
B) Absolutely. It's worth it at that price.
C) No way, because it's not worth it.
D) There is no way to answer this question because you really can't compare the price of something and the amount of satisfaction you expect to receive from it.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
In which of the following settings is an interpersonal utility comparison being made?
A) Brandon says to Jack, "I get a lot more satisfaction out of eating pizza than you do."
B) Stephanie says, "I don't know what Taylor is feeling or thinking; I can't read a person's heart or mind."
C) David says to Maria, "I know you like this course a lot more than I do."
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c
A) Brandon says to Jack, "I get a lot more satisfaction out of eating pizza than you do."
B) Stephanie says, "I don't know what Taylor is feeling or thinking; I can't read a person's heart or mind."
C) David says to Maria, "I know you like this course a lot more than I do."
D) a and c
E) a, b, and c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The less you have of any one good, the less you would be willing to pay for one more unit of it.
B) The less you have of any one good, the more you would be willing to pay for one more unit of it.
C) The amount you have of any one good does not influence the price you would be willing to pay for it, but it does affect the marginal utility received from consuming a particular unit.
D) none of the above
A) The less you have of any one good, the less you would be willing to pay for one more unit of it.
B) The less you have of any one good, the more you would be willing to pay for one more unit of it.
C) The amount you have of any one good does not influence the price you would be willing to pay for it, but it does affect the marginal utility received from consuming a particular unit.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Economists usually assume that money has __________ marginal utility.
A) increasing
B) constant
C) decreasing
D) zero
A) increasing
B) constant
C) decreasing
D) zero

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Suppose the marginal utility (MU)of paperback books is 40 utils and each costs $5 while the MU of DVD rentals is 20 utils and each rents for $4.If you consume one movie and one book per week,are you attaining consumer equilibrium?
A) Yes, so there is no need to change.
B) No. You need to buy more books and rent fewer DVDs.
C) No. You need to rent more DVDs and buy fewer books.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) Yes, so there is no need to change.
B) No. You need to buy more books and rent fewer DVDs.
C) No. You need to rent more DVDs and buy fewer books.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements is false?
A) A millionaire definitely receives less utility from an additional dollar than a poor person.
B) A poor person definitely receives less utility from an additional dollar than a rich person.
C) A millionaire definitely receives the same utility from an additional dollar as a poor person.
D) A millionaire generally receives less utility from an additional dollar than a poor person.
E) We do not know if any of the statements are true or false, because we do not know how much utility one person receives relative to another.
A) A millionaire definitely receives less utility from an additional dollar than a poor person.
B) A poor person definitely receives less utility from an additional dollar than a rich person.
C) A millionaire definitely receives the same utility from an additional dollar as a poor person.
D) A millionaire generally receives less utility from an additional dollar than a poor person.
E) We do not know if any of the statements are true or false, because we do not know how much utility one person receives relative to another.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is true?
A) If a consumer is in equilibrium, it does not necessarily follow that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
B) If a consumer is in equilibrium, it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
C) If a consumer is attaining the greatest marginal utility, then it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
D) If a consumer is attaining the greatest total utility, then it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest marginal utility.
A) If a consumer is in equilibrium, it does not necessarily follow that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
B) If a consumer is in equilibrium, it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
C) If a consumer is attaining the greatest marginal utility, then it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
D) If a consumer is attaining the greatest total utility, then it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest marginal utility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Total utility
A) is the total amount of satisfaction derived from consuming a particular quantity of a good.
B) for quantity Y can be calculated by summing the marginal utilities of each unit that comprises quantity Y.
C) is the sum of the amounts of utility derived from consuming each unit of a good.
D) a and b
E) all of the above
A) is the total amount of satisfaction derived from consuming a particular quantity of a good.
B) for quantity Y can be calculated by summing the marginal utilities of each unit that comprises quantity Y.
C) is the sum of the amounts of utility derived from consuming each unit of a good.
D) a and b
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Suppose that the total utility from consuming one unit of good X is 54 utils,the total utility of two units of good X is 74 utils,and the total utility of three units of good X is 84 utils. The marginal utility of the third unit is
A) 10 utils.
B) 70.67 utils.
C) 12.25 utils.
D) 20 utils.
A) 10 utils.
B) 70.67 utils.
C) 12.25 utils.
D) 20 utils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Suppose a consumer is purchasing Coke (c)and pretzels (p)in quantities such that he is achieving consumer equilibrium.Then the price of Coke increases.Which of the following will be true?
A) MUC/PC = MUP/PP
B) MUC/PC > MUP/PP
C) MUC/PC < MUP/PP
D) We cannot say for certain what will happen to the MUC/PC relative to the MUP/PP.
A) MUC/PC = MUP/PP
B) MUC/PC > MUP/PP
C) MUC/PC < MUP/PP
D) We cannot say for certain what will happen to the MUC/PC relative to the MUP/PP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Joe is currently in consumer equilibrium by consuming cheese and crackers,such that the last cracker consumed yielded 8 utils and the last piece of cheese consumed yielded 12 utils.Assume the price of crackers is two cents per cracker and the price of cheese is three cents per piece.If the price of crackers increases to four cents,Joe should __________ his consumption of crackers and his marginal utility from crackers will __________ and also __________ his consumption of cheese and his marginal utility from cheese will __________.
A) increase; increase; increase; increase
B) increase; increase; decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease; increase; decrease
D) decrease; increase; decrease; increase
E) decrease; increase; increase; decrease
A) increase; increase; increase; increase
B) increase; increase; decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease; increase; decrease
D) decrease; increase; decrease; increase
E) decrease; increase; increase; decrease

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Marginal utility is
A) the extra satisfaction derived from consuming an additional unit of a good.
B) the total satisfaction derived from consuming an additional unit of a good.
C) the total satisfaction derived from consuming a good.
D) the change in total satisfaction as an additional unit of a good is consumed.
E) a and d
A) the extra satisfaction derived from consuming an additional unit of a good.
B) the total satisfaction derived from consuming an additional unit of a good.
C) the total satisfaction derived from consuming a good.
D) the change in total satisfaction as an additional unit of a good is consumed.
E) a and d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Suppose that a consumer purchases a combination of X and Y such that MUX/PX = 15 utils per dollar and MUY /PY = 10 utils per dollar.To maximize utility,the consumer should buy
A) less of X and more of Y.
B) more of X and less of Y.
C) more of both X and Y.
D) less of both X and Y.
E) neither X nor Y.
A) less of X and more of Y.
B) more of X and less of Y.
C) more of both X and Y.
D) less of both X and Y.
E) neither X nor Y.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The diamond-water paradox is illustrated by which of the following statements?
A) Water, a necessity, has a relatively low price whereas diamonds, usually a luxury, have a relatively high price.
B) Although water appears to have a relatively low price when compared to diamonds, in reality, it has a relatively higher price.
C) Although water appears to have a relatively low price when compared to diamonds, in reality, the prices are equal.
D) Although water appears to have a relatively low price when compared to diamonds, at the margin, water has the relatively higher price.
E) Although water appears to have a relatively low price when compared to diamonds, at the margin, the prices are equal.
A) Water, a necessity, has a relatively low price whereas diamonds, usually a luxury, have a relatively high price.
B) Although water appears to have a relatively low price when compared to diamonds, in reality, it has a relatively higher price.
C) Although water appears to have a relatively low price when compared to diamonds, in reality, the prices are equal.
D) Although water appears to have a relatively low price when compared to diamonds, at the margin, water has the relatively higher price.
E) Although water appears to have a relatively low price when compared to diamonds, at the margin, the prices are equal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Suppose that the total utility from consuming one unit of good Z is 220 utils,the total utility from consuming two units of good Z is 320 utils,and the total utility from consuming three units of good Z is 400 utils. The marginal utility received from consuming the third unit of good Z is
A) 313.33 utils.
B) 80 utils.
C) 100 utils.
D) 50 utils.
A) 313.33 utils.
B) 80 utils.
C) 100 utils.
D) 50 utils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Given two goods,X and Y,their prices,PX and PY,a consumer is in equilibrium when the last dollar spent on X yields
A) zero marginal utility for Y.
B) the same marginal utility as if all the money were spent on Y.
C) a smaller marginal utility than the last dollar spent on Y.
D) the same marginal utility as the last dollar spent on Y.
E) none of the above
A) zero marginal utility for Y.
B) the same marginal utility as if all the money were spent on Y.
C) a smaller marginal utility than the last dollar spent on Y.
D) the same marginal utility as the last dollar spent on Y.
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
To an economist,utility refers to the
A) usefulness of a good or service.
B) satisfaction that results from the consumption of a good.
C) relative scarcity of a good.
D) rate of decline in the demand curve.
A) usefulness of a good or service.
B) satisfaction that results from the consumption of a good.
C) relative scarcity of a good.
D) rate of decline in the demand curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If the marginal utility of a good is negative,then
A) consumers should buy less of it.
B) consumers will consume it only if it is free.
C) consumers should buy more of it to make its marginal utility positive.
D) the law of diminishing marginal utility is being violated.
A) consumers should buy less of it.
B) consumers will consume it only if it is free.
C) consumers should buy more of it to make its marginal utility positive.
D) the law of diminishing marginal utility is being violated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Given two goods,X and Y,and their prices,PX and PY a consumer will maximize utility by allocating expenditures such that
A) MUX/PY = MUY/PX.
B) PY/MUX = PX/MUY.
C) MUX/PX = MUY /PY.
D) MUX = PX = MUY = PY = MU$.
E) MUX = MUY = PX = PY = MU$.
A) MUX/PY = MUY/PX.
B) PY/MUX = PX/MUY.
C) MUX/PX = MUY /PY.
D) MUX = PX = MUY = PY = MU$.
E) MUX = MUY = PX = PY = MU$.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Suppose a consumer is purchasing Coke and pretzels in quantities such that she is achieving consumer equilibrium.Then the price of Coke decreases.The consumer will likely __________ her consumption of Coke and the marginal utility of Coke will __________ while the total utility from Coke will __________.
A) increase; increase; increase
B) increase; decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease; increase
D) decrease; increase; increase
E) decrease; decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase; increase
B) increase; decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease; increase
D) decrease; increase; increase
E) decrease; decrease; decrease

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
To economists,utility means
A) marginal value.
B) relative value.
C) satisfaction.
D) usefulness.
E) a, c, and d
A) marginal value.
B) relative value.
C) satisfaction.
D) usefulness.
E) a, c, and d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
According to the traditional theory of marginal utility as presented in the textbook,as more units of a good are acquired,the consumer's marginal utility
A) always continues to rise.
B) diminishes.
C) remains constant.
D) may diminish at first, but it must eventually rise.
E) may rise at first, but it must eventually become constant.
A) always continues to rise.
B) diminishes.
C) remains constant.
D) may diminish at first, but it must eventually rise.
E) may rise at first, but it must eventually become constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The theory of consumer choice assumes that consumers attempt to maximize
A) the difference between total utility and marginal utility.
B) average utility.
C) total utility.
D) marginal utility.
A) the difference between total utility and marginal utility.
B) average utility.
C) total utility.
D) marginal utility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Diamonds are more expensive than water because
A) markets do not always reflect value.
B) they have fewer uses.
C) they are relatively scarce and they yield higher marginal utility.
D) they yield higher total utility.
E) all of the above
A) markets do not always reflect value.
B) they have fewer uses.
C) they are relatively scarce and they yield higher marginal utility.
D) they yield higher total utility.
E) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Suppose Valerie is consuming lipstick (L)and eye shadow (E)and nothing else.MUL = 24 and MUE = 40.The price of eye shadow is $5,and the price of lipstick is $4.What should Valerie do?
A) Consume more eye shadow and less lipstick.
B) Consume more lipstick and less eye shadow.
C) Consume less of both.
D) Consume more of both.
E) Not change her consumption of either good.
A) Consume more eye shadow and less lipstick.
B) Consume more lipstick and less eye shadow.
C) Consume less of both.
D) Consume more of both.
E) Not change her consumption of either good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
To resolve the diamond-water paradox,it is important to note that under most circumstances,
A) the marginal utility of water is lower than the marginal utility of diamonds.
B) the marginal utilities of water and diamonds are about the same.
C) the marginal utility of water is higher than the marginal utility of diamonds.
D) the marginal utilities of water and diamonds are inversely related.
E) the marginal utilities of water and diamonds are directly related.
A) the marginal utility of water is lower than the marginal utility of diamonds.
B) the marginal utilities of water and diamonds are about the same.
C) the marginal utility of water is higher than the marginal utility of diamonds.
D) the marginal utilities of water and diamonds are inversely related.
E) the marginal utilities of water and diamonds are directly related.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Given that MUX/PX < MUY/PY,consumers who spend all their income on these two goods
A) can never maximize utility.
B) have maximized total utility.
C) can increase utility by buying more of X and less of Y.
D) can increase utility by buying more of Y and less of X.
E) a and b
A) can never maximize utility.
B) have maximized total utility.
C) can increase utility by buying more of X and less of Y.
D) can increase utility by buying more of Y and less of X.
E) a and b

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Exhibit 21-1
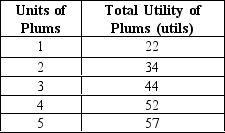
Refer to Exhibit 21-1.The marginal utility of the third plum is
A) 17 utils.
B) 10 utils.
C) 8 utils.
D) 3 utils.
E) cannot be determined

Refer to Exhibit 21-1.The marginal utility of the third plum is
A) 17 utils.
B) 10 utils.
C) 8 utils.
D) 3 utils.
E) cannot be determined

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Assuming only two goods X and Y,if MUX/PX = MUY/PY,then
A) the consumer is in equilibrium.
B) the consumer cannot be made better off by redirecting his purchases.
C) the consumer is deriving the same marginal utility per dollar for all goods.
D) a and c
E) a, b and c
A) the consumer is in equilibrium.
B) the consumer cannot be made better off by redirecting his purchases.
C) the consumer is deriving the same marginal utility per dollar for all goods.
D) a and c
E) a, b and c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Exhibit 21-1

Refer to Exhibit 21-1.The marginal utility of the fourth plum is
A) 8 utils.
B) 2 utils.
C) 10 utils.
D) 13.5 utils.
E) 50 utils.

Refer to Exhibit 21-1.The marginal utility of the fourth plum is
A) 8 utils.
B) 2 utils.
C) 10 utils.
D) 13.5 utils.
E) 50 utils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Exhibit 21-3
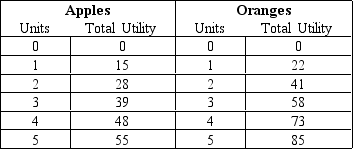
Refer to Exhibit 21-3.Linda spends $5 a week on apples and oranges.If the price of both goods is $1 per unit,how many apples and oranges,respectively,does she purchase per week if she wants to maximize her utility?
A) 0 and 5
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 2
E) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 21-3.Linda spends $5 a week on apples and oranges.If the price of both goods is $1 per unit,how many apples and oranges,respectively,does she purchase per week if she wants to maximize her utility?
A) 0 and 5
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 2
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Economist David Friedman pointed out that
A) the endowment effect is not limited to humans.
B) the law of diminishing marginal utility does not hold for money.
C) the diamond-water paradox would not exist if water was scarce and diamonds were plentiful.
D) the government should provide the necessities of life for free.
A) the endowment effect is not limited to humans.
B) the law of diminishing marginal utility does not hold for money.
C) the diamond-water paradox would not exist if water was scarce and diamonds were plentiful.
D) the government should provide the necessities of life for free.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Don receives 100 utils from consuming two oranges.The utility he derives from consuming the second orange equals 30 utils.The information provided
A) is consistent with the law of diminishing marginal utility.
B) is inconsistent with the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) is sufficient to determine the quantity of oranges Don will consume.
D) lends support to the inferiority of oranges as consumer goods.
A) is consistent with the law of diminishing marginal utility.
B) is inconsistent with the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) is sufficient to determine the quantity of oranges Don will consume.
D) lends support to the inferiority of oranges as consumer goods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Exhibit 21-3

Refer to Exhibit 21-3.Linda spends $5 a week on apples and oranges.If the price of both goods is $1 per unit,what is Linda's total utility from consuming the optimal bundle of goods?
A) 85
B) 86
C) 88
D) 209
E) 279

Refer to Exhibit 21-3.Linda spends $5 a week on apples and oranges.If the price of both goods is $1 per unit,what is Linda's total utility from consuming the optimal bundle of goods?
A) 85
B) 86
C) 88
D) 209
E) 279

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If total utility of a good is high while the price of the good is low,it is likely that the good
A) is plentiful.
B) is inferior.
C) is rare.
D) has high marginal utility.
A) is plentiful.
B) is inferior.
C) is rare.
D) has high marginal utility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Exhibit 21-3

Refer to Exhibit 21-3.Assume that the price of oranges increases to $2,while the price of apples remains at $1,and Linda allocates $5 of the weekly food budget to purchasing apples and oranges.If Linda wants to maximize her utility,her new consumption bundle will consist of
A) 1 apple and 2 oranges.
B) 3 apples and 1 orange.
C) 5 apples and no oranges.
D) none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 21-3.Assume that the price of oranges increases to $2,while the price of apples remains at $1,and Linda allocates $5 of the weekly food budget to purchasing apples and oranges.If Linda wants to maximize her utility,her new consumption bundle will consist of
A) 1 apple and 2 oranges.
B) 3 apples and 1 orange.
C) 5 apples and no oranges.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Don receives 100 utils from consuming two oranges.The utility he derives from consuming the second orange equals 30 utils.Which of the following conclusions is derived from the law of diminishing marginal utility?
A) The marginal utility Don receives from consuming the third orange will be less than 30 utils.
B) The marginal utility Don receives from consuming the third orange will be less than 100, but greater than 30 utils.
C) If the price of oranges decreases, Don will buy fewer oranges, ceteris paribus.
D) The total utility Don receives from consuming the first orange is less than the marginal utility from consuming the first orange.
A) The marginal utility Don receives from consuming the third orange will be less than 30 utils.
B) The marginal utility Don receives from consuming the third orange will be less than 100, but greater than 30 utils.
C) If the price of oranges decreases, Don will buy fewer oranges, ceteris paribus.
D) The total utility Don receives from consuming the first orange is less than the marginal utility from consuming the first orange.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Which of the following statements does not invoke interpersonal utility comparisons?
A) The total utility a millionaire derives from $100 is less than the total utility a poor person derives from $100.
B) The marginal utility a millionaire derives from the one-millionth dollar is less than the marginal utility a poor person derives from the one-hundredth dollar.
C) For both the millionaire and the pauper, the marginal utility they derive from the one-thousandth dollar is less than the marginal utility they derive from the five-hundredth dollar.
D) None of the above, because all rely on interpersonal utility comparisons.
A) The total utility a millionaire derives from $100 is less than the total utility a poor person derives from $100.
B) The marginal utility a millionaire derives from the one-millionth dollar is less than the marginal utility a poor person derives from the one-hundredth dollar.
C) For both the millionaire and the pauper, the marginal utility they derive from the one-thousandth dollar is less than the marginal utility they derive from the five-hundredth dollar.
D) None of the above, because all rely on interpersonal utility comparisons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
A person is said to be in consumer equilibrium if she
A) equates marginal utilities per dollar spent.
B) has diminishing marginal utility of money.
C) purchases only normal goods.
D) has an incentive to redirect her purchases.
A) equates marginal utilities per dollar spent.
B) has diminishing marginal utility of money.
C) purchases only normal goods.
D) has an incentive to redirect her purchases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Exhibit 21-2
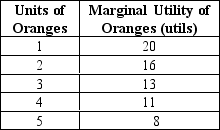
Refer to Exhibit 21-2.Total utility for the first three oranges is
A) 12 utils.
B) 62 utils.
C) 49 utils.
D) 15 utils.
E) 42 utils.

Refer to Exhibit 21-2.Total utility for the first three oranges is
A) 12 utils.
B) 62 utils.
C) 49 utils.
D) 15 utils.
E) 42 utils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Exhibit 21-1

Refer to Exhibit 21-1.The marginal utility of the second plum is
A) 18.5 utils.
B) 7.5 utils.
C) 37 utils.
D) 12 utils.

Refer to Exhibit 21-1.The marginal utility of the second plum is
A) 18.5 utils.
B) 7.5 utils.
C) 37 utils.
D) 12 utils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The endowment effect
A) states that we value an item more highly if we own it than if we do not own it.
B) is the same as compartmentalizing.
C) states that people are often willing to make themselves worse off in order to make someone else worse off.
D) states that people are often willing to make themselves worse off in order to make someone else better off.
E) a and d
A) states that we value an item more highly if we own it than if we do not own it.
B) is the same as compartmentalizing.
C) states that people are often willing to make themselves worse off in order to make someone else worse off.
D) states that people are often willing to make themselves worse off in order to make someone else better off.
E) a and d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Exhibit 21-2

Refer to Exhibit 21-2.Total utility for all five oranges is
A) 70 utils.
B) 12 utils.
C) 68 utils.
D) 80 utils.
E) 40 utils.

Refer to Exhibit 21-2.Total utility for all five oranges is
A) 70 utils.
B) 12 utils.
C) 68 utils.
D) 80 utils.
E) 40 utils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Exhibit 21-2

Refer to Exhibit 21-2.Total utility for the first four oranges is
A) 11 utils.
B) 60 utils.
C) 52 utils.
D) 15 utils.
E) 40 utils.

Refer to Exhibit 21-2.Total utility for the first four oranges is
A) 11 utils.
B) 60 utils.
C) 52 utils.
D) 15 utils.
E) 40 utils.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Exhibit 21-2

Refer to Exhibit 21-2.Total utility for the first two oranges is
A) 36 utils.
B) 20 utils.
C) 40 utils.
D) 36 utils.
E) cannot be determined

Refer to Exhibit 21-2.Total utility for the first two oranges is
A) 36 utils.
B) 20 utils.
C) 40 utils.
D) 36 utils.
E) cannot be determined

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Exhibit 21-1

Refer to Exhibit 21-1.In this example,marginal utility
A) constantly increases.
B) constantly diminishes.
C) increases then diminishes.
D) diminishes then increases.

Refer to Exhibit 21-1.In this example,marginal utility
A) constantly increases.
B) constantly diminishes.
C) increases then diminishes.
D) diminishes then increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
The law of diminishing marginal utility
A) allows us to make interpersonal utility comparisons.
B) tells us that an additional dollar is worth less to a millionaire than to a poor person.
C) tells us the worth of an additional dollar of income.
D) tells us that an additional dollar of income is worth less than the preceding dollar of income.
E) a, b, and d
A) allows us to make interpersonal utility comparisons.
B) tells us that an additional dollar is worth less to a millionaire than to a poor person.
C) tells us the worth of an additional dollar of income.
D) tells us that an additional dollar of income is worth less than the preceding dollar of income.
E) a, b, and d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 176 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








